吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 1061-1071.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230600
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于隐式关键点互联的人体姿态估计矫正器算法
- 1.长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
2.长春理工大学 空间光电技术研究所,长春 130022
3.吉林大学第一医院 泌尿外二科,长春 130061
4.东北师范大学 信息科学与技术学院,长春 130117
Human pose estimation corrector algorithm based on implicit key point interconnection
Hua CAI1( ),Rui-kun ZHU1,Qiang FU2,Wei-gang WANG3,Zhi-yong MA3,Jun-xi SUN4
),Rui-kun ZHU1,Qiang FU2,Wei-gang WANG3,Zhi-yong MA3,Jun-xi SUN4
- 1.School of Electronic Information Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Opto-Electronic Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.No. 2 Department of Urology,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
4.College of Information Science and Technology,North Normal University,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
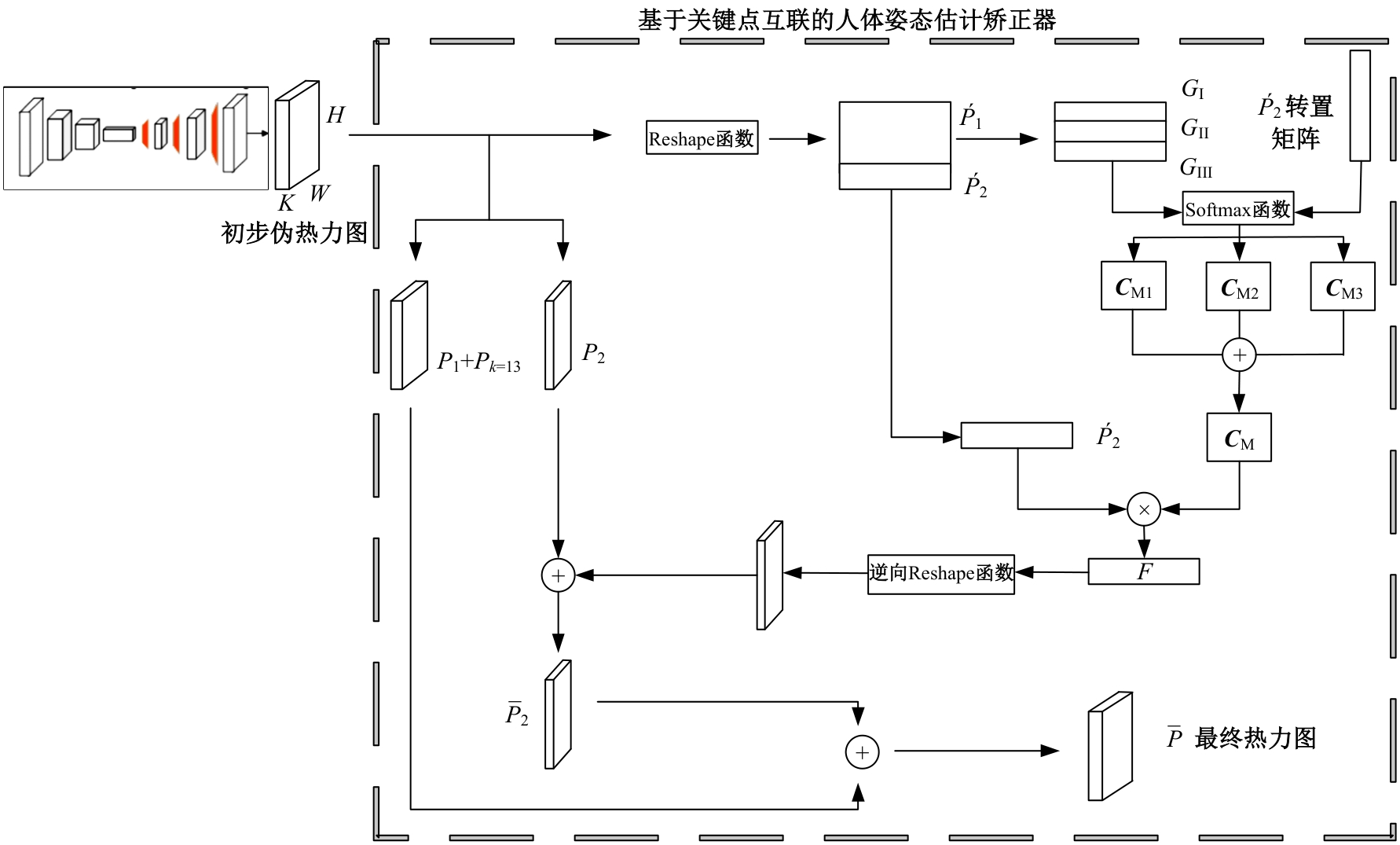
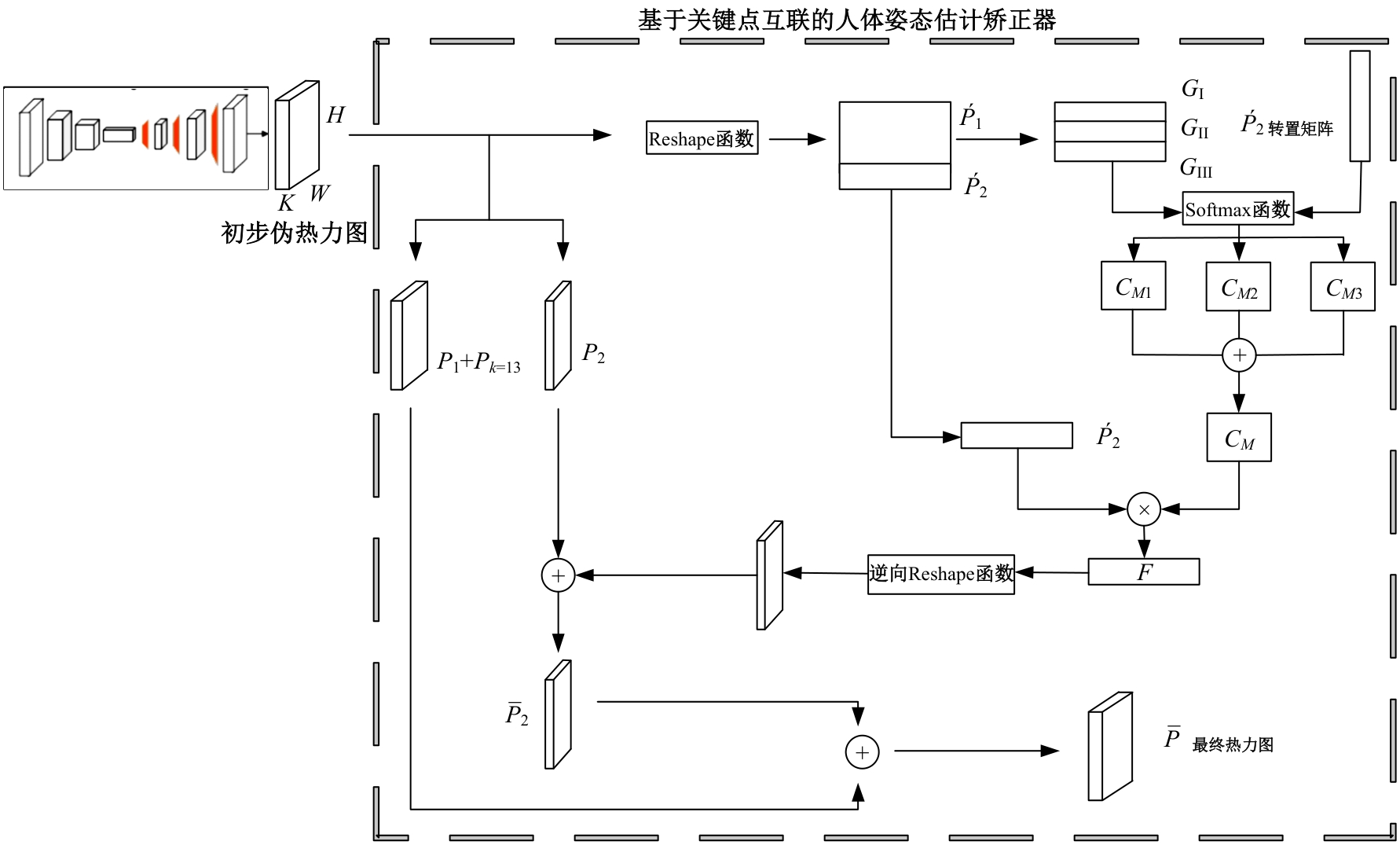
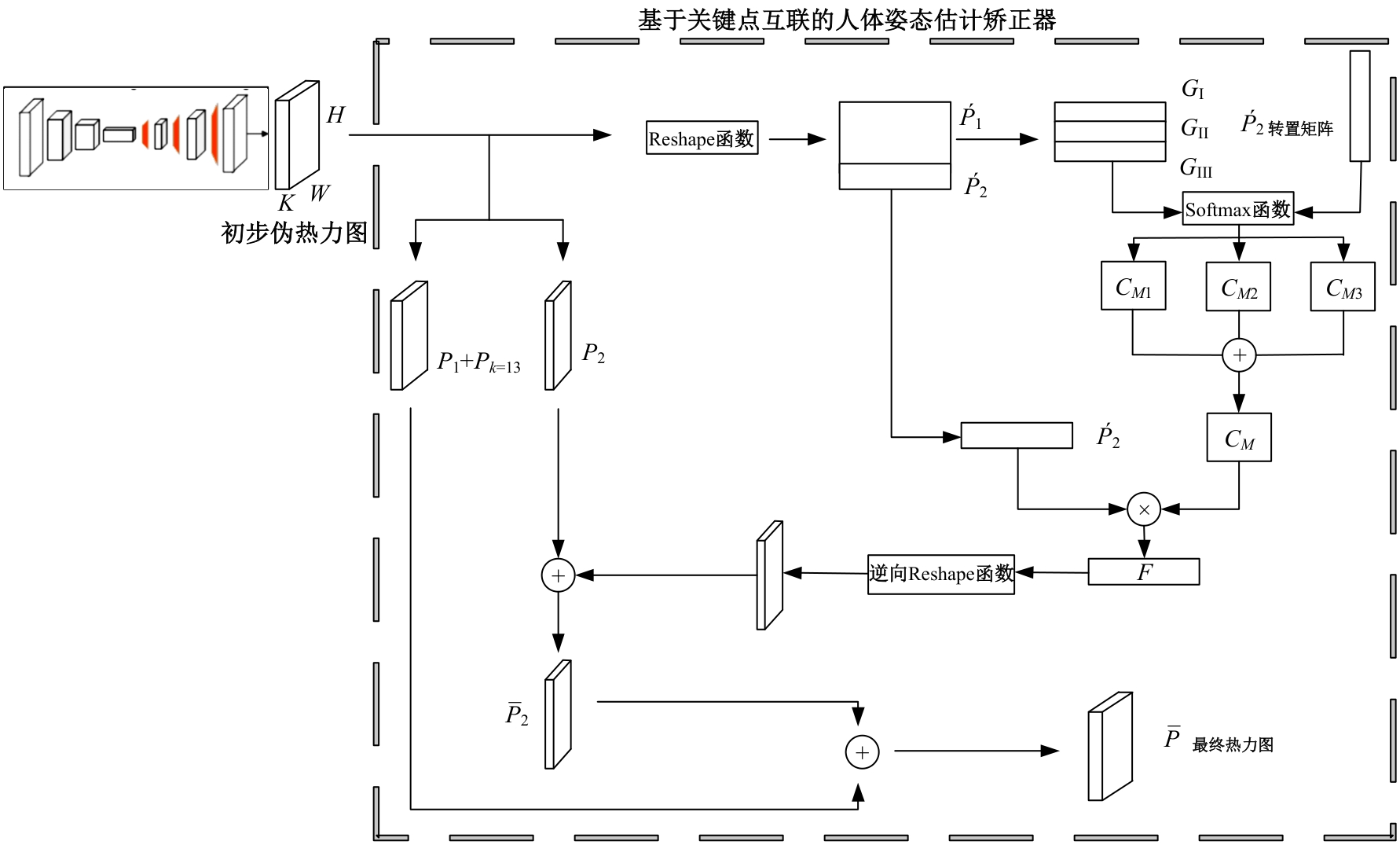
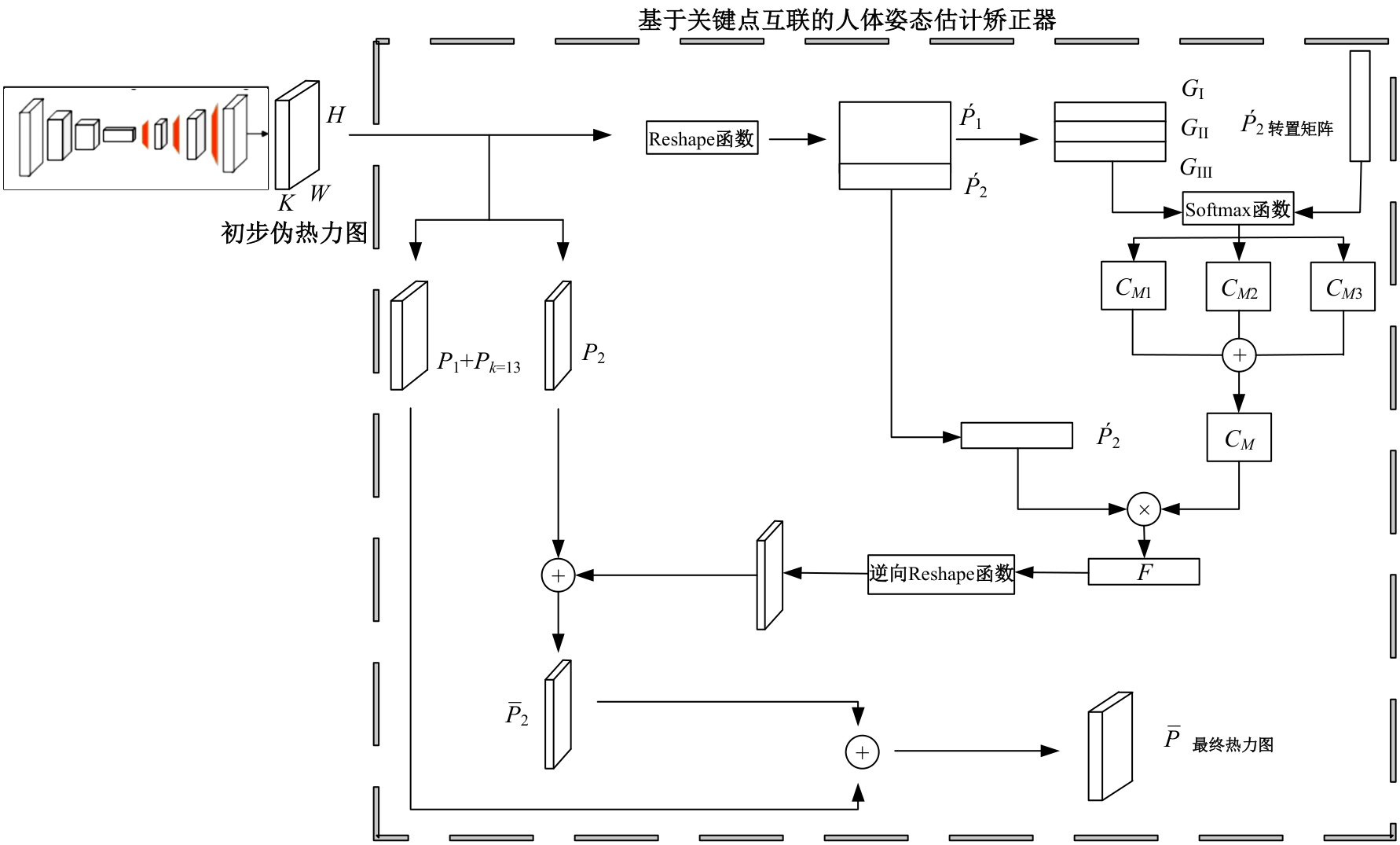
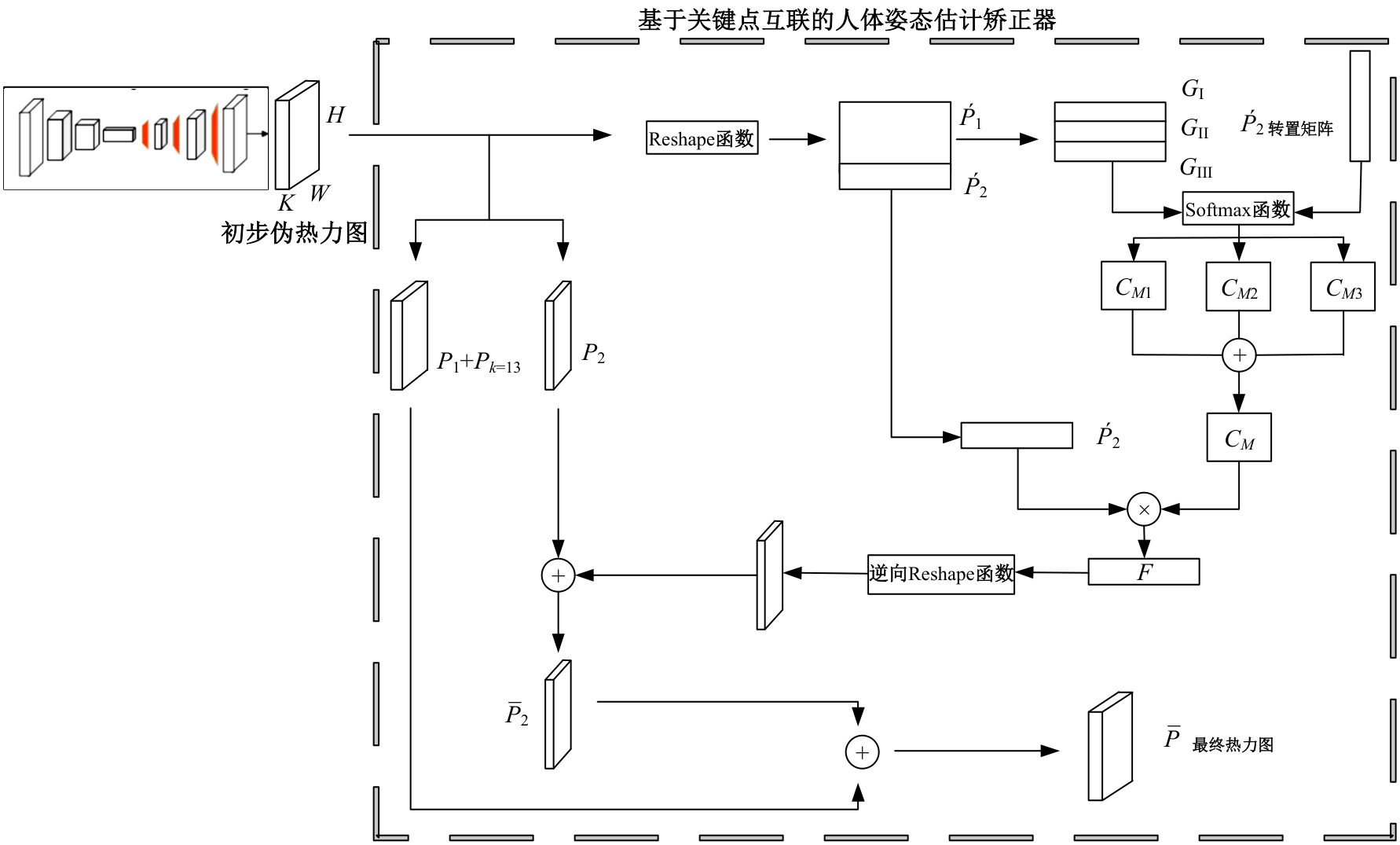
