吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 2319-2324.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210595
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
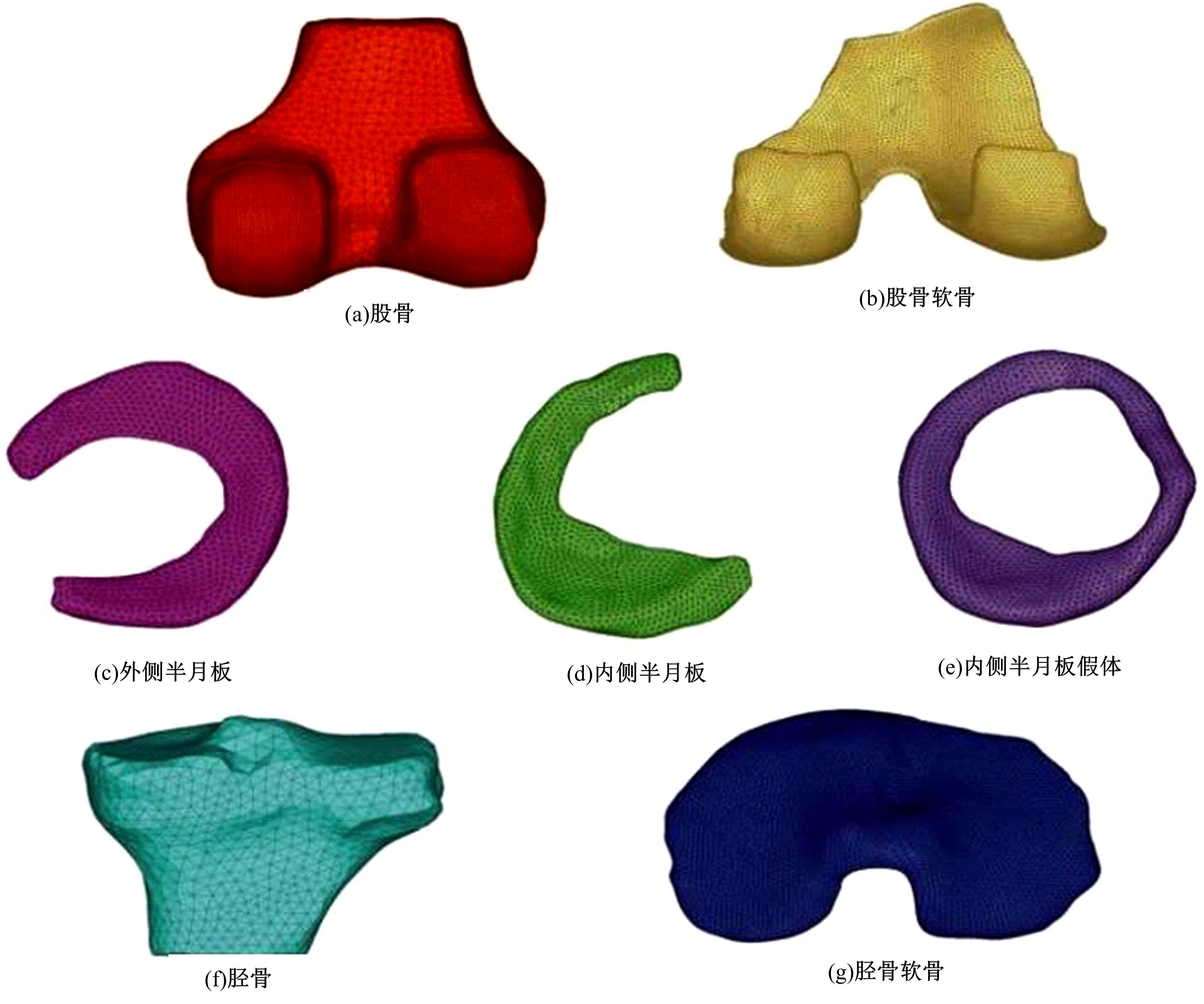
基于内侧半月板结构设计的仿生假体有限元分析
左建林1( ),刘恩渤1,贾政斌2,3,徐圣昊1,肖建林1(
),刘恩渤1,贾政斌2,3,徐圣昊1,肖建林1( )
)
- 1.吉林大学中日联谊医院 骨科,长春 130033
2.北京航空航天大学 生物与医学工程学院,北京 100191
3.北京航空航天大学 生物力学与力生物学教育部重点实验室,北京 100191
Finite element analysis of bionic prosthesis based on design of medial meniscus structure
Jian-lin ZUO1( ),En-bo LIU1,Zheng-bin JIA2,3,Sheng-hao XU1,Jian-lin XIAO1(
),En-bo LIU1,Zheng-bin JIA2,3,Sheng-hao XU1,Jian-lin XIAO1( )
)
- 1.Department of Orthopaedics,China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
2.School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering,Beihang University,Beijing 100191,China
3.Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology,Ministry of Education,Beihang University,Beijing 100191,China
摘要:
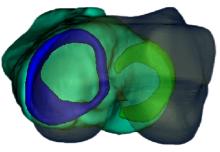
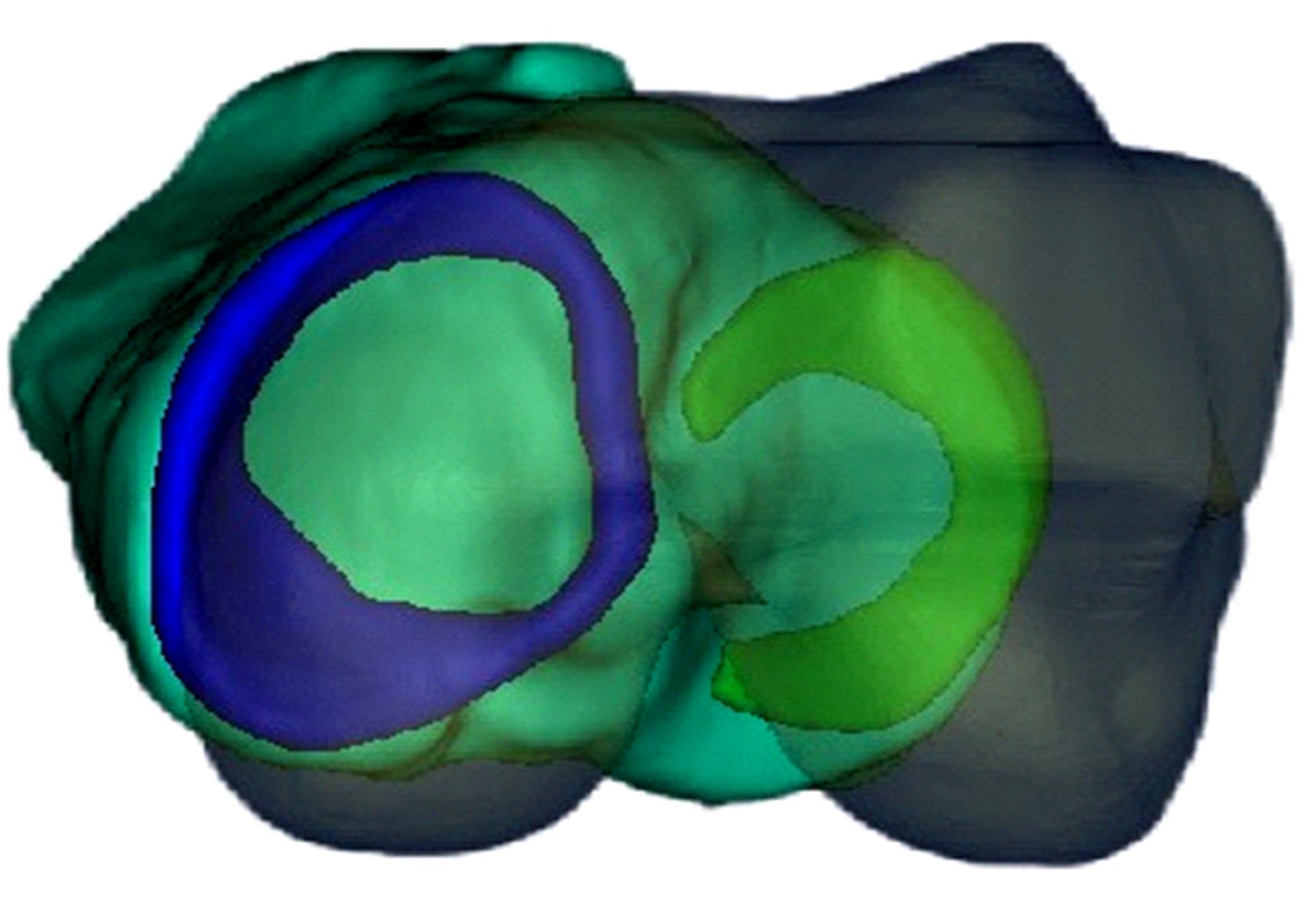
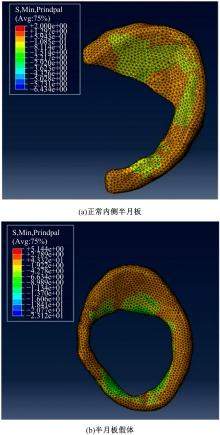
基于人体内侧半月板结构设计了游离式仿生内侧半月板假体,置换临床中无法修复的半月板。通过三维有限元分析方法,对假体进行了力学分析,验证了其可行性。数据结果显示,与健康半月板相比,半月板假体应力较高,两组模型高应力分布区域均在内侧中后部;所设计的半月板假体与健康半月板具有相似的生物力学性能。数据结果验证了假体的主要优势在于,其不需要额外固定模式,因而避免了因假体固定失效造成的失败。
中图分类号:
- R314
| 1 | Sacks D, Baxter B, Campbell B C V, et al. Multisociety consensus quality improvement revised consensus statement for endovascular therapy of acute ischemic stroke[J]. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 2018, 39(6): E61-E76. |
| 2 | Moroni L, Lambers F M, Wilson W, et al. Finite element analysis of meniscal anatomical 3D scaffolds: implications for tissue engineering[J]. The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2007, 1: 23-34. |
