吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4): 1280-1287.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20171272
• • 上一篇
喷丸处理后6061铝合金工件表面粗糙度的模拟计算及预测
- 重庆大学 材料科学与工程学院,重庆 400044
Simulation and prediction of surface roughness of 6061 aluminum alloy workpiece after shot peening
Wu⁃jiao XU( ),Cheng⁃shang LIU,Xin⁃yao LU
),Cheng⁃shang LIU,Xin⁃yao LU
- College of Material Science and Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
摘要:
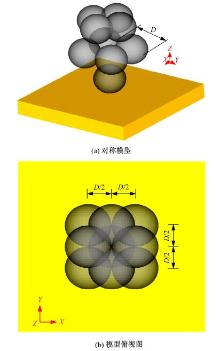
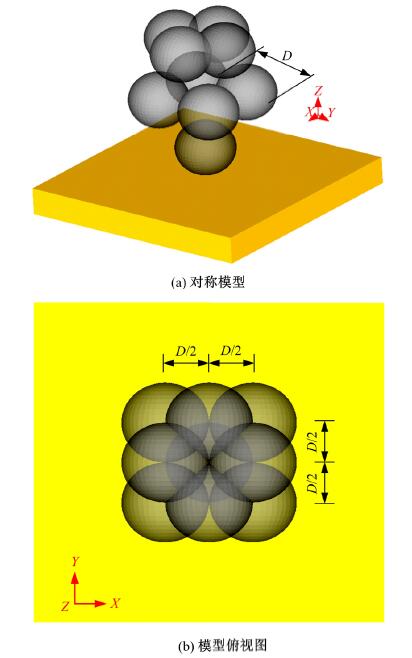
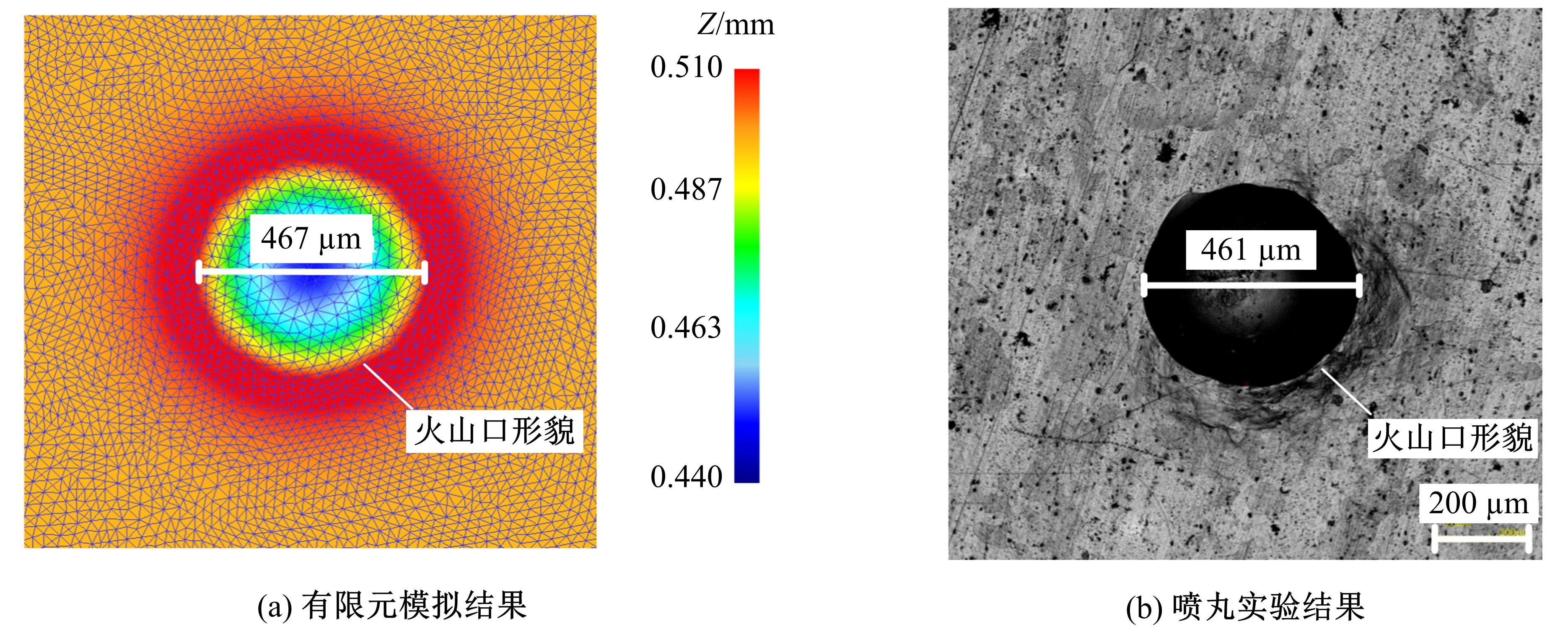
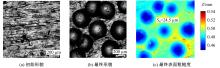
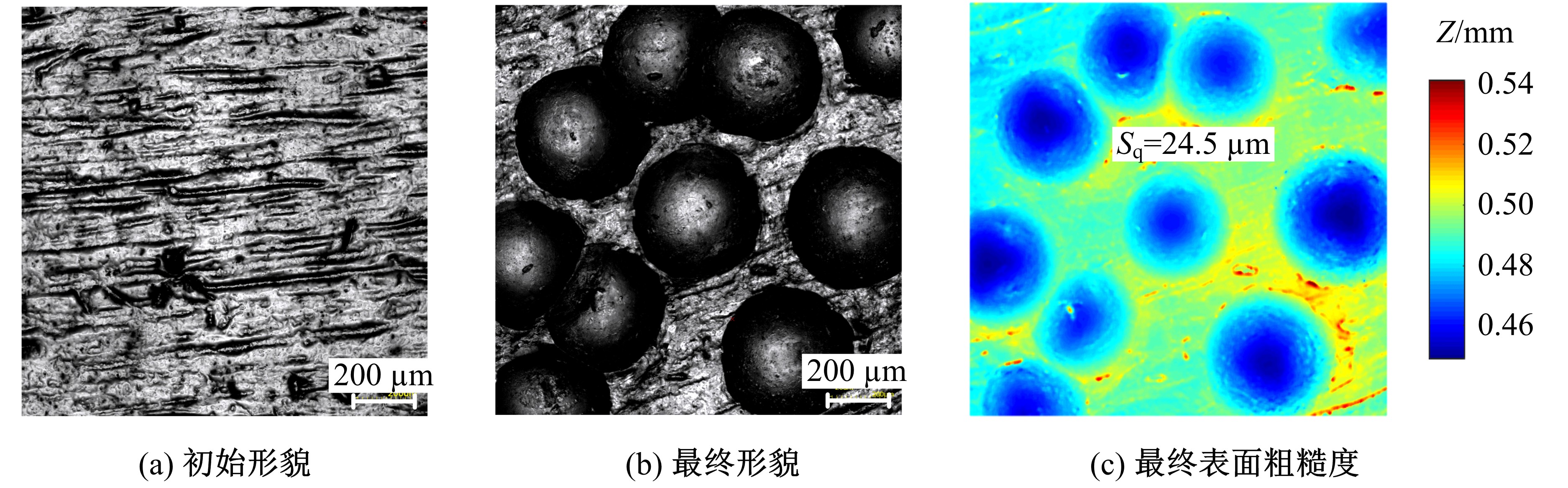
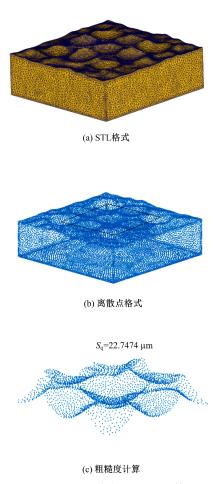
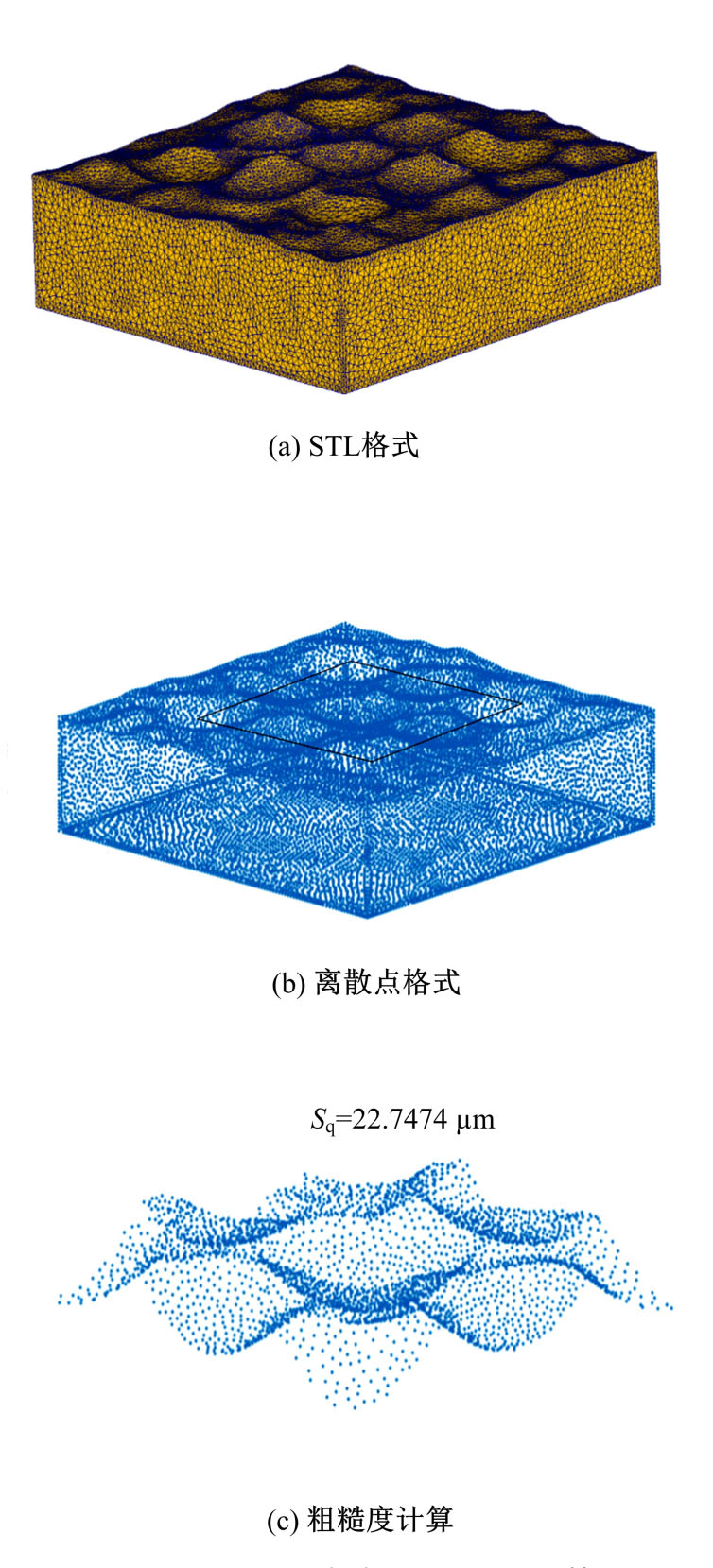
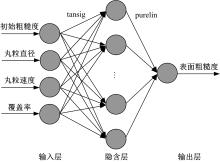
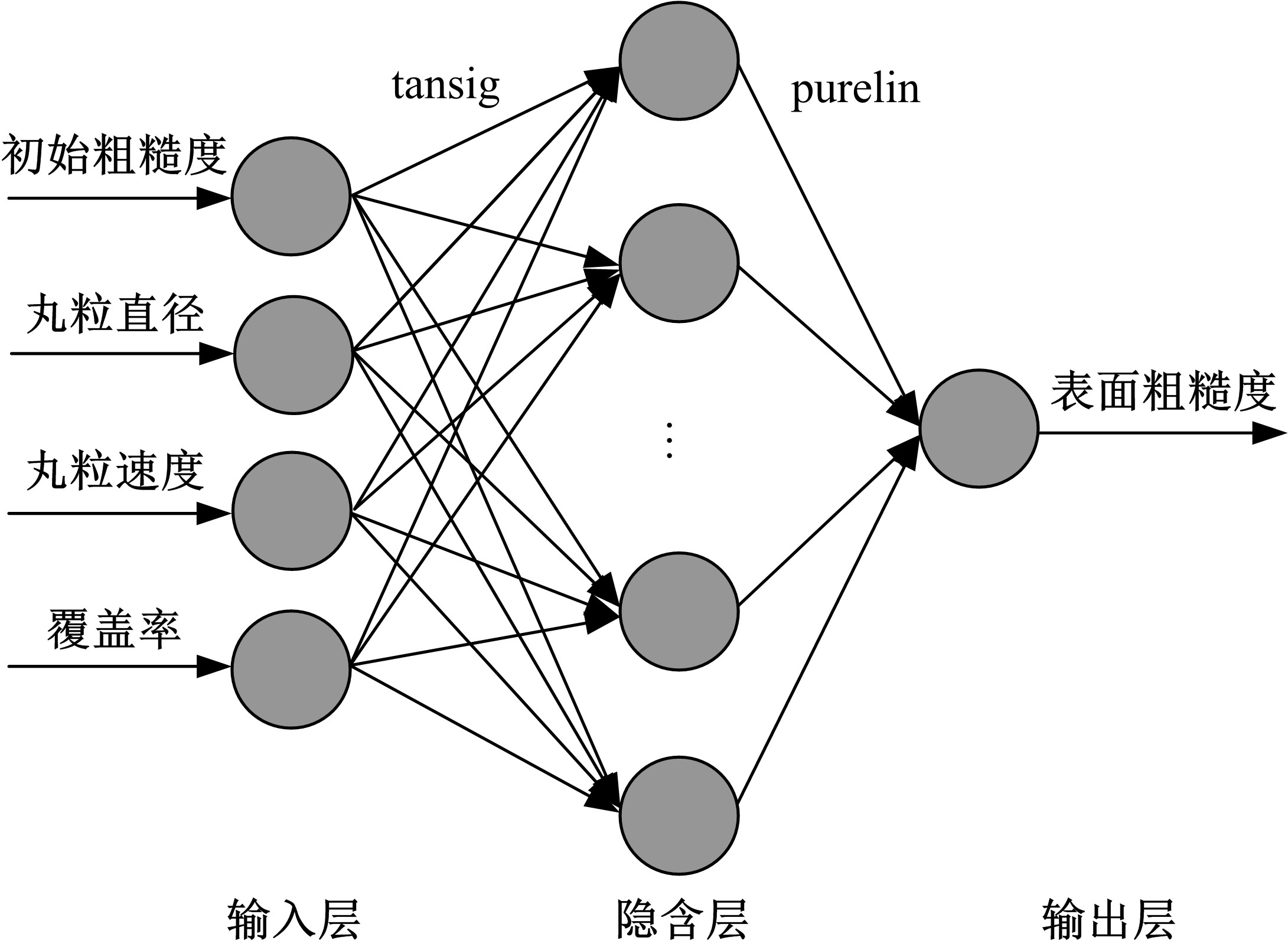
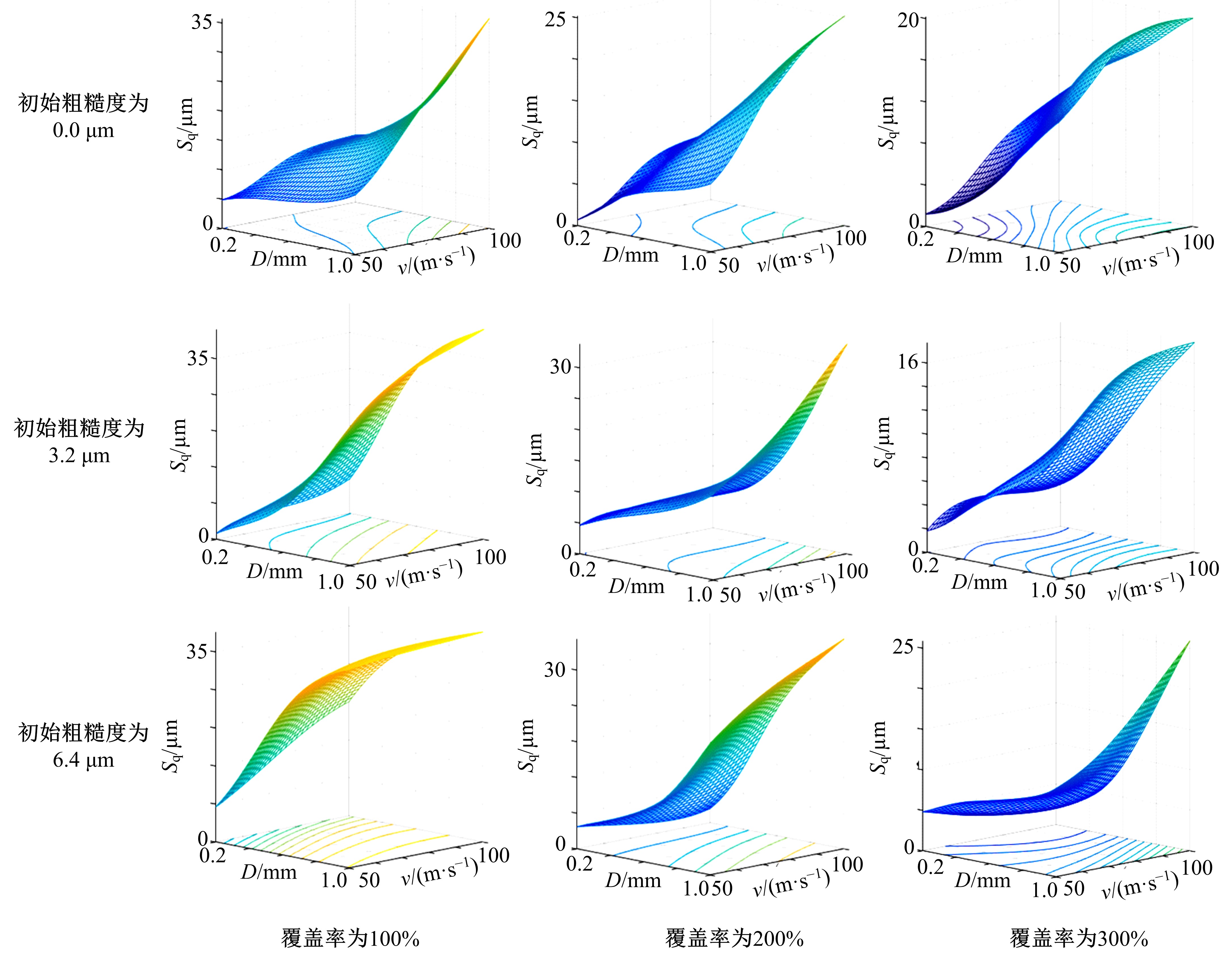
以6061铝合金工件为对象,研究了喷丸对工件表面粗糙度的影响。首先,建立了喷丸有限元仿真模型,分别模拟计算了单丸粒喷丸和多丸粒喷丸后铝合金工件的表面形貌。对应进行了单丸粒喷丸和多丸粒喷丸试验,采用激光共聚焦显微镜获取了喷丸后实际工件的表面形貌,以验证所建立的喷丸有限元仿真模型的有效性。在此基础上,对铝合金工件开展了9组喷丸的正交模拟试验,通过对喷丸表面进行离散计算得到三维粗糙度参数 S q,研究获得工件初始粗糙度、丸粒尺寸、丸粒速度和喷丸覆盖率对工件表面粗糙度的影响规律。采用BP神经网络模型对正交试验结果进行处理,获得铝合金工件喷丸处理后表面粗糙度的预测模型。将预测的经喷丸处理后的工件表面粗糙度与模拟试验的粗糙度数据进行对比可知,两者的平均误差仅为3.46%,预测精度能够满足实际喷丸需要;相应构建了喷丸处理后铝合金工件的表面粗糙度控制图,这对实际喷丸过程中较准确控制工件的表面粗糙度有重要价值。
中图分类号:
