吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 382-388.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181069
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
基于仿生鼻腔优化的油气检测方法与实验新技术
翁小辉1,2,3( ),孙友宏4,张书军1,2,5,谢军1,2,常志勇1,2,4(
),孙友宏4,张书军1,2,5,谢军1,2,常志勇1,2,4( )
)
- 1. 吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室, 长春 130022
2. 吉林大学 生物与农业工程学院, 长春 130022
3. 吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院, 长春 130022
4. 吉林大学 油页岩地下原位转化与钻采技术国家地方联合工程实验室, 长春 130021
5. 格罗斯特郡大学 计算机与技术学院, 公园区, 切尔滕纳姆 GL50 2RH, 英国
Oil and gas detection method and experimental new technology based on bionic nasal chamber optimization
Xiao-hui WENG1,2,3( ),You-hong SUN4,Shu-jun ZHANG1,2,5,Jun XIE1,2,Zhi-yong CHANG1,2,4(
),You-hong SUN4,Shu-jun ZHANG1,2,5,Jun XIE1,2,Zhi-yong CHANG1,2,4( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
2. College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
3. College of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
4. National?Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of In?situ Conversion, Drilling and Exploitation Technology for Oil Shale, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
5. School of Computing and Technology, University of Gloucestershire, The Park, Cheltenham GL50 2RH, UK
摘要:
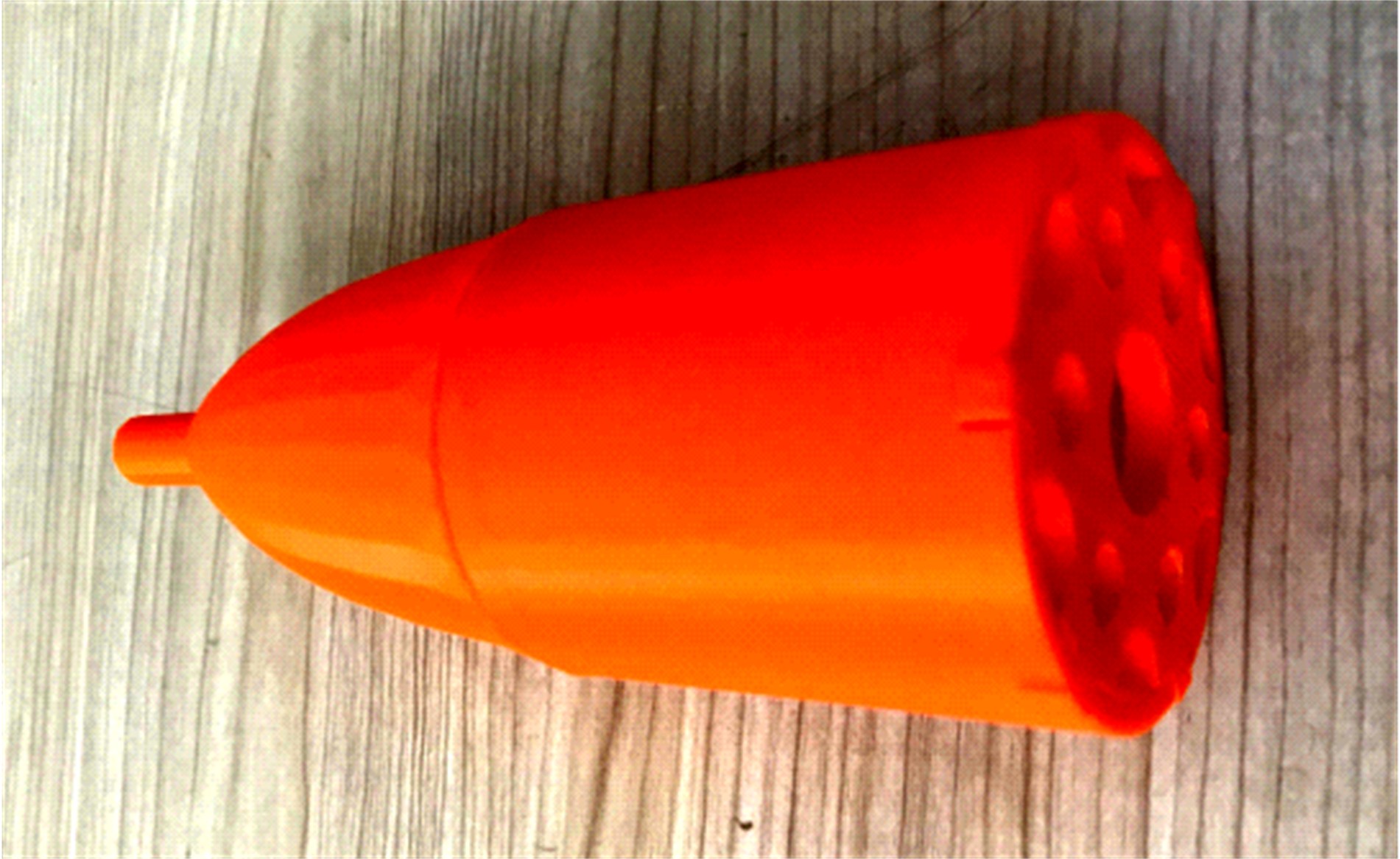
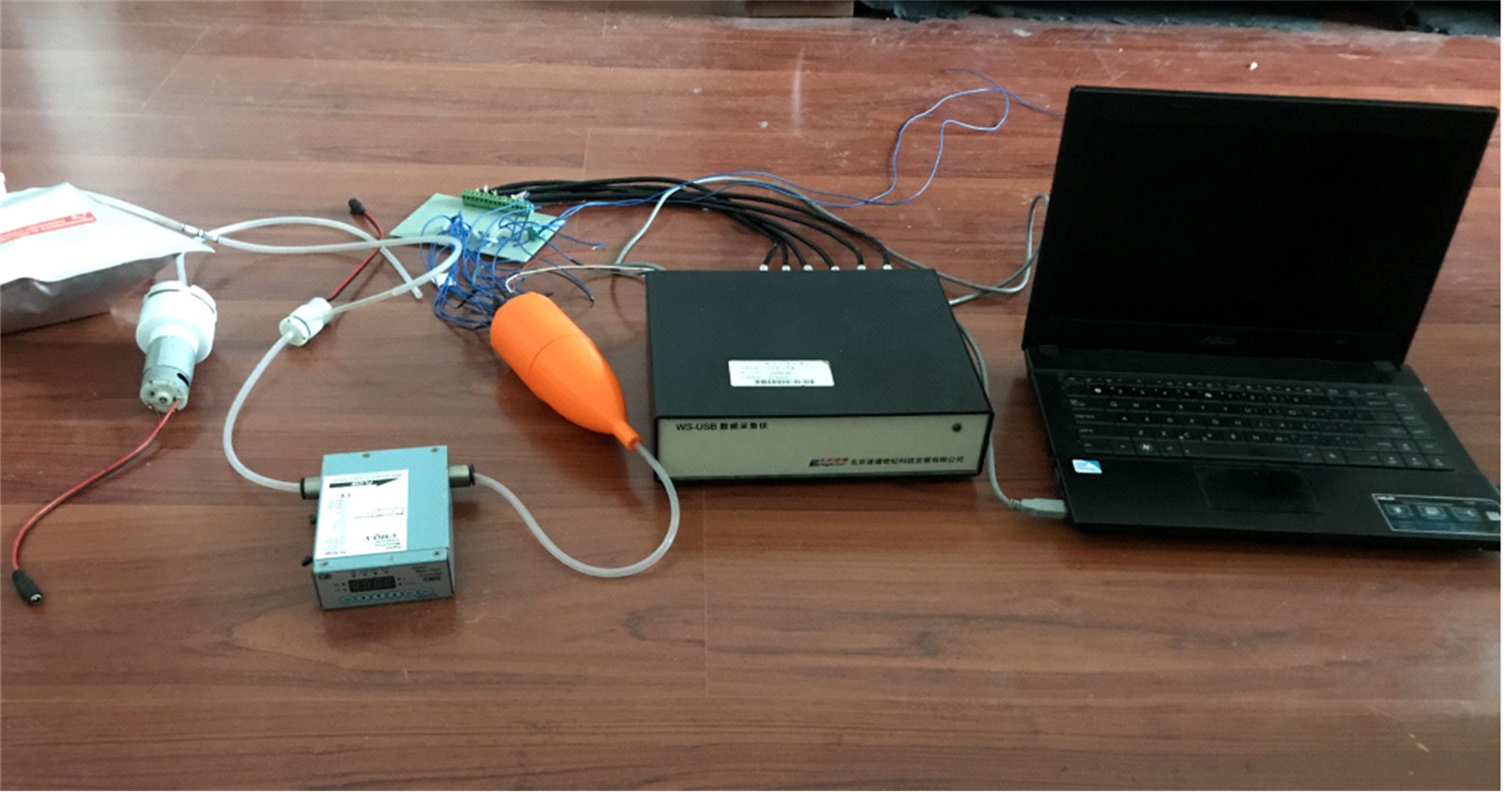
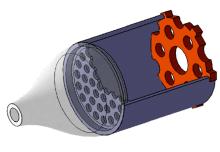
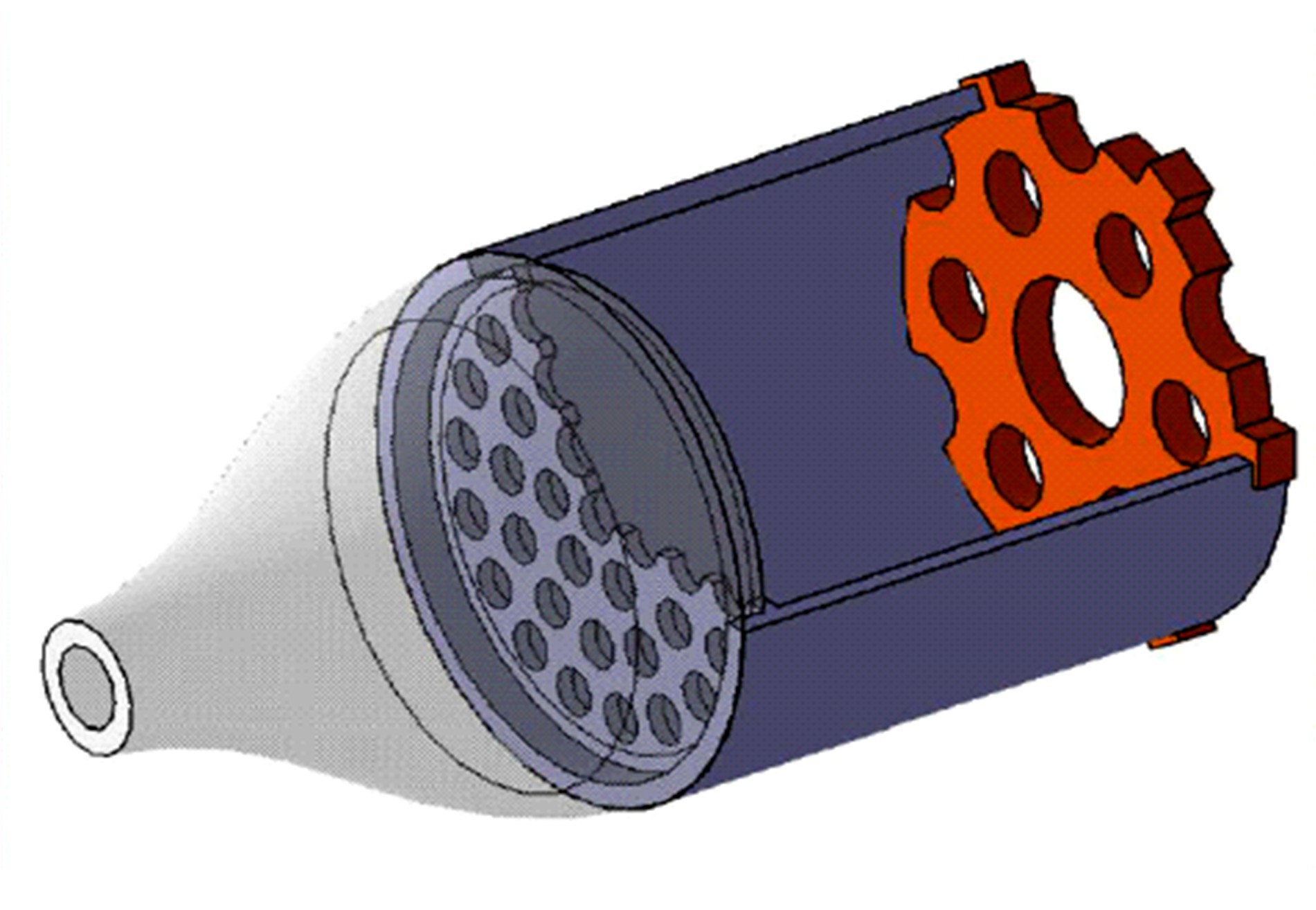
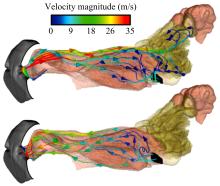
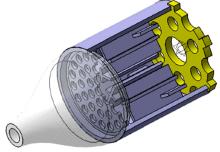
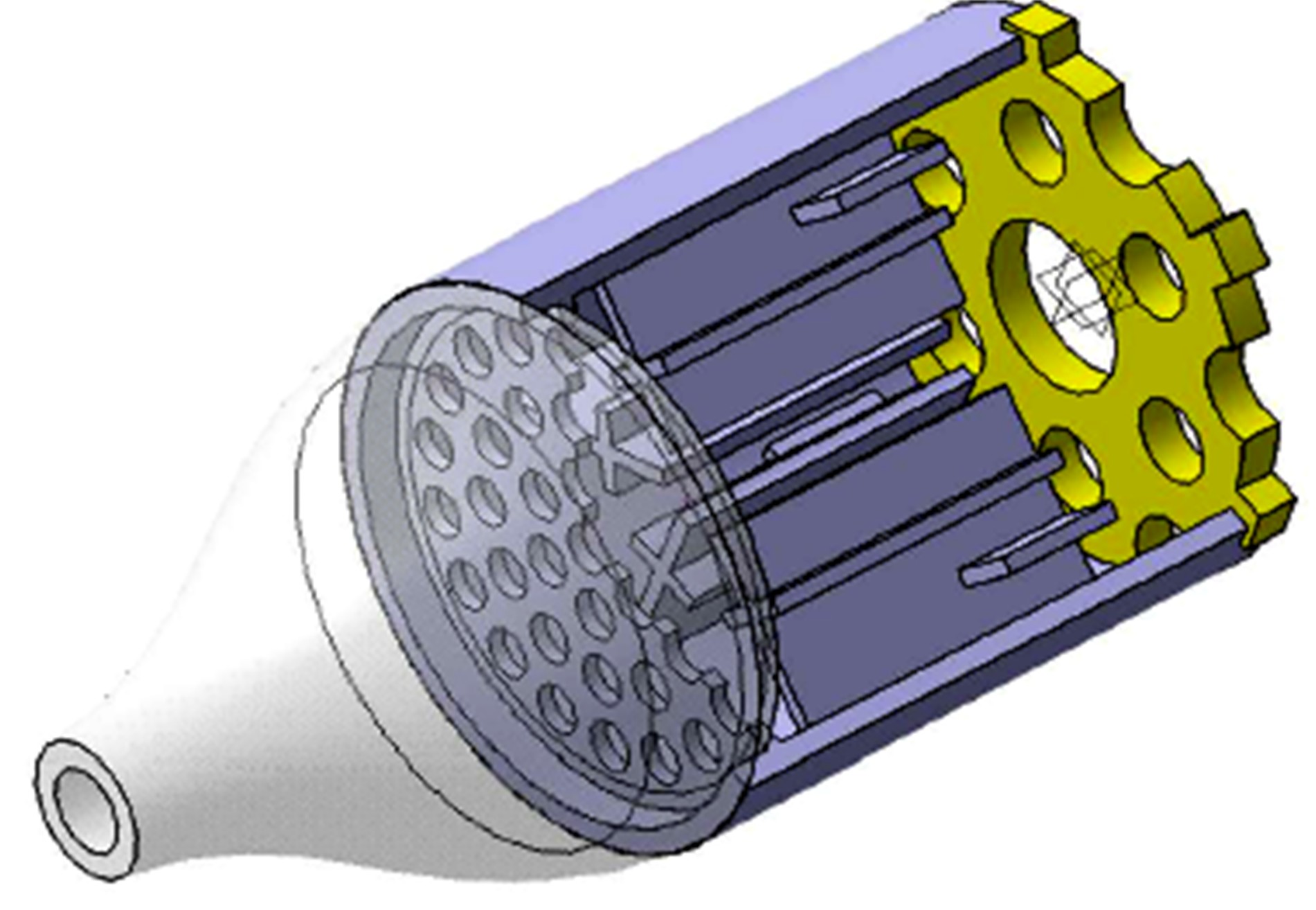
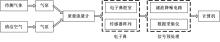
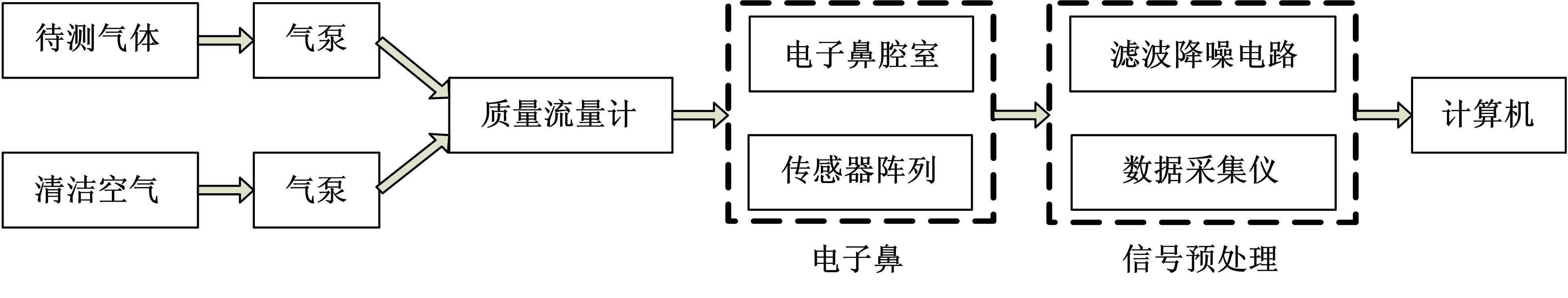
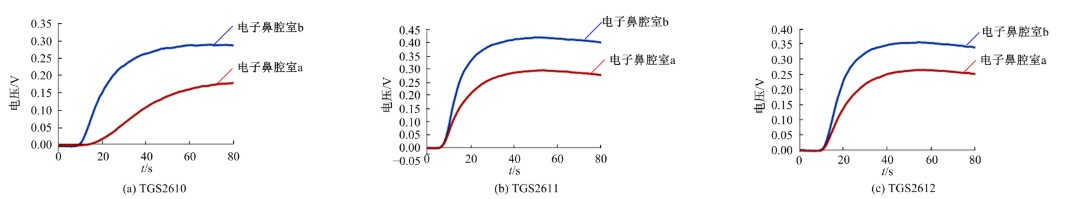
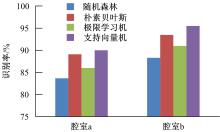
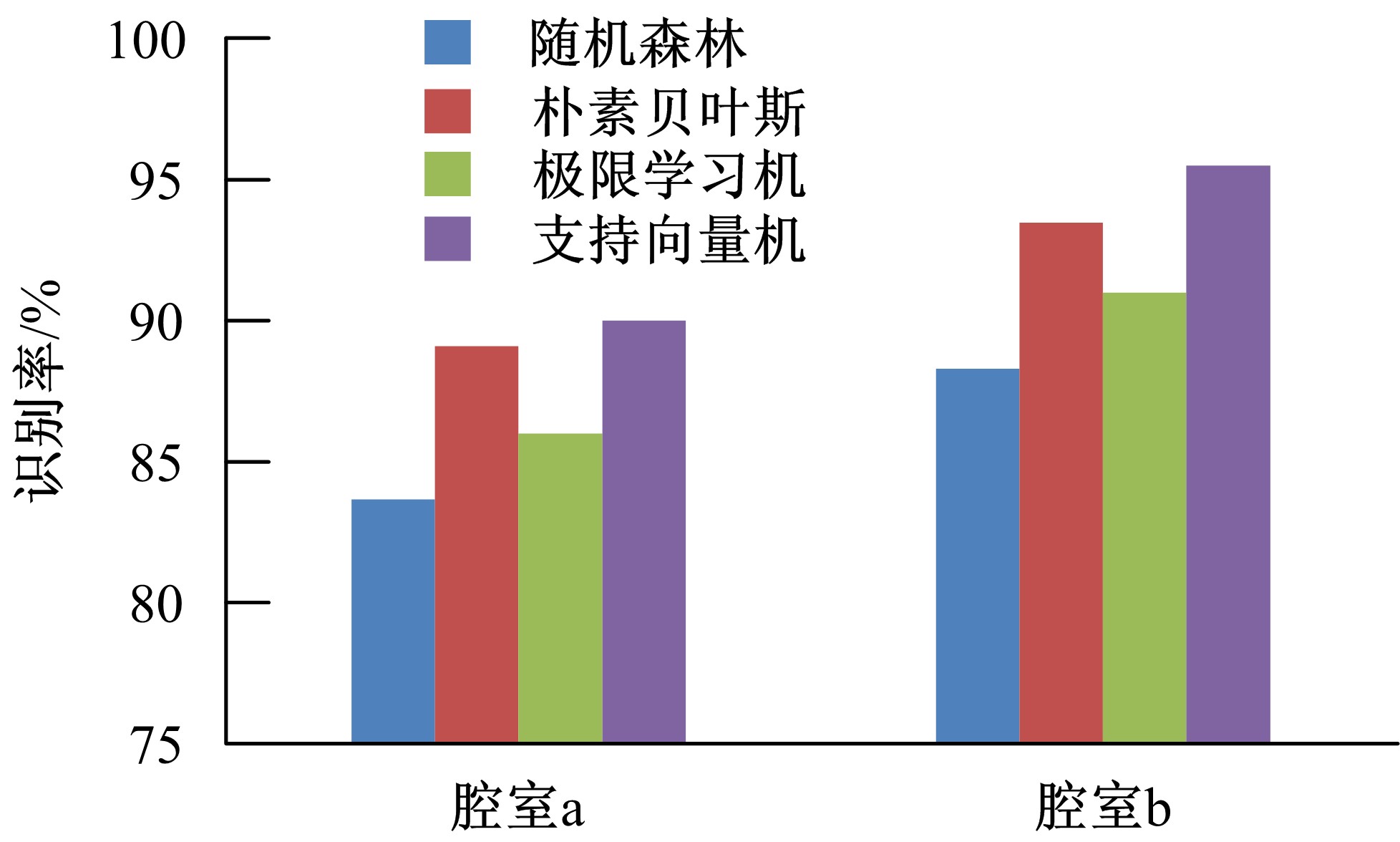
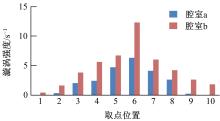
设计了一种适用于油气检测的小型仿生电子鼻系统。通过分析狗鼻腔鼻流道内部的结构特征及流场分布情况,提出了模拟狗鼻腔的仿生电子鼻腔室,解决油气检测装置尺寸臃肿、操作不灵活等问题。使用3D打印腔室样件进行烃类混合气体检测对比试验,采用十折交叉验证法比较随机森林、朴素贝叶斯、极限学习机和支持向量机算法识别效果。结果表明,优化检测腔室后的电子鼻系统灵敏度较普通腔室电子鼻系统有明显提高,识别率提高5.5%,构建的三维仿真腔室CFD分析结果也验证了本文仿生腔室的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TH763