| 3 | Hasan J, Fisher J, Ingham E. Current strategies in meniscal regeneration[J]. Reading & Writing, 2014, 102(3): 619-634. |
| 4 | Willinger L, Lang J J, von Deimling C, et al. Varus alignment increases medial meniscus extrusion and peak contact pressure: a biomechanical study[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2020, 28(S2): 1092-1098. |
| 5 | Anderson A F, Irrgang J J, Dunn W, et al. Interobserver reliability of the international society of arthroscopy, knee surgery and orthopaedic sports medicine (isakos) classification of meniscal tears[J] European Journal of Industrial Relations, 2011, 39(5): 926-932. |
| 6 | Irrgang J J, Anderson A F, Boland A L, et al. Responsiveness of the international knee documentation committee subjective knee form[J]. Chemistry—an Asian Journal, 2006, 34(10): 1567-1573. |
| 7 | Foad A. Self-limited healing of a radial tear of the lateral meniscus[J]. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy, 2012, 20(5): 933-936. |
| 8 | Baratz M E, Fu F H, Mengato R. Meniscal tears: the effect of meniscectomy and of repair on intraarticular contact areas and stress in the human knee. A preliminary report[J]. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 1986, 14(4): 270-275. |
| 9 | Adams S B, Randolph M A, Gill T J. Tissue engineering for meniscus repair[J]. The Journal of Knee Surgery, 2005, 18(1): 25-30. |
| 10 | Lee S R, Kim J G, Nam S W. The tips and pitfalls of meniscus allograft transplantation[J]. Knee Surgery & Related Research, 2012, 24(3): 137-145. |