- TG146.2
| 1 | 王仁智 . 金属材料的喷丸强化原理及其强化机理综[J]. 中国表面工程, 2012, 25(6): 1⁃8. |
| Wang Ren⁃zhi . Overview on the shot peening principle and its strengshening mechanisms for metallic materials[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2012, 25(6): 1⁃8. | |
| 2 | Vielma A T , Llaneza V , Belzunce F J . Shot peening intensity optimization to increase the fatigue life of a quenched and tempered structural steel[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 74: 273⁃278. |
| 3 | Gao Y K . Fatigue limit of chemical heat treated specimens and effect of shot peening[J]. Surface Engineering, 2008, 24(5): 322⁃326. |
| 4 | Gao Y K . Influence of shot peening on tension⁃tension fatigue property of two high strength Ti alloys[J]. Surface Engineering, 2006, 22(4): 299⁃303. |
| 5 | Villegas J C , Shaw L L . Nanocrystallization process and mechanism in a nickel alloy subjected to surface severe plastic deformation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57: 5782⁃5795. |
| 6 | Liu G , Wang S C , Lou X F , et al . Low carbon steel with nanostructured surface layer induced by high⁃energy shot peening[J]. Seripta Materialia, 2001, 44: 1791⁃1795. |
| 7 | 栾伟玲, 涂善东 . 喷丸表面改性技术的研究进展[J]. 中国机械工程, 2005, 16(15): 1405⁃1409. |
