吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 439-447.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210667
城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模
- 1.北京交通大学 综合交通运输大数据应用技术交通运输行业重点实验室,北京 100044
2.海康威视研究院,杭州 310012
Modelling on catchment area and attraction intensity of urban rail transit stations
Jing WANG1( ),Feng WAN2,Chun-jiao DONG1(
),Feng WAN2,Chun-jiao DONG1( ),Chun-fu SHAO1
),Chun-fu SHAO1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Big Data Application Technologies for Comprehensive Transport,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.Hikvision Research Institute,Hangzhou 310012,China
摘要:
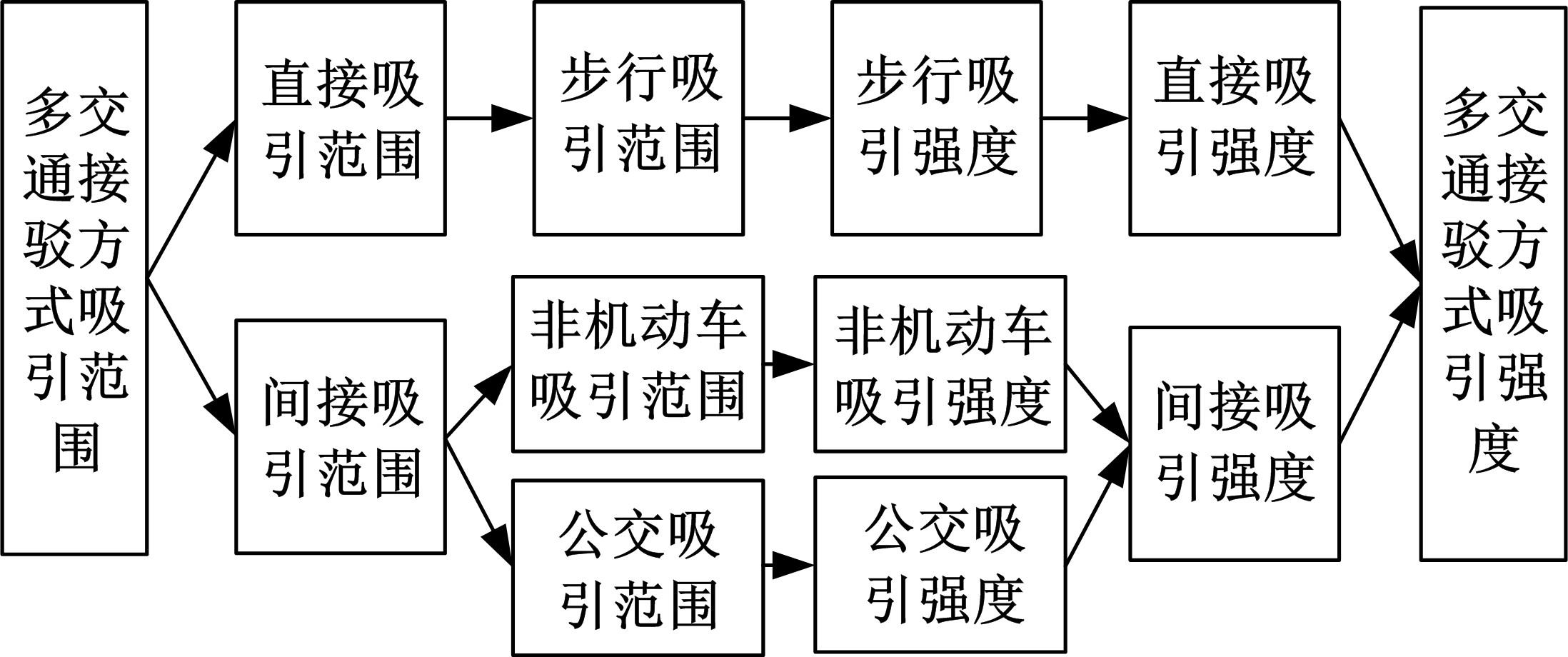