| 11 | Lee B S, Chung J W, Kim J M, et al. Morphologic changes in fresh-frozen meniscus allografts over 1 year: a prospective magnetic resonance imaging study on the width and thickness of transplants[J]. The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 2012, 40(6): 1384-1391. |
| 12 | Zhu L Y, Li L, Li Z A, et al. Design and biomechanical characteristics of porous meniscal implant structures using triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine, 2019, 17(1): No.89. |
| 13 | 梁云虹,任露泉.人类生活及其仿生学初探[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2016, 46(4): 1373-1384. |
| Liang Yun-hong, Ren Lu-quan. Preliminary study of bionics in human life[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(4): 1373-1384. | |
| 14 | Cidonio G, Glinka M, Dawson J I, et al. The cell in the ink: improving biofabrication by printing stem cells for skeletal regenerative medicine[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 209: 10-24. |
| 15 | Chae S, Lee S S, Choi Y J, et al. 3D cell-printing of biocompatible and functional meniscus constructs using meniscus-derived bioink[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 267: No.120466. |
| 16 | Warnecke D, Schild N B, Klose S, et al. Friction properties of a new silk fibroin scaffold for meniscal replacement[J]. Tribology International, 2017, 109: 586-592. |
| 17 | Sochacki K R, Varshneya K, Safran M R, et al. Reoperation rates following meniscus transplantation using the truven database[J]. Arthroscopy, 2020, 36(10): 2731-2735. |
| 18 | 李学勇,赵仲秋,张春松,等.基于有限元的人体-机械手交互力计算方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1612-1619. |
| Li Xue-yong, Zhao Zhong-qiu, Zhang Chun-song, et al. Finite element based calculation method of human-robot interaction force[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1612-1619. |
