吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 792-798.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200227
底部爆炸条件下车内乘员的腹部损伤
- 1.清华大学 汽车安全与节能国家重点实验室,北京 100084
2.中国北方车辆研究所,北京 100072
3.中国人民解放军32184部队,北京 100093
Abdominal injury of vehicle occupant in underbody blast events
Bo WANG1,2( ),Yang-yang HE3,Bing-bing NIE1,Shu-cai XU1,Jin-huan ZHANG1(
),Yang-yang HE3,Bing-bing NIE1,Shu-cai XU1,Jin-huan ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.State Key Laboratory Automotive Satety and Energy,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
2.China North Vehicle Research Institute,Beijing 100072,China
3.Unit 32184 of the PLA,Beijing 100093,China
摘要:
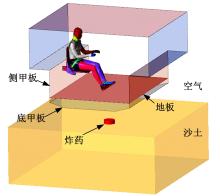
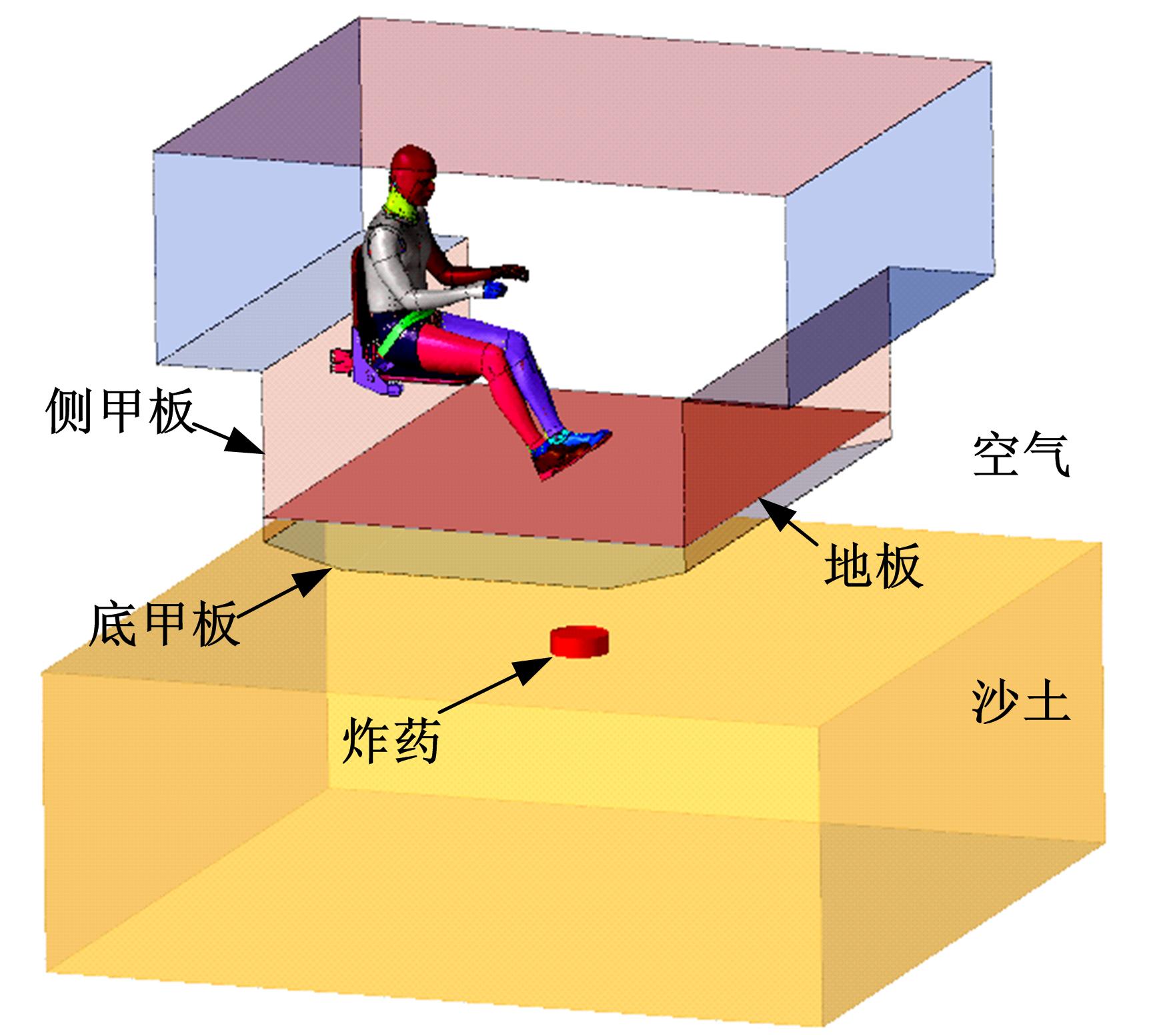
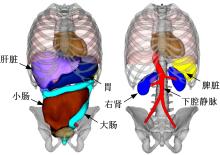
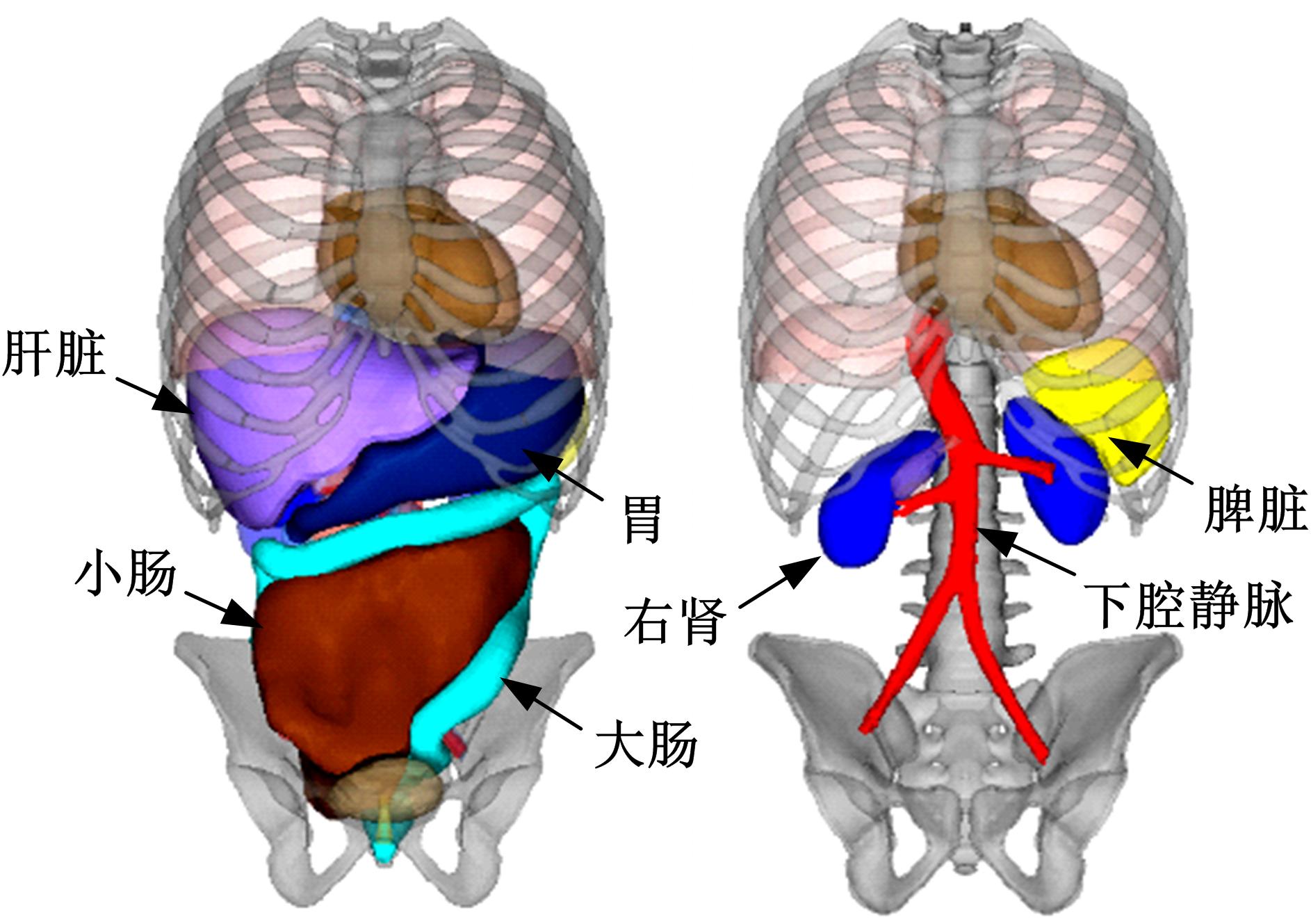
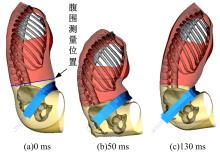
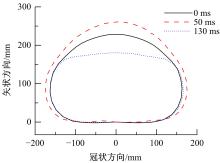
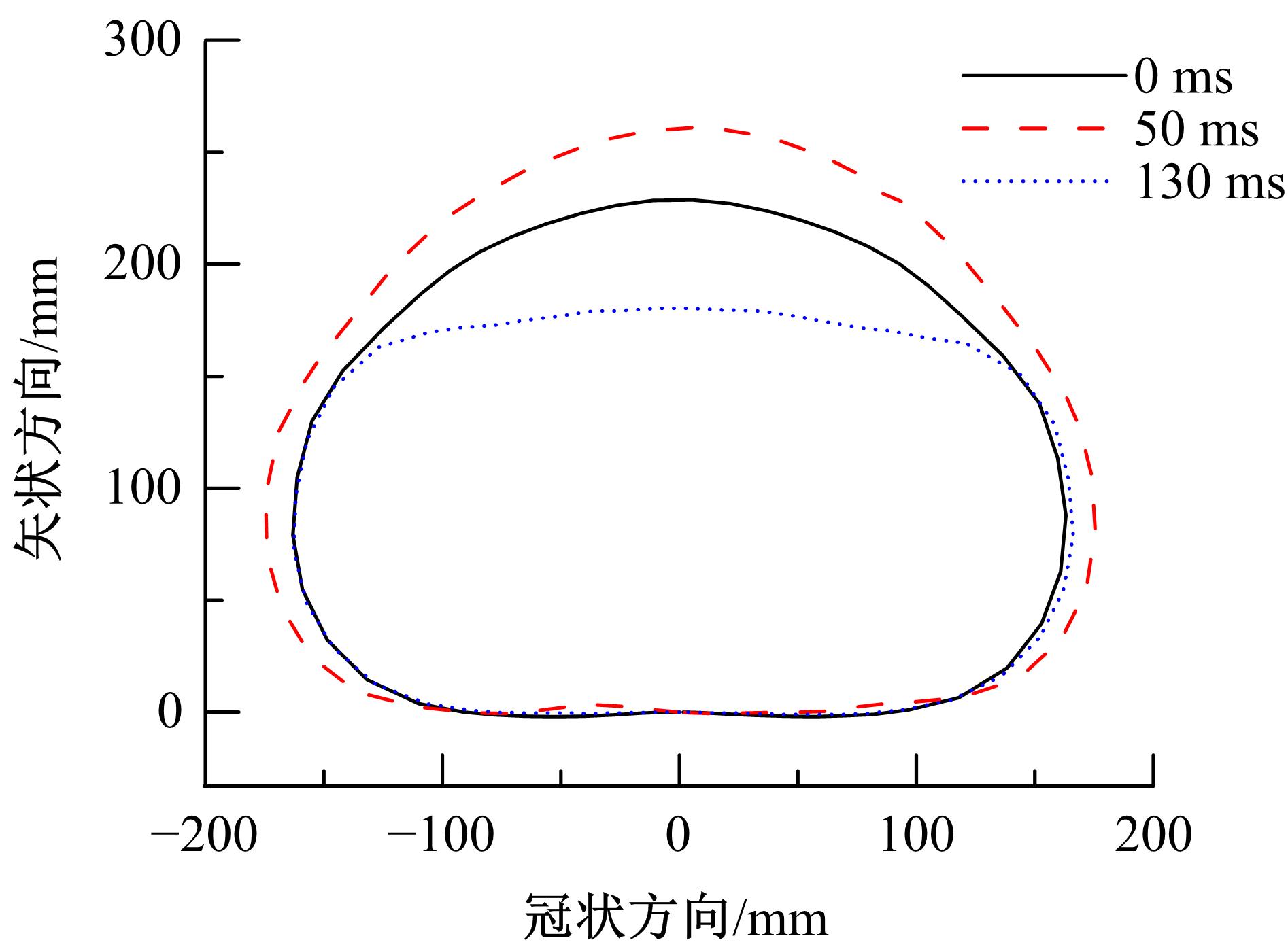
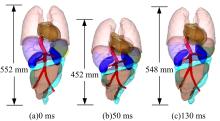
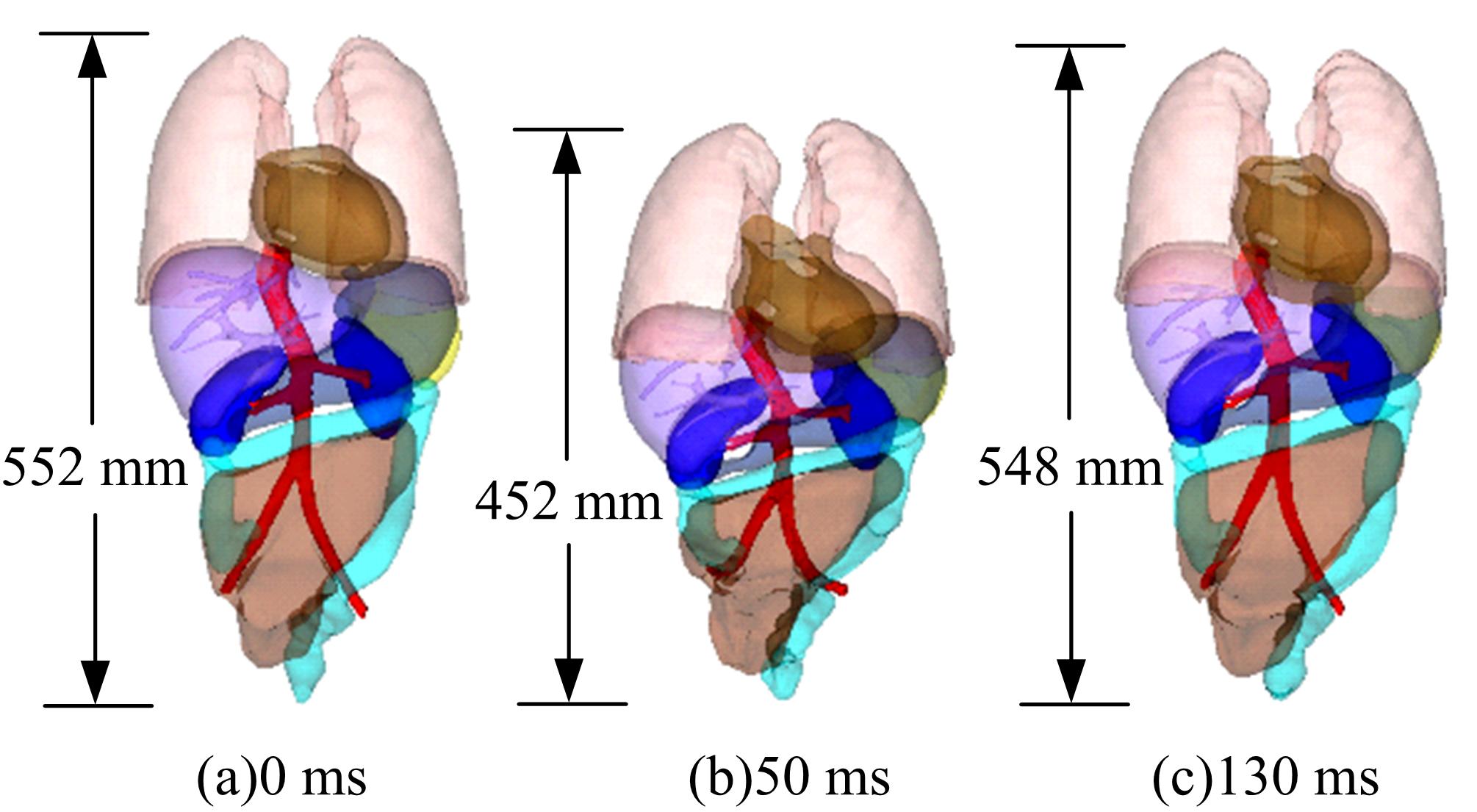
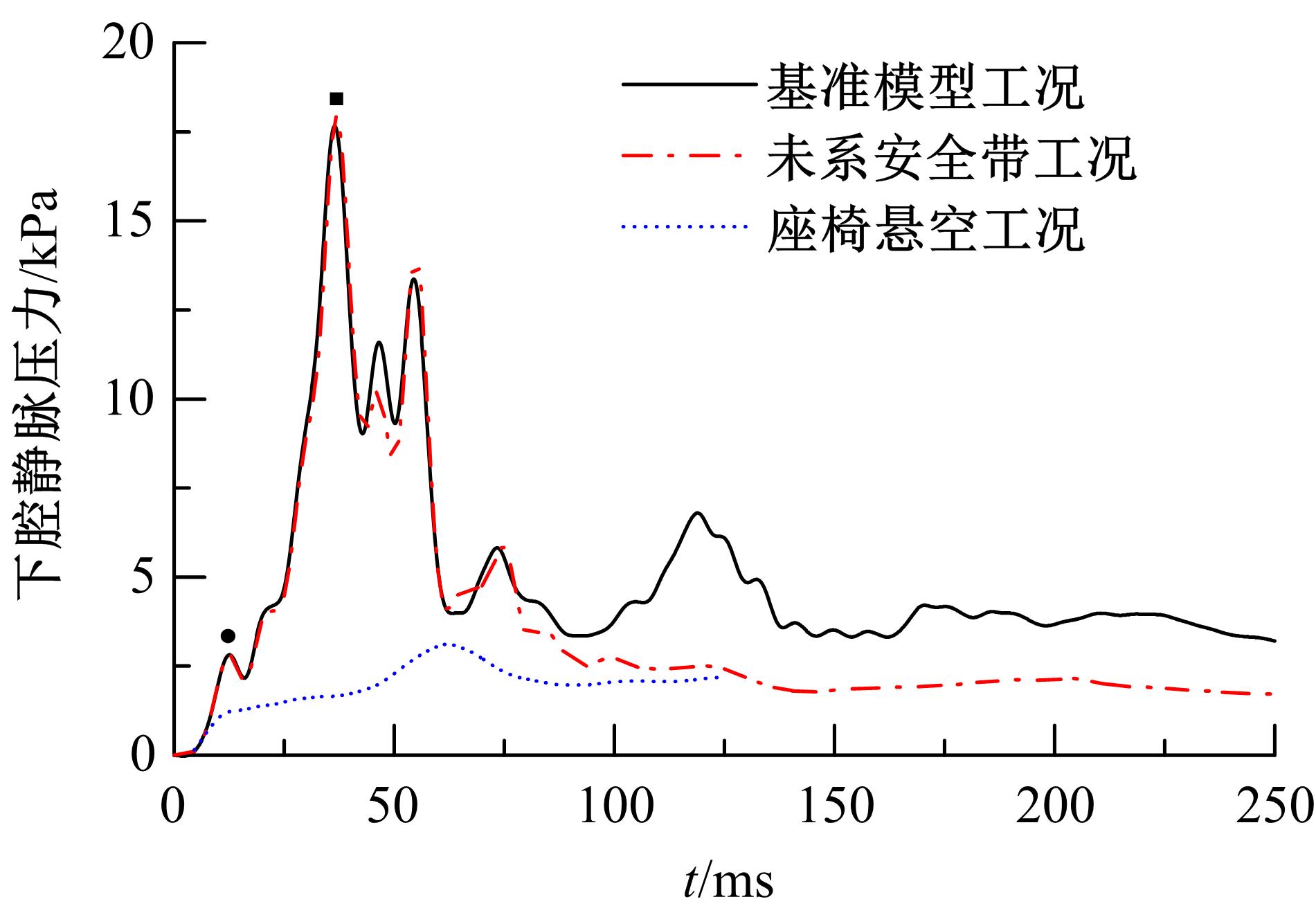
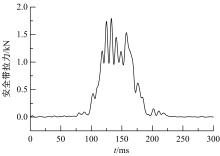
