吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 2164-2173.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200674
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
COVID⁃19 chest CT image segmentation based on federated learning and blockchain
Sheng-sheng WANG( ),Jing-yu CHEN,Yi-nan LU(
),Jing-yu CHEN,Yi-nan LU( )
)
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
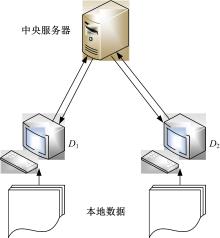
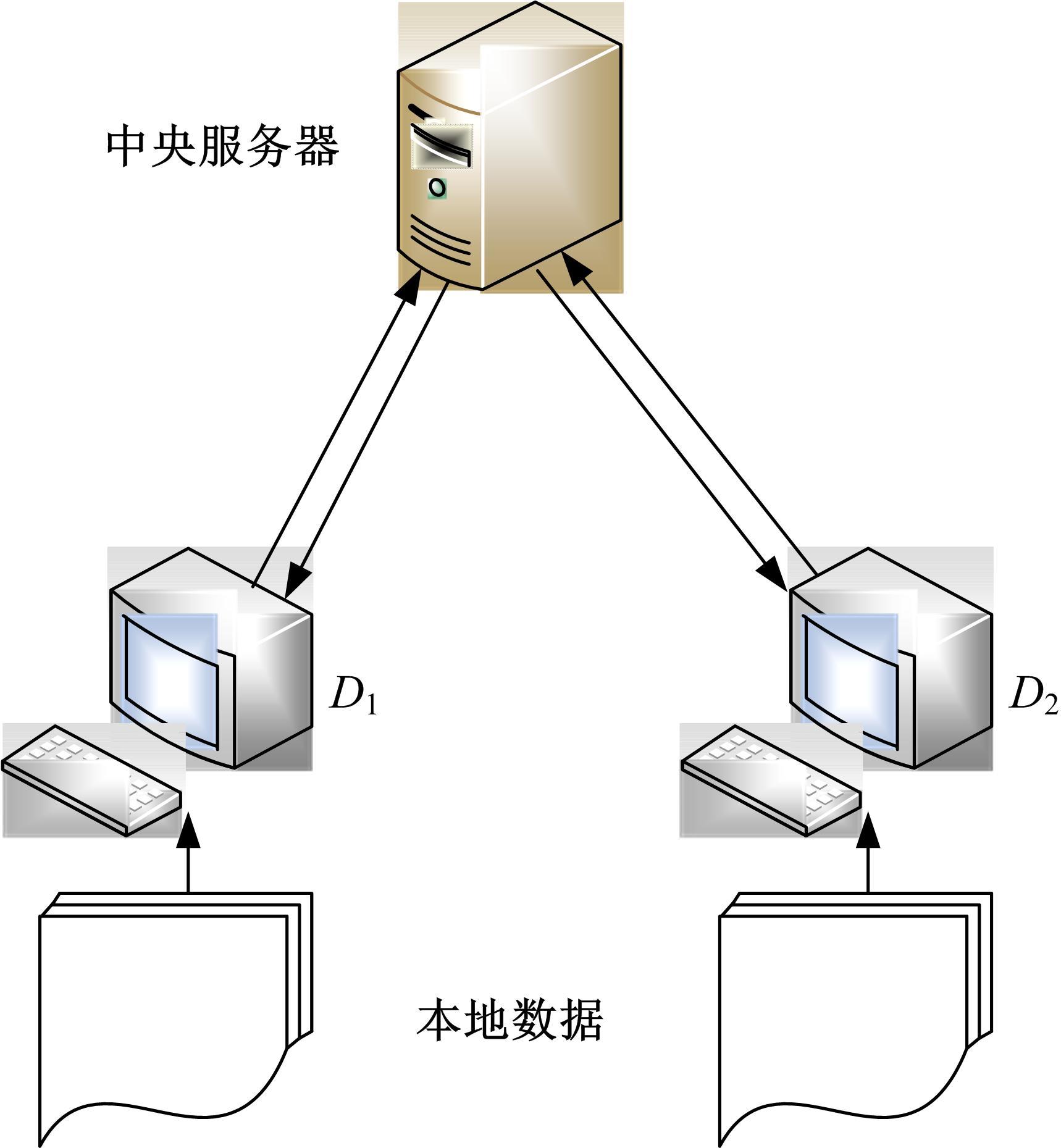
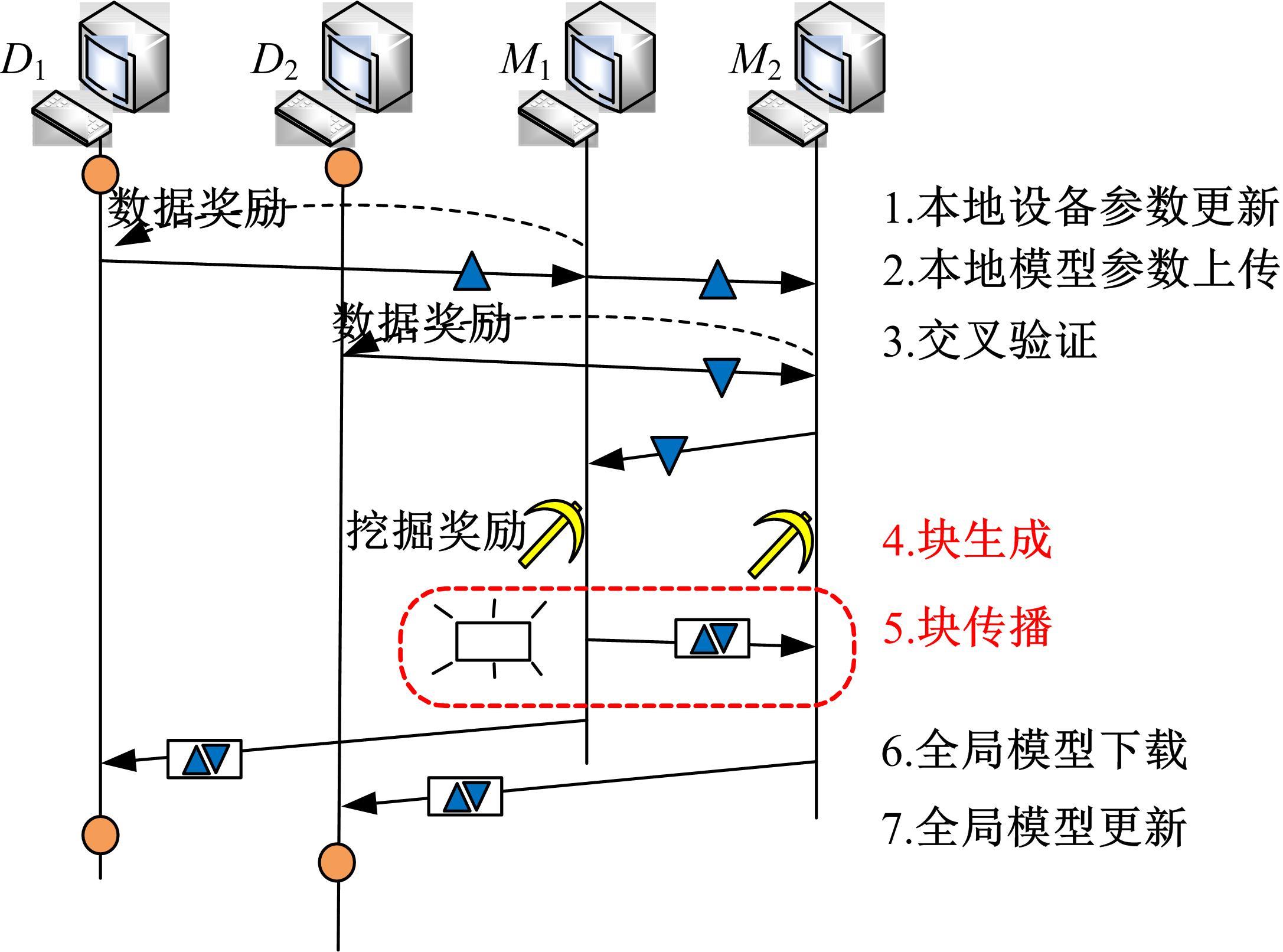
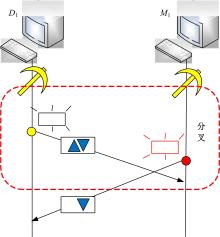
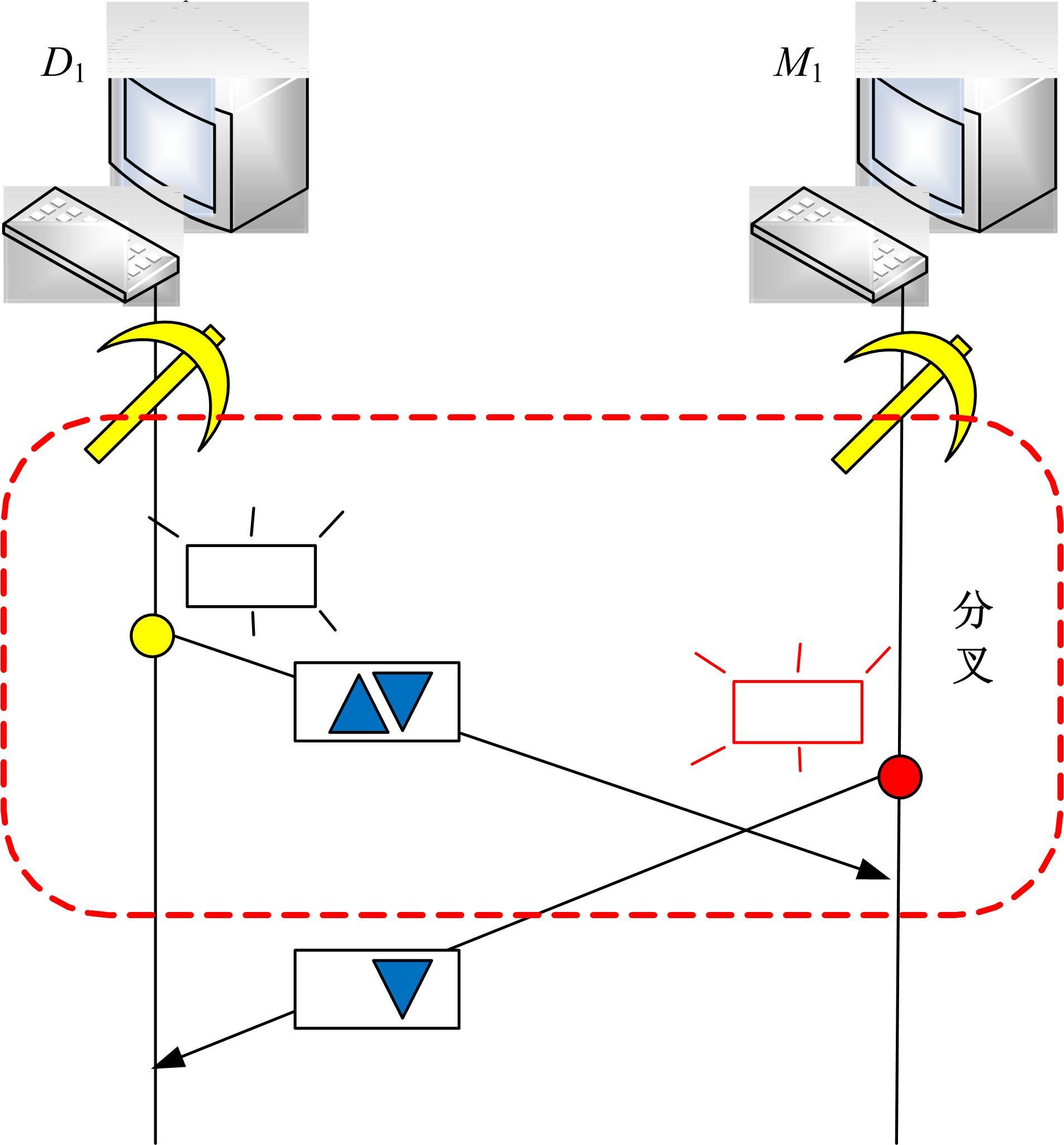
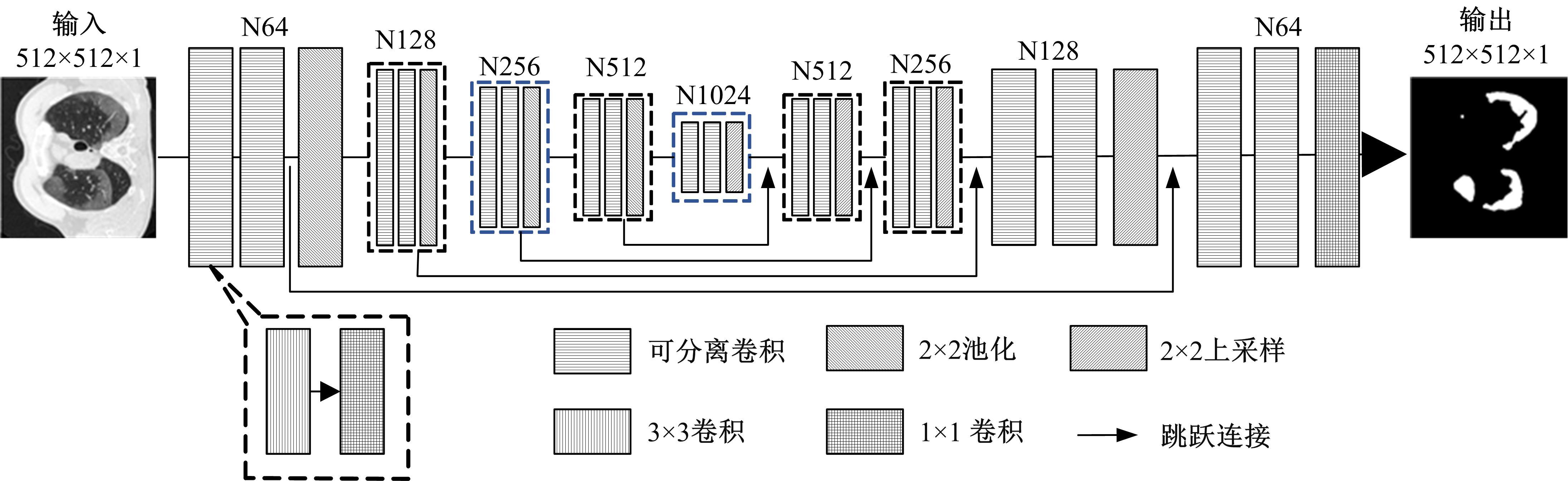
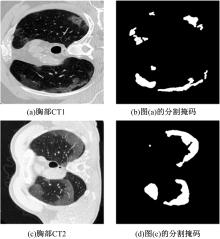
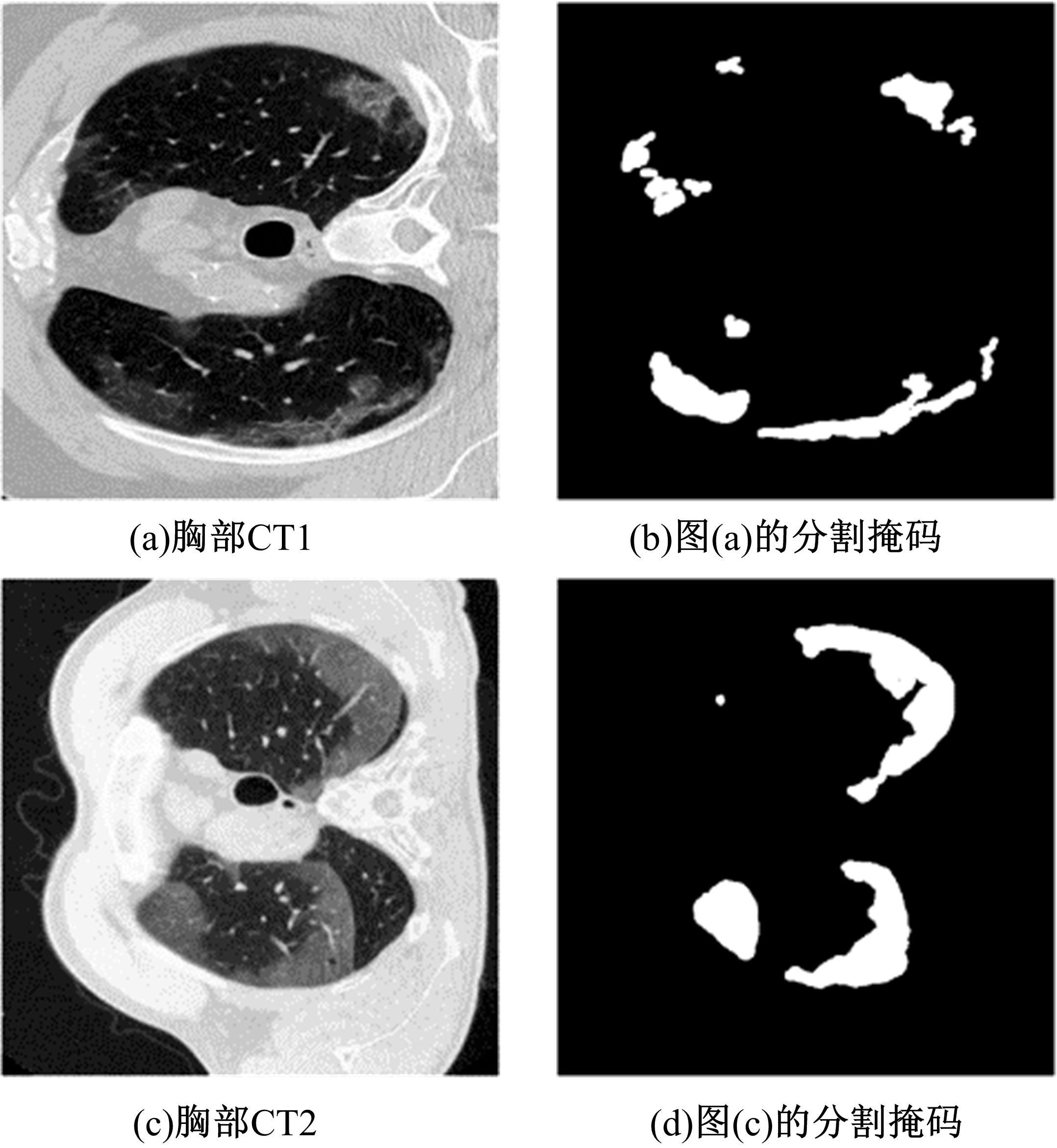
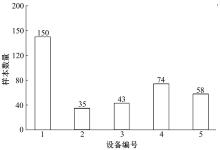
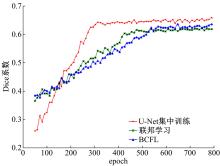
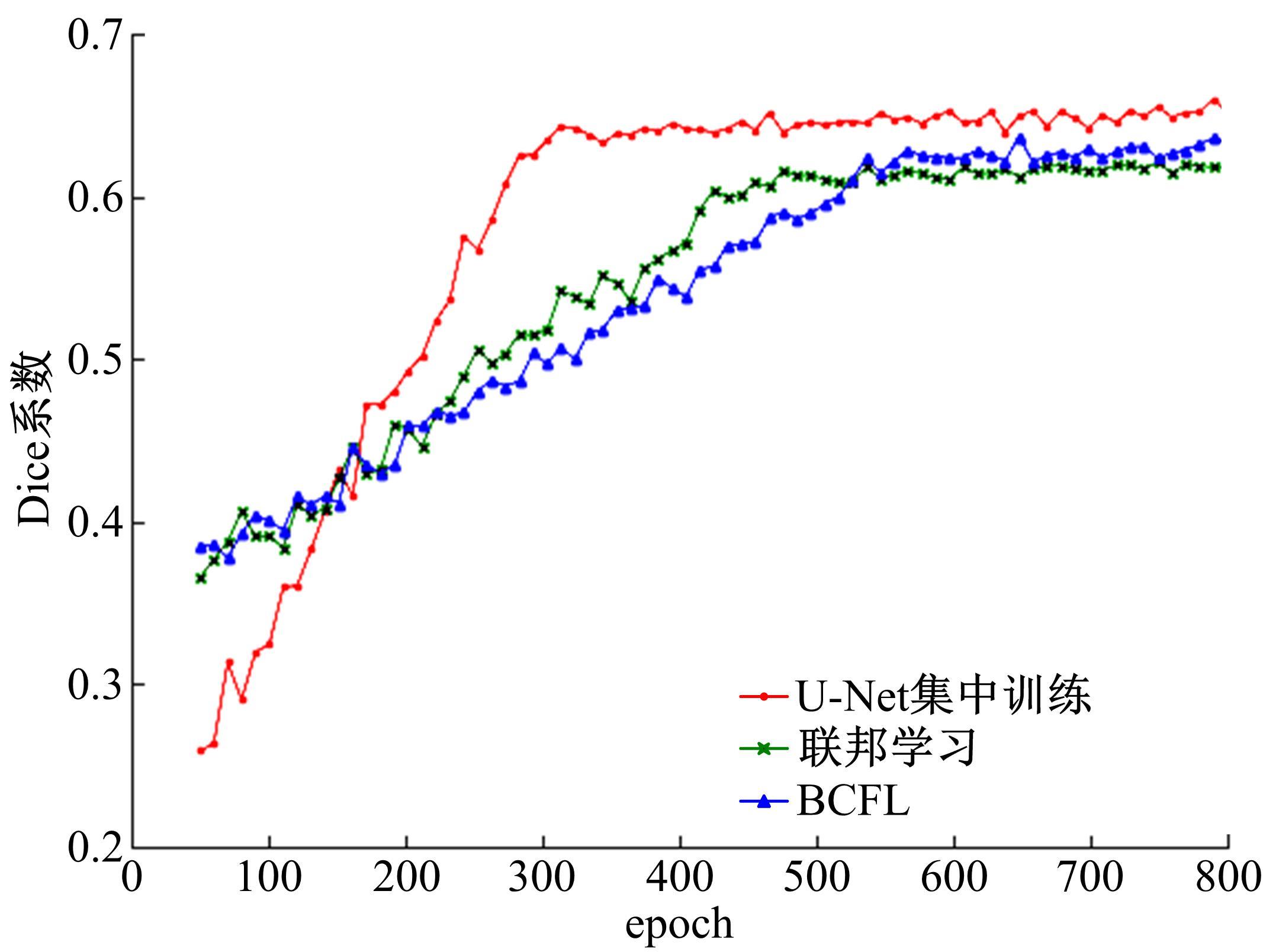
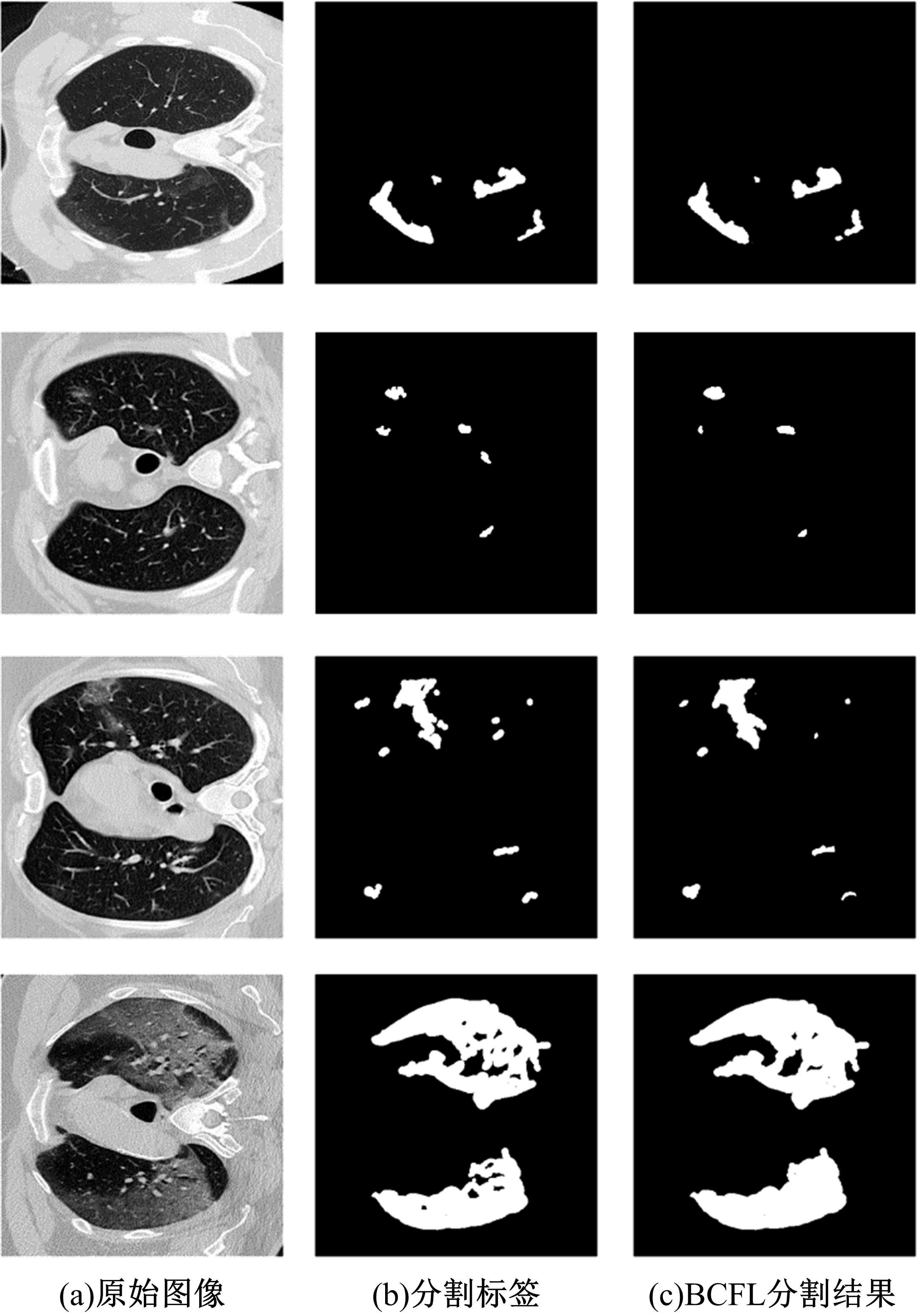
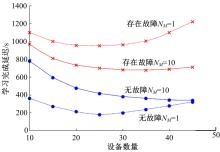
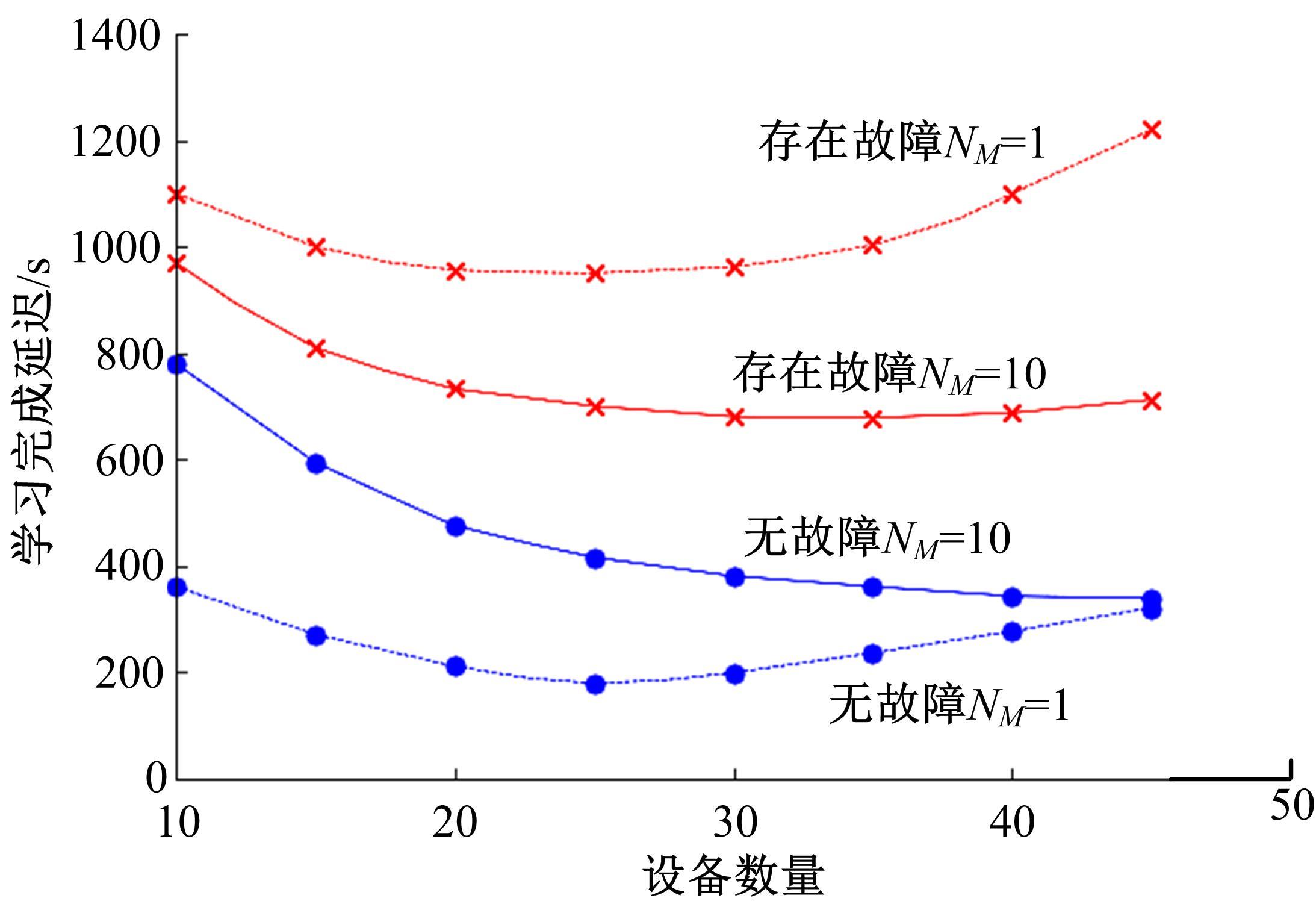
