吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1447-1453.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190963
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
模糊c-harmonic均值算法在不平衡数据上改进
刘富1,2( ),梁艺馨2,侯涛2,宋阳2,康冰2,刘云2(
),梁艺馨2,侯涛2,宋阳2,康冰2,刘云2( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
Improvement of fuzzy c-harmonic mean algorithm on unbalanced data
Fu LIU1,2( ),Yi-xin LIANG2,Tao HOU2,Yang SONG2,Bing KANG2,Yun LIU2(
),Yi-xin LIANG2,Tao HOU2,Yang SONG2,Bing KANG2,Yun LIU2( )
)
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
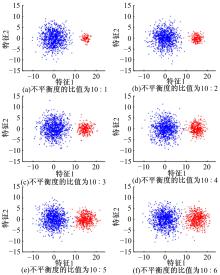
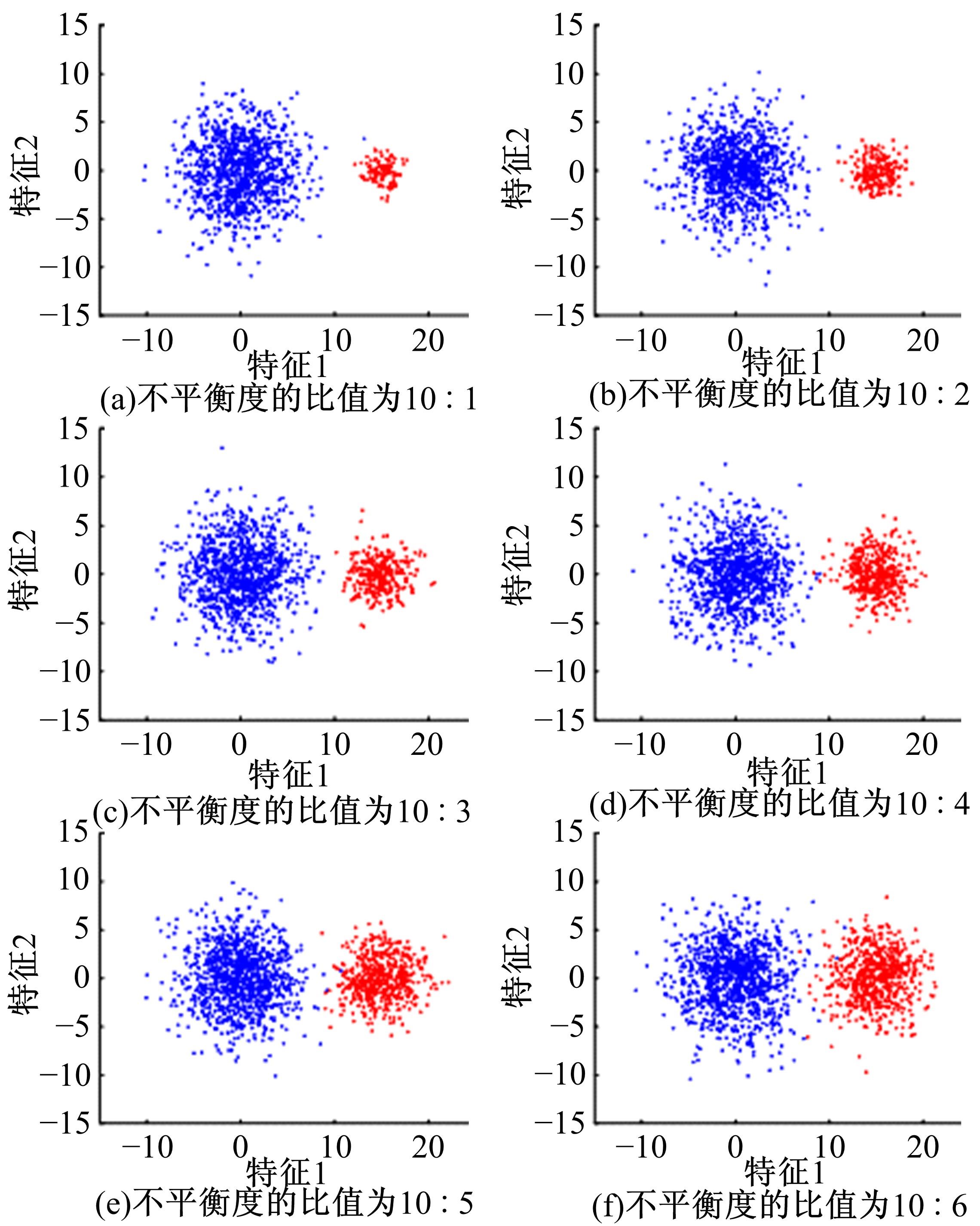
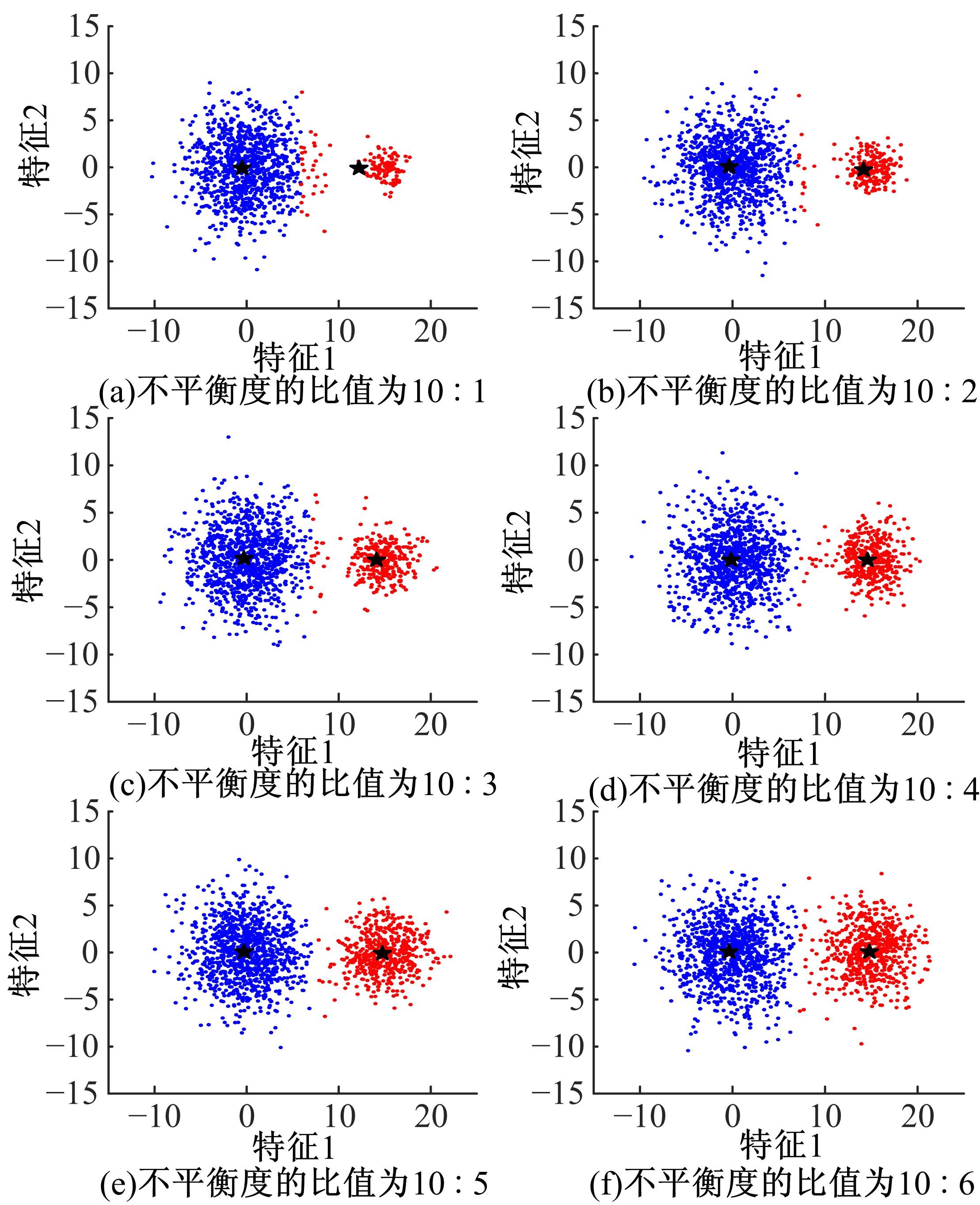
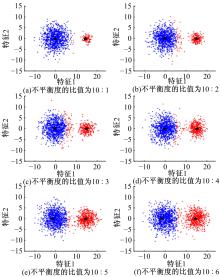
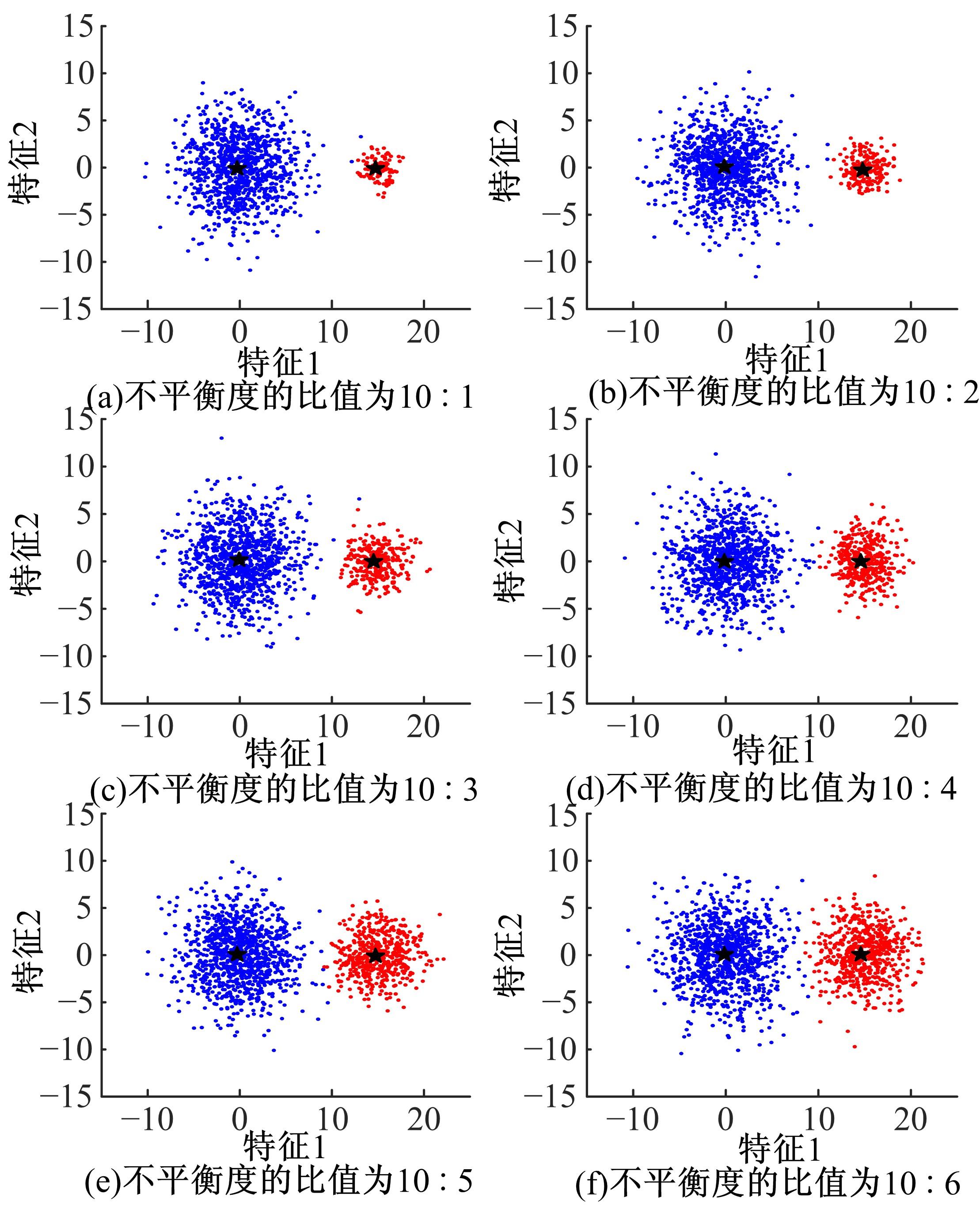
针对模糊c-harmonic均值算法(FCHM)在不平衡数据集上的聚类效果不理想的问题,提出了一种基于聚类体量约束的模糊c-harmonic均值算法。首先,利用隶属度矩阵定义各个类的体量,用于约束FCHM算法的代价函数,从而构建一个新的代价函数;然后,将该代价函数最小化,得到新的隶属度矩阵和聚类中心的计算公式;最后,在UCI数据集、模拟不平衡数据集及真实机床振动检测不平衡数据集上分别进行实验。实验结果表明,与同类算法相比,本文算法在保持传统算法全局最优性能的同时,在不平衡数据集上也能得到理想的聚类效果。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Henao-Restrepo A M, Camacho A, Longini I M, et al. Efficacy and effectiveness of an rVSV-vectored vaccine in preventing Ebola virus disease: final results from the guinea ring vaccination open-label cluster-randomised trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10068): 505-518. |
| 2 | Huzurbazar S, Kuang D Y, Lee L. Landmark-based algorithms for group average and pattern recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 86: 172-187. |
| 3 | 刘云, 刘富, 侯涛,等. 优化核参数的模糊C均值聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2016, 46(1):246-251. |
