吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 3027-3036.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221555
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
面向虚拟编组的多列车协同制动控制算法
- 1.北京交通大学 电子信息工程学院,北京 100044
2.交控科技股份有限公司,北京 100070
3.北京市地铁运营有限公司,北京 100044
Brake control algorithm for virtually coupled trains based on multi vehicle cooperation
Lei ZHANG1( ),Zi-mu LI2,Yong-yao YAN2,Fei DOU3,Hong-jie LIU1(
),Zi-mu LI2,Yong-yao YAN2,Fei DOU3,Hong-jie LIU1( )
)
- 1.School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.Traffic Control Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 100070,China
3.Beijing Mass Transit Railway Operation Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 100044,China
摘要:
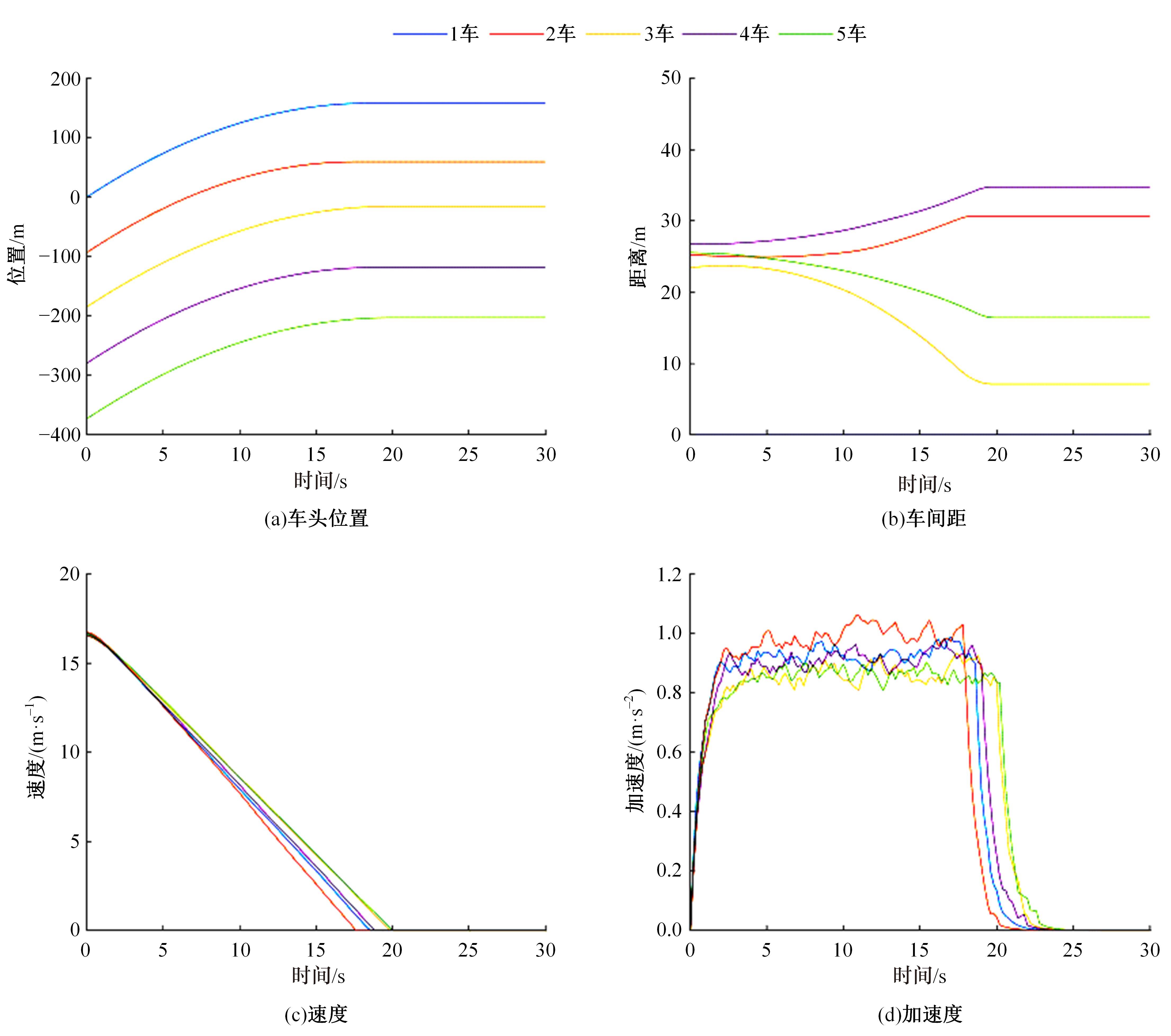
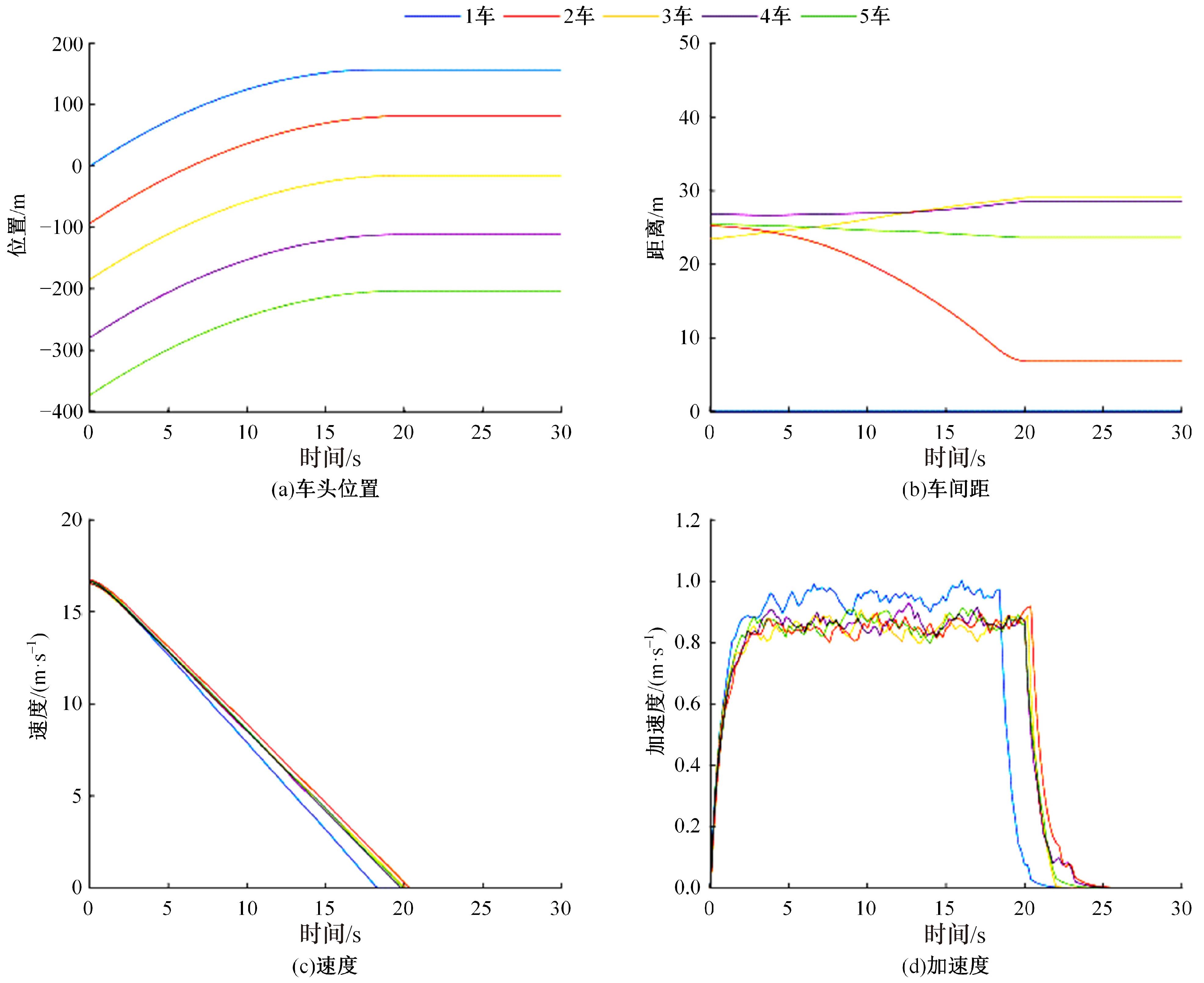
针对列车虚拟编组运行过程中,紧急停车时各列车单元通常采用统一的制动减速度,受实际工况影响在易发生因间距控制不均匀增大行车安全风险的问题,本文开展了基于多车协同的制动控制算法设计及优化分析。首先,分析了虚拟编组列车单元的紧急停车场景,并定义了总风险系数以评价安全风险;然后,以总风险系数最小为目标,设计了制动率计算方法。仿真结果显示,该算法具备更低的总风险系数和更少的碰撞次数,证明了其正确性和有效性。
中图分类号:
- U284
| 1 | 禹丹丹, 韩宝明, 张琦, 等. 基于灵活虚拟编组的轨道交通列车开行方案优化方法[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2015, 39(6): 21-31. |
| Yu Dan-dan, Han Bao-ming, Zhang Qi, et al. Optimization method for train plan of urban rail transit based on the flexible length of train formation[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015, 39(6): 21-31. | |
| 2 | 刘宏杰, 唐涛, 张艳兵, 等. 城轨虚拟编组关键性能指标及技术探讨[J]. 都市快轨交通, 2023, 36(1):28-35. |
| Liu Hong-jie, Tang Tao, Zhang Yan-bing, et al. Discussion on the key performance indicators and technologies of virtual coupling in metros[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2023, 36(1): 28-35. | |
| 3 | Di Meo C, Di Vaio M, Flammini F, et al. ERTMS/ETCS virtual coupling: proof of concept and numerical analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21(6): 2545-2556. |
