吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1739-1746.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190628
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于短期风速资料的基本风压计算方法
- 1.吉林建筑大学 土木工程学院,长春 130118
2.吉林省结构与抗震科技创新中心,长春 130118
Calculation of basic wind pressure based on short⁃term wind speed data
Bo WANG1,2( ),Yuan-zheng DONG1,Li-xin DONG1
),Yuan-zheng DONG1,Li-xin DONG1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering, Jilin Jianzhu University, Changchun 130118, China
2.Jilin Structural and Earthquake Resistance Technology Innovation Center, Changchun 130118, China
摘要:
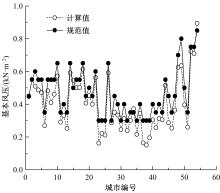
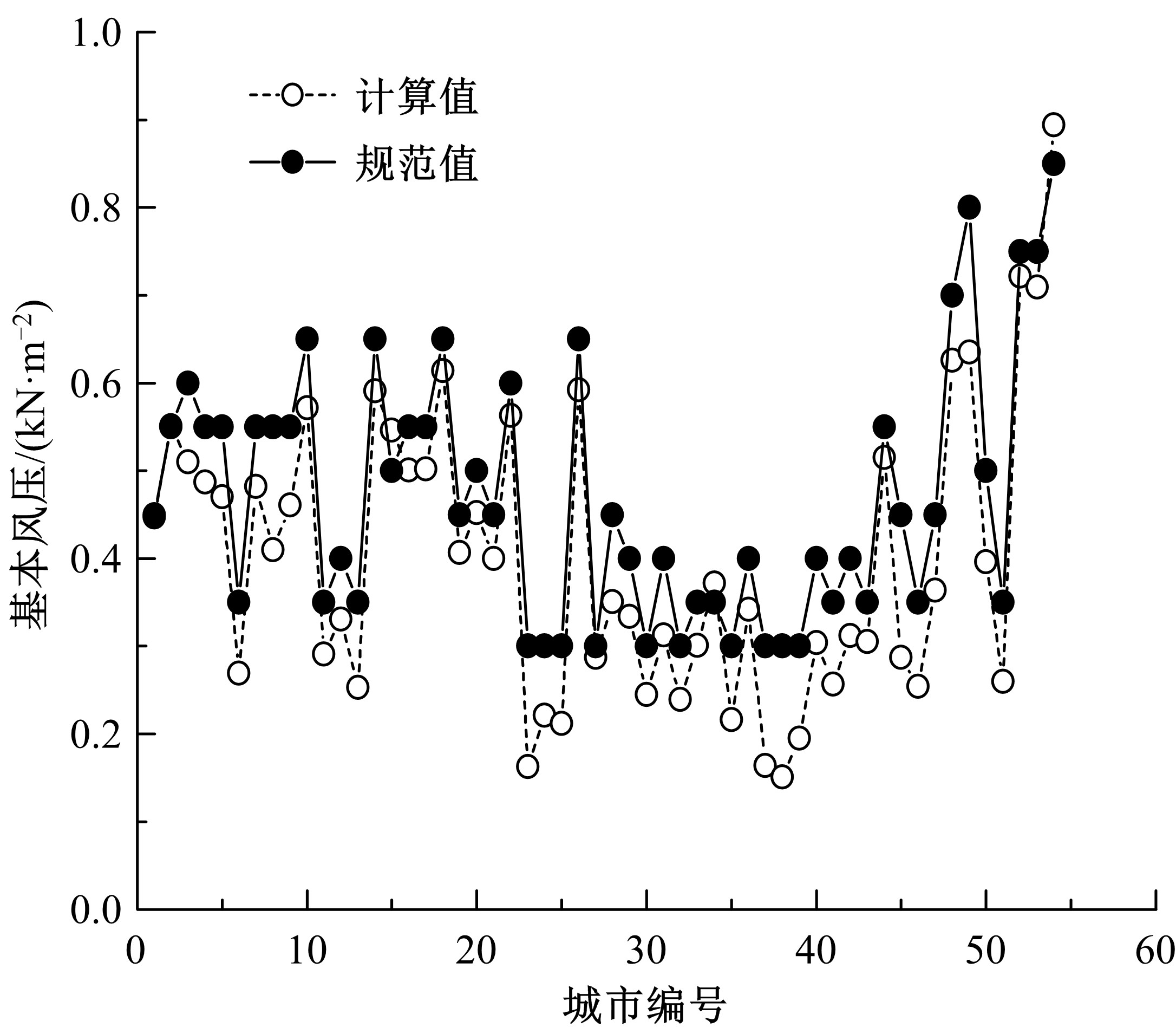
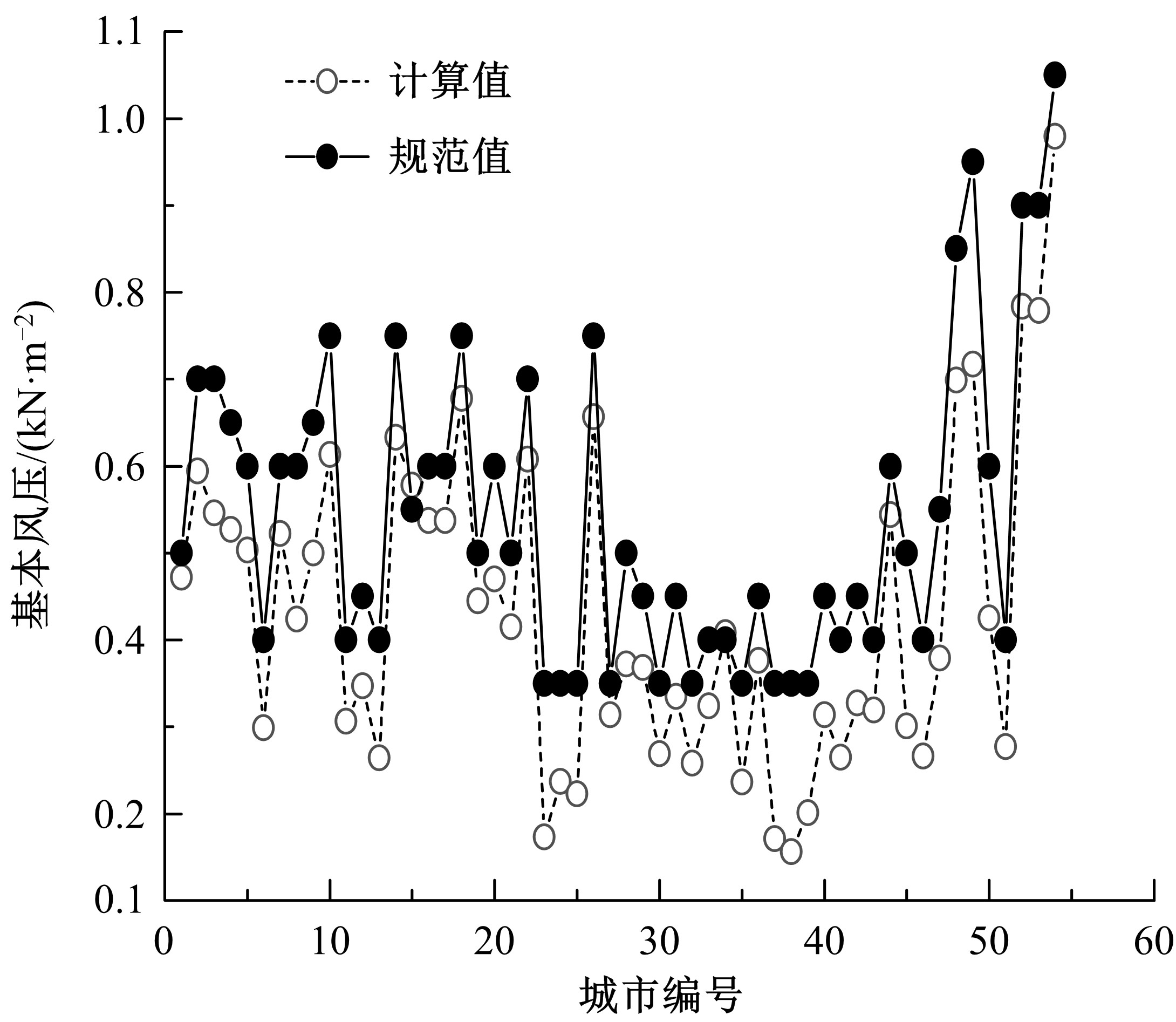
由于部分地区缺少长期风速资料,根据《建筑结构荷载规范》不能确定这些地区的基本风压,急需根据短期风速资料得到一个可供桥梁等工程结构设计使用的基本风压。选取中国54个代表性城市2013年~2017年的短期风速资料,使用月最大风速资料与极值I型分布函数进行拟合,矩估计法和Gumbel法分别对参数进行计算,采用柯尔莫格罗夫检验法进行检验。结果表明:54个城市的月最大风速资料均符合极值I型分布,用月最大风速资料与极值I型分布进行拟合时,Gumbel法比矩估计法的拟合效果好。因此,选用月最大风速资料拟合极值I型分布计算缺少长期风速资料地区的基本风压。采用该方法计算了重现期为6个月、50年、100年的基本风压,重现期为6个月的基本风压可以为设计使用年限较短的工程(如拆除工程)提供参考风压,重现期为50年、100年的基本风压可以为没有长期风速资料地区的桥梁等工程结构设计提供依据。最后,采用本文方法对缺少长期风速资料的阜阳市基本风压计算提供算例。本文方法对没有长期风速资料和重现期较小的风压确定具有重要工程意义。
中图分类号:
- TU312
| 1 | Wang B, Etheridge D W, Ohba M. Wind tunnel investigation of natural ventilation through multiple stacks. Part 1: mean values[J]. Building & Environment, 2011, 46(7): 1380-1392. |
| 2 | GB50009—2012. 建筑结构荷载规范[S]. |
| 3 | Mircea G. Estimation of extreme wind from short records[J]. Journal of the Structural Division, 1982, 108(5): 1034-1048. |
| 4 | 陈朝辉, 管前乾. 基于短期资料的重庆风速极值渐进分布分析[J]. 重庆大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 29(12): 88-92. |
| Chen Zhao-hui, Guan Qian-qian. Simulating of asymptotic distributions of extreme wind speed in Chongqing using short-term wind speed records[J]. Journal of Chongqing University(Natural Science Edition), 2006, 29(12): 88-92. | |
