吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1777-1787.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221042
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合
李延风1( ),刘名扬1,胡嘉明2,孙华栋2,孟婕妤2,王奥颖2,张涵玥1,杨华民1,韩开旭3(
),刘名扬1,胡嘉明2,孙华栋2,孟婕妤2,王奥颖2,张涵玥1,杨华民1,韩开旭3( )
)
- 1.长春理工大学 计算机科学技术学院,长春 130022
2.长春理工大学 人工智能学院,长春 130022
3.北部湾大学 电子与信息工程学院,广西 钦州 535011
Infrared and visible image fusion based on gradient transfer and auto-encoder
Yan-feng LI1( ),Ming-yang LIU1,Jia-ming HU2,Hua-dong SUN2,Jie-yu MENG2,Ao-ying WANG2,Han-yue ZHANG1,Hua-min YANG1,Kai-xu HAN3(
),Ming-yang LIU1,Jia-ming HU2,Hua-dong SUN2,Jie-yu MENG2,Ao-ying WANG2,Han-yue ZHANG1,Hua-min YANG1,Kai-xu HAN3( )
)
- 1.School of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Artificial Intelligence,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.School of Electronics and Information Engineering,Beibu Gulf University,Qinzhou 535011,China
摘要:
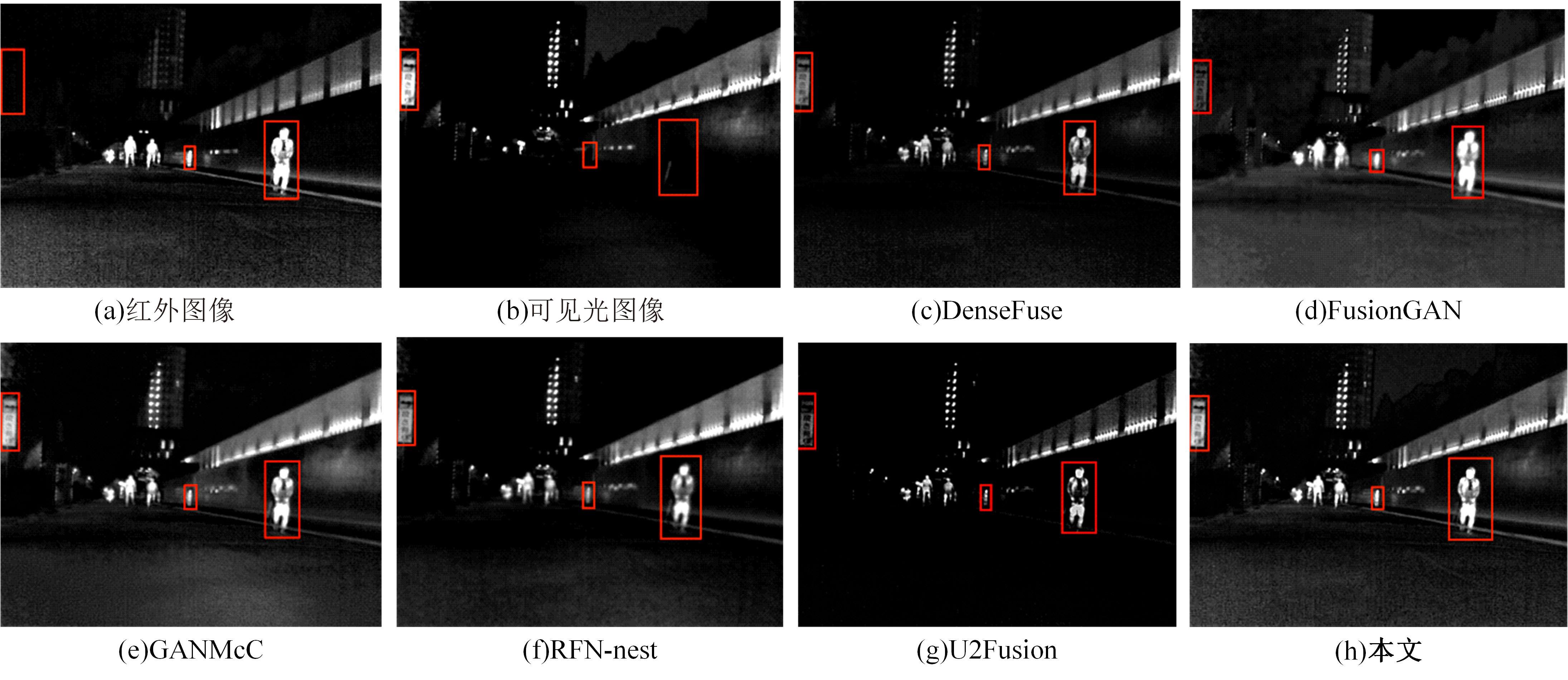
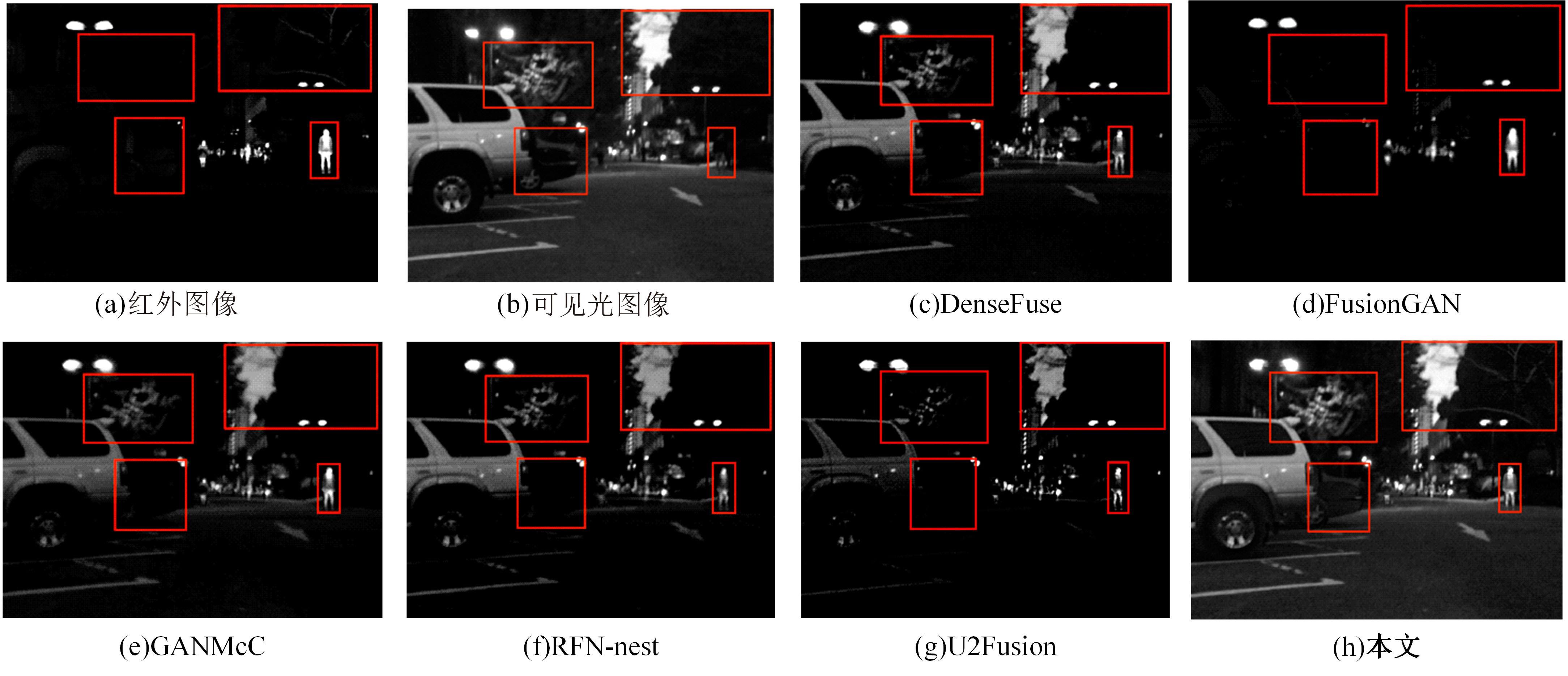
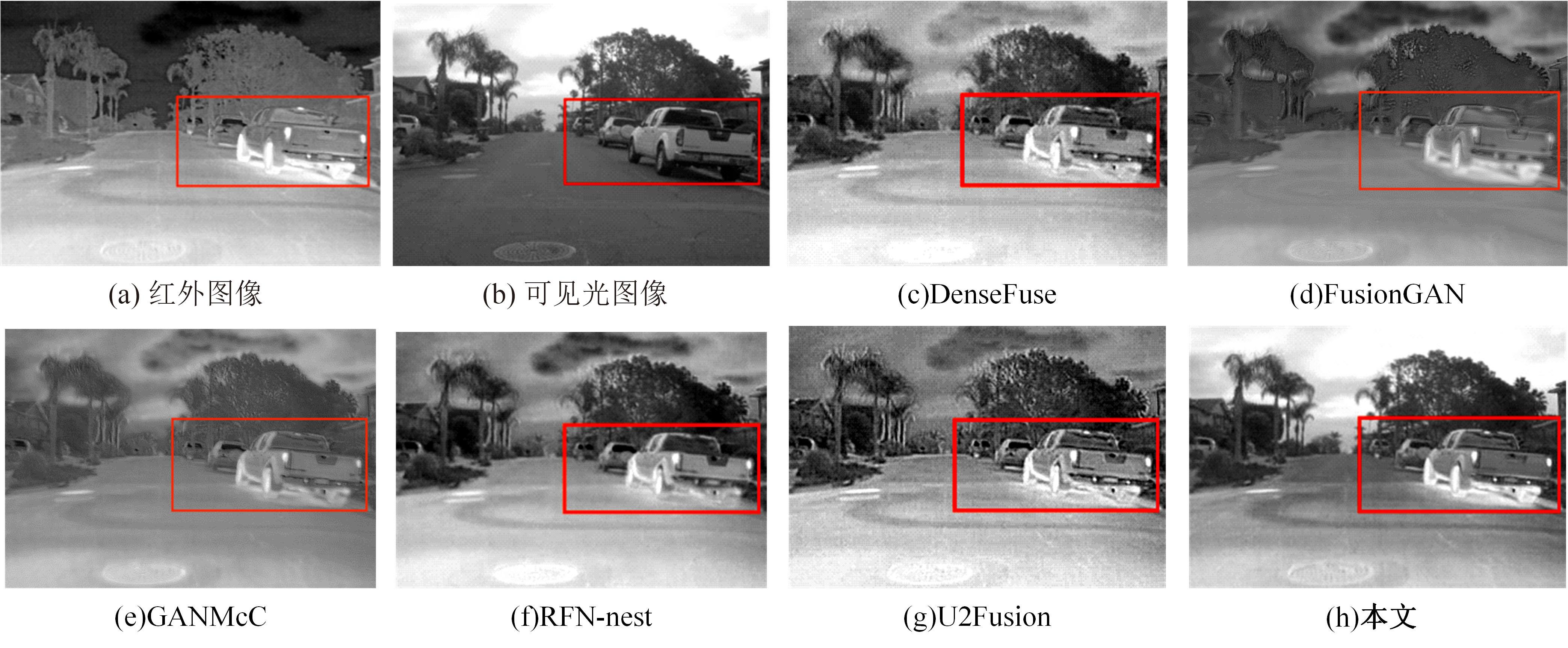
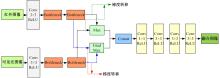
