吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1626-1638.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210652
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.空军航空大学 教学考评中心,长春 130021
Transfer learning of medical image segmentation based on optimal transport feature selection
Sheng-sheng WANG1( ),Lin-yan JIANG1,Yong-bo YANG2
),Lin-yan JIANG1,Yong-bo YANG2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Teaching Assessment Center,Air Force Aviation University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
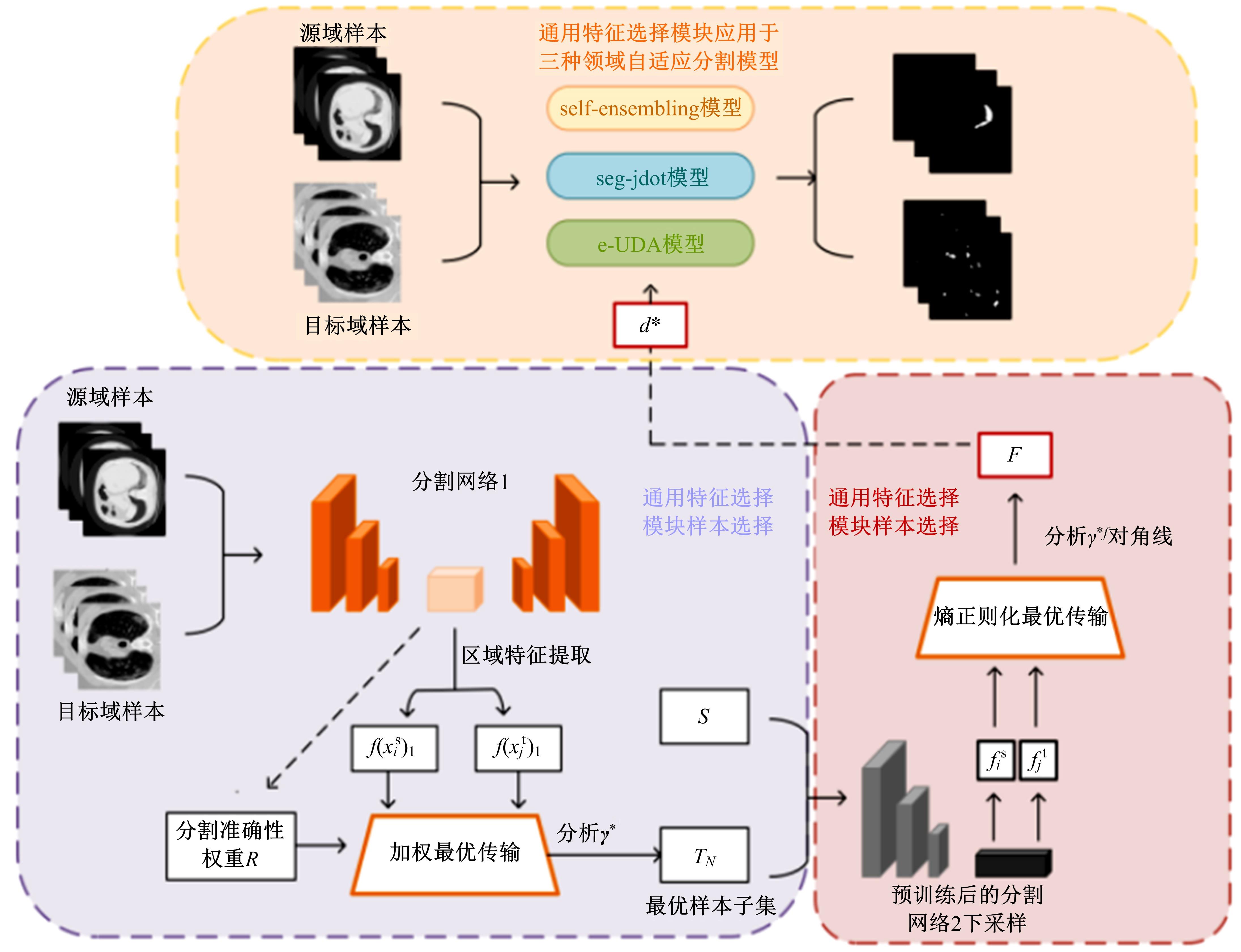
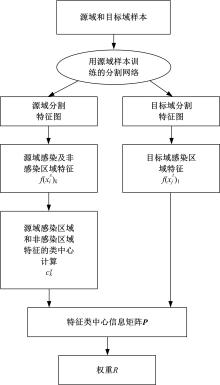
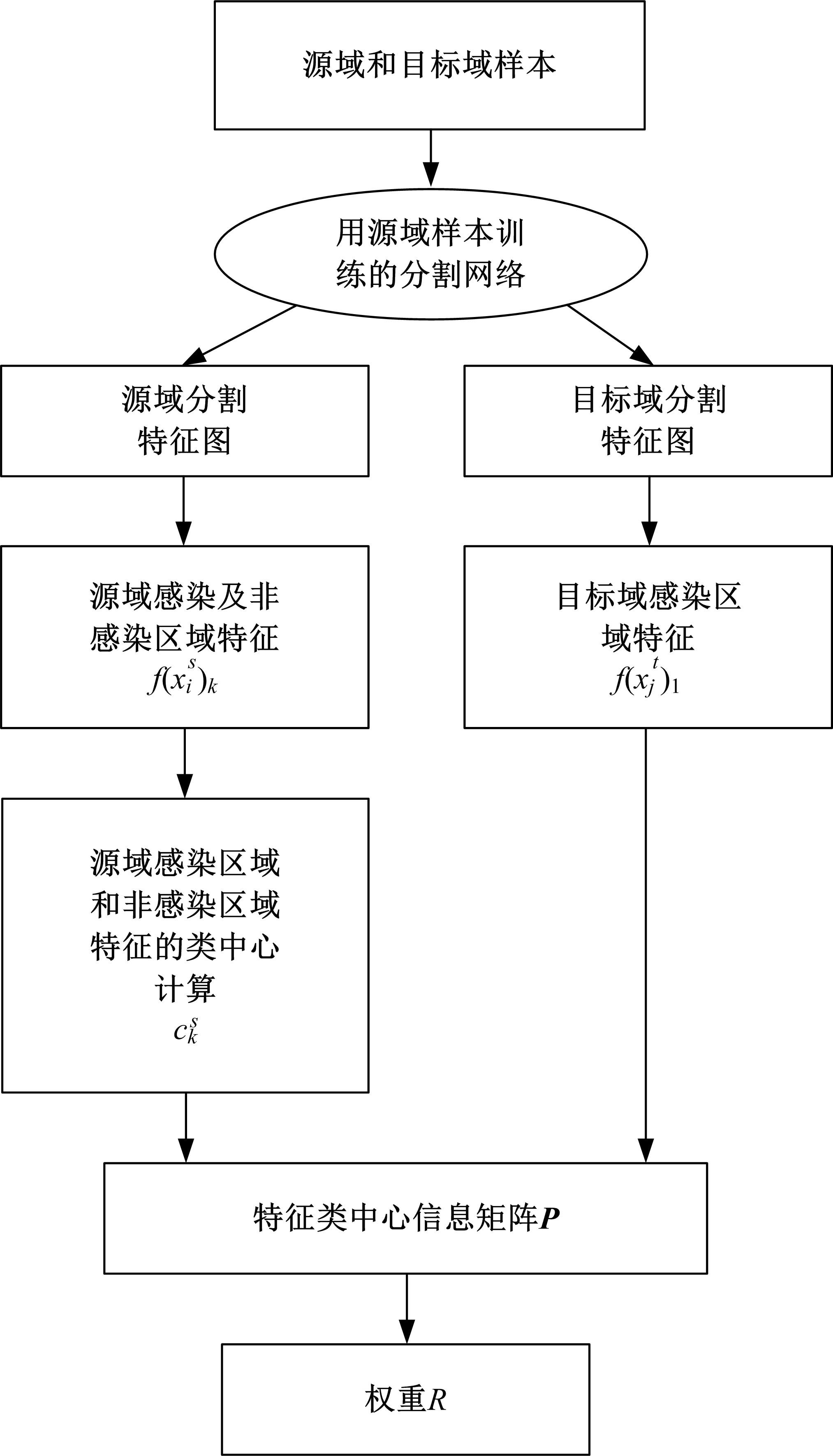
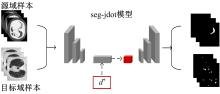
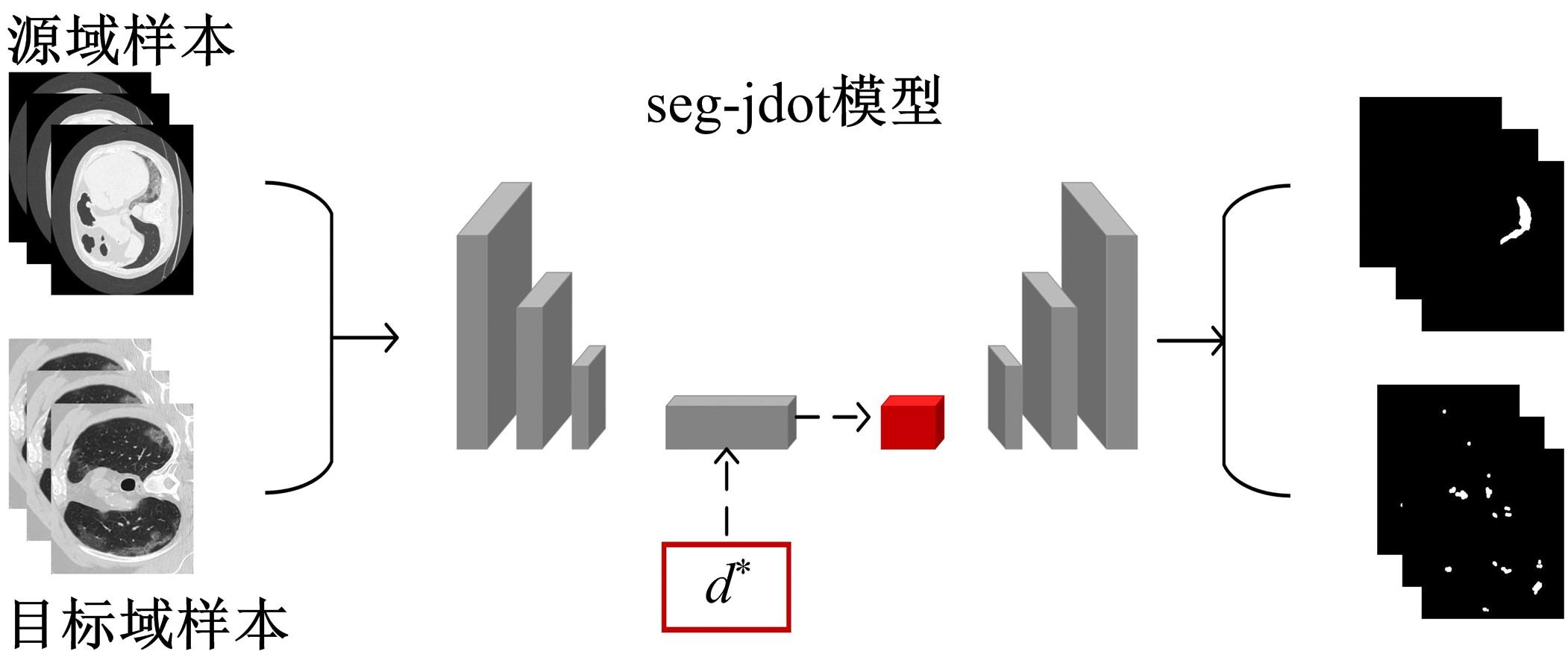
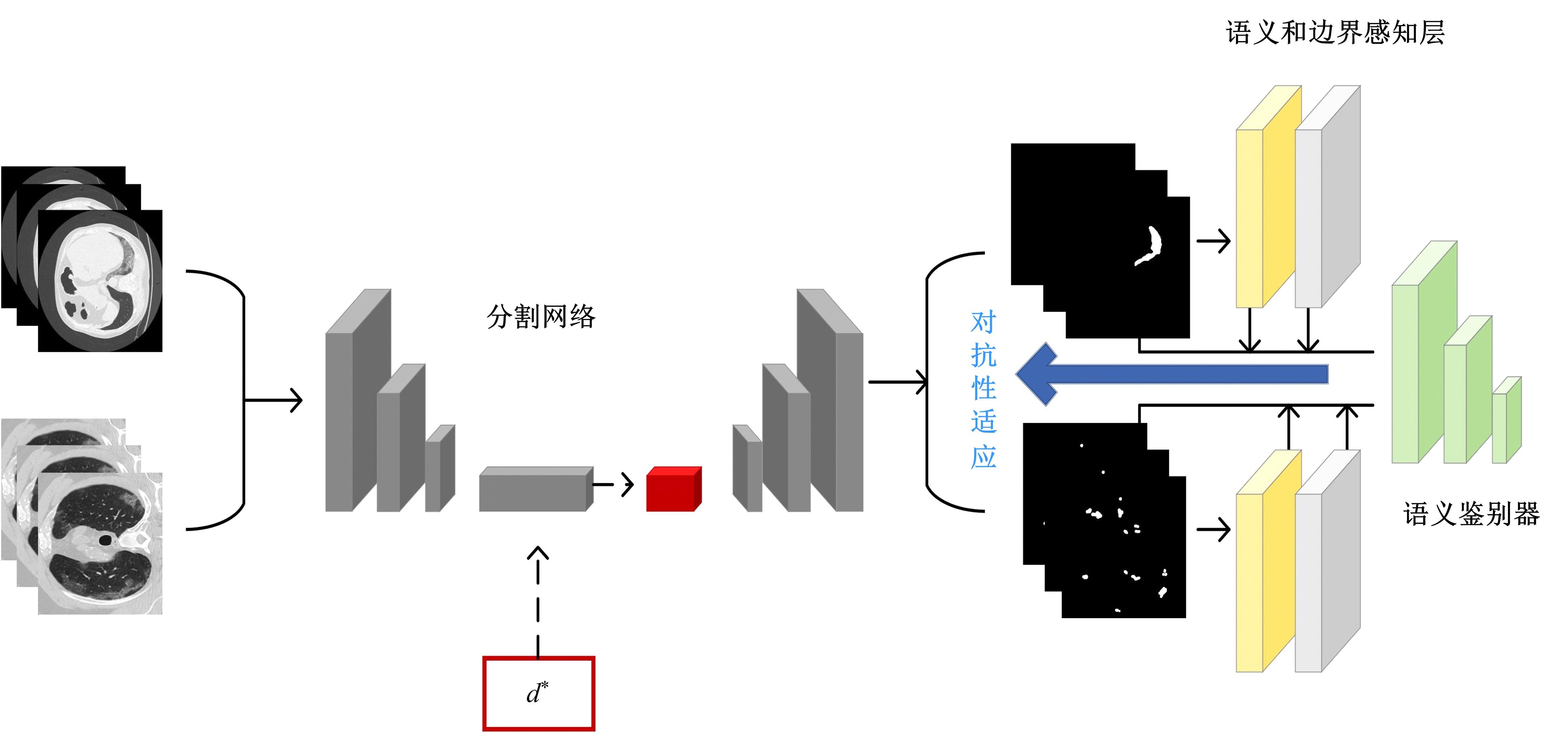
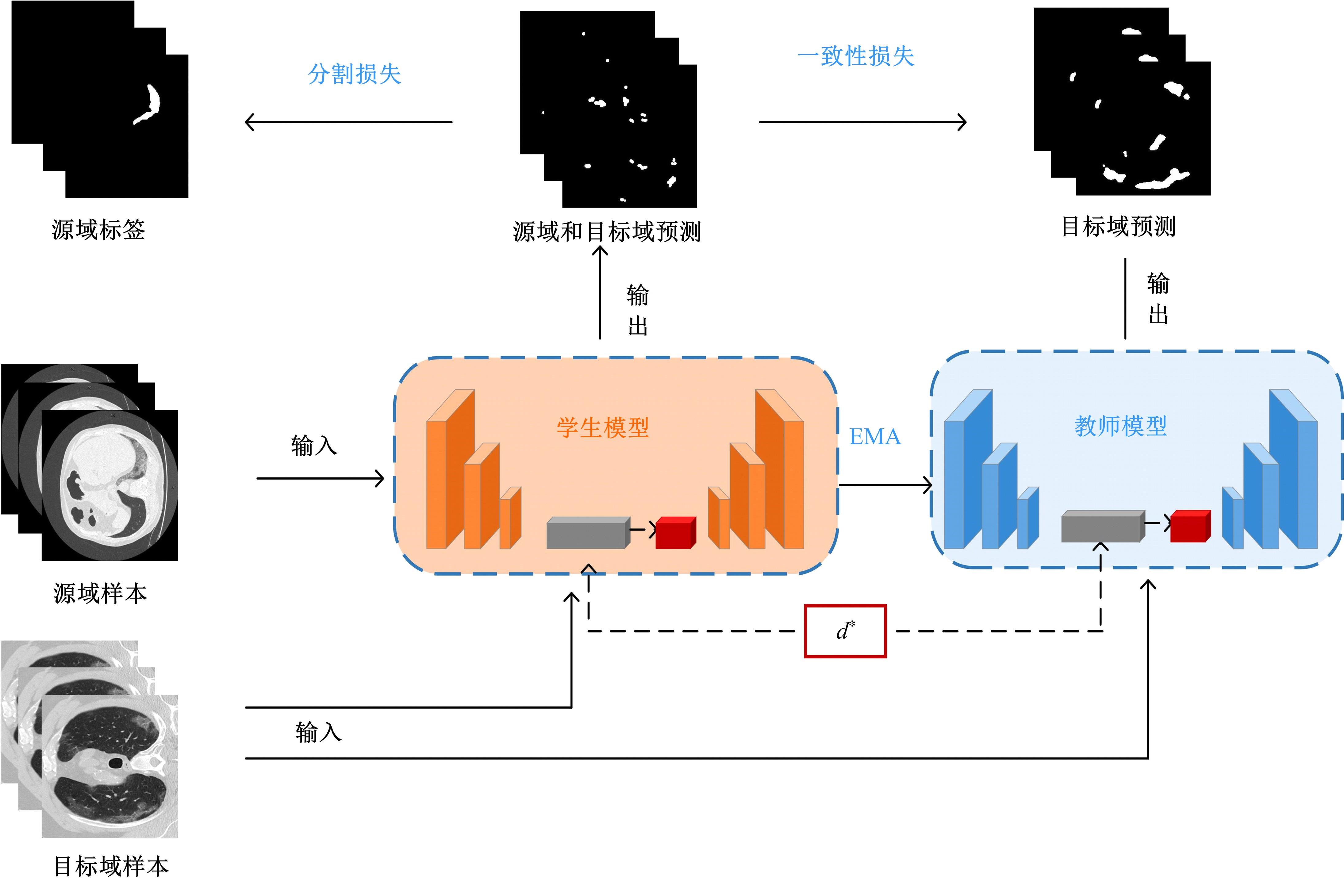
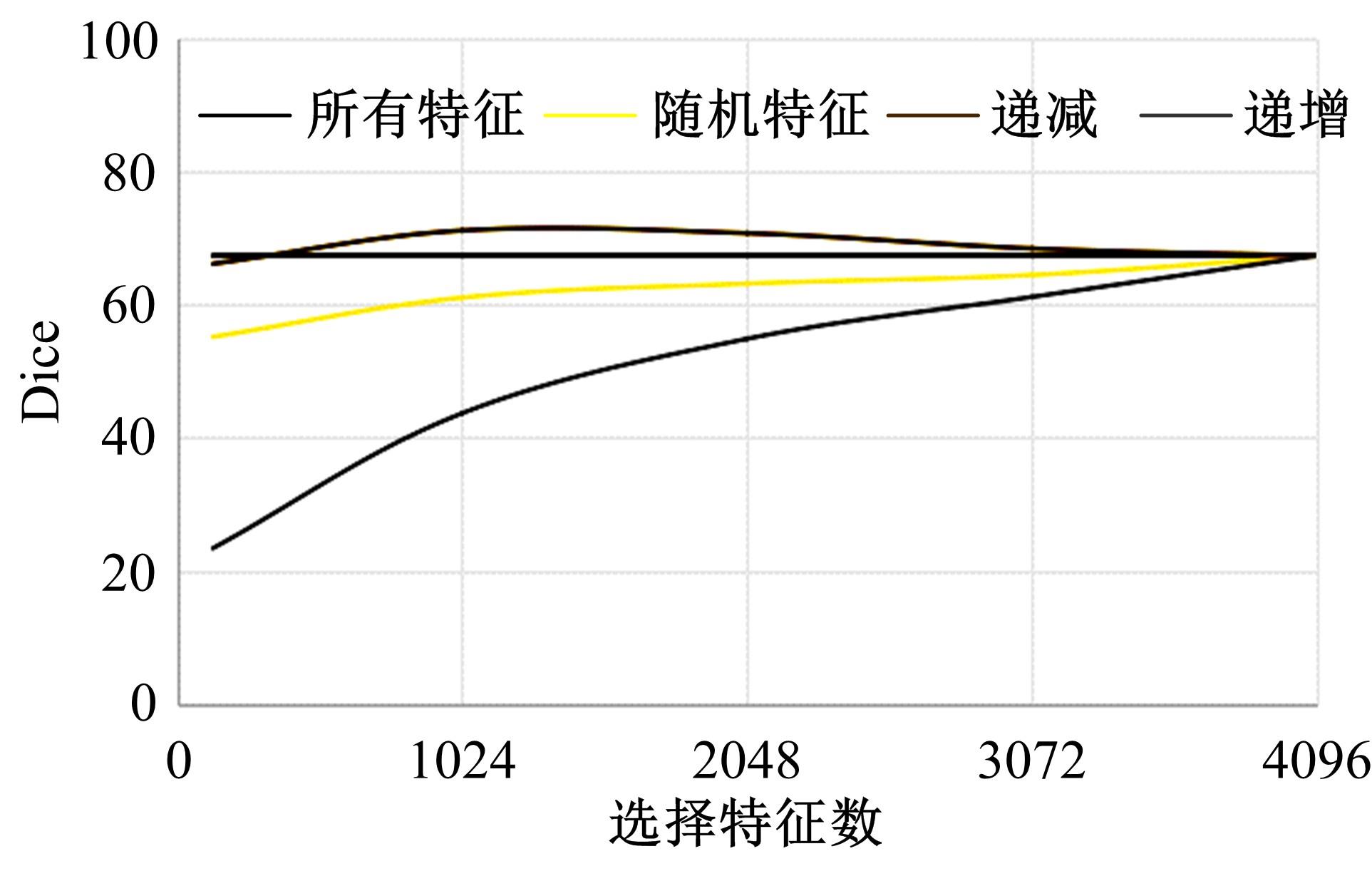
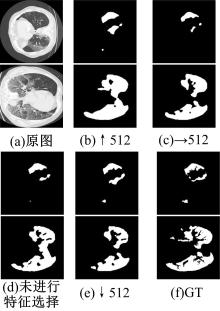
