吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 933-940.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221057
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
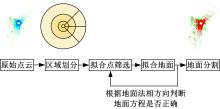
基于平面拟合的地面点云精确分割方法
- 1.西安工业大学 西安市主动光电成像探测技术重点实验室,西安 710021
2.长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
3.西安工业大学 光电工程学院,西安 710021
Accurate segmentation method of ground point cloud based on plane fitting
Chun-yang WANG1,2( ),Wen-qian QIU2,Xue-lian LIU1(
),Wen-qian QIU2,Xue-lian LIU1( ),Bo XIAO3,Chun-hao SHI2
),Bo XIAO3,Chun-hao SHI2
- 1.Xi'an Key Laboratory of Active Photoelectric Imaging Detection Technology,Xi'an Technological University,Xi'an 710021,China
2.College of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.School of Optoelectronic Engineering,Xi'an Technological University,Xi'an 710021,China
摘要:
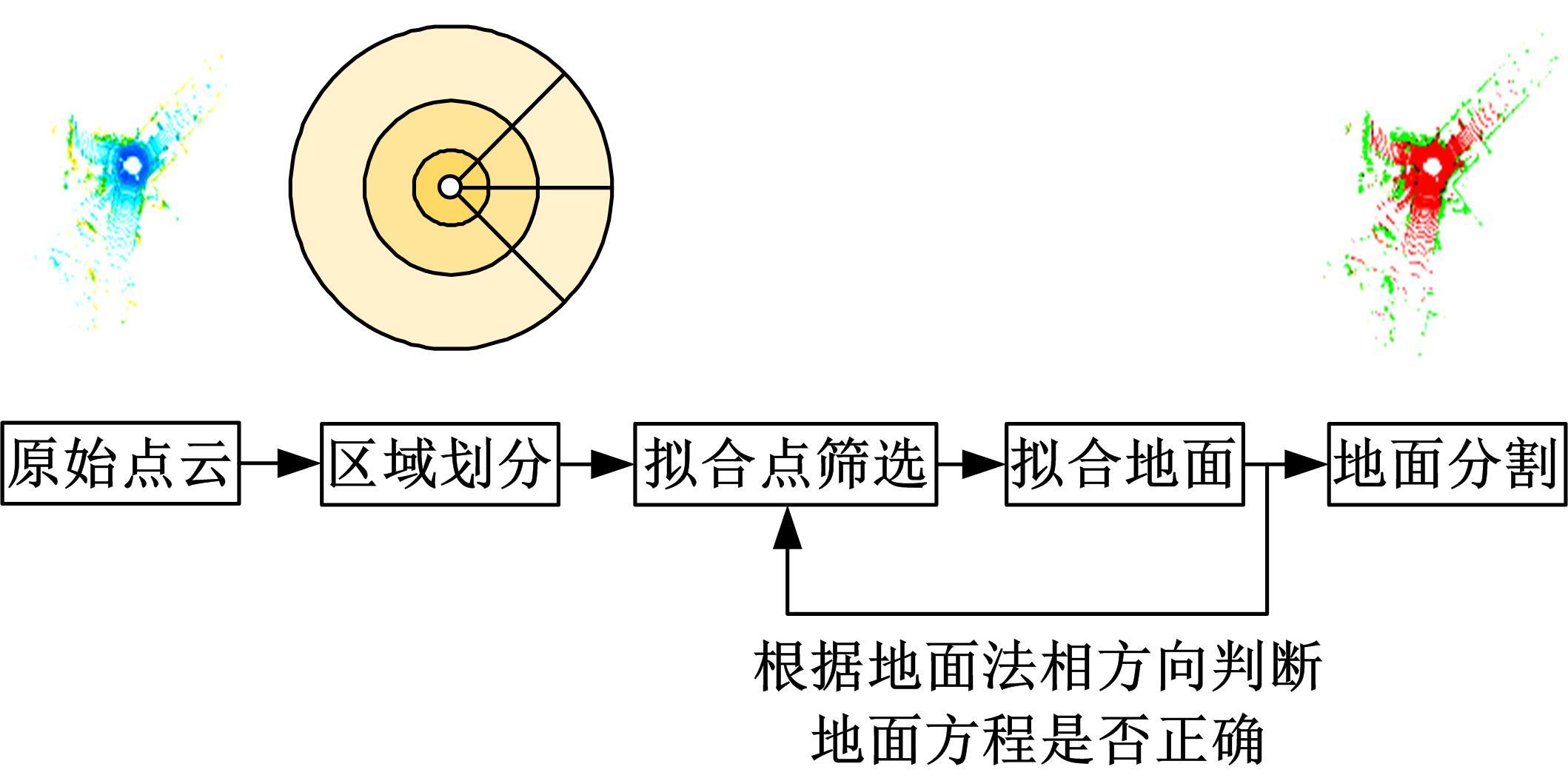
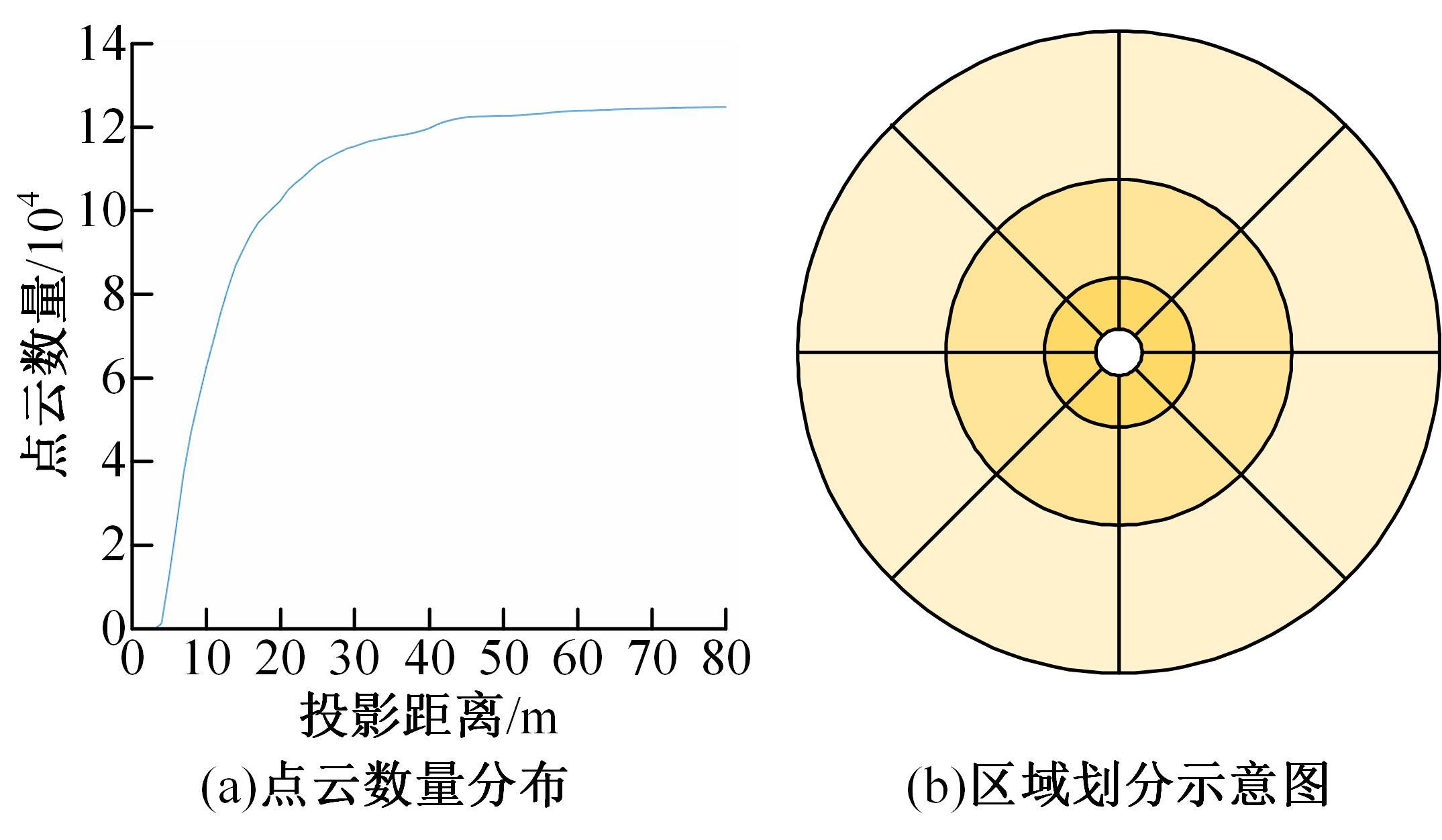
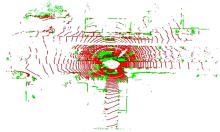
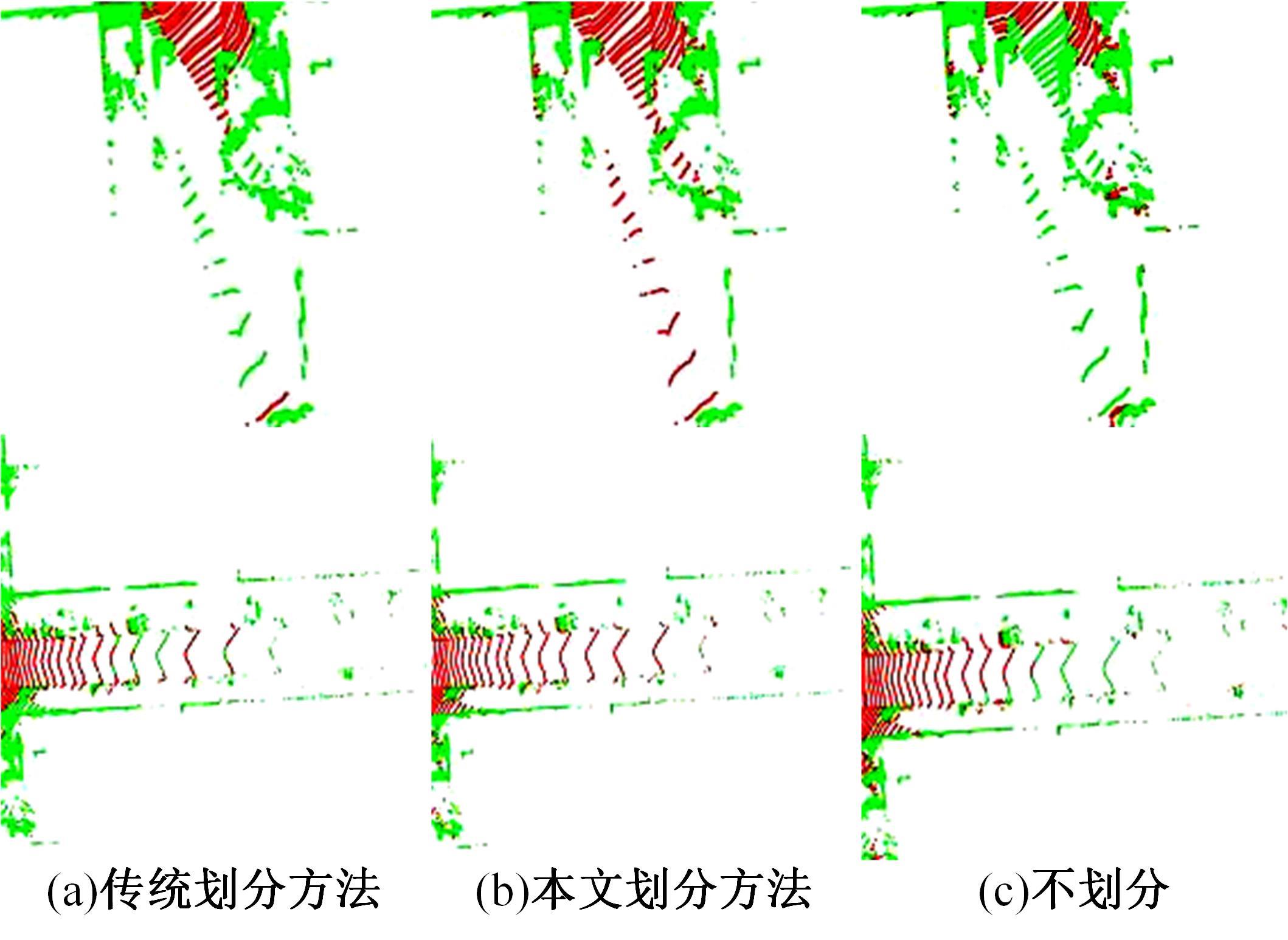
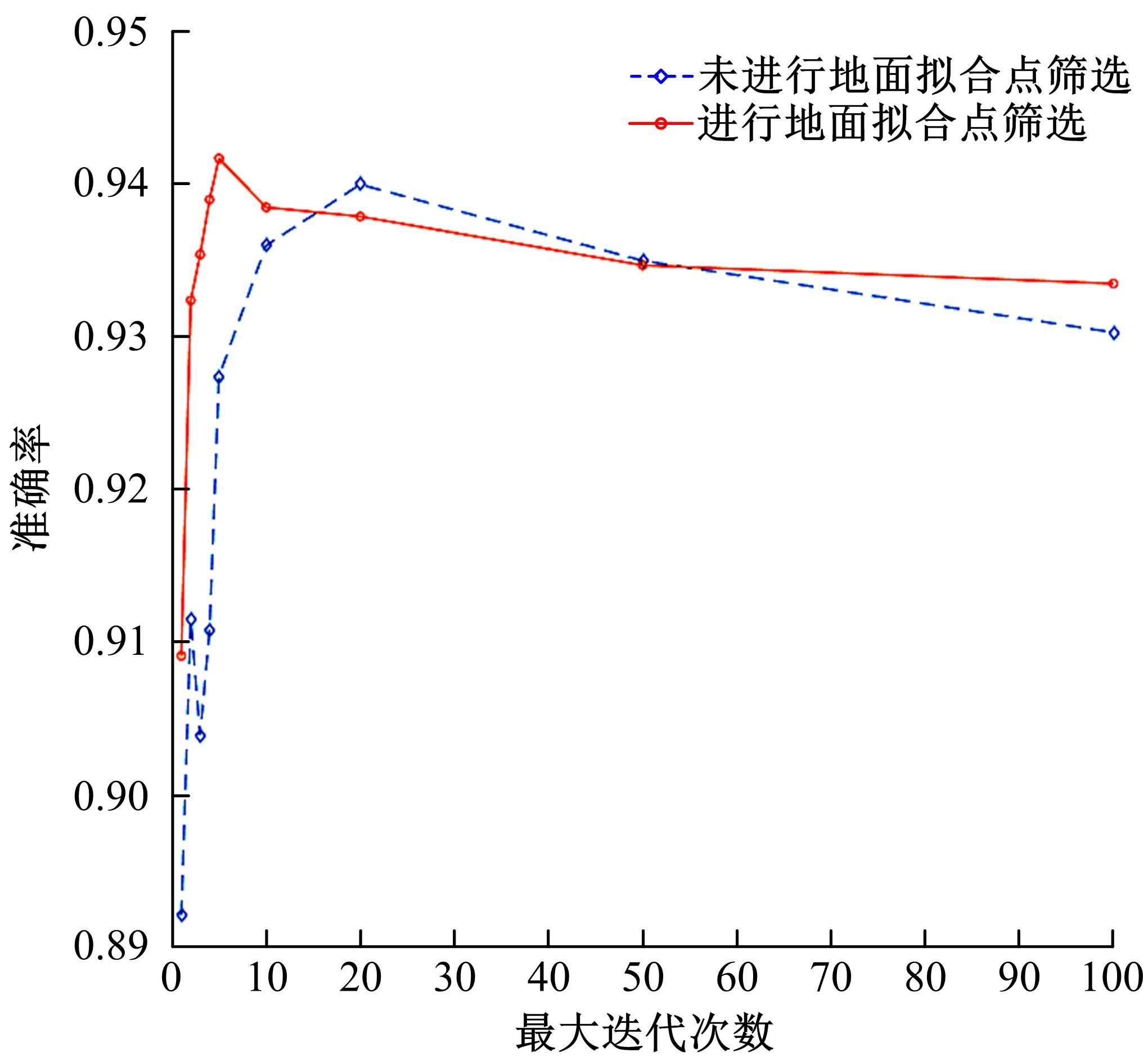
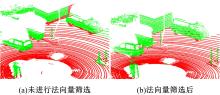
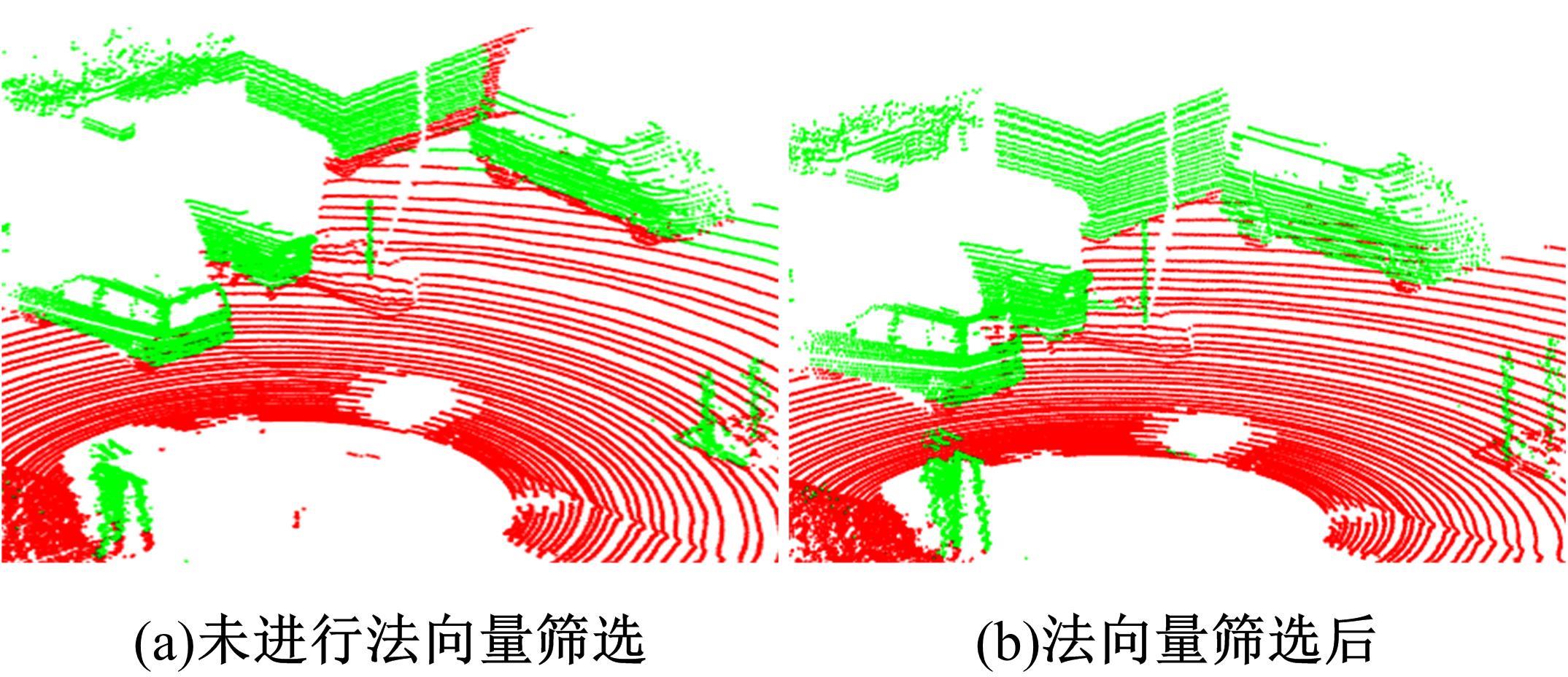
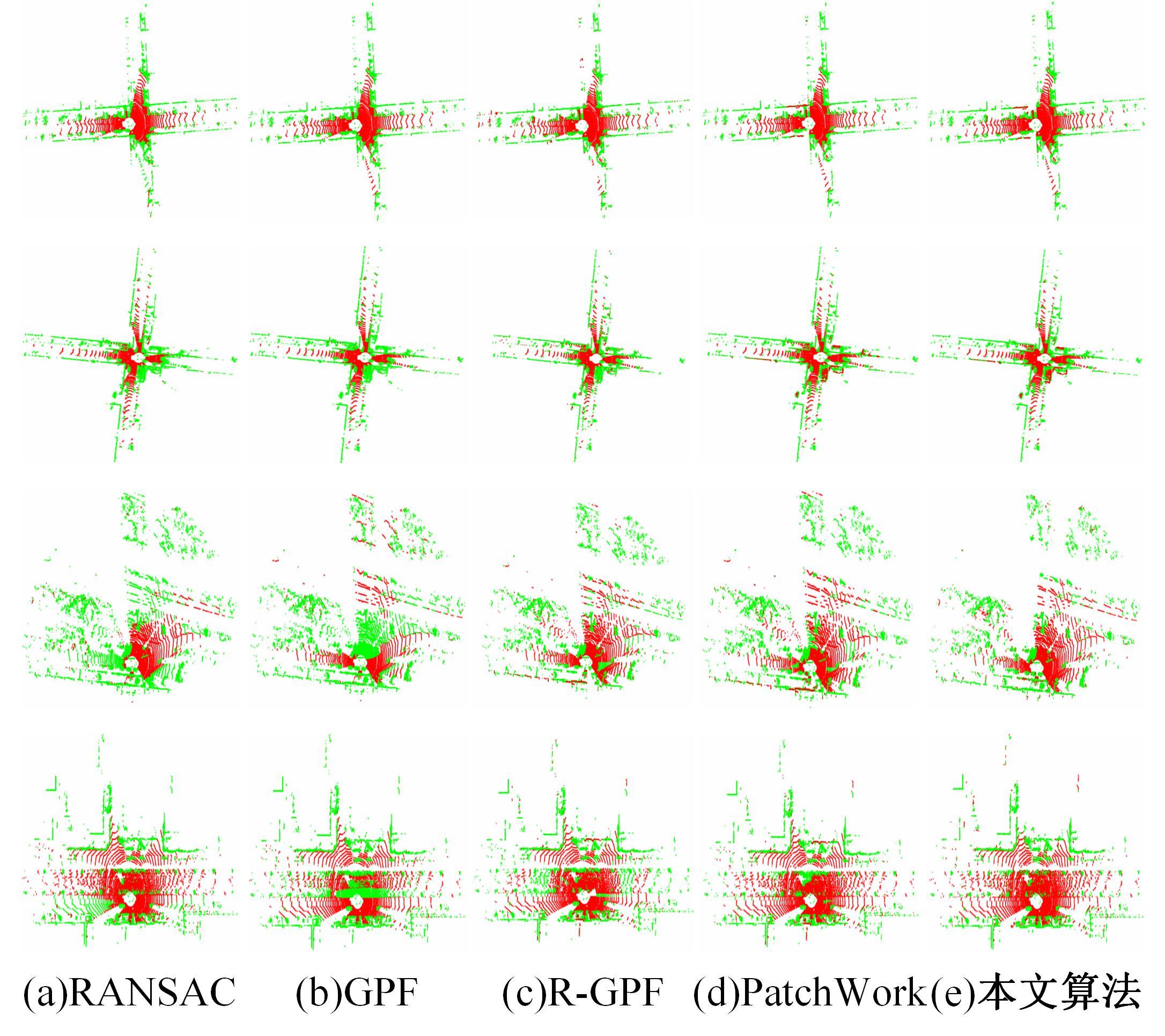
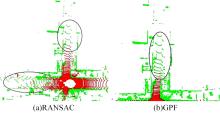
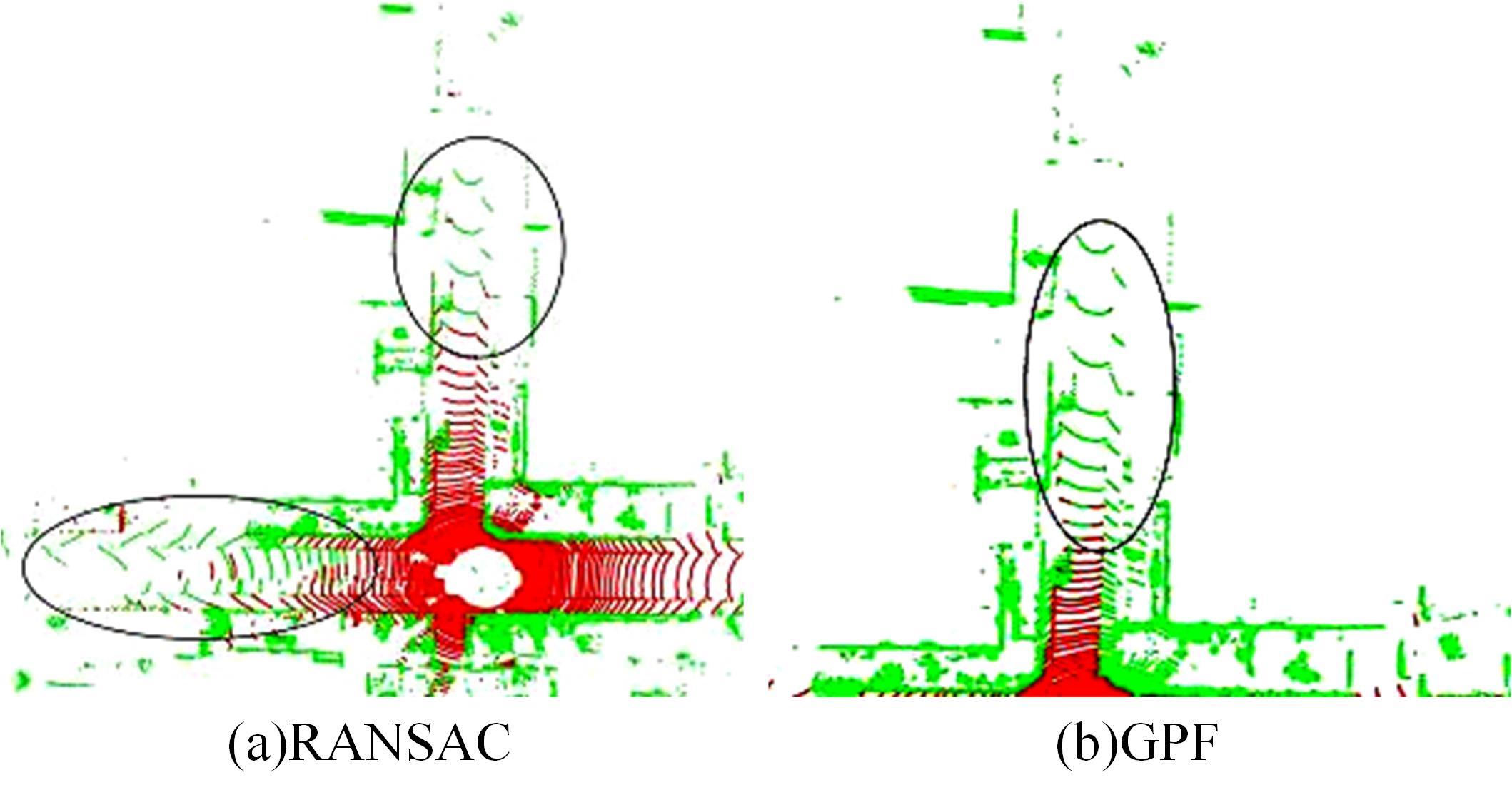
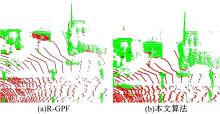
针对点云数据中的地面点会影响环境感知的精度与速度的问题,提出了一种基于平面拟合的地面点云精确分割方法。首先,根据投影距离将场景点云分为多个区域;其次,根据区域内的平均高度、分割地面点和地平面法向量的方向,确定地面平面拟合点并对地面平面进行拟合;最后,根据点到地面平面的距离,实现地面分割。本文基于KITTI数据集和实采数据将本文算法与RANSAC、GPF、R-GPF和PatchWork四种算法进行了对比,验证了区域划分、拟合点筛选以及地面平面法向量方向筛选对地面分割的有效性。实验结果表明,进行区域划分后,可以分割远距离稀疏地面;进行拟合点筛选后,在低迭代的条件下地面分割准确率达到0.9417;进行地平面法向量方向筛选后,能够避免将墙面拟合成地面;本文方法在F1分数、召回率和准确率上优于所对比的4种算法,速度可以达到42.78 Hz,能够精确、快速地对地面进行分割。