提出了基于联邦学习和区块链的COVID-19胸部CT图像分割方法,该方法可以自动分割出COVID-19肺部感染区域。首先,采用联邦学习进行分布式训练以应对患者样本数据少、分布在不同机构并且互不共享的现实情况。其次,利用区块链网络替代联邦学习中的中央服务器以解决联邦学习的服务器单点故障问题。最后,提出了轻量级深度可分离卷积U-Net降低运算量,减少时间成本。实验结果表明,本文方法经过训练后测试效果良好,Dice指标能够达到63.26%,有助于新冠肺炎的诊断。
中图分类号:
- TP39
| 1 | Bedford J, Enria D, Giesecke J, et al. COVID-19: towards controlling of a pandemic[J]. The Lancet, 2020, 395(10229): 1015-1018. |
| 2 | 国家卫生健康委办公厅. 新型冠状病毒肺炎诊疗方案(试行第七版)[J].传染病信息,2020,33(1):1-6, 26. |
| General office of the national health commission. COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment protocol (trial version 7)[J]. Infectious Disease Information, 2020, 33(1): 1-6, 26. | |
| 3 | Li Yan, Xia Li-ming. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): role of chest CT in diagnosis and management[J]. American Journal of Roentgenology, 2020, 214(6): 1280-1286. |
| 4 | 管汉雄, 熊颖, 申楠茜, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎 (COVID-19)临床影像学特征[J]. 放射学实践, 2020, 35(2): 125-130. |
| Guan Han-xiong, Xiong Ying, Shen Nan-qian, et al. Clinical and thin-section CT features of patients with the COVID-19 in Wuhan[J]. Radiologic Practice, 2020, 35(2): 125-130. | |
