吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1531-1538.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180257
• • 上一篇
冻融对粉砂土力学特性及路堤边坡稳定性的影响
- 1. 吉林建筑大学 交通科学与工程学院,长春 130118
2. 江苏东道交通科技集团有限公司,南京 210011
3. 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of silty sand and subgrade slope stability
Yun-long ZHANG1( ),Liu-guang ZHOU1,2,Jing WANG1,Chun-li WU3(
),Liu-guang ZHOU1,2,Jing WANG1,Chun-li WU3( ),Xiang LYU3
),Xiang LYU3
- 1. School of Transportation Science, Jilin Jianzhu University, Changchun 130118, China
2. Jiangsu Dong Dao Transportation Science & Technology Group,Nanjing 210011,China 3. College of Transportation, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
摘要:
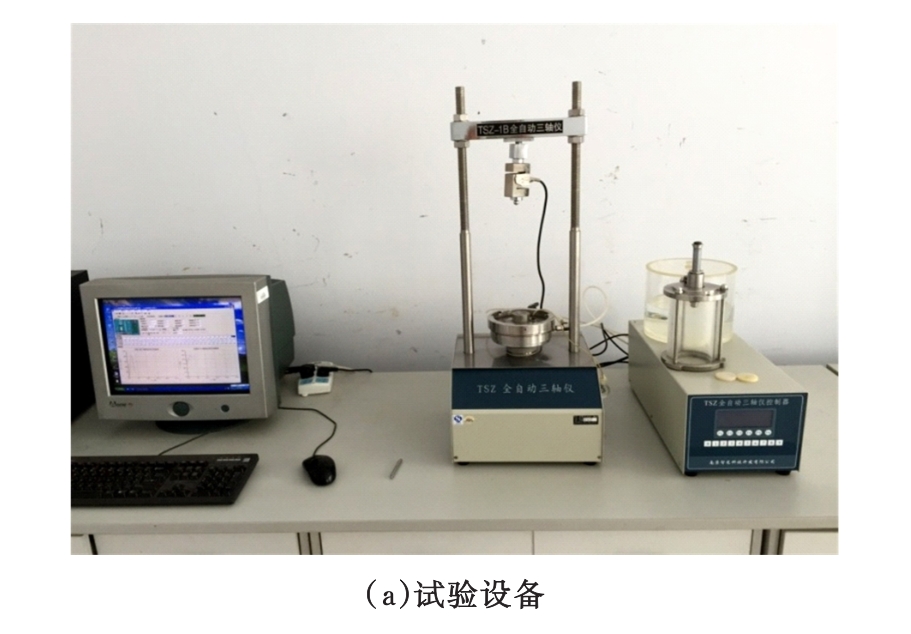
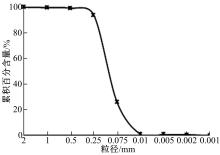
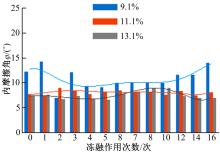
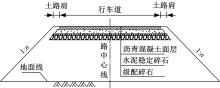
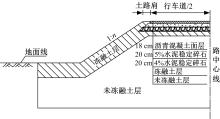
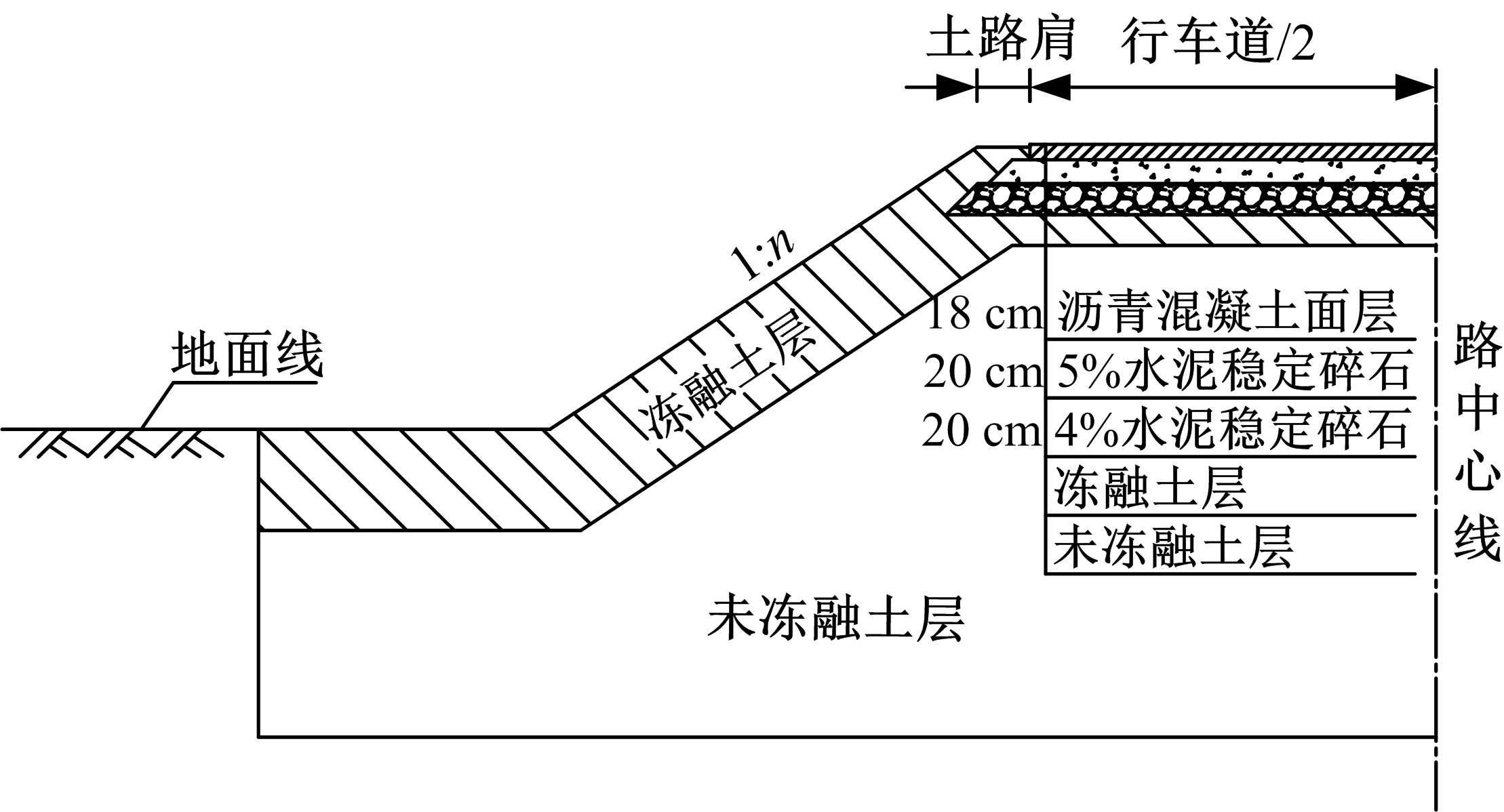
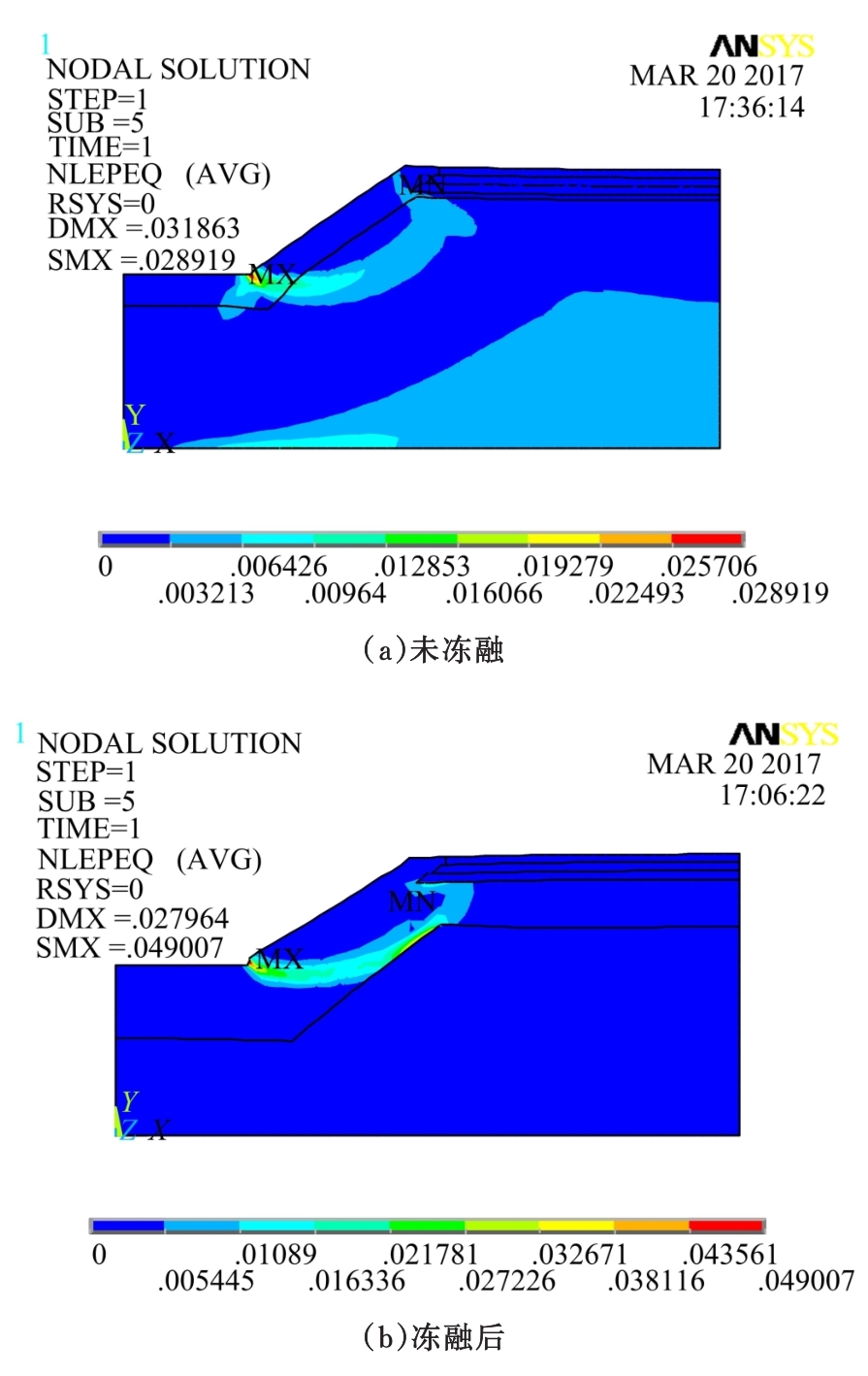
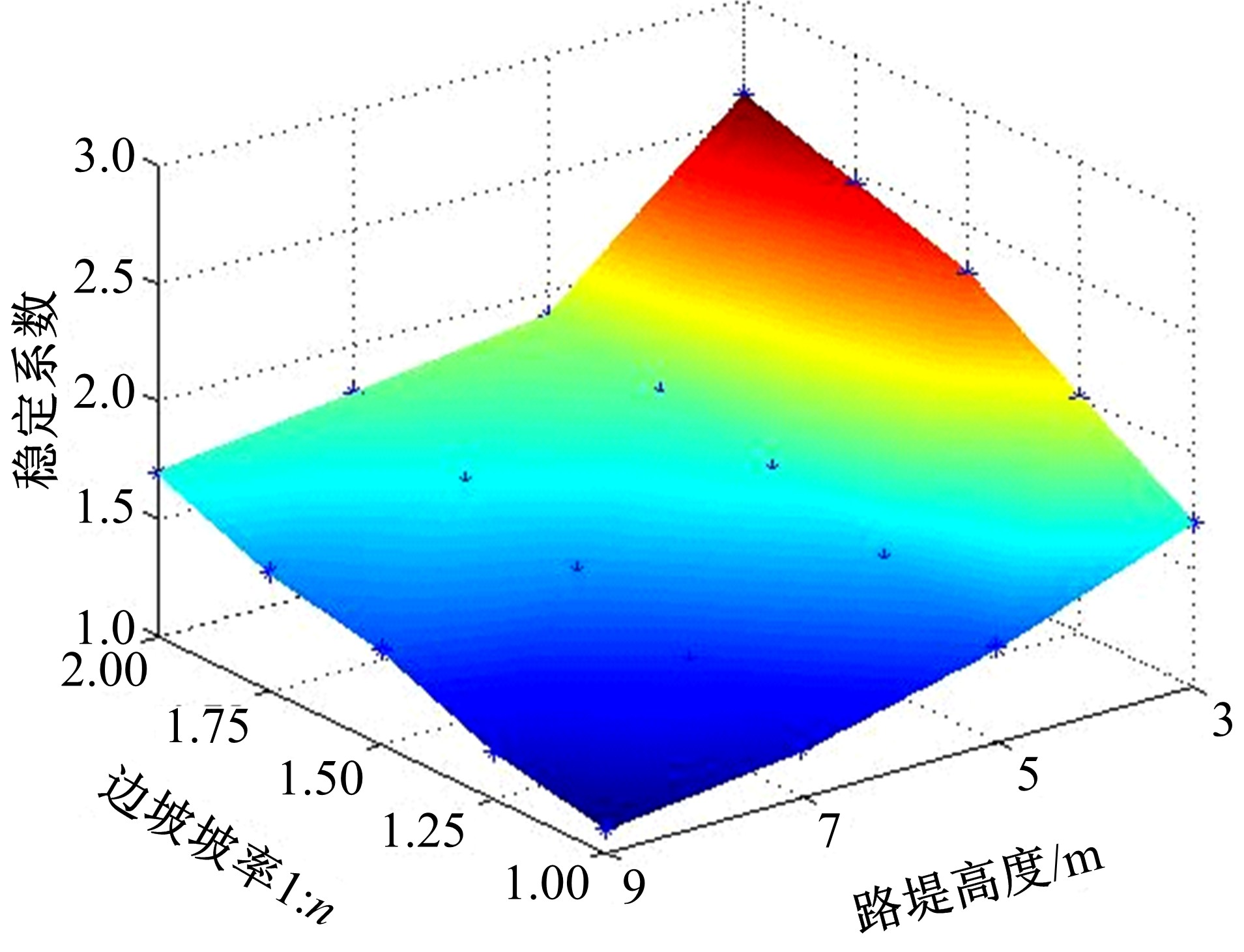