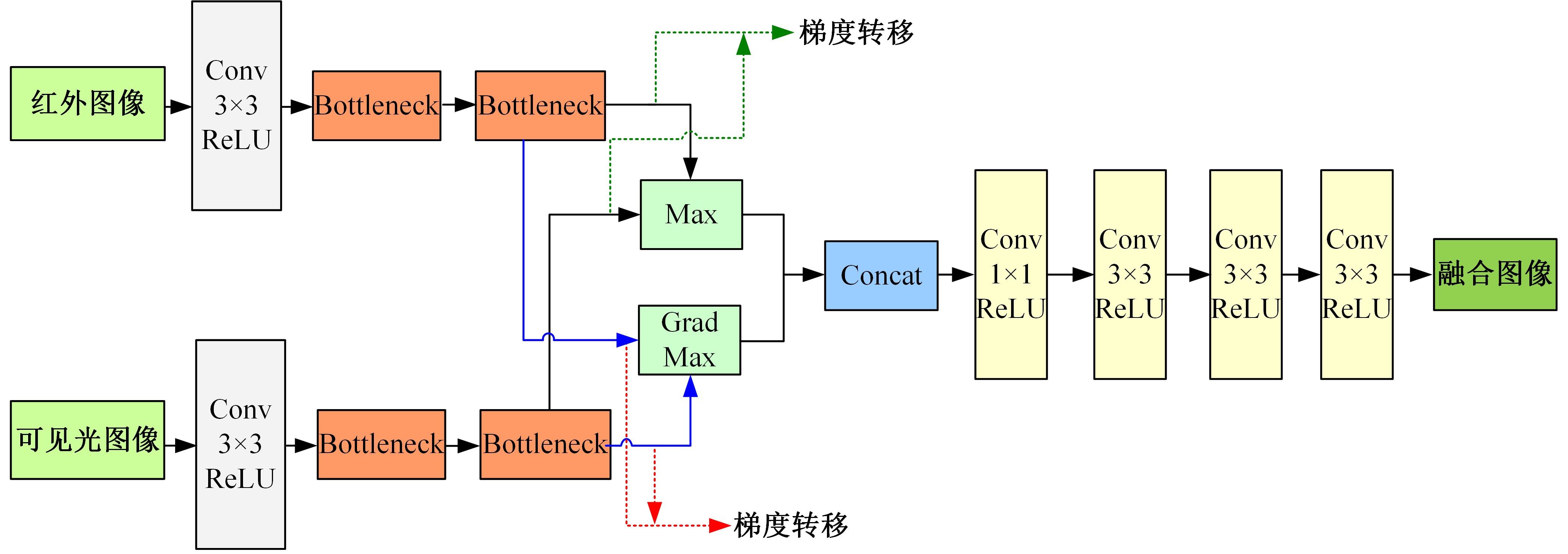
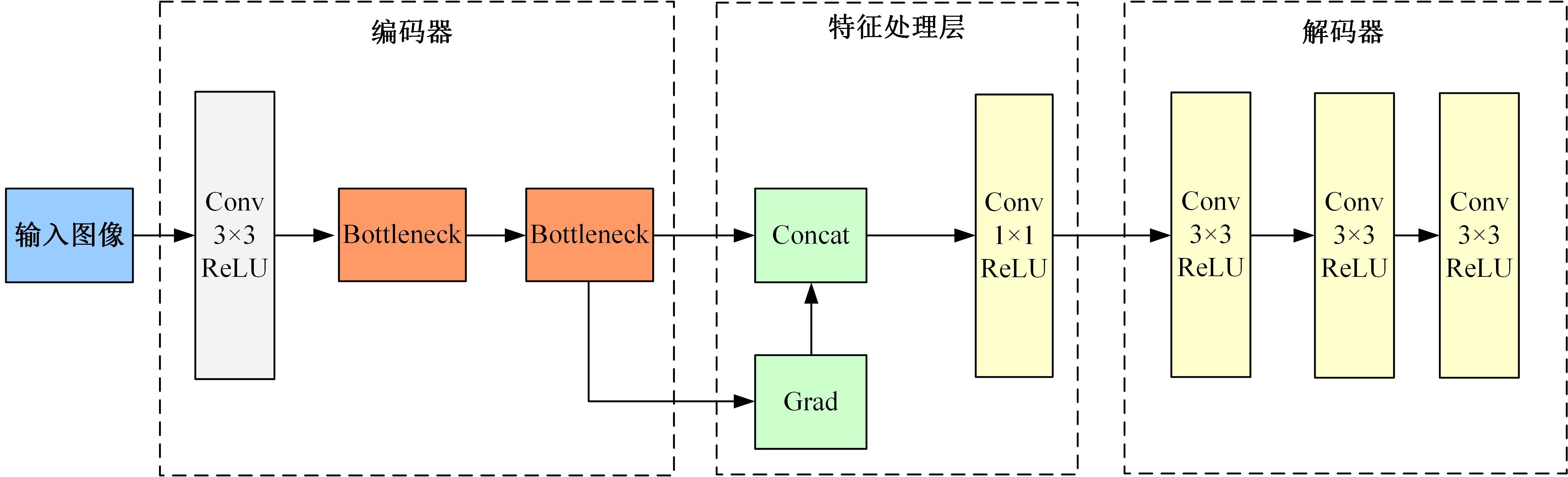
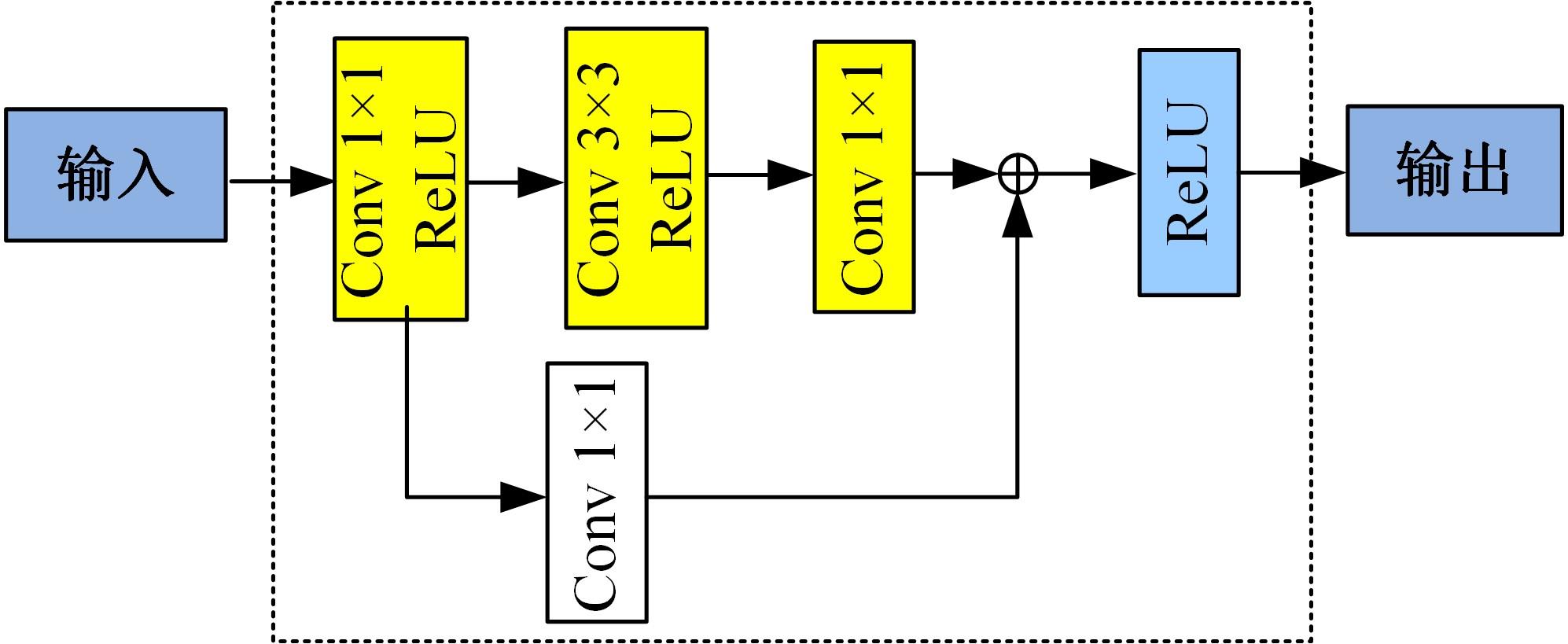
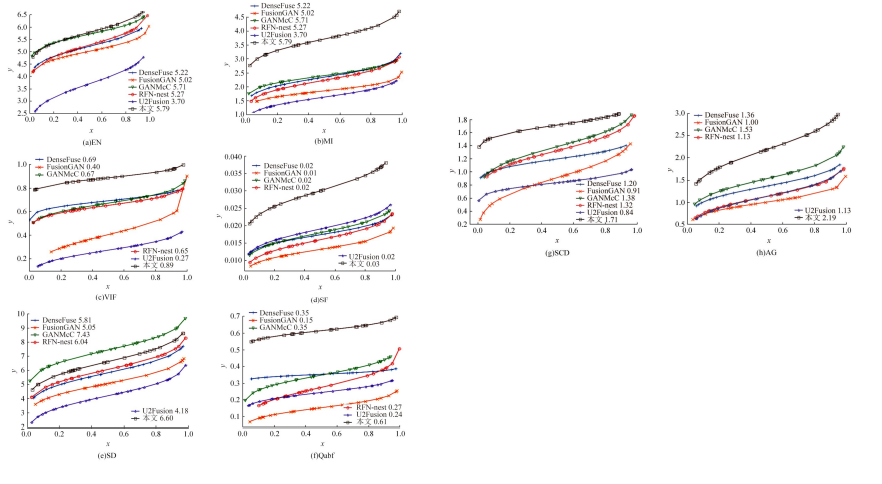
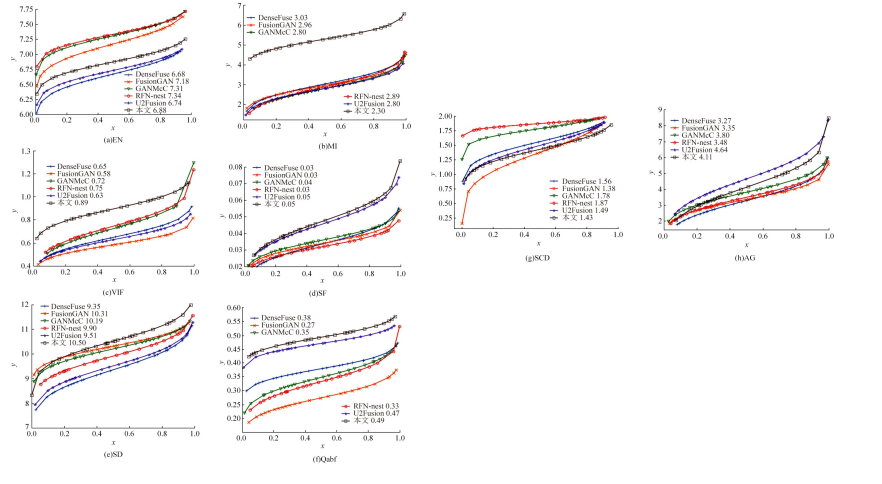
针对红外与可见光图像融合过程中图像特征提取不充分、易丢失中间层信息和训练时间长的问题,本文提出一种基于梯度转移结合自编码器的端到端轻量级图像融合网络结构。该网络结构由编码器、融合层和解码器三部分组成。首先,将Bottleneck块引入编码器当中,利用卷积层和Bottleneck块对输入的红外图像和可见光图像进行特征提取得到深度特征图,将梯度提取算子引入融合层,对获得的深度特征图进行处理获得对应的梯度图。其次,将每张深度特征图和对应的梯度图在融合层通过融合层策略对应融合,重新设计损失函数,将融合后的特征图和梯度图进行拼接并输入解码器进行解码重建出融合图像。最后,选取目前的代表性融合方法进行对比验证,在SF、MI、VIF、Qabf、SCD、AG、EN和SD 8个融合质量评估指标上,前七个指标性能提升显著,分别提高57.4%、54.6%、28.3%、74.2%、23.8%、43.1%、1.3%,第八个指标性能接近。并进行网络模型参数分析和时间复杂度对比实验,本文算法模型参数为12 352,算法用时为1.1246 s。实验结果表明:本文方法可以快速生成目标清晰、轮廓明显、纹理突出、符合人类视觉感受的融合图像。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | 沈英, 黄春红, 黄峰,等. 红外与可见光图像融合技术的研究进展[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(9): No.20200467. |
| Shen Ying, Huang Chun-hong, Huang Feng,et al. Research progress of infrared and visible image fusion technology[J].Infrared and Laser Engineering,2021, 50(9): No.20200467. | |
