吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 439-449.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211230
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于信息物理融合和数字孪生的可靠性分析
宋林1,2( ),王立平2,3,吴军3(
),王立平2,3,吴军3( ),关立文3,刘知贵2
),关立文3,刘知贵2
- 1.攀枝花学院 智能制造学院,四川 攀枝花 617000
2.西南科技大学 信息工程学院,四川 绵阳 621000
3.清华大学 机械工程系,北京 100084
Reliability analysis based on cyber⁃physical system and digital twin
Lin SONG1,2( ),Li-ping WANG2,3,Jun WU3(
),Li-ping WANG2,3,Jun WU3( ),Li-wen GUAN3,Zhi-gui LIU2
),Li-wen GUAN3,Zhi-gui LIU2
- 1.College of Intelligent Manufacturing,Panzhihua University,Panzhihua 617000,China
2.College of Information Engineering,Southwest University of Science and Technology,Mianyang 621000,China
3.Department of Mechanical Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
摘要:
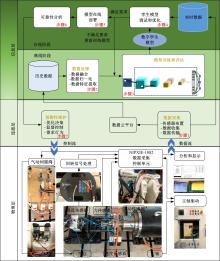
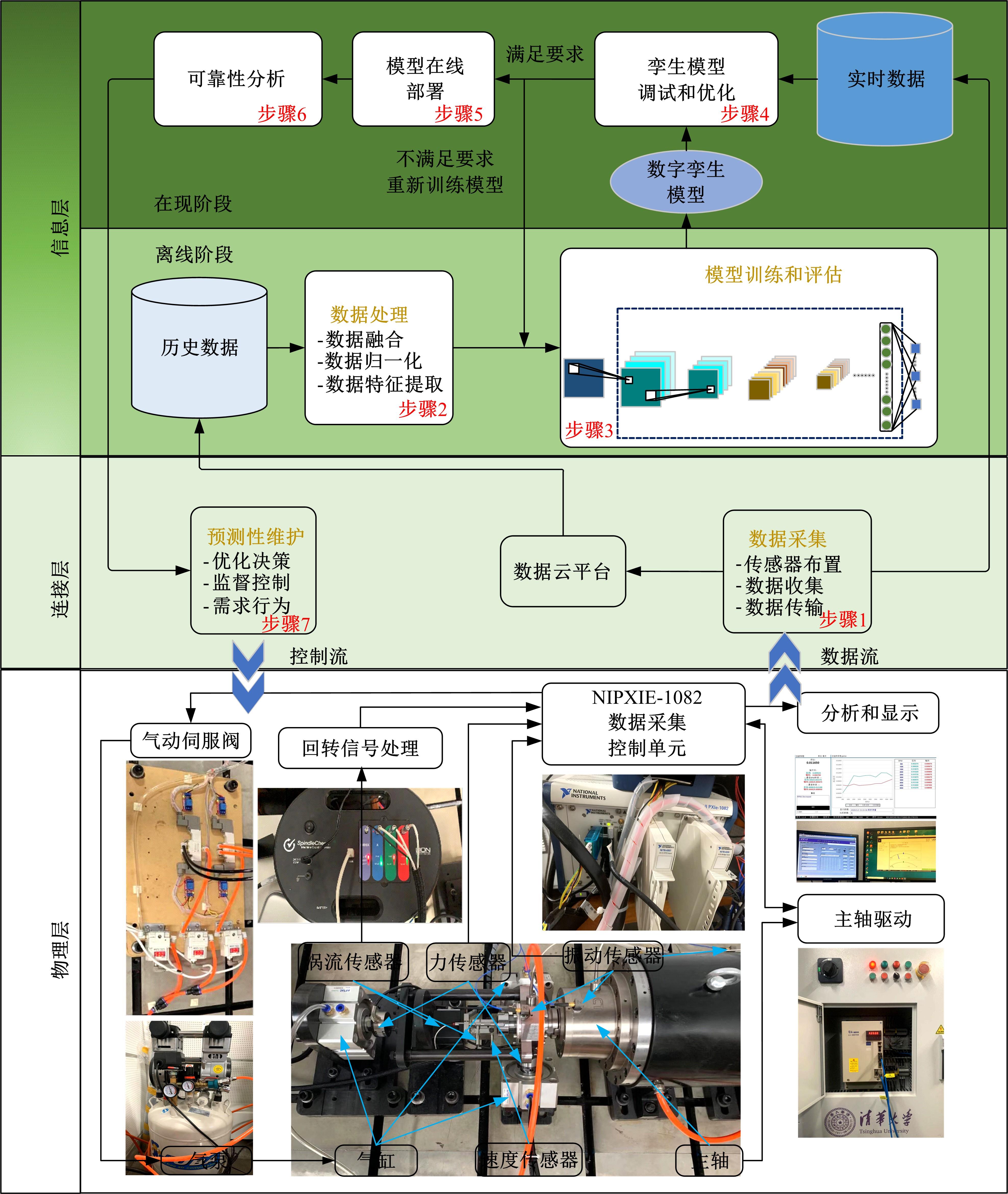
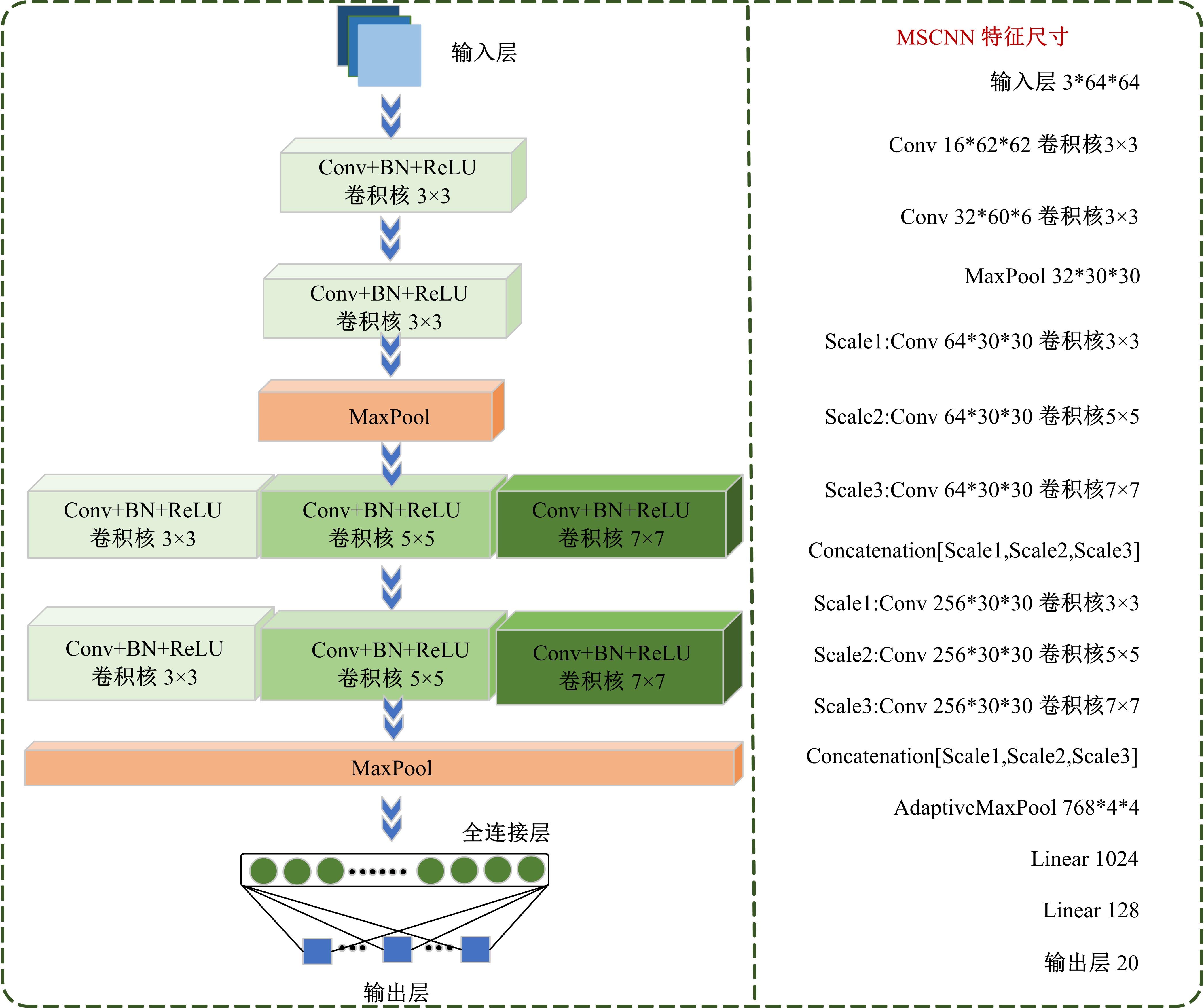
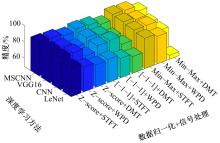
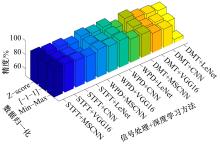
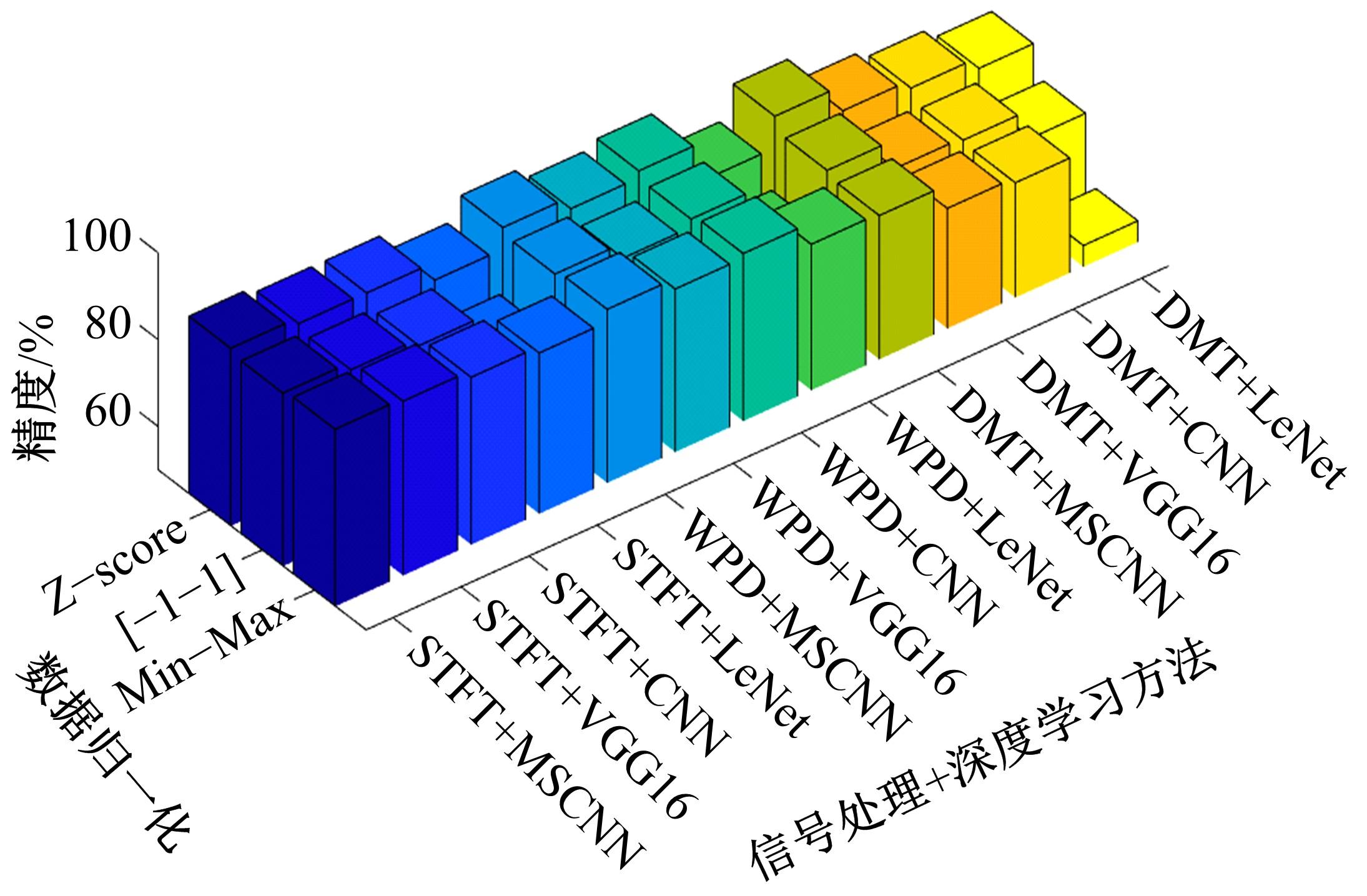