针对现有人体姿态估计模型中忽略人体关键点之间相互联系的问题,提出了一种基于相关矩阵建立隐式关键点互联的人体姿态估计矫正算法。该算法采用双阶段网络结构,第一阶段使用现有模型获得关键点的准确率,第二阶段计算相关系数矩阵,构建关键点矫正器,实现隐式的关键点互联,通过选取效果较好的部分关键点作为指导,优化效果较差的另一部分关键点。将伪热力图信息重组后分为指引区域和待索引区域两个矩阵,指引矩阵根据准确率分为3个区域,并和转置后的待索引矩阵分别相乘得到相关矩阵,为不同相关矩阵增加不同的影响因子,通过公式得到总相关矩阵,与待索引矩阵相乘得到索引区域,最终逆向信息重组恢复到最初维度,与伪热力图进行逐像素相加,得到最终预测热力图,自动建立各关键点之间的联系,矫正现有模型忽略的关键点相互关系。在COCO2017数据集上的实验结果表明:本文人体姿态估计矫正算法在关键点识别准确度为70.5%,比现有模型SimpleBaseLine平均提升了0.4%。在一些容易被遮挡的部位,例如脚踝和手腕,体积小,处于四肢末端,遮挡的概率高,相邻的关键点个数少,表层信息特征少,人体姿态估计矫正器通过加强四肢末端关键点和其他全身关键点的联系,建立更多的特征联系。实验表明:脚踝和手腕识别的准确率相对提升1.5%,相比于其他现有模型,准确率也有较大的提升,证明了隐式关键点互联的人体姿态估计矫正算法的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Andriluka M, Iqbal U, Insafutdinov E, et al. PoseTrack:a benchmark for human pose estimation and tracking[C]∥IEEE / CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City,USA, 2018: 5167-5176. |
| 2 | Liu Q, Zhang Y, Bai S, et al. Explicit occlusion reasoning for multi-person 3D human pose estimation[C] ∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Switzerland, 2022: 497-517. |
| 3 | Wu H, Ma X, Li Y. Multi-level channel attention excitation network for human action recognition in videos[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2023, 114: No. 116940. |
| 4 | Nguyen P, Liu T, Prasad G, et al. Weakly supervised action localization by sparse temporal pooling network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 6752-6761. |