| [1] | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,李建桥,邓湘金,邹猛,薛龙. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [2] | 王波,何洋扬,聂冰冰,许述财,张金换. 底部爆炸条件下车内乘员的腹部损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 792-798. |
| [3] | 宫亚峰,宋加祥,毕海鹏,谭国金,胡国海,林思远. 装配式箱涵结构缩尺模型静载试验及有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1728-1738. |
| [4] | 古海东,罗春红. 疏排桩-土钉墙组合支护基坑土拱效应模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1712-1724. |
| [5] | 刘国政, 史文库, 陈志勇. 考虑安装误差的准双曲面齿轮传动误差有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 984-989. |
| [6] | 陈吉清, 杜天亚, 兰凤崇. 钝性碰撞中人体肝脏生物力学响应数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 398-406. |
| [7] | 孙荣军, 谷拴成, 居培, 高科. 基于有限元分析的煤矿井下新型弧角型聚晶金刚石复合片钻头优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1991-1998. |
| [8] | 陈东辉, 刘伟, 吕建华, 常志勇, 吴婷, 慕海锋. 基于虾夷扇贝体表结构的玉米茬根捡拾器仿生设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1185-1193. |
| [9] | 高继东, 曾必强, 彭伟. 电动自行车与轿车碰撞中骑车人的伤害特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1786-1791. |
| [10] | 钱志辉, 苗怀彬, 任雷, 任露泉. 基于多种步态的德国牧羊犬下肢关节角[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1857-1862. |
| [11] | 张彦玲, 孙瞳, 侯忠明, 李运生. 隔板式钢-混凝土曲线组合梁弯扭性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1107-1114. |
| [12] | 吴越, 杨志刚, 陈龙, 康晓涛, 张东伟. 压电悬臂梁多模态发电装置的仿真与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1162-1167. |
| [13] | 田桂中, 刘之岭, 周宏根, 宋江超, 朱涛. 家蚕前部丝腺准静态轴向拉伸力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 872-877. |
| [14] | 于振环,张娜,刘顺安. 基于流-固耦合的车辆减振器动态非线性仿真分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 16-21. |
| [15] | 钱志辉, 苗怀彬, 商震, 任露泉. 基于多种步态的德国牧羊犬足-地接触分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1692-1697. |
|
||