| 5 | 罗乃东. 基于可靠度的高层、高耸结构抗风分析[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学土木工程学院, 2002. |
| Luo Nai-dong. Study of wind-resistant of tall building base on reliability theory[D]. Dalian: School of Civil Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2002. | |
| 6 | Lee B H, Ahn D J, Kim H G, et al. An estimation of the extreme wind speed using the Korea wind map[J]. Renewable Energy, 2012, 42: 4-10. |
| 7 | 孟庆珍, 唐谟智. 成都地面气温与风速年极大值的渐近分布及参数估计[J]. 成都气象学院学报, 1997, 12(4): 284-291. |
| Meng Qing-zhen, Tang Mo-zhi. On asymptotic distribution of yearly maximum values of surface temperature and wind speed over Chengdu and the estimation of their parameters[J]. Journal of Chengdu Institute of Meteorology, 1997, 12(4): 284-291. | |
| 8 | Harris I. Generalised pareto methods for wind extremes. Useful tool or mathematical mirage?[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, 2005, 93(5): 341-360. |
| 9 | Galambos J. The Cassical Extreme Value Model: Mathematical Results Versus Statistical Inference[M]. New York: Statistics for the 21st Century, 2000: 173-187. |
| 10 | Elahi A S, Ghoranneviss M, Emami M. Comparative measurements of plasma position using multipole moments method and analytical solution of grad-shafranov equation in IR-T1 tokamak[J]. Journal of Fusion Energy, 2009, 28(4): 385-389. |
| 11 | 张勇. 基本风压、雪压统计分析与荷载组合系数研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学土木工程学院, 2011. |
| Zhang Yong. Statistical analysis about basic wind and snow pressure and research about load combinatorial coefficient[D]. Shenyang: School of Civil Engineering, Shenyang University of Architecture, 2011 | |
| 12 | 段忠东, 周道成. 极值概率分布参数估计方法的比较研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2004, 36(12): 1605-1609. |