| 1 | 李樟云 . 随钻气体分离先导技术研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学化学化工学院, 2011. |
| Li Zhang-yun . Study on pilot technology of gas separation while drilling[D]. Xiamen: College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Xiamen University, 2011. | |
| 2 | Sun Xi-yang , Liu Lin-feng , Wang Zhan . An optimized multi-classifiers ensemble learning for identification of ginsengs based on electronic nose[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2017, 266: 135-144. |
| 3 | 张哲 . 仿生电子鼻传感器阵列设计及其在牛肉品质检验中的应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学生物与农业工程学院, 2008. |
| Zhang Zhe . Designs of sensor matrixes for biomimetic electronic nose and their application in detection of beef quality[D]. Changchun: College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering,Jilin University, 2008. | |
| 4 | 常志勇, 陈东辉, 佟月英, 等 . 基于人体嗅觉特征的猪肉新鲜度仿生电子鼻检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2012, 42(增刊1): 131-134. |
| Chang Zhi-yong , Chen Dong-hui , Tong yue-ying , et al . Human olfactory feature based bionic electronic nose technology for pork freshness detection[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(Sup.1): 131-134. | |
| 5 | Zhou H , Luo D , Gholam H H , et al . Identification of Chinese herbal medicines with electronic nose technology: applications and challenges[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(5):No.1073. |
| 6 | Li Shang-zhen , Zeng Su-ling , Wu Yan , et al . Cultivar differentiation of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium by a combination of hierarchical three-step filtering metabolomics analysis, DNA barcoding and electronic nose[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1056: 62-69. |
| 7 | Sun H , Tian F , Liang Z , et al . Sensor array optimization of electronic nose for detection of bacteria in wound infection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(9): 7350-7358. |
| 8 | Domenico Cipriano , Laura Capelli . Evolution of electronic noses from research objects to engineered environmental odour monitoring systems: a review of standardization approaches[J]. Biosensors, 2019, 92(2): No.75. |
