吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1785-1791.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200532
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法
- 1.兰州理工大学 计算机与通信学院,兰州 730050
2.甘肃省城市轨道交通智能运营工程研究中心,兰州 730050
3.兰州理工大学 电气工程与信息工程学院,兰州 730050
Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors
Jie CAO1,2( ),Xue QU3,Xiao-xu LI1(
),Xue QU3,Xiao-xu LI1( )
)
- 1.School of Computer and Communication,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Engineering Research Center of Urban Railway Transportation of Gansu Province,Lanzhou 730050,China
3.School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
摘要:
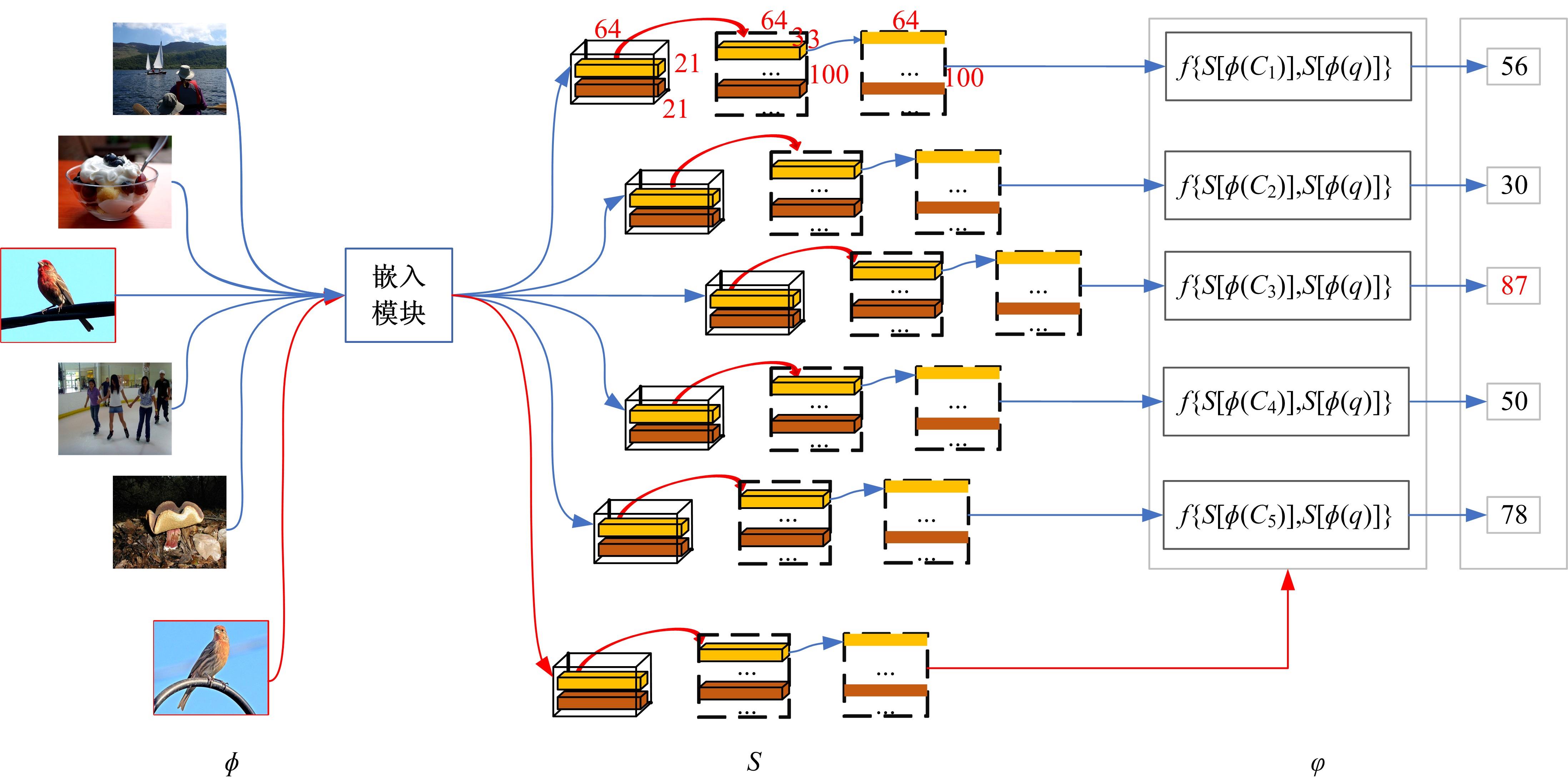
针对在小样本图像分类中,几个样本的特征图不足以描述整个类特征空间,导致误分类的问题,提出了滑动特征向量神经网络(SFV),该方法通过集合同类样本的滑动特征向量构建类特征空间,并利用样本-类的特征向量度量方式分类查询样本。SFV融合了特征块的边缘信息以及位置结构的相关性,最大限度地利用深层特征信息的同时扩充了类特征空间。实验表明:在各数据集中SFV均能取得不错的效果,在细粒度数据集上,达到了最佳精度。
中图分类号:
- TP183
| 1 | 车翔玖, 董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| Che Xiang-jiu, Dong You-zheng. Improved image recognition algorithm based on multi⁃scale information fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. | |
| 2 | Wang Y, Yao Q, Kwok J T, et al. Generalizing from a few examples: a survey on few-shot learning[J].ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2020, 53(3): 1-34. |
| 3 | Finn C, Abbeel P, Levine S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, 2017: 1126-1135. |
| 4 | Ravi S, Larochelle H. Optimization as a model for few-shot learning[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, 2016: 1-11. |
| 5 | Chen W Y, Liu Y C, Kira Z, et al. A closer look at few-shot classification[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, 2019: 04232. |
| 6 | Cai Q, Pan Y, Yao T, et al. Memory matching networks for one-shot image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 4080-4088. |
| 7 | Koch G, Zemel R, Salakhutdinov R. Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015. |
| 8 | Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]∥Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, 2016: 3630-3638. |
| 9 | Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]∥Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, 2017: 4077-4087. |
| 10 | Sung F, Yang Y, Zhang L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 1199-1208. |
| 11 | 刘萍萍, 赵宏伟, 耿庆田, 等. 基于局部特征和视皮层识别机制的图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(5): 1401-1406. |