| Duan Zhong-dong, Zhou Dao-cheng. A comparative study on parameter estimate method for extremal value distribution[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2004, 36(12): 1605-1609. | |
| 13 | 康朝杰, 杜文风, 杨雪. 基于极大似然法的雪荷载计算与分析[J]. 河南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 46(2): 220-225. |
| Kang Chao-jie, Du Wen-feng, Yang Xue, et al. Calculation and analysis of snow loads based on the maximum likelihood method[J]. Journal of Henan University(Natural Science), 2016, 46(2): 220-225. | |
| 14 | Zhang C L, Fan J H. An X-ray luminosity analysis for FRIs and FRIIs[J]. Science in China Series G Physics Mechanics and Astronomy, 2009, 52(9): 1434-1441. |
| 15 | 方晓, 张运福, 房一禾. 辽宁省沿海地区极值风速概率分布特征[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(22): 256-257, 259. |
| Fang Xiao, Zhang Yun-fu, Fang Yi-he. Characteristic of probability distribution of extreme wind speeds in coast area of Liaoning province[J]. XianDai NongYe KeJi, 2015(22): 256-257, 259. | |
| 16 | 叶征伟. 山区高墩大跨连续刚构桥风环境及风荷载研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学建筑工程学院, 2012. |
| Ye Zheng-wei. Study on the wind-environment and wind loads of the long-span continuous rigid frame bridge with tall piers in mountainous areas[D]. Hangzhou: College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University, 2012. | |
| 17 | 屠其璞. 气象应用概率统计学[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1984. |
| 18 | 王卫锋, 颜全胜, 李立军, 等. 大跨度斜拉桥侧风非线性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2007, 37(4): 786-789. |
| Wang Wei-feng, Yan Quan-sheng, Li Li-jun, et al. Nonlinear analysis for a long span cable stayed bridge under lateral wind loads[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2007, 37(4): 786-789. | |
| 19 | 姜浩, 郭学东, 张艳辉. 基于时域分析的风载激励下桥梁结构动力特性识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011,41(5): 1279-1283. |