为了解车辆发生底部爆炸时乘员腹部致伤机制及损伤风险,构建了包含乘员、车体结构和爆炸流场的有限元仿真模型,研究了6 kg TNT爆炸当量下乘员胸腹部器官的动力学响应,对比了座椅冲击、地板冲击及安全带约束作用对腹部压力的影响,并基于实质性脏器平均应变能密度和腹部血管压力变化率两个指标分析了乘员腹部损伤风险。在冲击过程中,座椅推动乘员向上运动,造成腹部扩张;当乘员与座椅分离后,安全带限制了乘员向上运动,造成腹部收缩。仿真结果表明:座椅冲击对乘员腹部压力影响最大,其次为安全带约束作用;在本文模型中,乘员腹部血管压力变化率峰值为2.1 kPa/ms,腹部脏器发生损伤的风险较低。本文研究结果可为车辆防护设计提供参考。
中图分类号:
- U461.91
| 1 | Owens B D, Kragh J F, Wenke J C, et al. Combat wounds in operation iraqi freedom and operation enduring freedom[J]. Journal of Trauma-injury Infection and Critical Care, 2008, 64(2):295-299. |
| 2 | Mckay B J, Bir C A. Lower extremity injury criteria for evaluating military vehicle occupant injury in underbelly blast events[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2009, 53:229-249. |
| 3 | Yoganandan N, Moore J, Arun M W, et al. Dynamic responses of intact post mortem human surrogates from inferior-to-superior loading at the pelvis[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2014, 58:123-143. |
| 4 | Dong L, Zhu F, Jin X, et al. Blast effect on the lower extremities and its mitigation: a computational study[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2013, 28:111-124. |