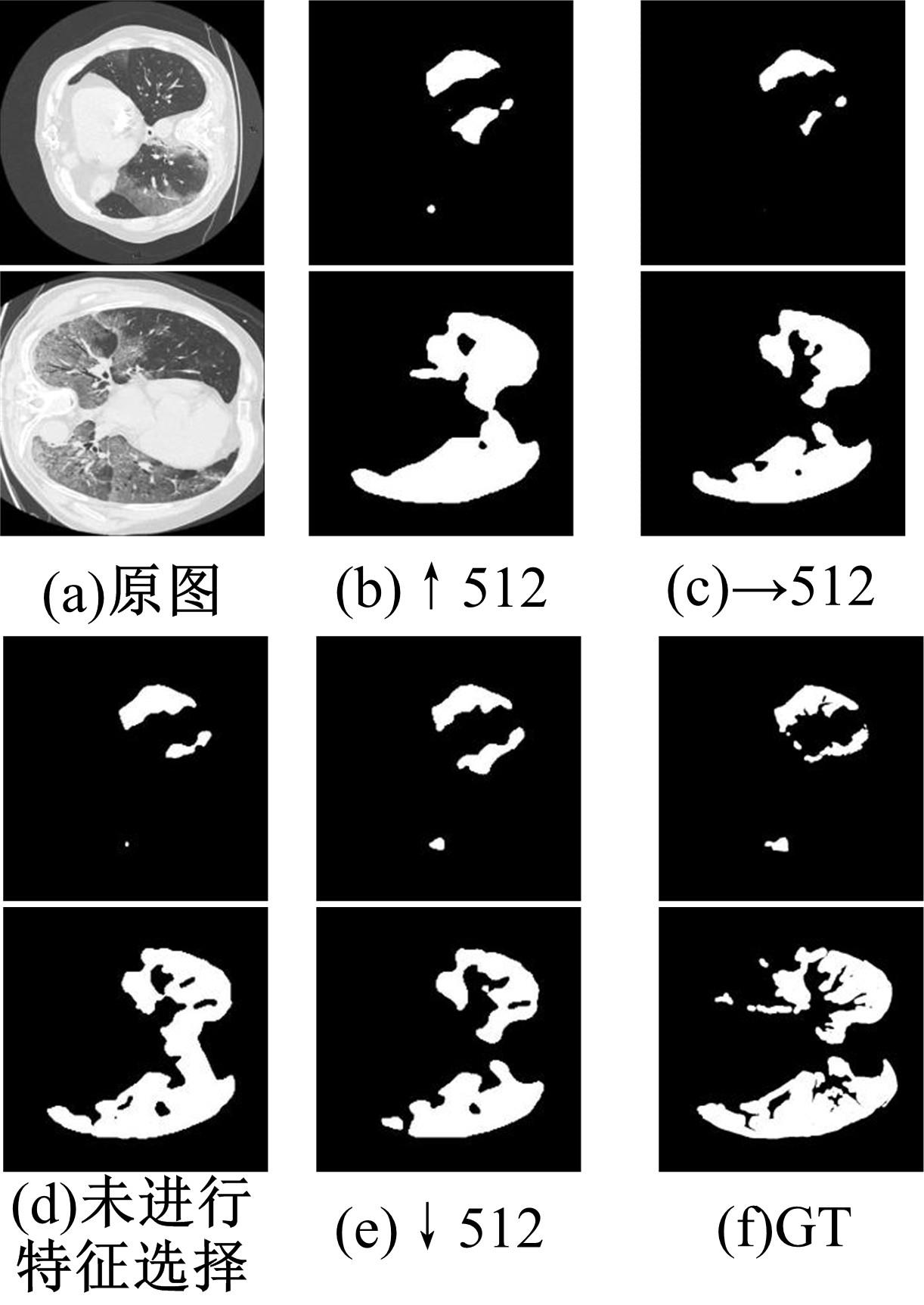
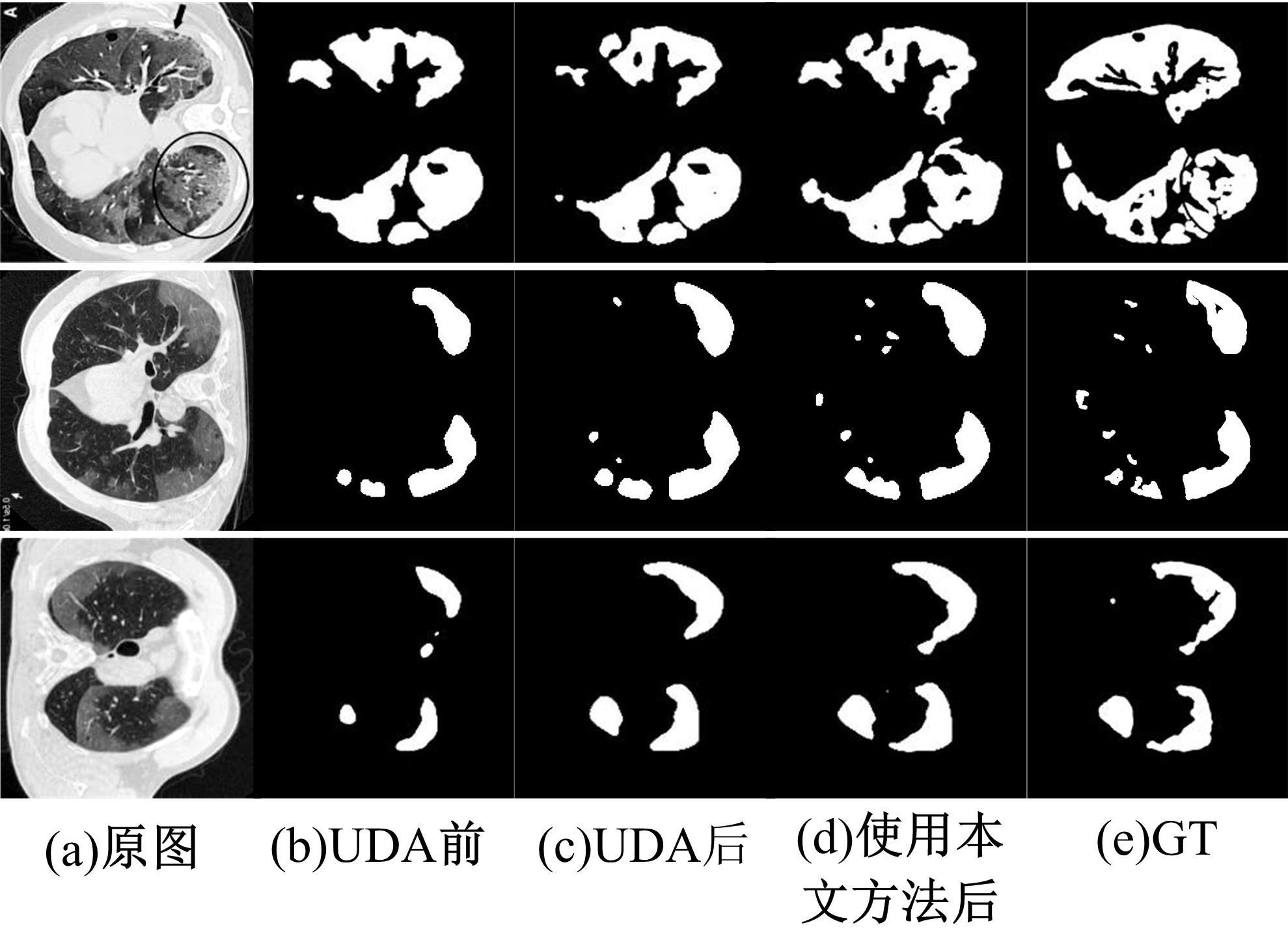
在无监督领域自适应迁移学习过程中,域无关特征导致模型分割性能下降,而目前并没有针对迁移学习分割模型有效的特征选择方法。为解决该问题,提出了一个基于最优传输的迁移学习通用特征选择模块,可以应用到多种无监督领域自适应图像分割模型中。该模块利用分割准确性加权最优传输选择两个域的最优样本子集,再将样本子集特征进行熵正则化最优传输,得到两个域特征相似性降序列表来去掉域无关特征。将通用特征选择模块应用到三种无监督领域自适应模型中解决新冠肺炎图像分割问题,均在一定程度上提升了模型性能。
中图分类号:
- TP18
| 1 | Huang J, Smola A J, Gretton A, et al.Correcting sample selection bias by unlabeled data[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2007, 19: 601-608. |
| 2 | Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H, et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks[J]. Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, 17(1): 2096-2130. |
| 3 | 许新征, 丁世飞, 史忠植,等. 图像分割的新理论和新方法[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(): 76-82. |
| Xu Xin-zheng, Ding Shi-fei, Shi Zhong-zhi, et al. New theories and methods of image segmentation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(Sup.): 76-82. | |