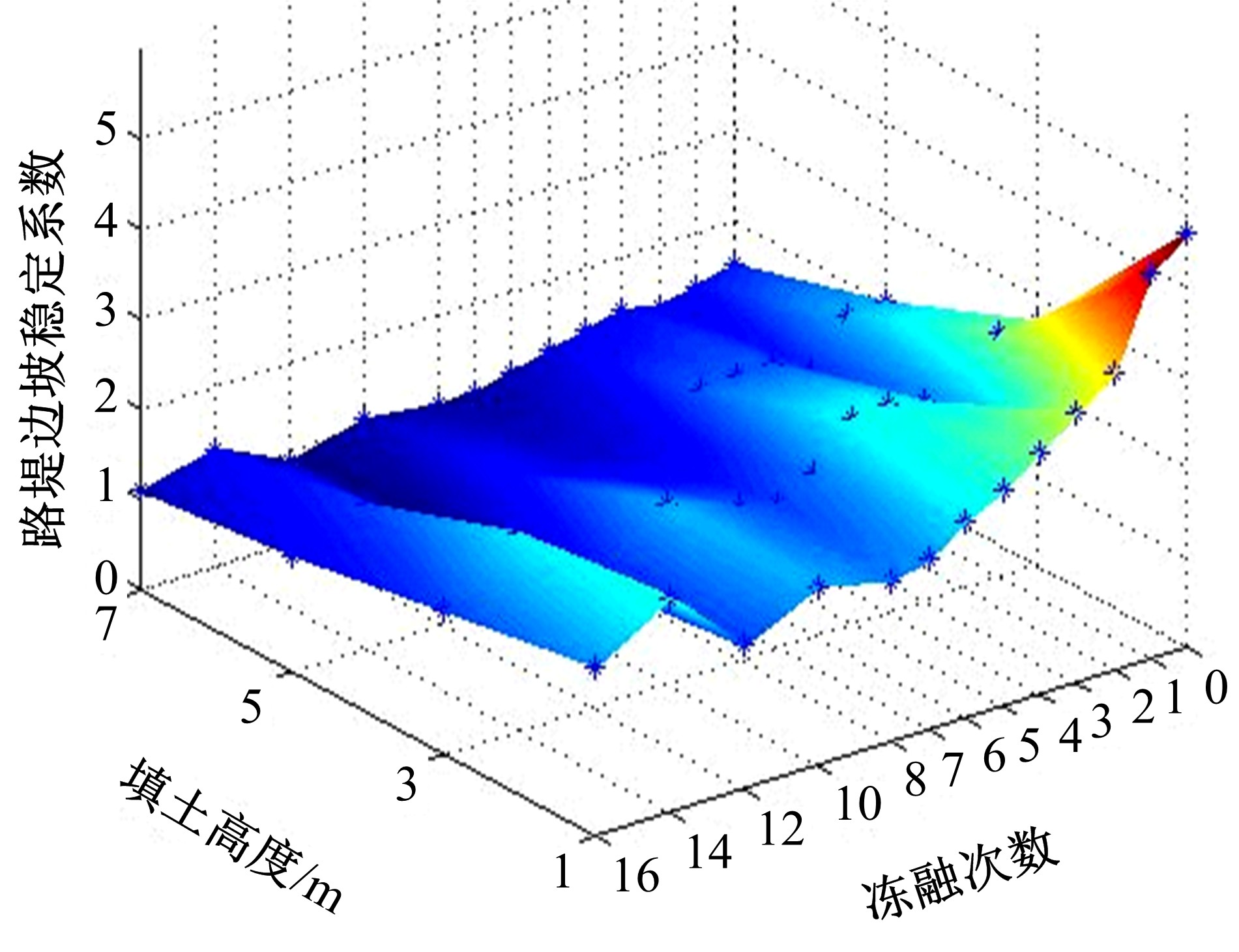
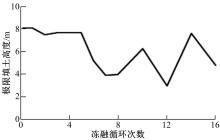
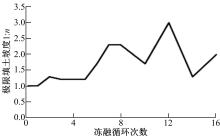
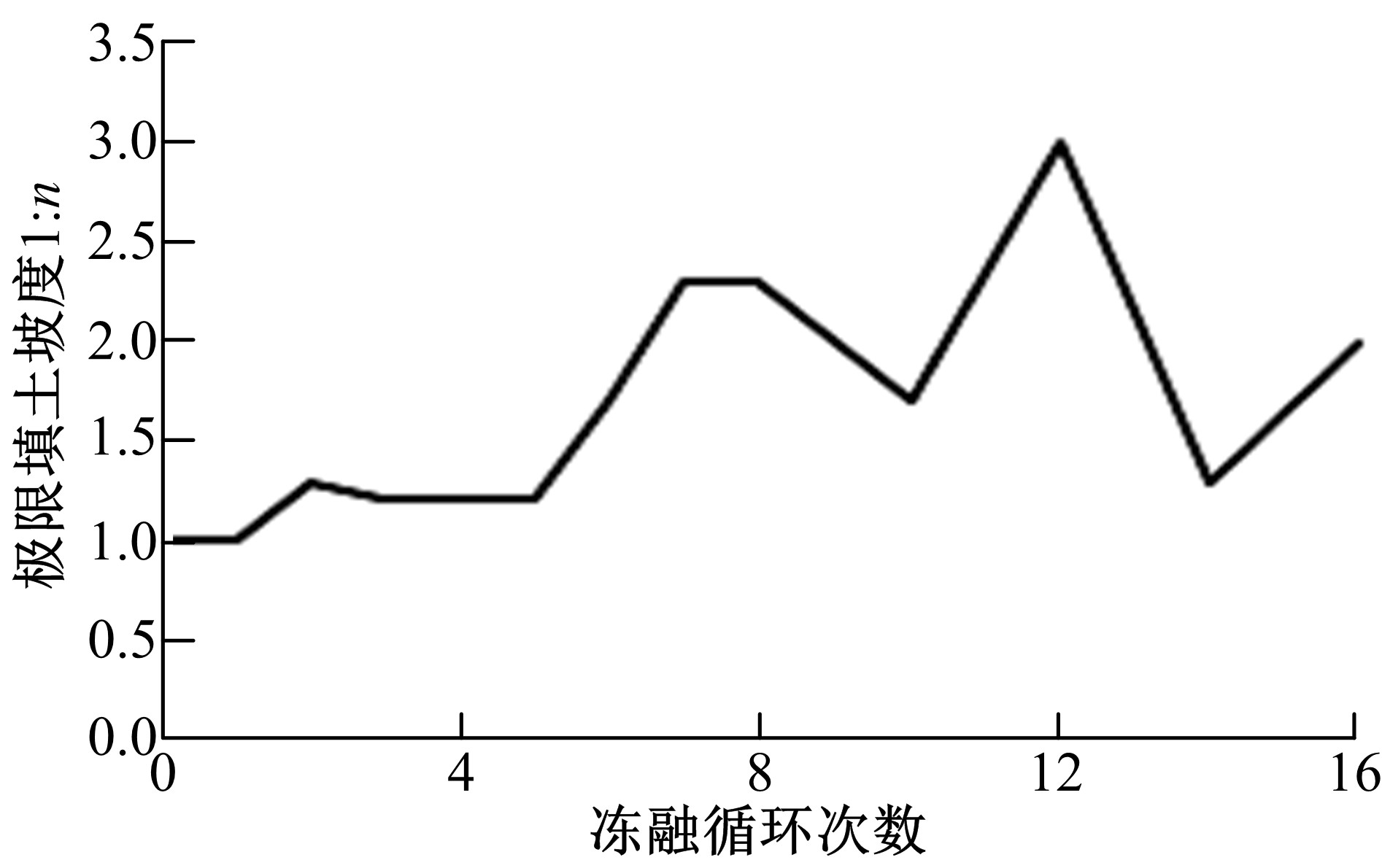
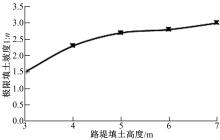
为研究粉砂土路堤在冻融循环作用下的力学特性以及采用粉砂土填筑的路堤边坡稳定性,基于静三轴试验,研究了不同含水量状态下,季冻区粉砂土在经历不同次数冻融循环后的粘聚力、内摩擦角等宏观力学特性的变化规律。以此为依据,采用有限元数值模型,针对不同坡度和不同填土高度对应的粉砂土填方路基,进行了冻融循环作用对边坡稳定系数的影响规律研究。研究结果表明:随含水量增大,冻融循环次数对粉砂土粘聚力的影响程度逐渐增强,当含水量较大时,粘聚力下降70%~80%;随冻融循环次数增加,粉砂土内摩擦角先降低,后略有增大;随含水量增大,冻融循环对粉砂土内摩擦角的影响有减弱趋势;冻融循环作用可使粉砂土路堤边坡稳定系数明显降低,冻融后的边坡稳定系数最大降幅可达到冻融前的49%;季冻区粉砂土路堤的最大填土高度不应超过4 m,小于3 m的填方路堤,极限坡度不应陡于1∶1.5,超过3 m的极限坡度不应超过1∶2.5。
中图分类号:
- U416.1
| 1 | BondarenkoG I, SadovskyA V. Water content effect of the thawing clay soils on shear strength[C]∥Proceedings of 7th International Symposium on Ground Freezing, Rotterdam, Netherlands, 1991: 123-127. |
| 2 | OgataN, KataokaT, KomiyaA. Effect of freezing-thawing on the mechanical properties of soil[C]∥Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Ground Freezing, Sapporo, 1985: 5-7. |