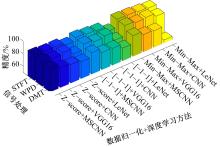
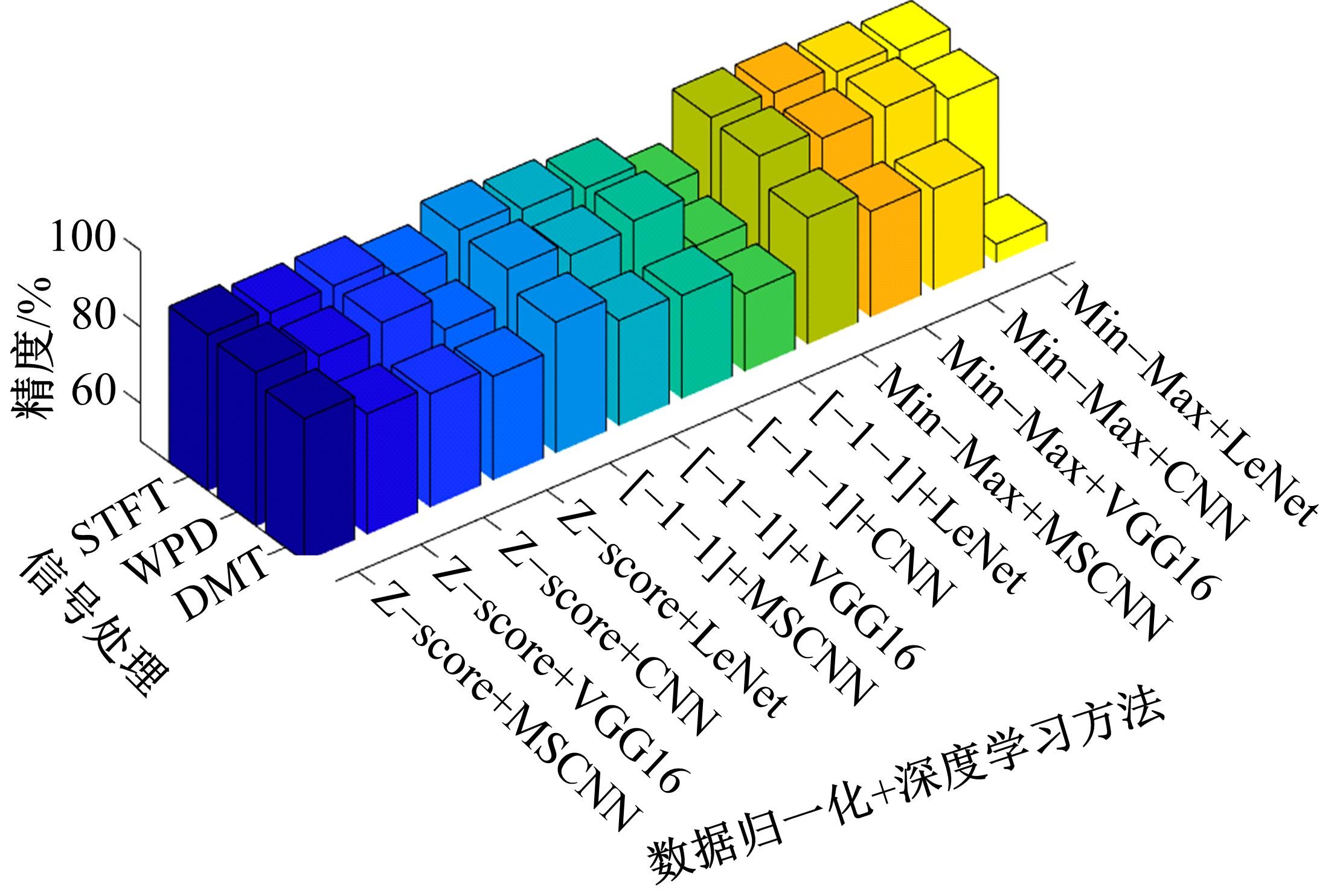
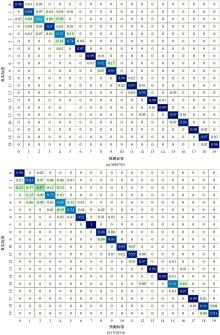
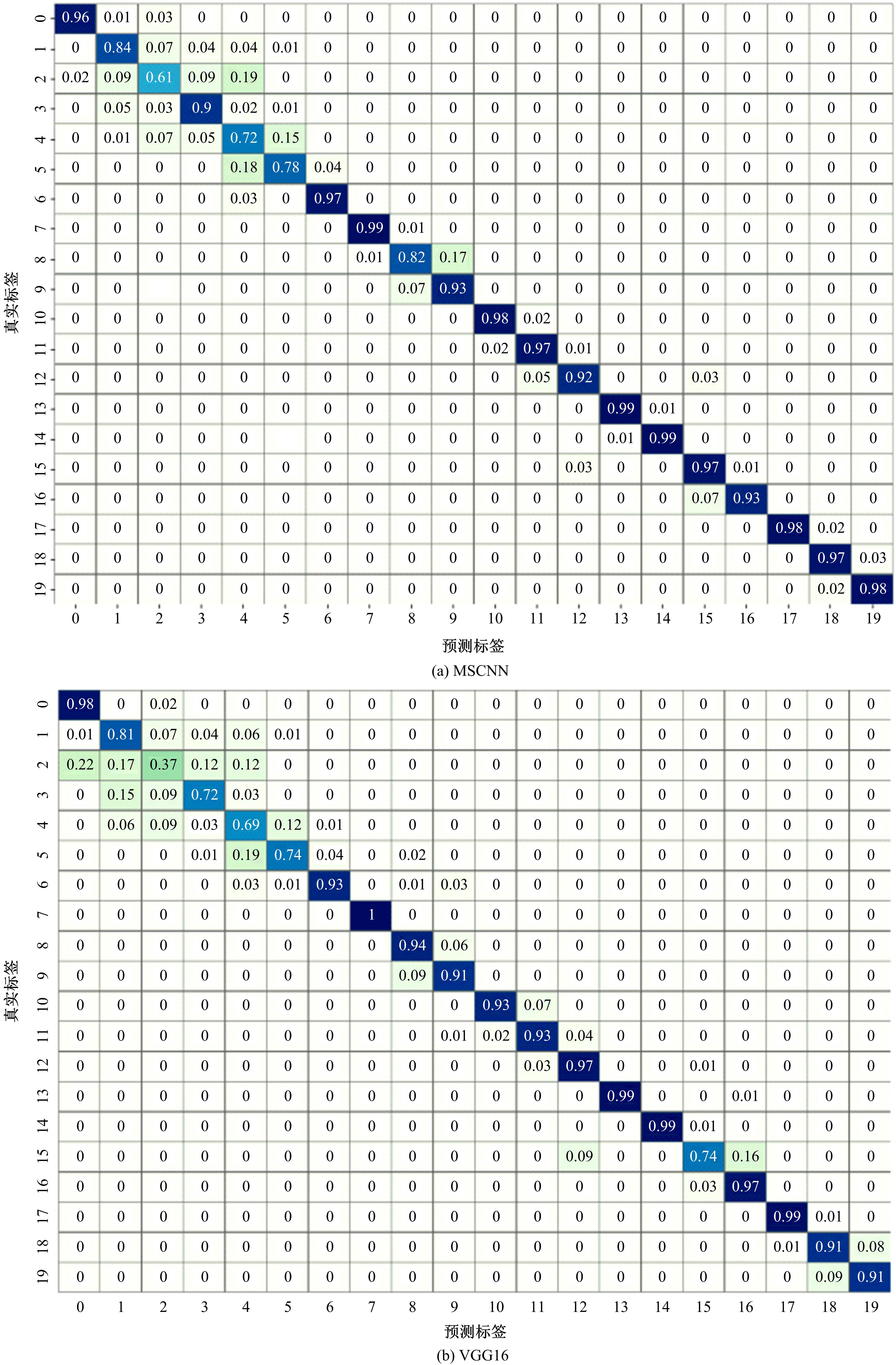
针对实际应用中缺乏统一集成的用于数控装备可靠性分析的信息物理融合系统框架和算法实现,本文提出了一种基于数字孪生的方法,研究了具体的框架搭建和算法实现。通过数据采集、数据处理、数字孪生模型训练和评估、模型调试和优化、模型在线部署、可靠性分析、预测性维护7步序列化的工作流程实现了从物理层到信息层再返回物理层的闭环控制。通过数控装备主轴回转误差预测可靠性实验验证了该信息物理融合框架的可行性和有效性,该框架和算法能够对数控装备进行可靠性分析,有助于支持更有效和科学的预测性维护。
中图分类号:
- TH161
| 1 | Chen B, Liu Y, Zhang C, et al. Time series data for equipment reliability analysis with deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8(99): 105484-105493. |
| 2 | Zuo Y, Wang H, Wu G, et al. Research on remote state monitoring and intelligent maintenance system of CNC machine tools[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 23: 8671-8675. |
| 3 | Kang Z, Catal C, Tekinerdogan B. Machine learning applications in production lines: a systematic literature review[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 149: 106773. |