| Luan Wei⁃ling , Tu Shan⁃dong . Recent trends on surface modification technology of shot peening[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 16(15):1405⁃1409. | |
| 8 | Dalaei K , Karlsson B , Svensson L E . Stability of shot peening induced residual stresses and their influence on fatigue lifetime[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2011, 528(3): 1008⁃1015. |
| 9 | Mylonas G I , Labeas G . Numerical modelling of shot peening process and corresponding products: residual stress, surface roughness and cold work prediction[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2011, 205(19): 4480⁃4494. |
| 10 | 田唐永 . TC4钛合金喷丸强化组织与性能研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2012. |
| Tian Tang⁃yong . Microstructures and properties of TC4 titanium alloy treated by shot peening[D]. Dalian: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2012. | |
| 11 | Wang S , Li Y , Wang R . Compressive residual stress introduced by shot peening[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1998, 73(1): 64⁃73. |
| 12 | Kim T , Jin H L , Lee H , et al . An area⁃average approach to peening residual stress under multi⁃impacts using a three⁃dimensional symmetry⁃cell finite element model with plastic shots[J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(1): 50⁃59. |
| 13 | Lammi C J , Lados D A . Numerical predictions and Experimental measurements of residual stresses on fatigue crack growth specimens[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2011, 78(6): 1114⁃1124. |
| 14 | Zhao L , Jing H , Xu L , et al . Effect of residual stress on creep crack growth behavior in ASME P92 steel[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2013, 110(1): 233⁃248. |
| 15 | 王强, 张志刚, 高玉魁, 等 . 喷丸材料及粒径对300M钢原始表面粗糙度的影响[J]. 材料保护, 2011, 44(7): 35⁃37. |
| Wang Qiang , Zhang Zhi⁃gang , Gao Yu⁃kui , et al . Effect of shot peening material and grit size on the sur face roughness of 300M steel[J]. Materials Protection, 2011, 44(7): 35⁃37. | |
| 16 | Llaneza V , Belzunce F J . Study of the effects produced by shot peening on the surface of quenched and tempered steels: roughness, residual stresses and work hardening[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 356: 475⁃485. |
| 17 | Hong A T , Ooi J Y , Shaw B . A numerical simulation to relate the shot peening parameters to the induced residual stresses[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2008, 15(8): 1097⁃1110. |
| 18 | 强斌, 李亚东, 顾颖, 等 . 钢板喷丸处理残余应力场和表面粗糙度数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(4): 691⁃697. |