| Liu Yun, Liu Fu, Hou Tao, et al. Kernel-based fuzzy C-means clustering method based on parameter optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(1): 246-251. | |
| 4 | Gao Z M, Wang L, Zhou L P. A probabilistic approach to cross-region matching-based image retrival[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(3): 1191-1204. |
| 5 | Zhang B. Generalized k-harmonic Means-Boosting in unsupervised Learning[M]. Palo Alto: Hewlett, 2000. |
| 6 | Zhang B, Hsu M, Dayal U. K-harmonic means-a spatial clustering algorithm with boosting[C]∥International Workshop on Temporal, Spatial, and Spatio-Temporal Data Mining, Lyon, France, 2000, 12: 31-45. |
| 7 | Wu X H, Wu B, Sun J, et al. A hybrid fuzzy K-harmonic means clustering algorithm[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39(12): 3398-3409. |
| 8 | Jiang H, Yi S, Li J, et al. Ant clustering algorithm with K -harmonic means clustering[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2010, 37(12): 8679-8684. |
| 9 | 汪中, 刘贵全, 陈恩红. 基于模糊K-harmonic means的谱聚类算法[J]. 智能系统学报, 2009,4(2): 95-99. |
| Wang Zhong, Liu Gui-quan, Chen En-hong, et al. A spectral clustering algorithm based on fuzzy K-harmonic means[J]. CAAI Tranctions on Intelligent Systems, 2009, 4(2): 95-99. | |
| 10 | Yang F, Sun T, Zhang C. An efficient hybrid data clustering method based on K-harmonic means and particle swarm optimization[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36(6): 9847-9852. |
| 11 | 赵恒, 杨万海, 张高煜. 模糊K-Harmonic Means聚类算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2005,32(4):603-606, 638. |
| Zhao Heng, Yang Wan-hai, Zhang Gao-yu, et al. Fuzzy K-Harmonic Means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science), 2005, 32(4): 603-606, 638. | |