| 3 | 谈云志, 吴翩, 付伟, 等. 改良粉土强度的冻融循环效应与微观机制[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(10): 2827-2834. |
| TanYun-zhi, WuPian, FuWei, et al. Strength and micromechanism of improved silt under freeze-thaw cycle effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(10): 2827-2834. | |
| 4 | 朱志铎, 刘松玉, 邵光辉, 等. 粉土及其稳定土的三轴试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2005, 26(12): 1967-1971. |
| ZhuZhi-duo, LiuSong-yu, ShaoGuang-hui, et al. Research on silts and silts treated with stabilizers by triaxial shear tests[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(12): 1967-1971. | |
| 5 | 严晗, 王天亮, 刘建坤, 等. 反复冻融条件下粉砂土动力学参数试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(3): 683-688. |
| YanHan, WangTian-liang, LiuJian-kun, et al. Experimental study of dynamic parameters of silty soil subjected to repeated freeze-thaw[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3):683-688. | |
| 6 | 严晗, 王天亮, 刘建坤. 粉砂土反复冻胀融沉特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(11): 3159-3165. |
| YanHan, WangTian-liang, LiuJian-kun. Experimental study of repeated frost heave and thaw settlement properties of silty sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(11): 3159-3165. | |
| 7 | 蔡迎春, 郑元勋, 刘忠玉, 等. 飞机荷载作用下粉砂土路基动力响应研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(9): 2863-2868. |
| CaiYing-chun, ZhengYuan-xun, LiuZhong-yu, et al. Study of dynamic response of silty sand subgrade loaded by airplane[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 2863-2868. | |
| 8 | 常丹, 刘建坤, 李旭. 冻融循环下粉砂土应力-应变归一化特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(12): 3500-3505. |
| ChangDan, LiuJian-kun, LiXu. Normalized stress-strain behavior of silty sand under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(12): 3500-3505. | |
| 9 | 严晗, 刘建坤, 王天亮. 冻融对粉砂土力学性能影响的试验研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2013, 37(4): 73-77. |
| YanHan, LiuJian-kun, WangTian-liang. Experimental research of influences of freeze-thaw on the mechanical properties of silty soil[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiao Tong University, 2013, 37(4): 73-77. | |