中图分类号:
- TN911.7
| 1 | 曾昊旻,李松,张智宇,等.车载激光雷达Risley棱镜光束扫描系统[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(7):1444-1450. |
| Zeng Hao-min, Li Song, Zhang Zhi-yu, et al. Risley-prism-based beam scanning system for mobile lidar[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(7):1444-1450. | |
| 2 | Douillard B, Underwood J, Kuntz N, et al. On the segmentation of 3DLIDAR point clouds[C]∥2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai,China,2011:2798-2805. |
| 3 | Byun J, Na K I, Seo B S, et al. Drivable road detection with 3D point clouds based on the MRF for intelligent vehicle[J]. Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, 2015, 105: 49-60. |
| 4 | Asvadi A, Peixoto P, Nunes U . et al . Detection and tracking of moving objects using 2.5D motion grids[C]∥2015 IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Gran Canaria,Spain,2015: 788-793. |
| 5 | 张名芳,付锐,郭应时,等. 基于三维不规则点云的地面分割算法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2017,47(5):1387-1394. |
| Zhang Ming-fang, Fu Rui, Guo Ying-shi, et al. Road segmentation method based on irregular three dimensional point cloud[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(5): 1387-1394. | |
| 6 | 伍锡如,薛其威. 基于激光雷达的无人驾驶系统三维车辆检测[J]. 光学精密工程, 2022, 30(4): 489-497. |
| Wu Xi-ru, Xue Qi-wei. 3D vehicle detection for unmanned driving systerm based on lidar[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(4): 489-497. | |
| 7 | 邹兵,陈鹏,刘登洪. 一种基于栅格投影的快速地面点云分割算法[J]. 城市勘测, 2021(3): 112-116. |
| Zou Bing, Chen Peng, Liu Deng-hong. A fast ground point cloud segmentation algorithm based on raster projection[J]. Urban Surveys, 2021(3): 112-116. | |