| 4 | Quaglietta E, Wang M, Goverde R M P. A multi-state train-following model for the analysis of virtual coupling railway operations[J]. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 2020, 15: No.100195. |
| 5 | Tang T, Huang Y N, Yin J T.Chinese metro train control system(CMTCS): from automatic to autonomous[J]. IRSE News, 2022, 289: 3-7. |
| 6 | Shift2Rail Joint Undertaking. Shift2Rail Annual Activity Report 2021[R]. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union, 2021. |
| 7 | 谢正光, 魏运. 新时代我国城市轨道交通运营新模式探讨[J]. 都市快轨交通, 2022, 35(1): 54-59. |
| Xie Zheng-guang, Wei Yun. New modes of urban rail operations in the new era of China[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2022, 35(1): 54-59. | |
| 8 | 魏运, 白文飞, 李宇杰.智慧地铁需求分析及功能规划研究[J].都市快轨交通, 2020, 33(1): 40-48. |
| Wei Yun, Bai Wen-fei, Li Yu-jie. Development demand and function planning of smart metro[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2020, 33(1): 40-48. | |
| 9 | Bock U, Bikker G. Design and development of a future freight train concept-"virtually coupled train formations"[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2000, 33(9): 395-400. |
| 10 | Ning B. Absolute braking and relative distance braking-train operation control modes in moving block systems[J]. WIT Transactions on The Built Environment, 1998, 37:991-1001. |
| 11 | 荀径, 陈明亮, 宁滨, 等. 虚拟重联条件下地铁列车追踪运行性能衡量[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2019, 43(1): 96-103. |
| Xun Jing, Chen Ming-liang, Ning Bin, et al. Train tracking performance measurement under virtual coupling in subway[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019, 43 (1): 96-103. | |
| 12 | Zhou Q, Zhang C Y, Bao F, et al. The safety braking protection model of virtually coupled train platoon in subway[C]//2020 10th Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems(CYBER), Xi'an, China, 2020:No.9278960. |
| 13 | 吴萌岭, 马天和, 田春, 等. 列车制动技术发展趋势探讨[J].中国铁道科学, 2019, 40(1): 134-144. |