| 5 | Ren Z, Zhang Q, Gao X, et al. Multi-modality learning for human action recognition[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(11): 16185-16203. |
| 6 | Tang Y, Liu R. Skeleton embedding of multiple granularity attention network for human action recognition[C]∥International Conference on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 12878-12885. |
| 7 | Liang Z J, Wang X L, Huang R, et al. An expressive deep model for human action parsing from a single image[C]∥EEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Chengdu,China, 2014: 1-6. |
| 8 | Goh E S, Sunar M S, & Ismail A W. 3D object manipulation techniques in handheld mobile augmented reality interface: a review[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 40581-40601. |
| 9 | Yang X, Chen Y, Liu J, et al. Rapid prototyping of tangible augmented reality interfaces: towards exploratory learning for science education[J].Interactive Learning Environments, 2019, 27(4): 469-483. |
| 10 | Zhang D, Peng Y, Yang W, et al. Multi-viewpoint interaction with social robots: a case study of speech therapy for children with autism[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2018, 92(3/4): 359-3728. |
| 11 | Zhang R, Li J, Xiao T, et al. BodyPoseNet: body pose estimation driven by deep neural networks[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 99:No.116290. |
| 12 | Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4):834-848. |
| 13 | Zeng W, Gao Y, Zheng Y, et al. DenseReg: fully convolutional dense regression for accurate 3D human pose estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2830-2842. |
| 14 | Li J, Wang C, Zhu H, et al. Efficient crowded scenes pose estimation and a new benchmark[EB/OL].[2023-05-01]. |
| 15 | Moon G, Chang J Y, Lee K M. PoseFix: Model-agnostic general human pose refinement network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 7773-7781. |
| 16 | Zhou C, Chen S, Ding C, et al. Learning contextual and attentive information for brain tumor segmentation[C]∥Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, Granada, Spain, 2019: 497-507. |
| 17 | Ji X, Yang Q, Yang X, et al. Human pose estimation: multi-stage network based on HRNet[J]Journal of Physics, 2022, 2400(1): No.012034. |
| 18 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. |
| 19 | Papandreou G, Zhu T, Kanazawa N, et al. Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4903-4911. |
| 20 | Wei L, Zhang S, Dai J, et al. ST-GCN: spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Sait Lake City, USA, 2018: 7452-7461. |