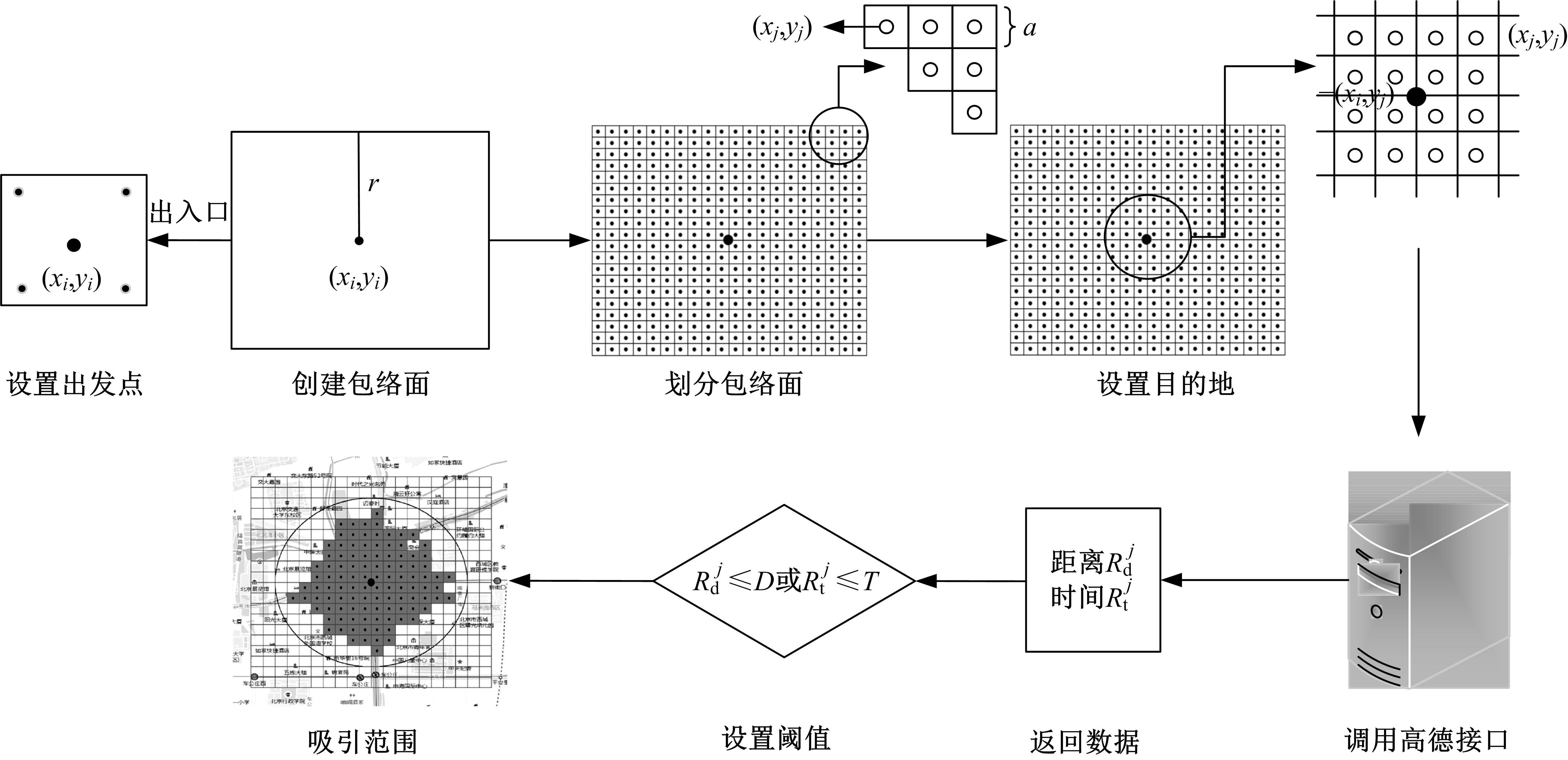
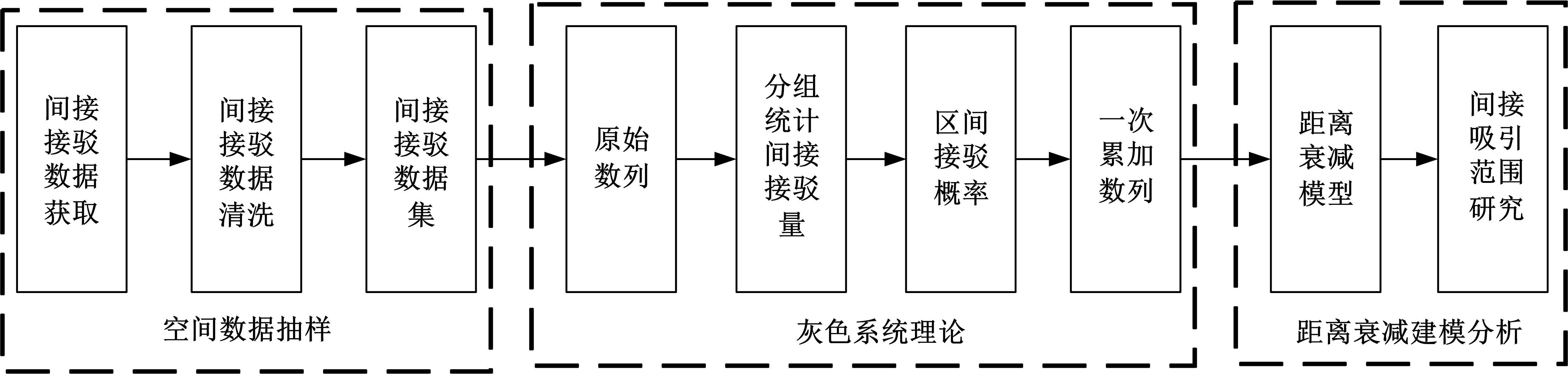
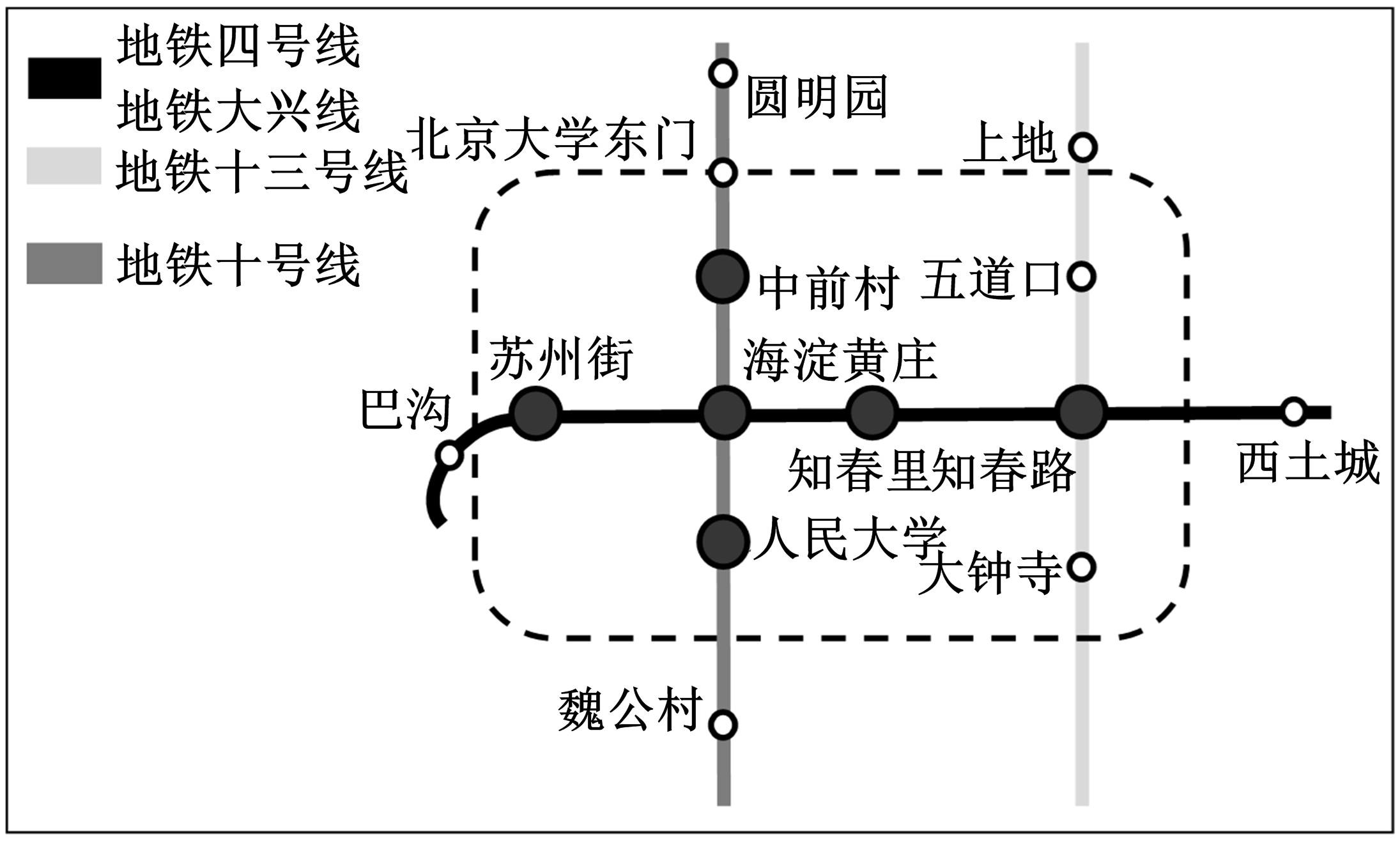
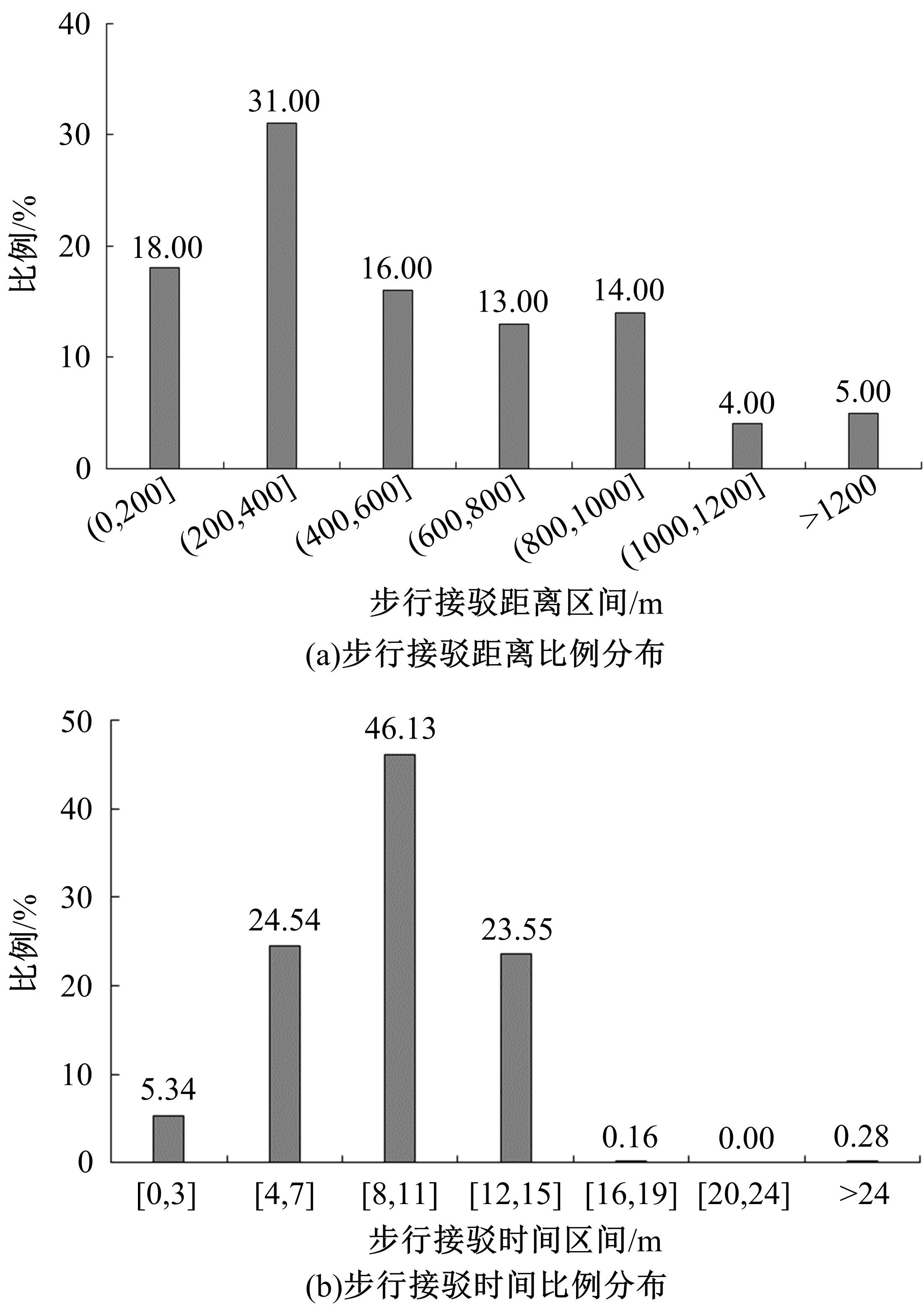
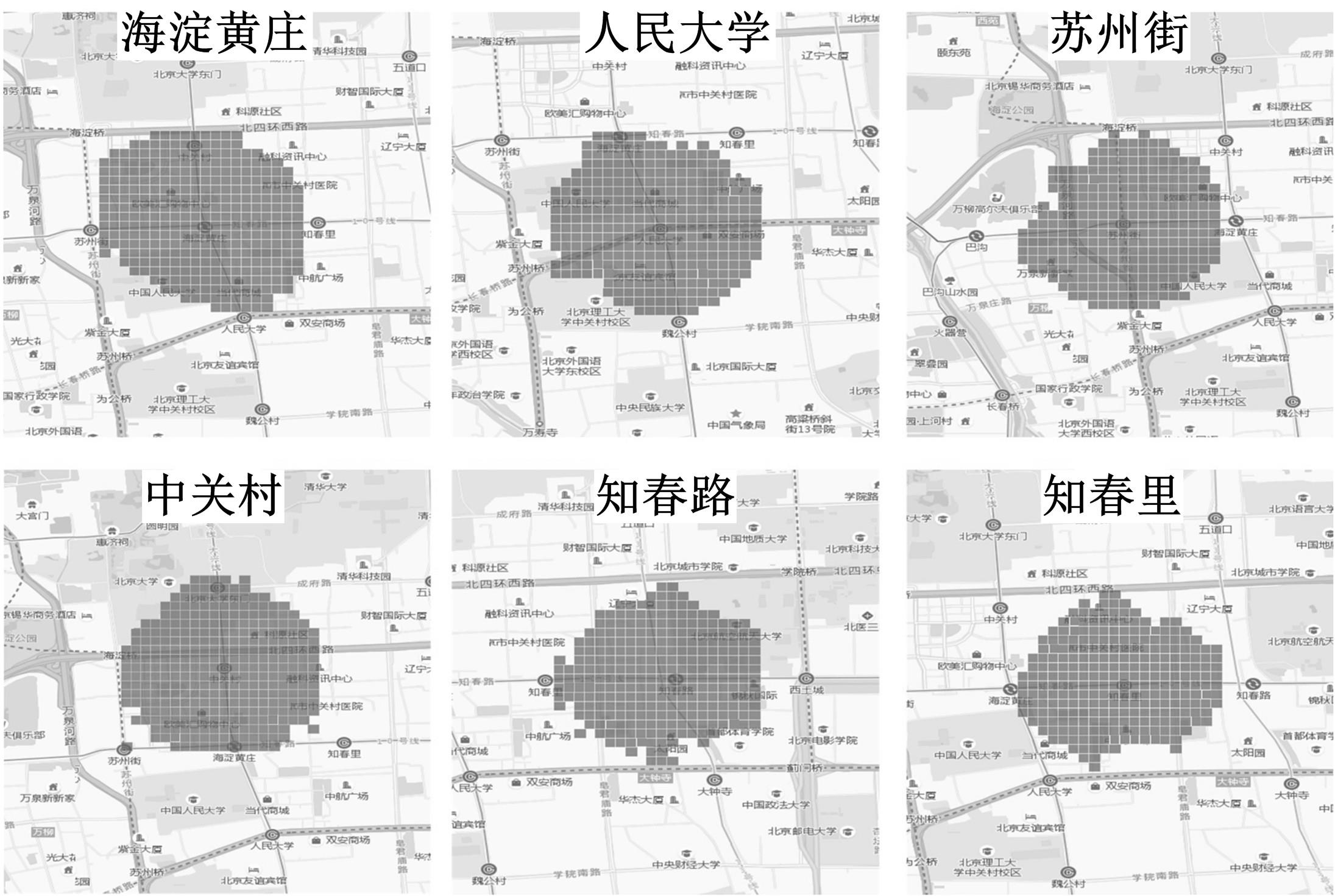
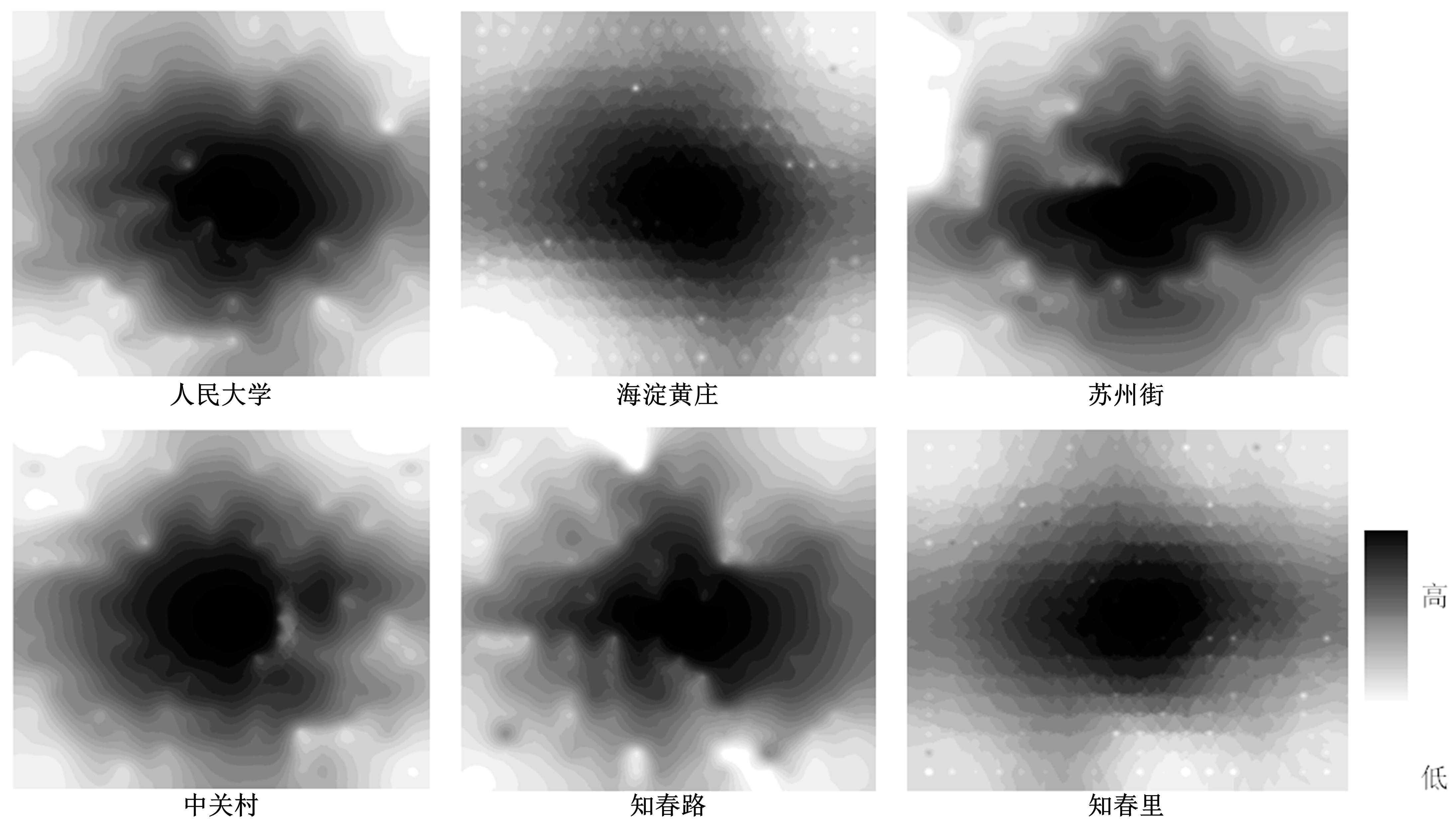
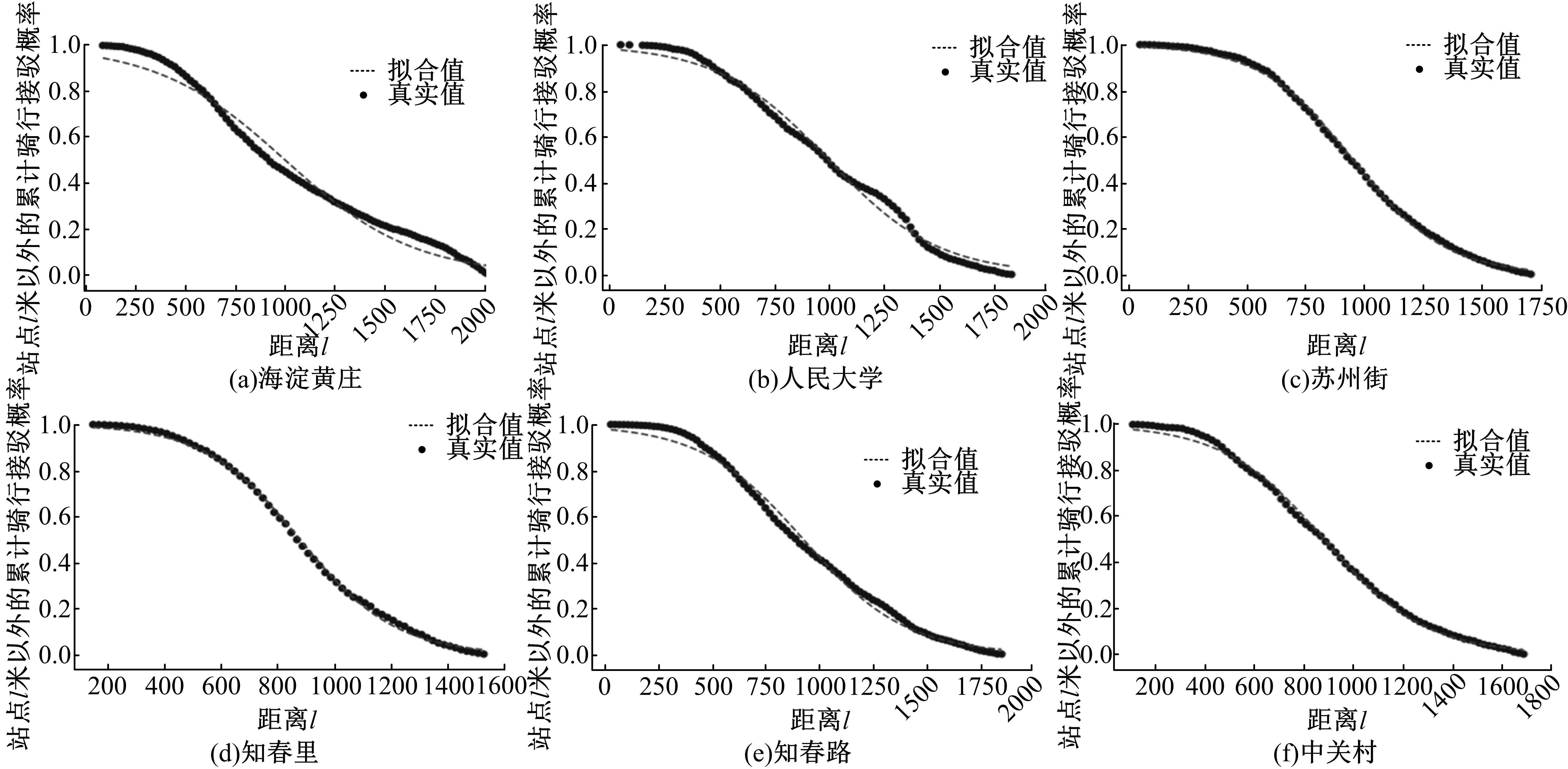
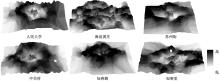
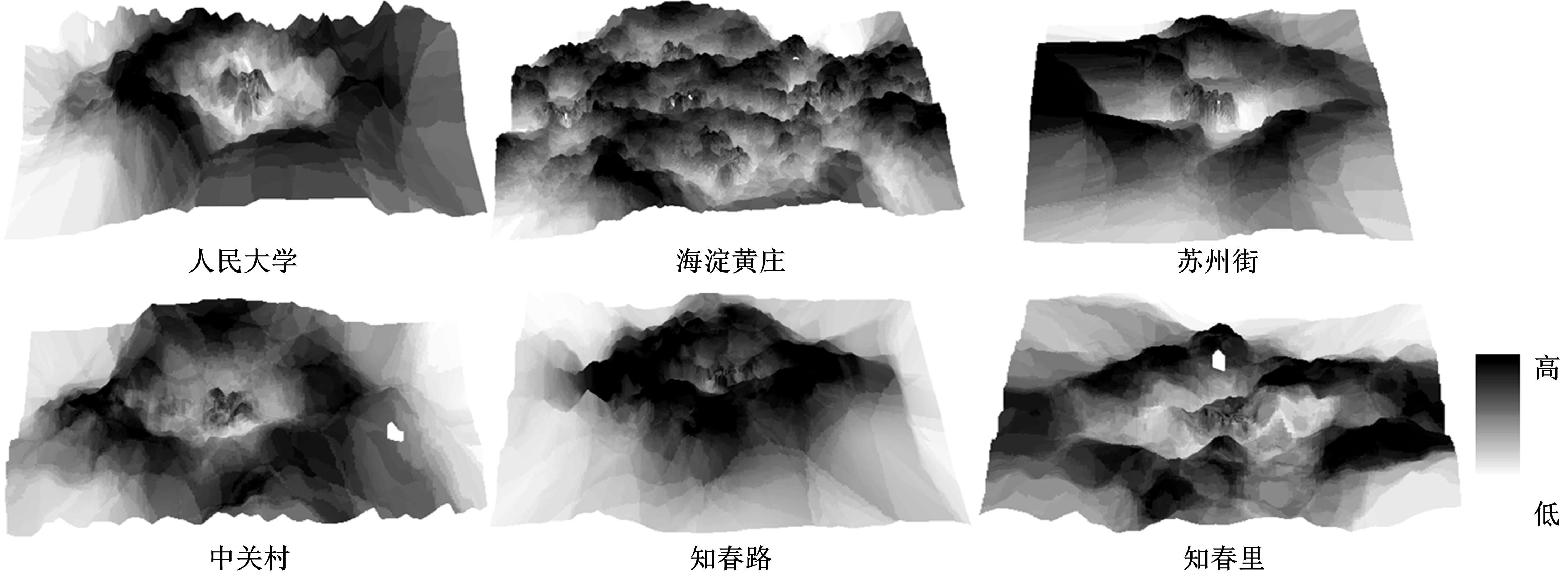
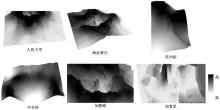
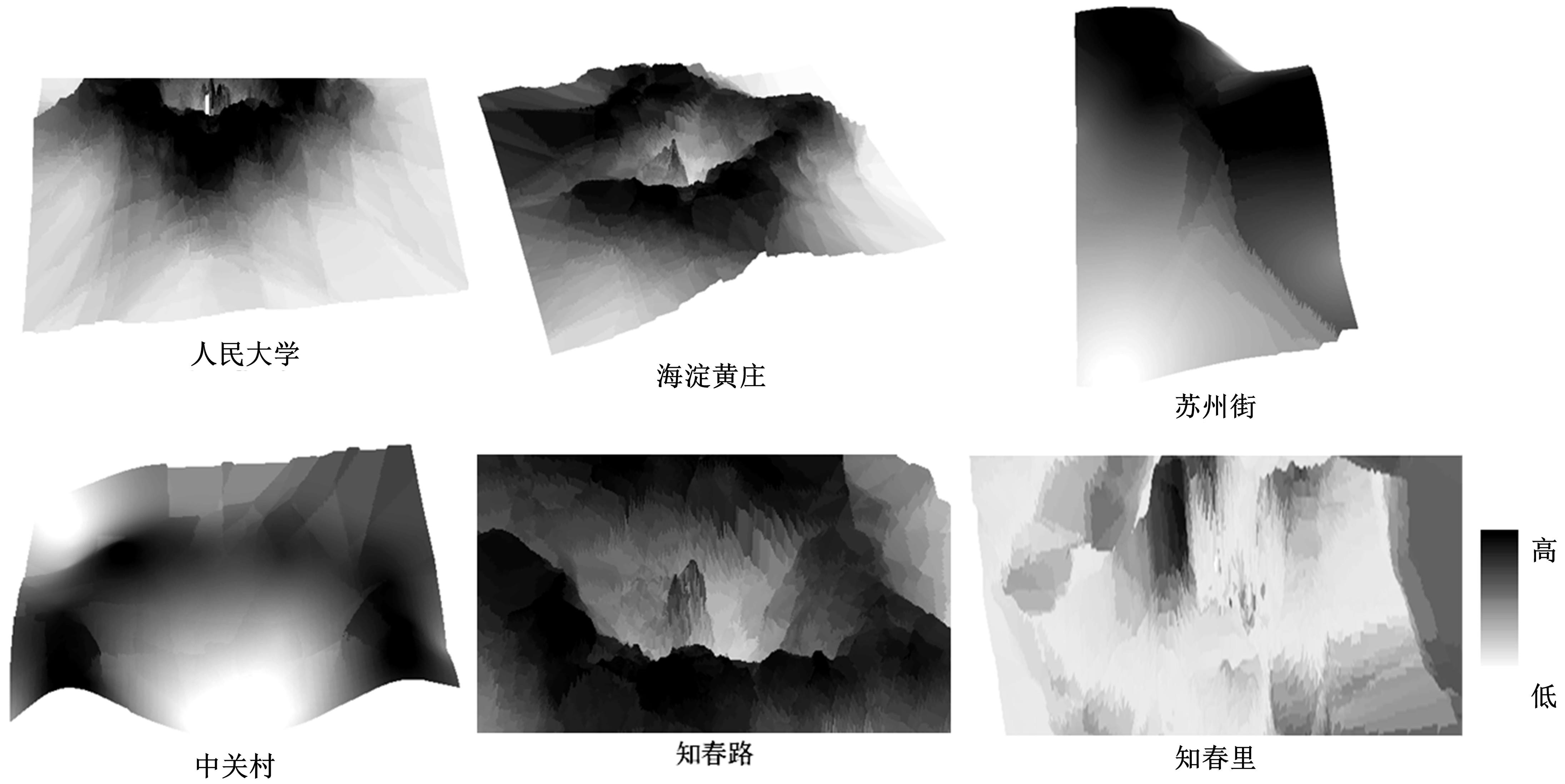
为明确城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及吸引强度,提出轨道站点多接驳方式吸引范围及吸引强度模型。基于轨道交通最主要接驳方式,将轨道站点吸引范围分为直接吸引范围及间接吸引范围两类。考虑站点空间特征,分别提出基于阈值的点阵算法及灰色距离衰减模型研究直接和间接吸引范围。在此基础上,构建了轨道交通站点的多接驳方式吸引强度模型。结果表明:直接吸引范围不是规律的圆形,各站点直接吸引范围不相同,随着距离的增大,直接吸引强度呈现逐渐减小的趋势;间接吸引范围中,各站点的间接吸引范围同样存在差异,随着距离的增大,间接吸引强度呈现先降后增再降的趋势。