| 9 | Zarra T , Cimatoribus C , Naddeo V , et al . Environmental odour monitoring by electronic nose[J]. Global Nest Journal, 2019, 20(3): 664-668. |
| 10 | Yang H , Nguyen Q T , Ping Z , et al . Desorption and pervaporation properties of zeolite-filied poly(dimethylsiloxane) membranes[J]. Material Research Innovations, 2001, 5(2): 101-106. |
| 11 | Wen J , Inthavong K , Tu J , et al . Numerical simulations for detailed airflow dynamics in a human nasal chamber[J]. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology, 2008, 161(2): 125-135. |
| 12 | Falcitelli M , Benassi A , Francesco F D , et al . Fluid dynamic simulation of a measurement chamber for electronic noses[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2002, 85(1/2): 166-174. |
| 13 | Waldrop L D , Hann M , Henry A K , et al . Ontogenetic changes in the olfactory antennules of the shore crab, Hemigrapsus Oregonensis, maintain sniffing function during growth[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2015, 102 (12):1-19. |
| 14 | Che H F K , Taylor J E , Covington J A , et al . An electronic nose employing dual-channel odour separation columns with large chemosensor arrays for advanced odour discrimination[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2009, 141(1): 134-140. |
| 15 | Giacomo Viccione , Daniele Spiniello , Tiziano Zarra , et al . Fluid dynamic simulation of odour measurement chamber[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2014, 40: 109-114. |
| 16 | 魏荣兴 . 影响犬嗅觉能力的相关因素[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2016(16): 189-190. |
| Wei Rong-xing . Related factors affecting dogs'olfactory ability[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2016(16): 189-190. | |
| 17 | Craven Brent A , Paterson Eric G , Settles Gary S . The fluid dynamics of canine olfaction: unique nasal airflow patterns as an explanation of macrosmia[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2009, 47(7): 933-943. |
| 18 | Craven Brent A , Paterson Eric G , Settles Gary S . Development and verification of a high-fidelity computational fluid dynamics model of canine nasal airflow[J]. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 2009, 131(9): 091002. |