| 4 | Liu P L, Du Z C, Li H M, et al. Thermal error modeling based on BiLSTM deep learning for CNC machine tool[J]. Advances in Manufacturing, 2021(9): 235-249. |
| 5 | Chen Y, Bian R, Ding W Z, et al. A Fault Diagnosis Method of CNC Machine Tool Spindle Based on Deep Transfer Learning[C]∥Computer Information Analytics and Intelligent Systems, Kuala Lumpur, 2019: 136-140. |
| 6 | Duan C Q, Deng C, Li N. Reliability assessment for CNC equipment based on degradation data[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 100(2): 421- 434. |
| 7 | Marani M, Zeinali M, Songmene V, et al. Tool wear prediction in high-speed turning of a steel alloy using long short-term memory modelling[J]. Measurement, 2021, 177: 109329. |
| 8 | 于向军, 槐元辉, 姚宗伟, 等. 工程车辆无人驾驶关键技术[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. |
| Yu Xiang-jun, Huai Yuan-hui, Yao Zong-wei, et al. Key technologies in autonomous vehicle for engineering[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. | |
| 9 | He B, Liu L, Zhang D. Digital twin driven remaining useful life prediction for gear performance degradation: a review[J]. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering, 2021, 21(3): 030801. |
| 10 | Wang J, Ye L, Gao R, et al. Digital twin for rotating machinery fault diagnosis in smart manufacturing[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2019, 57: 3920-3934. |
| 11 | Luo W, Hu T, Zhang C, et al. Digital twin for CNC machine tool: modeling and using strategy[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2018, 10(3): 1-12. |
| 12 | Luo W, Hu T, Ye Y, et al. A hybrid predictive maintenance approach for CNC machine tool driven by digital twin[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2020, 65: 101974. |
| 13 | Tao F, Zhang M, Liu Y, et al. Digital twin driven prognostics and health management for complex equipment[J]. Cirp Annals, 2018, 67: 169-172. |
| 14 | Tong M, Jing X Y, Zheng Y, et al. A survey on machine learning for data fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 57(1): 115-129. |