| 8 | Leng Zhi-xin, Li Shu, Li Xin, et al. An improved fast ground segmentation algorithm for 3D point cloud[C]∥2020 Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Hefei, China, 2020: 5016-5020. |
| 9 | Cheng Jie, He Dong, Lee Chang-hee. A simple ground segmentation method for LiDAR3D point clouds[C]∥2020 2nd International Conference on Advances in Computer Technology, Information Science and Communications, Guangzhou, China, 2020:171-175. |
| 10 | Zhou Ying, Wang Dan, Xie Xiang, et al. A fast and accurate segmentation method for ordered LiDAR point cloud of large-scale scenes[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014,11(11):1981-1985. |
| 11 | Paigwar A, Erkent Ö, Sierra-Gonzalez D, et al. GndNet: fast ground plane estimation and point cloud segmentation for autonomous vehicles[C]∥2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas,USA,2020:2150-2156. |
| 12 | Fischler M A, Bolles R C. Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography[J]. Commun, ACM, 1981,24(6): 381-395. |
| 13 | Zermas D, Izzat I, Papanikolopoulos N. Fast segmentation of 3D point clouds: a paradigm on LiDAR data for autonomous vehicle applications[C]∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Maria Bay Sands,Singapore,2017: 5067-5073. |
| 14 | Lim H, Hwang S, Myung H. ERASOR: egocentric ratio of pseudo occupancy-based dynamic object removal for static 3D Point cloud map building[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021,6(2):2272-2279. |