| 12 | Bensaid A M, Hall L O, Bezdek J C. Partially supervised clustering for image segmentation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1996, 29(5): 859-871. |
| 13 | Noordam J C, van den Broek W H A M, Buydens L M C. Multivariate image segmentation with cluster size insensitive fuzzy C-means[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2002, 64(1): 65-78. |
| 14 | Liang J Y, Bai L, Dang C Y, et al. The K-Means-Type algorithms versus imbalanced data distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(4): 728-745. |
| 15 | Likas A, Vlassis N, Verbeek J J. The global k-means clustering algorithm[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2002, 36(2): 451-461. |
| 16 | Bagirov A M. Modified global k-means algorithm for minimum sum-of-squares clustering problems[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(10): 3192-3199. |
| 17 | Zhang Bin, Hsu M, Dayal U, et al. K-Harmonic means—a data clustering algorithm[J]. Hewlett Packard Research Laboratory Technical Report, 1999. |
| 18 | Kim D W, Lee K H, Lee D. On cluster validity index for estimation of the optimal number of fuzzy clusters[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2004, 37(10): 2009-2025. |
| 19 | Capitaine H L, Frelicot C. A cluster-validity index combining an overlap measure and a separation measure based on fuzzy-aggregation operators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(3): 580–588. |
| 20 | Zahid N, Limouri M, Essaid A. A new cluster-validity for fuzzy clustering[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1999, 32(7): 1089-1097. |
| 21 | Wu K L, Yang M S. A cluster validity index for fuzzy clustering[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2005, 26(9): 1275-1291. |