中图分类号:
- U231.4
| 1 | Jun M J, Choi K, Jeong J E, et al. Land use characteristics of subway catchment areas and their influence on subway ridership in Seoul[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2015, 48: 30-40. |
| 2 | Li S Y, Lyu D J, Huang G P, et al. Spatially varying impacts of built environment factors on rail transit ridership at station level: a case study in guangzhou, china[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2020, 82: 102631. |
| 3 | Yang R R, Yan H, Xiong W, et al. The study of pedestrian accessibility to rail transit stations based on KLP model[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2013, 96: 714-722. |
| 4 | 申犁帆, 王烨, 张纯, 等. 轨道站点合理步行可达范围建成环境与轨道通勤的关系研究——以北京市44个轨道站点为例[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(12): 2423-2439. |
| Shen Li-fan, Wang Ye, Zhang Chun, et al. Relationship between built environment of rational pedestrian catchment areas and URT commuting ridership: evidence from 44 URT stations in Beijing[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(12): 2423-2439. | |
| 5 | Eom J K, Choi J, Park M S, et al. Exploring the catchment area of an urban railway station by using transit card data: case study in seoul[J]. Cities, 2019, 95: 102364. |
| 6 | Lin D, Zhang Y, Zhu R X, et al. The analysis of catchment areas of metro stations using trajectory data generated by dockless shared bikes[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2019, 49: 101598. |
| 7 | 王淑伟, 孙立山, 荣建. 北京市轨道站点吸引范围研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2013, 13(3):183-188. |
| Wang Shu-wei, Sun Li-shan, Rong Jian. Catchment area analysis of beijing transit stations[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2013, 13(3): 183-188. | |
| 8 | 赵丹, 邵春福, 王军利, 等. 多方式诱导下通勤出行链交通方式组合选择行为模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(6): 1763-1770. |
| Zhao Dan, Shao Chun-fu, Wang Jun-li, et al. Modelling combined mode choice behavior of commute trip chain under multi-modal guidance[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(6): 1763-1770. | |