| 5 | Lei J Y, Zhu F, Jiang B H, et al. Underbody blast effect on the pelvis and lumbar spine: a computational study[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2018, 79:9-19. |
| 6 | Elhagediab A M, Rouhana S W. Patterns of abdominal injury in frontal automotive crashes[C]∥Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles, Windsor Ontario, Canada, 1998:327-337. |
| 7 | Trollope M L, Stalnaker R L, Mcelhaney J H, et al. The mechanism of injury in blunt abdominal trauma[J]. The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care, 1973, 13(11):962-970. |
| 8 | Hardy W N, Schneider L W, Rouhana S W. Abdominal impact response to rigid-bar, seatbelt, and airbag loading[C]∥SAE Paper, 2001-22-0001. |
| 9 | Ruan J S, Eljawahri R, Barbat S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of human abdominal impact responses and injuries through finite element simulations of a full human body model[C]∥SAE Paper, 2005-22-0016. |
| 10 | Champion H R, Holcomb J B, Young L A. Injuries from explosions: physics, biophysics, pathology, and required research focus[J]. Journal of Trauma, 2009, 66(5):1468-1477. |
| 11 | Ramasamy A, Hill A M, Masouros S, et al. Blast-related fracture patterns: a forensic biomechanical approach[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2011, 8(58): 689-698. |