| 10 | 常丹, 刘建坤, 李旭. 冻融循环下粉砂土屈服及强度特性的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(8): 1721-1728. |
| ChangDan, LiuJian-kun, LiXu. Experimental study on yielding and strength properties of silty sand under freezing-thawing cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(8): 1721-1728. | |
| 11 | 陈鹏, 徐博侯. 基于因素敏感性的边坡稳定可靠度分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2012, 25(4): 42-48. |
| ChenPeng, XuBo-hou. Reliability analysis of slope stability based on factors sensitivity[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2012, 25(4): 42-48. | |
| 12 | 李航, 于玲. 冻融循环作用下路基边坡稳定性变化研究[J]. 路基工程, 2011(5): 26-28, 32. |
| LiHang,YuLing. Study on subgrade slope stability under the effect of freeze-thaw cycle[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2011(5): 26-28, 32. | |
| 13 | 陈国庆, 黄润秋, 石豫川, 等. 基于动态和整体强度折减法的边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(2): 243-256. |
| ChenGuo-qing,HuangRun-qiu,ShiYu-chuan,et al. Stability analysis of slope based on dynamic and whole strength reduction methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(2): 243-256. | |
| 14 | 栾茂田, 武亚军, 年廷凯. 强度折减有限元法中边坡失稳的塑性区判据及其应用[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2003, 23(3): 1-8. |
| LuanMao-tian, WuYa-jun, Ting-kaiNian . An alternative criterion for evaluating slope stability based on development of plastic zone by shear strength reduction FEM[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2003, 23(3): 1-8. | |
| 15 | 陈祖煜. 土质边坡稳定分析[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2003. |
| [1] | 彭勇,高华,万蕾,刘贵应. 沥青混合料劈裂强度影响因素数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [2] | 于天来,李海生,黄巍,王思佳. 预应力钢丝绳加固钢筋混凝土梁桥抗剪性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [3] | 李晓珍,柳俊哲,戴燕华,贺智敏,巴明芳,李玉顺. 碳化作用下水泥浆内亚硝酸根离子的含量分布[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [4] | 黄晓明,曹青青,刘修宇,陈嘉颖,周兴林. 基于路表分形摩擦理论的整车雨天制动性能模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [5] | 王静,吕翔,曲肖龙,钟春玲,张云龙. 