| 15 | Lim H, Oh M, Myung H. PatchWork: concentric zone-based region-wiseground segmentation with ground likelihood estimation using a 3D LiDAR sensor[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2021,6(4):6458-6465. |
| [1] | 李雪梅,王春阳,刘雪莲,施春浩,李国瑞. 基于超体素双向最近邻距离比的点云配准方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1918-1925. |
| [2] | 李雪梅,王春阳,刘雪莲,谢达. 基于SESTH的线性调频连续波激光雷达信号时延估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 950-958. |
| [3] | 魏民祥,杨佳伟,陈凯,王志浩,沙朝. 基于改进大脑情感学习模型的车辆纵向跟随[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2994-3005. |
| [4] | 林乐平,卢增通,欧阳宁. 面向非配合场景的人脸重建及识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2941-2946. |
| [5] | 窦慧晶,丁钢,高佳,梁霄. 基于压缩感知理论的宽带信号波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2237-2245. |
| [6] | 金立生,郭柏苍,王芳荣,石健. 基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [7] | 刘志伟,刘建荣,邓卫. 基于潜在类别的无人驾驶汽车选择行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1261-1268. |
| [8] | 于向军,槐元辉,姚宗伟,孙中朝,俞安. 工程车辆无人驾驶关键技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. |
| [9] | 朱伟刚,朱超,张亚球,魏海斌. 基于卷积格网曲面拟合滤波算法的数字高程模型构建及质量评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [10] | 曾小华,李晓建,杜劭峰,马涛,王振伟,宋大凤. 多轮混合动力驱动无人驾驶框架车整车控制器开发[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 63-71. |
| [11] | 金心宇,谢慕寒,孙斌. 基于半张量积压缩感知的粮情信息采集[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 379-385. |
| [12] | 王晓辉,吴禄慎,陈华伟. 基于法向量距离分类的散乱点云数据去噪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 278-288. |
| [13] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [14] | 杨顺,蒋渊德,吴坚,刘海贞. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [15] | 郭立民,陈鑫,陈涛. 基于AlexNet模型的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 1000-1008. |
|
||