| 19 | Zhao K , Dalton P , Yang G C , et al . Numerical modeling of turbulent and laminar airow and odorant transport during snifng in the human and rat nose[J]. Chemical Senses, 2006, 31(2): 107-118. |
| 20 | Francesco F D , Falcitelli M , Marano L , et al . A radially symmetric measurement chamber for electronic noses[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2005, 105(2): 295-303. |
| [1] | 于斌斌,胡亮,迟令. 可抵抗内外部攻击的无线传感器网络数字签名方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1676-1681. |
| [2] | 闫光,卢建中,张开宇,孟凡勇,祝连庆. 温度解耦大量程光纤光栅应变传感器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1682-1688. |
| [3] | 王鹏宇,赵世杰,马天飞,熊晓勇,程馨. 基于联合概率数据关联的车用多传感器目标跟踪融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1420-1427. |
| [4] | 王家序,蒋倩倩,李俊阳,韩彦峰,张雷,唐挺. 双圆弧谐波传动柔轮齿形参数多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1194-1202. |
| [5] | 陈东良,臧睿,段鹏,赵伟鹏,翁旭涛,孙杨,唐艺鹏. 基于新月鱼尾推进理论的多连杆鱼骨仿生设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1246-1257. |
| [6] | 丁宁, 常玉春, 赵健博, 王超, 杨小天. 基于USB 3.0的高速CMOS图像传感器数据采集系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1298-1304. |