| Jiang Hao, Guo Xue-dong, Zhang Yan-hui. Dynamic behavior identification of concrete bridge structure under wind load excitation based on time-domain analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1279-1283. |
| [1] | 薛素铎,鲁建,李雄彦,刘人杰. 跳格布置对环形交叉索桁结构静动力性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1687-1697. |
| [2] | 李明,王浩然,赵唯坚. 单向带抗剪键叠合板的受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 654-667. |
| [3] | 王鹏辉,乔宏霞,冯琼,曹辉,温少勇. 氯氧镁涂层钢筋混凝土两重因素耦合作用下的耐久性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 191-201. |
| [4] | 李明,王浩然,赵唯坚. 带抗剪键叠合板的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1509-1520. |
| [5] | 张军,钱诚,郭春燕,钱玉君. 基于多源时空数据的建筑宜居性动态设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1169-1173. |
| [6] | 梁宁慧,缪庆旭,刘新荣,代继飞,钟祖良. 聚丙烯纤维增强混凝土断裂韧度及软化本构曲线确定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1144-1152. |
| [7] | 张磊,刘保国,储昭飞. 深厚孔隙砂岩含水层疏干排水对盾构斜井的 影响模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 788-797. |
| [8] | 郑一峰, 赵群, 暴伟, 李壮, 于笑非. 大跨径刚构连续梁桥悬臂施工阶段抗风性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 466-472. |
| [9] | 王腾, 周茗如, 马连生, 乔宏霞. 基于断裂理论的湿陷性黄土劈裂注浆裂纹扩展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1472-1481. |
| [10] | 郭楠, 张平阳, 左煜, 左宏亮. 竹板增强胶合木梁受弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 778-788. |
| [11] | 张静, 刘向东. 混沌粒子群算法优化最小二乘支持向量机的混凝土强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. |
| [12] | 郭学东, 马立军, 张云龙. 集中力作用下考虑剪切滑移效应的双层结合面组合梁解析解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 432-438. |
| [13] | 赵玉, 李衍赫, 张培, 赵科, 刘伟超. 粘土的动力特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1791-1797. |
| [14] | 侯忠明, 王元清, 夏禾, 张天申. 移动荷载作用下的钢-混简支结合梁动力响应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1420-1427. |
| [15] | 王甲春, 阎培渝. 海洋环境下钢筋混凝土中钢筋锈蚀的概率[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 352-357. |
|
||