| Qiang Bin , Li Ya⁃dong , Gu Ying , et al . Numerical simulation of residual stress field and surface roughness for steel plate subjected to shot peening[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong Universty, 2015, 50(4): 691⁃697. | |
| 19 | Bagherifard S , Ghelichi R , Guagliano M . On the shot peening surface coverage and its assessment by means of finite element simulation: a critical review and some original developments[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 259: 184⁃194. |
| 20 | Unal O , Varol R . Surface severe plastic deformation of AISI 304 via conventional shot peening, severe shot peening and repeening[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 351: 289⁃295. |
| 21 | 郑林彬, 王建明, 何讯超 . 2024铝合金喷丸粗糙度试验与数值模拟[J]. 山东大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(1): 84⁃89. |
| Zheng Lin⁃bin , Wang Jian⁃ming , He Xun⁃chao , et al . Experiment and numerical simulation for surface roughness of 2024 aluminum alloy treated by shot peening[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2017, 47(1): 84⁃89. | |
| 22 | Manes A , Peroni L , Scapin M , et al . Analysis of strain rate behavior of an Al 6061 T6 alloy[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 10: 3477⁃3482. |
| 23 | Dong W P , Sullivan P J , Stout K J . Comprehensive study of parameters for characterization 3⁃D surface topography[J]. Wear, 1994, 178(1): 29⁃60. |
| 24 | Carneiro K , Jensen C P , Jørgensen J F , et al . Roughness parameters of surface by atomic force microscopy[J]. Annals of the CIRP, 1995, 44(l): 517⁃522. |
| 25 | Bagherifard S , Ghelichi R , Guagliano M . Numerical and experimental analysis of surface roughness generated by shot peening[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258: 6831⁃6840. |
| 26 | Ge L . Procedure neural networks based on being learned by hybrid genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005, 37(7): 986⁃988. |
| 27 | Cybenko G . Approximation by superpositions of sigmoidal function[J]. Mathematics of Control Signals and Systems, 1989, 2(4): 303⁃314. |
| 28 | Hornik K , Stinchombe M , White H . Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators[J]. Neural Networks, 1989, 2(2): 359⁃366. |
| [1] | 李静,石求军,刘鹏,户亚威. 基于纵向车速估算的商用车ABS神经网络滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1017-1025. |
| [2] | 李于朋,孙大千,宫文彪. 6082⁃T6铝合金薄板双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊温度场[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [3] | 陈磊,王江锋,谷远利,闫学东. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [4] | 鲁金忠,周婉婷,张圣洋,邵亦锴,王长雨,罗开玉. 激光冲击强化层数对6061⁃T6铝合金抗腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 842-849. |