| 5 | Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X Y, et al. CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(1): 202-207. |
| 6 | Shi H Y, Han X Y, Jiang N C, et al. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study[J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2020, 20(4): 425-434. |
| 7 | 李欢,程尼涛,孙文博,等. 人工智能辅助定量分析新型冠状病毒肺炎的CT进展类型[J]. 武汉大学学报:医学版, 2021, 42(1):1-5. |
| Li Huan, Cheng Ni-tao, Sun Wen-bo, et al. AI-assisted quantitative analysis of chest CT progression patterns of COVID-19[J]. Medical Journal of Wuhan University, 2021, 42(1):1-5. | |
| 8 | Sheller M J, Reina G A, Edwards B, et al. Multi-institutional deep learning modeling without sharing patient data: a feasibility study on brain tumor segmentation[C]∥International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. Cham: Springer, 2018: 92-104. |
| 9 | Nakamoto S. Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system[J/OL]. [2020-08-23]. |
| 10 | 袁勇,王飞跃. 区块链技术发展现状与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):481-494. |
| Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-yue. Blockchain: the state of the art and future trends[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):481-494. | |
| 11 | Konečný J, McMahan H B, Ramage D, et al. Federated optimization: distributed machine learning for on-device intelligence[J/OL]. [2020-08-10]. |
| 12 | Yang Q, Liu Y, Chen T J, et al. Federated machine learning: concept and applications[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2019, 10(2):No.12. |
| 13 | 杨强. AI与数据隐私保护:“联邦学习”的破解之道[J]. 信息安全研究, 2019, 5(11):961-965. |
| Yang Qiang. AI and data privacy protection:the way to federated learning[J]. Journal of Information Security Research, 2019, 5(11):961-965. | |
| 14 | 王赫彬. 区块链技术与应用前瞻综述[J].科技创新导报, 2020, 17(14):126-127. |
| Wang He-bin. Overview of blockchain technology and application prospects[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2020, 17(14): 126-127. | |
| 15 | Rahman M U, Guidi B, Baiardi F. Blockchain-based access control management for decentralized online social networks[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2020, 144: 41-54. |