| Wu Meng-ling, Ma Tian-he, Tian Chun, et al. Discussion on development trend of train braking technology[J]. China Railway Science, 2019, 40(1): 134-144. | |
| 14 | 刘豫湘, 方长征, 万建兵, 等. 列车制动系统技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆, 2014,37(5): 1-4. |
| Liu Yu-xiang, Fang Chang-zheng, Wan Jian-bing, et al. Technology status and development trend of train braking system[J]. Electric Locomotives & Mass Transit Vehicles, 2014, 37(5): 1-4. | |
| 15 | Wang J, Liu H, Tang T, et al. A space-time interval based protection method for virtual coupling[C]∥2022 China Automation Congress(CAC), Xiamen, China, 2022: 4906-4911. |
| 16 | Quaglietta E. Deliverable D4.1 market potential and operational scenarios for virtual coupling[R/OL].[2019-07-29].. |
| 17 | Stickel S, Schenker M, Dittus H, et al. Technical feasibility analysis and introduction strategy of the virtually coupled train set concept[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 4248. |
| 18 | 穆俊斌, 孙景辉. 某型城际动车组制动力分级控制方式[J]. 电子世界, 2014(10): 339-339. |
| Mu Jun-bin, Sun Jing-hui. Grading control mode of braking force for a certain type of intercity multiple unit[J].Electronics World, 2014(10): 339-339. | |
| 19 | 侯德藻. 汽车纵向主动避撞系统的研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学车辆与运载学院, 2004. |
| Hou De-zao. Study on vehicle forward collision avoidance system[D].Beijing:School of Vehicle and Mobility, Tsinghua University, 2004. | |
| 20 | 胡满江, 徐彪, 秦洪懋, 等. 基于MPC的多车纵向协同避撞算法[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版,2017, 57(12): 1280-1286. |
| Hu Man-jiang, Xu Biao, Qin Hong-mao, et al. MPC based longitudinal coordinated collision avoidance for multiple connected vehicles[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2017, 57(12): 1280-1286. | |
| 21 | 张玮, 张树培, 罗崇恩, 等.智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(7):1515-1523. |
| Zhang Wei, Zhang Shu-pei, Luo Chong-en, et al. Collision avoidance trajectory planning for intelligent vehicles in emergency conditions[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. | |