| 4 | He B S, Zhu F, Shi Y G. Medical image segmentation[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 760-762(4): 1590-1593. |
| 5 | Courty N, Flamary R, Tuia D, et al. Optimal transport for domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(9): 1853-1865. |
| 6 | Courty N, Flamary R, Habrard A, et al. Joint distribution optimal transportation for domain adaptation[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 3731-3740. |
| 7 | Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Zhang N, et al. Deep domain confusion: maximizing for domain invariance[J/OL]. [2021-06-10]. |
| 8 | Ruan C, Wang W, Hu H, et al. Category-level adversaries for semantic domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 83198-83208. |
| 9 | Hoffman J, Tzeng E, Park T, et al. CyCADA: cycle-consistent adversarial domain adaptation[C]∥The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3162-3174. |
| 10 | Dou Q, Ouyang C, Chen C, et al. Unsupervised cross-modality domain adaptation of convnets for biomedical image segmentations with adversarial loss[C]∥Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2018: 691-697. |
| 11 | Redko I, Habrard A, Sebban M. Theoretical analysis of domain adaptation with optimal transport[C]∥Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, London, England, 2017: 737-753. |
| 12 | Balaji Y, Chellappa R, Feizi S. Normalized wasserstein for mixture distributions with applications in adversarial learning and domain adaptation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 6509-6517. |
| 13 | Damodaran B B, Kellenberger B, Flamary R, et al. DeepJDOT: Deep joint distribution optimal transport for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), New York, USA, 2018: 447-463. |