| [5] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
| [6] | 席利贺,张欣,孙传扬,王泽兴,姜涛. 增程式电动汽车自适应能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1636-1644. |
| [7] | 江涛,林学东,李德刚,杨淼,汤雪林. 基于人工神经网络的放热规律的量化预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1747-1754. |
| [8] | 关庆丰,张福涛,彭韬,吕鹏,李姚君,许亮,丁佐军. 含硼、钴9%Cr耐热钢的热变形行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1799-1805. |
| [9] | 赵爽,沈继红,张刘,赵晗,陈柯帆. 微细电火花加工表面粗糙度快速高斯评定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1838-1843. |
| [10] | 徐岩,孙美双. 基于卷积神经网络的水下图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1895-1903. |
| [11] | 胡志清, 颜庭旭, 李洪杰, 吕振华, 廖伟, 刘庚. 深冷处理对铝合金薄板冲剪成形性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1524-1530. |
| [12] | 关庆丰, 董书恒, 郑欢欢, 李晨, 张从林, 吕鹏. 强流脉冲电子束作用下45#钢表面Cr合金化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1161-1168. |
| [13] | 底晓强, 王英政, 李锦青, 从立钢, 祁晖. 基于量子细胞神经网络超混沌的视频加密方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 919-928. |
| [14] | 李雄飞, 冯婷婷, 骆实, 张小利. 基于递归神经网络的自动作曲算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 866-873. |
| [15] | 赵宇光, 杨雪慧, 徐晓峰, 张阳阳, 宁玉恒. Al-10Sr变质剂状态、变质温度及变质时间对ZL114A合金组织的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 212-220. |
|
||