路基土抗剪强度与化学及矿物成分的关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [6] | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军. 沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [7] | 臧国帅, 孙立军. 基于惰性弯沉点的刚性下卧层深度设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [8] | 念腾飞, 李萍, 林梅. 冻融循环下沥青特征官能团含量与流变参数灰熵分析及微观形貌[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [9] | 宫亚峰, 申杨凡, 谭国金, 韩春鹏, 何钰龙. 不同孔隙率下纤维土无侧限抗压强度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [10] | 程永春, 毕海鹏, 马桂荣, 宫亚峰, 田振宏, 吕泽华, 徐志枢. 纳米TiO2/CaCO3-玄武岩纤维复合改性沥青的路用性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [11] | 季文玉, 李旺旺, 过民龙, 王珏. 预应力RPC-NC叠合梁挠度试验及计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 129-136. |
| [12] | 张仰鹏, 魏海斌, 贾江坤, 陈昭. 季冻区组合冷阻层应用表现的数值评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [13] | 马晔, 尼颖升, 徐栋, 刁波. 基于空间网格模型分析的体外预应力加固[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
| [14] | 罗蓉, 曾哲, 张德润, 冯光乐, 董华均. 基于插板法膜压力模型的沥青混合料水稳定性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1753-1759. |
| [15] | 尼颖升, 马晔, 徐栋, 李金凯. 波纹钢腹板斜拉桥剪力滞效应空间网格分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1453-1464. |
|
||