| 16 | Yue X, Wang H J, Jin D W, et al. Healthcare data gateways: found healthcare intelligence on blockchain with novel privacy risk control[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2016, 40(10):No.218. |
| 17 | Zheng Z B, Xie S A, Dai H N, et al. An overview of blockchain technology: architecture, consensus, and future trends[C]∥2017 IEEE International Congress on Big Data, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 557-564. |
| 18 | 肖明尧, 李雄飞, 张小利, 等. 基于多尺度的区域生长的图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(5): 1591-1597. |
| Xiao Ming-yao, Li Xiong-fei, Zhang Xiao-li, et al. Medical image segmentation algorithm based on multi-scale region growing[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(5): 1591-1597. | |
| 19 | Al-Amri S S, Kalyankar N V, Khamitkar S D. Image segmentation by using edge detection[J]. International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering, 2010, 2(3): 804-807. |
| 20 | Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| 21 | Kumar A, Upadhyay N, Ghosal P, et al. CSNet: a new deepnet framework for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2020,193: No.105524. |
| 22 | Zhou Z X, He Z S, Jia Y Y. AFPNet: a 3D fully convolutional neural network with atrous-convolution feature pyramid for brain tumor segmentation via mri images[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 402: 235-244. |
| 23 | 郜峰利,陶敏,李雪妍,等. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| Gao Feng-li, Tao Min, Li Xue-yan, et al. Accurate segmentation of stroke in CT image based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. | |
| 24 | Samarakoon S, Bennis M, Saad W, et al. Distributed federated learning for ultra-reliable low-latency vehicular communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 68(2): 1146-1159. |
| 25 | 朱辉,秦品乐. 基于多尺度特征结构的U-Net肺结节检测算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2019, 45(4): 254-261. |
| Zhu Hui,Qin Pin-le. U-Net pulmonary nodule detection algorithm based on multi-scale feature structure[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45(4): 254-261. | |