| 15 | Zhao Z, Li T, Wu J, et al. Deep learning algorithms for rotating machinery intelligent diagnosis: an open source benchmark study[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 107: 224-255. |
| 16 | 金立生, 郭柏苍, 王芳荣, 等.基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| Jin Li-sheng, Guo Bai-cang, Wang Fang-rong, et al. Dynamic multiple object detection algorithm for vehicle forward based on improved YOLOv3[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. | |
| 17 | 王立平, 张彬彬, 吴军. 基于最小二乘法的电主轴回转精度评价简[J]. 制造技术与机床, 2018(2): 54-60. |
| Wang Li-ping, Zhang Bin-bin, Wu Jun. Rotation accuracy evaluation of electric spindle based on least square method[J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 2018(2): 54-60. | |
| 18 | 王立平, 赵钦志, 张彬彬. 加工中心高速电主轴综合精度分析[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 58(8): 746-751. |
| Wang Li-ping, Zhao Qin-zhi,Zhang Bin-bin. Accuracy of an electric spindle[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2018, 58(8):746-751. | |
| 19 | Anandan K P, Ozdoganlar O B. A multi orientation error separation technique for spindle metrology of miniature ultra-high-speed spindles[J]. Precision Engineering, 2016, 43(1): 119-131. |
| 20 | Liang J, Wang L, Wu J, et al. Prediction of spindle rotation error through vibration signal based on Bi-LSTM classification network[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 1043(4): 42011-42033. |
| 21 | 陈代伟, 吴军, 张彬彬, 等. 基于S试件的加工中心电主轴载荷谱编制[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 58(12): 1107-1114. |
| Chen Dai-wei, Wu Jun, Zhang Bin-bin, et al. Load spectrum compilation for machining center spindles based on S-shaped specimens[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2018, 58(12): 1107-1114. |
| [1] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [2] | 刘桂霞,裴志尧,宋佳智. 基于深度学习的蛋白质⁃ATP结合位点预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 187-194. |
| [3] | 杜尊令,张义民. 基于随机流量下柱塞泵的可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1967-1974. |
| [4] | 张杰,景雯,陈富. 基于被动分簇算法的即时通信网络协议漏洞检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2253-2258. |