| 14 | Ackaouy A, Courty N, Vallée E, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation with optimal transport in multi-site segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions from MRI data[J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 19. |
| 15 | Xu R, Liu P, Wang L,et al. Reliable weighted optimal transport for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 4394-4403. |
| 16 | Li M, Zhai Y M, Luo Y W, et al. Enhanced transport distance for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13936-13944. |
| 17 | Li J, Zhao J, Lu K. Joint feature selection and structure preservation for domain adaptation[C]∥Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2016: 1697-1703. |
| 18 | Sun F, Wu H, Luo Z, et al. Informative feature selection for domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 142551-142563. |
| 19 | Gautheron L, Redko I, Lartizien C. Feature selection for unsupervised domain adaptation using optimal transport[C]∥Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, London, England, 2018: 759-776. |
| 20 | Villani C. Optimal transport old and new[J]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2007, 338(23/24): 480-488. |
| 21 | Cuturi M. Sinkhorn distances: lightspeed computation of optimal transport[C]∥Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Spain, 2013: 2292-2300. |
| 22 | Knight P A. The Sinkhorn-knopp algorithm: convergence and applications[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2008, 30(1): 261-275. |
| 23 | Li H, Loehr T, Sekuboyina A, et al. e-UDA: efficient unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-site medical image segmentation[J/OL]. [2021-6-10]. . |
| 24 | Perone C S, Ballester P, Barros R C, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for medical imaging segmentation with self-ensembling[J]. NeuroImage, 2019, 194: 1-11. |