| 26 | 魏柳,向智霆,刘剑聪,等.基于回环残差注意力机制U-net的胰腺分割[J].重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 33(4): 653-660. |
| Wei Liu, Xiang Zhi-ting, Liu Jian-cong,et al. Pancreas segmentation based on ringed residual attention U-net[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 33(4): 653-660. | |
| 27 | 郝华颖, 赵昆, 苏攀, 等. 一种基于改进ResU-Net的角膜神经分割算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(1): 217-223. |
| Hao Hua-ying, Zhao Kun, Su Pan, et al. A corneal nerve segmentation algorithm based on improved ResU-Net[J]. Computer Engineering, 2021, 47(1): 217-223. | |
| 28 | Decker C, Wattenhofer R. Information propagation in the bitcoin network[C]∥IEEE P2P 2013 Proceedings, Trento, Italy, 2013: 1-10. |
| 29 | Rodrigues P. COVID-19 CT segmentation dataset[DB/OL]. [2020-08-30]. |
| [1] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [2] | 赵宏伟,张子健,李蛟,张媛,胡黄水,臧雪柏. 基于查询树的双向分段防碰撞算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1830-1837. |
| [3] | 王春波,底晓强. 基于标签分类的云数据完整性验证审计方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1364-1369. |
| [4] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [5] | 沈淑涛,尼玛扎西. 基于区块链技术的双混沌可识篡改图像加密方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1055-1059. |
| [6] | 许骞艺,秦贵和,孙铭会,孟诚训. 基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 704-711. |
| [7] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [8] | 吴禄慎,程伟,胡赟. 应用改进布谷鸟算法优化多阈值图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 358-369. |
| [9] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [10] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [11] | 郜峰利,陶敏,李雪妍,何昕,杨帆,王卓,宋俊峰,佟丹. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| [12] | 刘仲民,王阳,李战明,胡文瑾. 基于简单线性迭代聚类和快速最近邻区域合并的图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1931-1937. |
| [13] | 肖明尧, 李雄飞, 张小利, 张刘. 基于多尺度的区域生长的图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1591-1597. |
| [14] | 刘仲民, 李战明, 李博皓, 胡文瑾. 基于稀疏矩阵的谱聚类图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1308-1313. |
| [15] | 赵夫群, 周明全, 耿国华. 基于GA-Otsu法的图像阈值分割及定量识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 959-964. |
|
||