| [7] | 仇艳凯, 李宝仁, 杨钢, 曹博, 刘真. 新型液压消声器吸收液压系统压力脉动的机理和特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1085-1091. |
| [8] | 董颖, 崔梦瑶, 吴昊, 王雨后. 基于能量预测的分簇可充电无线传感器网络充电调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1265-1273. |
| [9] | 陈鸣, 陈杰, 肖璟博. 一种应用于CMOS图像传感器的流水线模数转换器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 968-976. |
| [10] | 吴疆, 徐壮, 刘丽佳, 嵇艳鞠, 李肃义. 基于环绕式血氧探头的睡眠呼吸暂停综合征检测装置原型设计与开发[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 640-644. |
| [11] | 刘洲洲, 彭寒. 基于节点可靠度的无线传感器网络拓扑控制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 571-577. |
| [12] | 杨诚, 宋萍, 彭文家, 金昊龙, 潘志强. 基于混合总线的装甲车辆实车综合测试系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 186-198. |
| [13] | 钱志辉, 周亮, 任雷, 任露泉. 具有仿生距下关节和跖趾关节的完全被动步行机[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 205-211. |
| [14] | 杨诚, 宋萍, 彭文家, 邓高寿, 刘雄军. 装甲车辆综合测试系统上位机平台设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1796-1803. |
| [15] | 朱枫, 张葆, 李贤涛, 王正玺, 张士涛. 基于强跟踪卡尔曼滤波的陀螺信号处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1868-1875. |
|
||