| 12 | AEP-55 VOL 2: 2011. Procedures for evaluating the protection level of armored vehicles—mine threat[S]. |
| 13 | Dey S, Hopperstad O S, Borvik T, et al. Constitutive relation and failure criterion for three structural steels at high strain rates[J/OL]. [2020-03-25]. |
| 14 | Saleh M, Edwards L. Evaluation of soil and fluid structure interaction in blast modelling of the flying plate test[J]. Computers and Structures, 2015, 151:96-114. |
| 15 | Rouhana S W, Lau I V, Ridella S A. Influence of velocity and forced compression on the severity of abdominal injury in blunt, nonpenetrating lateral impact[J]. The Journal of Trauma, 1985, 25(6):490-500. |
| 16 | Lamielle S, Vezin P, Verriest J P, et al. 3D deformation and dynamics of the human cadaver abdomen under seatbelt loading[C]∥SAE Paper, 2008-22-0011. |
| 17 | Miller M A. The biomechanical response of the lower abdomen to belt restraint loading[J]. The Journal of Trauma, 1989, 29(11): 1571-1584. |
| 18 | Snedeker J G, Barbezat M, Niederer P, et al. Strain energy density as a rupture criterion for the kidney: impact tests on porcine organs, finite element simulation, and a baseline comparison between human and porcine tissues[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2005, 38(5):993-1001. |
| 19 | Beillas P, Berthet F. Development of simulation based liver and spleen injury risk curves for the GHBMC detailed models[C]∥Proceedings of International Research Council on Biomechanics of Injury Conference, Athens, Greece, 2018:369-381. |
| 20 | Melvin J W, Stalnaker R L, Roberts V L, et al. Impact injury mechanisms in abdominal organs[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th Stapp Car Crash Conference, Oklahoma, USA, 1973:115-126. |
| 21 | Zhang N, Hiroo K, Zhao J. Development of injury criteria for spleen and kidney in side impacts with the full-body human model[J/OL]. [2020-03-25]. |
| 22 | Sparks J L, Bolte J H, Dupaix R B, et al. Using pressure to predict liver injury risk from blunt impact[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2007, 51:402-432. |
| 23 | Kremer M A, Gustafson H M, Bolte J H, et al. Pressure-based abdominal injury criteria using isolated liver and full-body post-mortem human subject impact tests[C]∥SAE Paper, 2011-22-0012. |