| 22 | 孟柯, 吴超仲, 陈志军, 等.人车碰撞风险识别及智能车辆控制系统[J].交通信息与安全,2016,34(6):22-29. |
| Meng Ke, Wu Chao-zhong, Chen Zhi-jun, et al. A system for risk identification of pedestrain-vehicular collisions and intelligent control[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2016, 34(6): 22-29. | |
| 23 | Funke J, Brown M, Erlien S M, et al. Collision avoidance and stabilization for autonomous vehicles in emergency scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2016, 25(4): 1204-1216. |
| [1] | 张娜,陈峰,王剑坡,朱亚迪. 基于时空序列相似性的城轨乘客出行模式识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2588-2599. |
| [2] | 马洁,刘智丽,王书灵,董皓. 轨道交通车站出入口客流预测——以北京市为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2197-2205. |
| [3] | 任颖,朵建华,宋瑞霞. 基于变结构PID控制的轨道交通信号联合控制系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2364-2369. |
| [4] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [5] | 宋成举,贾洪飞,秦昊溥. 网联车混入条件下混合交通流跟驰稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 419-426. |
| [6] | 陈小波,陈玲. 定位噪声统计特性未知的变分贝叶斯协同目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
| [7] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [8] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [9] | 张惠臻,高正凯,李建强,王晨曦,潘玉彪,王成,王靖. 基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 430-438. |
| [10] | 王清永,曲伟强. 基于线性规划的城市轨道交通运行调度优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3446-3451. |
| [11] | 魏路,高磊,李晋宏,杨建,田玉林. 基于密度峰值聚类的交通控制子区划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 124-131. |
| [12] | 张廷萍,万迪. 基于粗糙集理论的轨道交通节点重要度评估算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2845-2851. |
| [13] | 刘东波,沈莉潇,代磊磊,陆建. 基于多目标雷达数据的单点交通信号控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2456-2465. |
| [14] | 薛锋,何传磊,黄倩,罗建. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [15] | 贾超,徐洪泽,王龙生. 基于多质点模型的列车自动驾驶非线性模型预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1913-1922. |
|
||