| [1] |
Mengmeng ZHAO,Yalu WANG,Yuxiang XU,Kaige YANG,Yuwen CAO,Wenhu ZHOU,Jing FEI,Wen WANG,Chenghua LUO,Jianming HU.
Effects of hydrogen sulfide synthase CBS and CSE on malignant biological behaviour of breast cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 34-43.
|
| [2] |
Lu YANG,Jiacai FU,Fengjin LI,Ling QI.
Inhibitory effect of schisandrin on migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 44-50.
|
| [3] |
Xin WANG,Jierui ZHAO,Yumiao GUO,Shutong CHEN,Zonghao HOU,Ruowen ZHANG.
Effect of silencing CD147 gene on proliferation, migration, invasion, and inducing apoptosis of prostate cancer cells inhibited by curcumin
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1572-1586.
|
| [4] |
Bin ZHAO,Jinye YANG,Zhiyao LI,Chengwei BI,Libo YANG,Zhiyu SHI,Xin LI,Jianpeng ZHANG,Yuanlong SHI,Yong YANG,Guoying ZHANG.
Inhibitory effect of miR-30c-5p on proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1632-1643.
|
| [5] |
Jing LOU,Lei ZHAO,Yanjie ZHU,Shuaiqiang YUAN,Fei WANG,Hangzhou ZHANG,Jiaojiao XU,Xiaoke YU,Liufa HOU.
Effect of Fuzheng Ruanjian Anticancer Formula on malignant biological behaviors of hepatocellulars carcinoma HepG2 cells by regulating Akt/MDM2/P53 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1654-1663.
|
| [6] |
Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU.
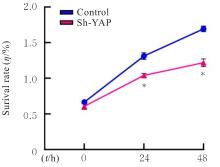
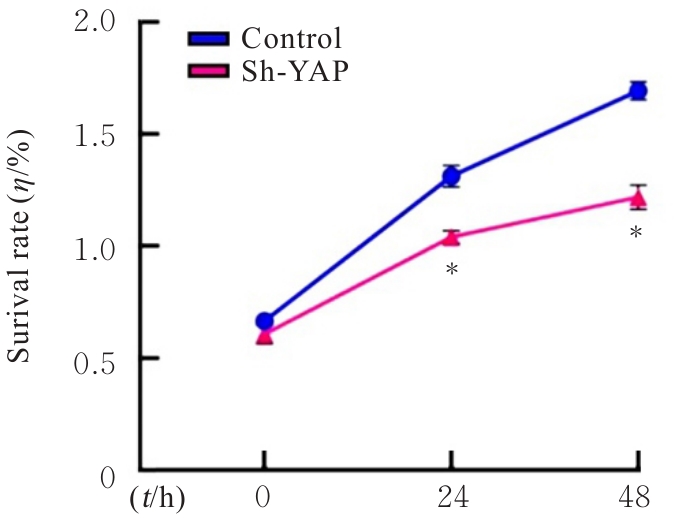
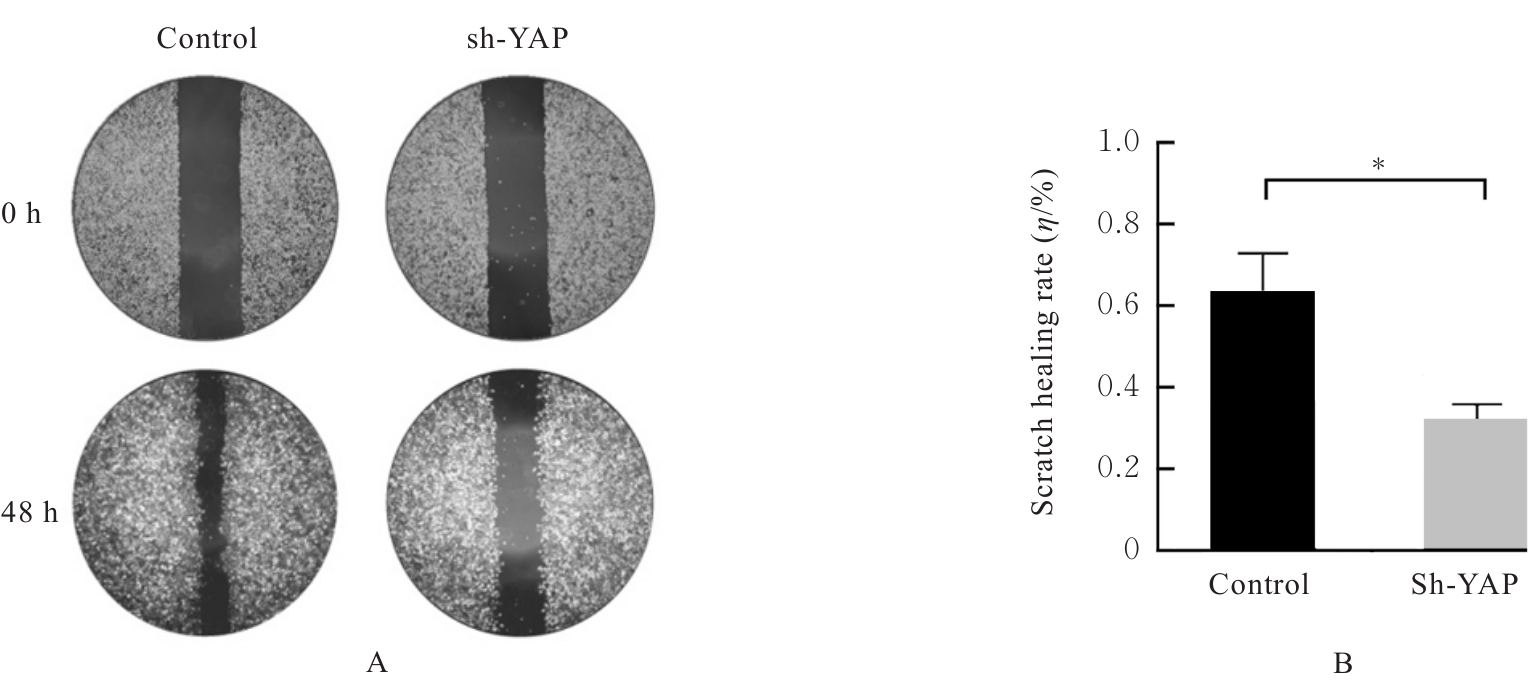
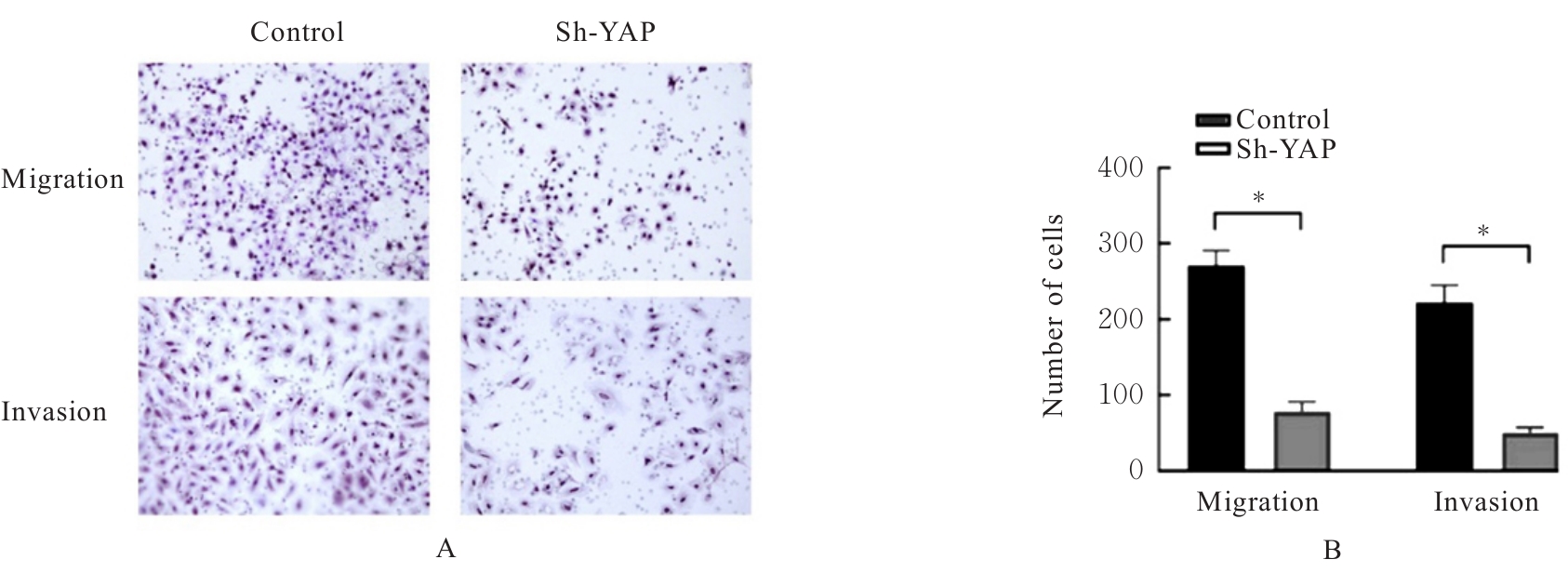
Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008.
|
| [7] |
Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO.
Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015.
|
| [8] |
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU.
Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043.
|
| [9] |
Yilin REN,Yichen ZANG,Lele XUE,Kaige YANG,Sufang CHEN,Weinan WANG,Chenghua LUO,Weihua LIANG,Lianghai WANG,Feng LI,Jianming HU.
Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 881-890.
|
| [10] |
Guoxing YU,Xin ZHANG,Hengwei DU,Bingjie CUI,Na GAO,Cuilan LIU,Jing DU.
Effect of urolithin C on proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of human acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 908-916.
|
| [11] |
Shan CAO,Yijia ZHANG,Yang BAI,Fang CHEN,Sha XIE,Qianqian HAN.
Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 925-938.
|
| [12] |
Yuan WANG,Zhijuan WANG,Mingshu ZHANG,Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Liping YE.
Effects of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 on invasion and migration of lung cancer A549 and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 666-675.
|
| [13] |
Bo YUAN,Jiayi XIE,Siyu JIANG,Yajun MENG,Qinghua ZHU,Xiaofei LI,Xiumei FU,Lide XIE.
Effect of adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes on migration ability of macrophages in vitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 718-727.
|
| [14] |
Shuang CHEN,Hong LI.
Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378.
|
| [15] |
Changji ZHU,Xingzhe LIU,Yanhua XUAN.
Effect of hypoxia on expressions of Gli1 and Sox2 in cervical cancer SiHa cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 442-450.
|
 ),Xuemei JIN1(
),Xuemei JIN1( )
)