| 21 | Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C,et al. U2-Net: going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106: No.107404. |
| 22 | Zhou F, Zhu M, Bai J, et al. Deformable ConvNets v2: more deformable, better results[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Sait Lake City,USA, 2018: 9308-9316. |
| 23 | Carreira J, Agrawal P, Fragkiadaki K, et al. Associative embedding: end-to-end learning for joint detection and grouping[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2274-2284. |
| 24 | Papandreou G, Zhu T, Chen L C, et al. PersonLab: person pose estimation and instance segmentation with a bottom-up, part-based, geometric embedding model[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany,2018: 282-299. |
| 25 | Kreiss S, Bertoni A, Alahi A. PifPaf: composite fields for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019:11977-11986. |
| 26 | Insafutdinov M, Pishchulin L, Andres B, et al. DeepCut: joint subset partition and labeling for multi person pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: No.533. |
| 27 | Newell A, Yang A, Deng J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, Holland, 2016 :483-499. |
| 28 | Chen Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, et al. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Sait Lake City,USA, 2018: 7103-7112. |
| 29 | Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5693-5703. |
| 30 | Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y. Simple baseline for human pose estimation and tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 742-757. |
| 31 | Wei L, Zhang S, Yin W, et al. Convolutional pose machines[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Munich, Germany, 2016: 4724-4732. |
| 32 | Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al.Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. |
| 33 | Lin G, Li Q, Li M, et al. A novel bottleneck-activated feedback neural network model for time series prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(4): 1621-1635. |
| 34 | Cao Z, Hidalgo Martinez G, Simon T, et al. OpenPose: realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 43(1): 172-186. |
| [1] | 李延风,刘名扬,胡嘉明,孙华栋,孟婕妤,王奥颖,张涵玥,杨华民,韩开旭. 基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1777-1787. |
| [2] | 王宇,赵凯. 基于亚像素定位的人体姿态热图后处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [3] | 张自超,陈建. 基于双目仿鹰眼视觉与超分辨的果园三维点云重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1469-1481. |
| [4] | 龙关旭,张修石,辛公锋,王涛,杨干. 融合机器视觉的桥梁动态称重方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 188-197. |