| 25 | Laradji I, Rodriguez P, Manas O, et al. A weakly supervised consistency-based learning method for COVID-19 segmentation in CT images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 2453-2462. |
| 26 | Zhou T, Canu S, Ruan S. An automatic COVID-19 CT segmentation network using spatial and channel attention mechanism[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2020, 21(1): 16-27. |
| 27 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations, New York, USA, 2015: 1-14. |
| [1] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [2] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [3] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [4] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [5] | 雷景佩,欧阳丹彤,张立明. 基于知识图谱嵌入的定义域值域约束补全方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 154-161. |
| [6] | 李志华,张烨超,詹国华. 三维水声海底地形地貌实时拼接与可视化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 180-186. |
| [7] | 汤松梅. 基于群智能的图书馆人脸识别系统关键技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2216-2224. |
| [8] | 欧阳丹彤,张必歌,田乃予,张立明. 结合格局检测与局部搜索的故障数据缩减方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [9] | 徐艳蕾,何润,翟钰婷,赵宾,李陈孝. 基于轻量卷积网络的田间自然环境杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
| [10] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [11] | 杨勇,陈强,曲福恒,刘俊杰,张磊. 基于模拟划分的SP⁃k⁃means-+算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1808-1816. |
| [12] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [13] | 李景彬,杨禹锟,温宝琴,坎杂,孙雯,杨朔. 基于根茬检测的秋后残膜回收导航路径提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1528-1539. |
| [14] | 董延华,刘靓葳,赵靖华,李亮,解方喜. 基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1405-1413. |
| [15] | 刘富,梁艺馨,侯涛,宋阳,康冰,刘云. 模糊c-harmonic均值算法在不平衡数据上改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1447-1453. |
|
||