| 24 | Ramachandra R, Kang Y S, Bolte J H, et al. Biomechanical responses of PMHS subjected to abdominal seatbelt loading[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2016, 60:59-87. |
| 25 | van der Horsr M J, Leerdam P J C. Experimental and numerical analysis of occupant safety in blast mine loading under vehicles[J/OL].[2020-03-26]. |
| 26 | J211/1_201403. Instrumentation for impact test-part1-electronic instrumentation[S]. |
| 27 | Foret-Bruno J Y, Trosseille X, Page Y, et al. Comparison of thoracic injury risk in frontal car crashes for occupant restrained without belt load limiters and those restrained with 6 kN and 4 kN belt load limiters[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2001, 45:205-224. |
| [1] | 宋大凤,杨丽丽,曾小华,王星琦,梁伟智,杨南南. 基于行驶工况合成的混合动力汽车电池寿命优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [2] | 张家旭,王欣志,赵健,施正堂. 汽车高速换道避让路径规划及离散滑模跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
| [3] | 王伟达,武燕杰,史家磊,李亮. 基于驾驶员意图识别的电子液压制动助力系统控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 406-413. |
| [4] | 陈国迎,姚军,王鹏,夏其坤. 适用于后轮轮毂驱动车辆的稳定性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 397-405. |