| 9 | 尹超英, 邵春福, 王晓全, 等. 考虑空间异质性的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| Yin Chao-ying, Shao Chun-fu, Wang Xiao-quan, et al. Influence of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial heterogeneity[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. | |
| 10 | Wang N, Du Y C. Resident walking distance threshold of community[J]. Transport Research, 2015, 1(2): 20-24. |
| 11 | 陈卓, 金凤君, 杨宇, 等. 高速公路流的距离衰减模式与空间分异特征——基于福建省高速公路收费站数据的实证研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(8): 1086-1095. |
| Chen Zhuo, Jin Feng-jun, Yang Yu, et al. Distance-decay pattern and spatial differentiation of expressway flow: an empirical study using data of expressway toll station in fujian province[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(8): 1086-1095. | |
| 12 | 于向军, 槐元辉, 李学飞, 等. 基于克里金和粒子群算法的装载机铲掘轨迹规划[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 437-444. |
| Yu Xiang-jun, Huai Yuan-hui, Li Xue-fei, et al. Shoveling trajectory planning method for wheel loader based on kriging and particle swarm optimization[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 437-444. |
| [1] | 张惠臻,高正凯,李建强,王晨曦,潘玉彪,王成,王靖. 基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 430-438. |
| [2] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [3] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [4] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [5] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [6] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [7] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [8] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [9] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [10] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [11] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [12] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [13] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [14] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [15] | 程国柱,孙秋月,刘玥波,陈纪龙. 基于博弈论的城市道路变道切入行为模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2839-2844. |
|