| [5] | 李国发,陈泽权,何佳龙. 新型结构可靠性分析自适应加点策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1975-1981. |
| [6] | 董丽丽,杨丹,张翔. 基于深度学习的大规模语义文本重叠区域检索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1817-1822. |
| [7] | 金立生,郭柏苍,王芳荣,石健. 基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [8] | 樊学平,杨光红,肖青凯,刘月飞. 大跨桥梁主梁失效概率分析的最优R-Vine Copula[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1296-1305. |
| [9] | 于向军,槐元辉,姚宗伟,孙中朝,俞安. 工程车辆无人驾驶关键技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. |
| [10] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [11] | 李锦青,周健,底晓强. 基于循环生成对抗网络的学习型光学图像加密方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1060-1066. |
| [12] | 宋震,李俊良,刘贵强. 基于深度学习和限幅模糊的变转速液压动力源恒流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| [13] | 袁哲明,袁鸿杰,言雨璇,李钎,刘双清,谭泗桥. 基于深度学习的轻量化田间昆虫识别及分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [14] | 彭博,张媛媛,王玉婷,唐聚,谢济铭. 基于自动编码机-分类器的视频交通状态自动识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [15] | 李国龙,陶小会,徐凯,李喆裕. 数控机床转台位置相关几何误差的快速测量与辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 458-467. |
|
||