| [5] | 李寿涛,王蕊,徐靖淳,王德军,田彦涛,于丁力. 一种基于模型预测复合控制的车辆避碰控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 738-746. |
| [6] | 熊璐,魏琰超,高乐天. 基于惯性测量单元/轮速融合的车辆零速检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 134-138. |
| [7] | 马芳武,梁鸿宇,王强,蒲永锋. 双材料负泊松比结构的面内冲击动力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 114-121. |
| [8] | 吴岛,张立斌,张云翔,单洪颖,单红梅. 基于滑移率辨识的汽车制动时序视觉检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 206-216. |
| [9] | 张恩慧,何仁,苏卫东. 不同挡板结构对油箱内油液晃动特性的数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 83-95. |
| [10] | 高菲,肖阳,张文华,祁锦轩,李子樵,马骁远. 高温和荷电状态对锂离子电池单体力学响应的耦合影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1574-1583. |
| [11] | 李静,石求军,洪良,刘鹏. 基于车辆状态估计的商用车ESC神经网络滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1545-1555. |
| [12] | 杜常清,曹锡良,何彪,任卫群. 基于混合粒子群算法的双离合变速器参数优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1556-1564. |
| [13] | 陈吉清,蓝庆生,兰凤崇,刘照麟. 基于轮胎力预判与拟合的轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1565-1573. |
| [14] | 杨志刚,范亚军,夏超,储世俊,单希壮. 基于双稳态尾迹的方背Ahmed模型减阻[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1635-1644. |
| [15] | 沈哲,王毅刚,杨志刚,贺银芝. 风洞中未知声源漂移误差的逼近修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1584-1589. |
|
||