| [5] | 刘思远,侯跃谦,寇莹,任真,胡正乙,赵雪微,葛云鹏. 基于线结构光视觉的平面度误差测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3358-3366. |
| [6] | 包昊菁,刘思远,任真,张云辉,胡正乙,葛宇鹏. 基于机器视觉的链轮尺寸测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2795-2806. |
| [7] | 李景彬,杨禹锟,温宝琴,坎杂,孙雯,杨朔. 基于根茬检测的秋后残膜回收导航路径提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1528-1539. |
| [8] | 刘恩泽,吴文福. 基于机器视觉的农作物表面多特征决策融合病变判断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1873-1878. |
| [9] | 林金花, 王延杰, 王璐, 姚禹. 全局相机姿态优化下的快速表面重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 909-918. |
| [10] | 张飞, 单忠德, 任永新, 聂军刚, 刘丰. 缸盖缺陷检测系统线阵相机现场标定方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 540-545. |
| [11] | 周晓东, 张雅超, 谭庆昌, 张维君. 基于结构光视觉技术的圆柱度测量新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 524-529. |
| [12] | 张波,王文军,魏民国,成波. 基于机器视觉的驾驶人使用手持电话行为检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1688-1695. |
| [13] | 张保华, 黄文倩, 李江波, 赵春江, 刘成良, 黄丹枫. 基于I-RELIEF和SVM的畸形马铃薯在线分选[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1811-1817. |
| [14] | 刘长英1, 蔡文静1, 王天皓2, 李机智1, 贾艳梅1, 宋玉河1. 汽车连杆裂解槽视觉检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1076-1080. |
| [15] | 万川, 田彦涛, 刘帅师, 陈宏伟. 基于主动机器视觉的人脸跟踪与表情识别系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 459-465. |
|
||