| Liu Ping-ping, Zhao Hong-wei, Geng Qing-tian, et al. Image classification method based on local feature and visual cortex recognition mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1401-1406. | |
| 12 | Li W, Wang L, Xu J, et al. Revisiting local descriptor based image-to-class measure for few-shot learning [C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, 2019: 7260-7268. |
| 13 | Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. |
| 14 | Welinder P, Branson S, Mita T, et al. Caltech-UCSD birds 200[R]. Technical Report CNS-TR-2010-001, California Institute of Technology, 2010: 1-15. |
| 15 | Krause J, Stark M, Deng J, et al. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vsion Workshops, Sydney, 2013: 554-561. |
| 16 | Khosla A, Jayadevaprakash N, Yao B, et al. Novel dataset for fine-grained image categorization: stanford dogs[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, USA, 2012: 3181866. |
| 17 | Oreshkin B N, Rodriguez P, Lacoste A. TADAM: task dependent adaptive metric for improved few-shot learning[C]∥Neural Information Processing Systems, Canada, 2018: 721-731. |
| 18 | Rusu A A, Rao D, Sygnowski J, et al. Meta-learning with latent embedding optimization[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, 2019: 05960. |
| [1] | 王春波,底晓强. 基于标签分类的云数据完整性验证审计方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1364-1369. |
| [2] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [3] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [4] | 许骞艺,秦贵和,孙铭会,孟诚训. 基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 704-711. |
| [5] | 徐涛,马克,刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [6] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [7] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [8] | 赵宏伟,李明昭,刘静,胡黄水,王丹,臧雪柏. 基于自然性和视觉特征通道的场景分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1668-1675. |
| [9] | 车翔玖, 王利, 郭晓新. 基于多尺度特征融合的边界检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [10] | 许岩岩, 陈辉, 刘家驹, 袁金钊. CELL处理器并行实现立体匹配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 952-958. |
| [11] | 胡冠宇, 乔佩利. 基于云群的高维差分进化算法及其在网络安全态势预测上的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 568-577. |
| [12] | 张培林, 陈彦龙, 王怀光, 李胜. 考虑信号特点的合成量子启发结构元素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1181-1188. |
| [13] | 杨焱, 刘飒, 廉世彬, 朱晓冬. 基于计算机视觉的果树害虫的形态特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 235-238. |
| [14] | 佟金, 王亚辉, 樊雪梅, 张书军, 陈东辉. 生鲜农产品冷链物流状态监控信息系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(06): 1707-1711. |
| [15] | 吴迪, 曹洁. 智能环境下基于核相关权重鉴别分析算法的多特征融合人脸识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 439-443. |
|
||