| 2 | 陈广秋, 陈昱存, 李佳悦, 等. 基于DNST和卷积稀疏表示的红外与可见光图像融合[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(3): 996-1010. |
| Chen Guang-qiu, Chen Yu-cun, Li Jia-yue,et al.Infrared and visible image fusion based on discrete nonseparable shearlet transform and convolutional sparse representation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2021,51(3): 996-1010. | |
| 3 | 李雄飞, 宋璐, 张小利. 基于协同经验小波变换的遥 感图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1307-1319. |
| Li Xiong-fei, Song Lu, Zhang Xiao-li. Remote sensing image fusion based on cooperative empirical wave let transform[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineer-ing and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4):1307-109. | |
| 4 | Zhang X C, Ye P, Leung H,et al. Object fusion tracking based on visible and infrared images:a comprehensive review[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 63(1): 166-187. |
| 5 | 陈卓, 方明, 柴旭, 等. 红外与可见光图像融合的U-GAN模型[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2020, 38(4): 904-912. |
| Chen Zhuo, Fang Ming, Chai Xu, et al. U-GAN model for infrared and visible images fusion[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2020, 38(4): 904-912. | |
| 6 | Ma J Y, Ma Y, Li C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 45(1): 153-178. |
| 7 | 陈潮起, 孟祥超, 邵枫, 等. 一种基于多尺度低秩分解的红外与可见光图像融合方法[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(11): 72-80. |
| Chen Chao-qi, Meng Xiang-chao, Shao Feng, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on multiscale low-rank decomposition[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(11): 72-80. | |
| 8 | 霍星, 邹韵, 陈影, 等. 双尺度分解和显著性分析相结合的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(12): 2813-2825. |
| Huo Xing, Zou Yun, Chen Ying, et al.Dual-scale decomposition and saliency analysis based infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(12): 2813-2825. | |
| 9 | 裴佩佩, 杨艳春, 党建武, 等. 基于滚动引导滤波器和卷积稀疏表示的红外与可见光图像融合方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(12): 56-63. |
| Pei Pei-pei, Yang Yan-chun, Dang Jian-wu, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on rolling guide filter and convolutional sparse representation[J]. Laser and Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(12): 56-63. | |