| 22 | Han H, Wang W Y, Mao B H. Borderline-SMOTE: a new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning[J]. International Conference on Intelligent Computing, 2005, 3644(5): 878-887. |
| 23 | Su C T, Chen L S, Yih Y. Knowledge acquisition through information granulation for imbalanced data[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2006, 31(3): 531-541. |
| [1] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [2] | 董延华,刘靓葳,赵靖华,李亮,解方喜. 基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1405-1413. |
| [3] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [4] | 尚福华,曹茂俊,王才志. 基于人工智能技术的局部离群数据挖掘方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 692-696. |
| [5] | 赵海英,周伟,侯小刚,张小利. 基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 293-302. |
| [6] | 欧阳丹彤,马骢,雷景佩,冯莎莎. 知识图谱嵌入中的自适应筛选[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 685-691. |
| [7] | 李贻斌,郭佳旻,张勤. 人体步态识别方法与技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 1-18. |
| [8] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [9] | 刘巧斌,史文库,陈志勇,骆联盟,苏志勇,黄开军. 混合可靠性模型参数的核密度和引力搜索估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1818-1825. |
| [10] | 李军军,曹建农,程贝贝,廖娟,朱莹莹. 联合像素与多尺度对象的高分辨率遥感影像谱聚类分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2098-2108. |
| [11] | 李宾,周旭,梅芳,潘帅宁. 基于K-means和矩阵分解的位置推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1653-1660. |
| [12] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [13] | 刘玉梅,乔宁国,庄娇娇,刘鹏程,胡婷,陈立军. 基于多传感器数据融合的轨道车辆齿轮箱异常检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1465-1470. |
| [14] | 高万夫,张平,胡亮. 基于已选特征动态变化的非线性特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1293-1300. |
| [15] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
|
||