| 10 | 申铉京, 张雪峰, 王玉, 等. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| Shen Xuan-jing, Zhang Xue-feng, Wang Yu,et al. Multi⁃focus image fusion algorithm based on pixel⁃level convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. | |
| 11 | Liu Y, Chen X, Peng H, et al. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network[J].Information Fusion, 2017, 36(1): 191-207. |
| 12 | Prabhakar K R, Srikar V S, Babu R V. DeepFuse: a deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 4714-4722. |
| 13 | Li H, Wu X J. DenseFuse: a fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(5): 2614-2623. |
| 14 | Tang L, Yuan J, Zhang H, et al. PIAFusion: a progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware[J]. Information Fusion, 2022,3(7): 79-92. |
| 15 | Xu H, Ma J, Jiang J, et al. U2Fusion: a unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020,44(1): 502-518. |
| 16 | Ha Q, Watanabe K, Karasawa T, et al.MFNet: towards realtime semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 5108-5115. |
| 17 | Ma J, Wei Y, Liang P, et al. FusionGAN: a generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48(1): 11-26. |
| 18 | Ma J, Zhang H, Shao Z,et al. GANMcC: a generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 70: 1-14. |
| 19 | Li H, Wu X J, Josef K. RFN-Nest: an end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 72-86. |
| 20 | van Aardt J.Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classifification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2008, 2(1): No. 023522. |
| 21 | Qu G, Zhang D, Yan P. Information measure for performance of image fusion[J]. Electronics Letters, 2002, 38(7): 313-315. |
| 22 | Eskicioglu A M, Fisher P S.Image quality measures and their performance[J]. IEEE Trans. Commun., 1995, 43(12): 2959-2965. |
| 23 | Han Y, Cai Y, Cao Y, et al. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fifidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2013,14(2): 127-135. |
| [1] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [2] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [3] | 张自超,陈建. 基于双目仿鹰眼视觉与超分辨的果园三维点云重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1469-1481. |
| [4] | 梁礼明,周珑颂,尹江,盛校棋. 融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [5] | 夏超,王梦佳,朱剑月,杨志刚. 基于分层卷积自编码器的钝体湍流流场降阶分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 874-882. |
| [6] | 张云佐,郭威,李文博. 遥感图像密集小目标全方位精准检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1105-1113. |
| [7] | 龙关旭,张修石,辛公锋,王涛,杨干. 融合机器视觉的桥梁动态称重方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 188-197. |
| [8] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [9] | 肖明尧,李雄飞,朱芮. 基于NSST域像素相关分析的医学图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [10] | 张云佐,董旭,蔡昭权. 拟合下肢几何特征的多视角步态周期检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
| [11] | 何颖,王卓然,周旭,刘衍珩. 融合社交地理信息加权矩阵分解的兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [12] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [13] | 赵亚慧,李飞雨,崔荣一,金国哲,张振国,李德,金小峰. 基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [14] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [15] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
|
||