吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 187-194.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200723
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于深度学习的蛋白质⁃ATP结合位点预测
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Prediction of protein-ATP binding site based on deep learning
Gui-xia LIU1,2( ),Zhi-yao PEI1,2,Jia-zhi SONG1,2
),Zhi-yao PEI1,2,Jia-zhi SONG1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbol Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
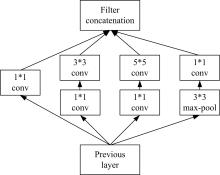
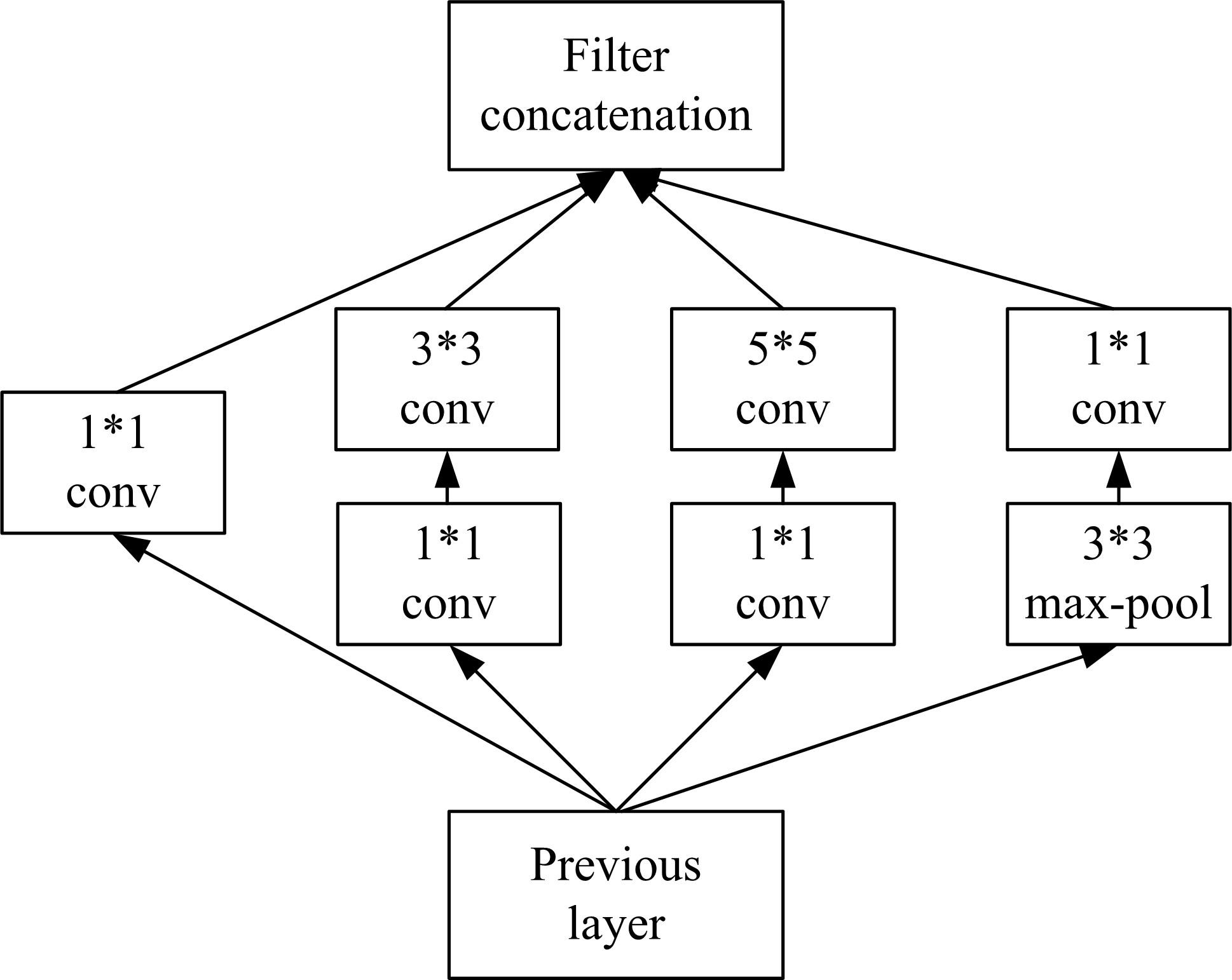
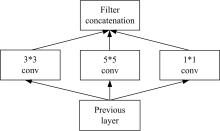
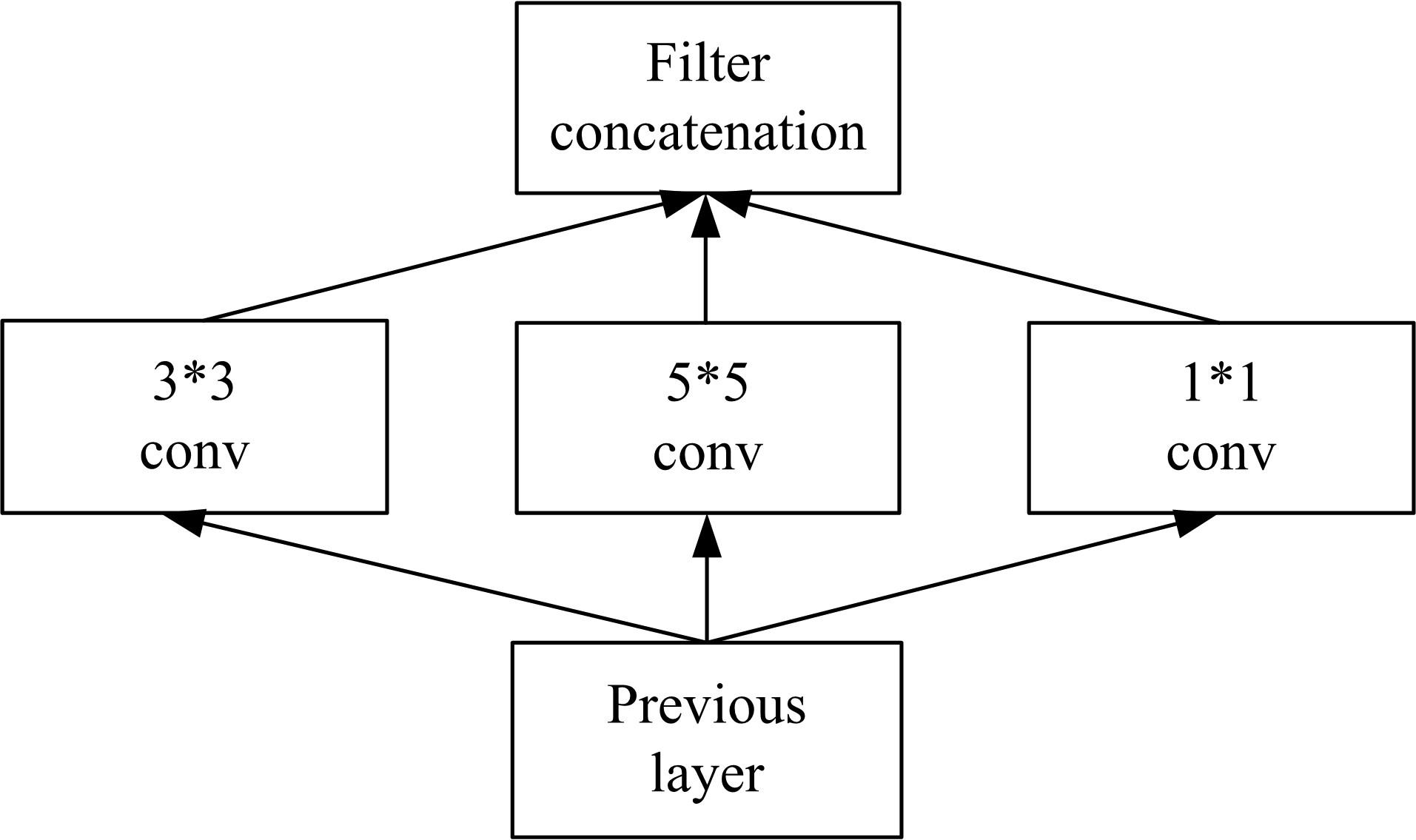
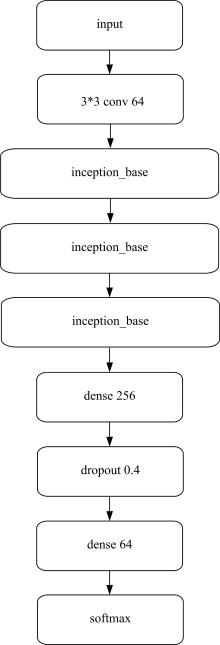
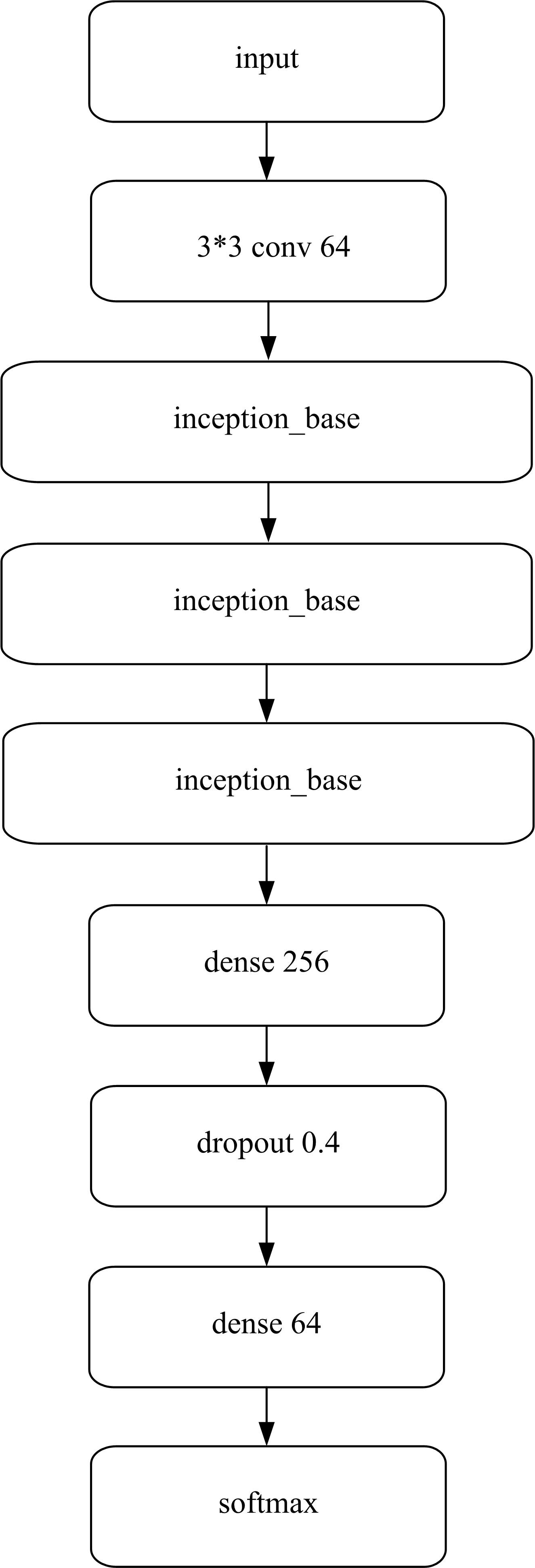
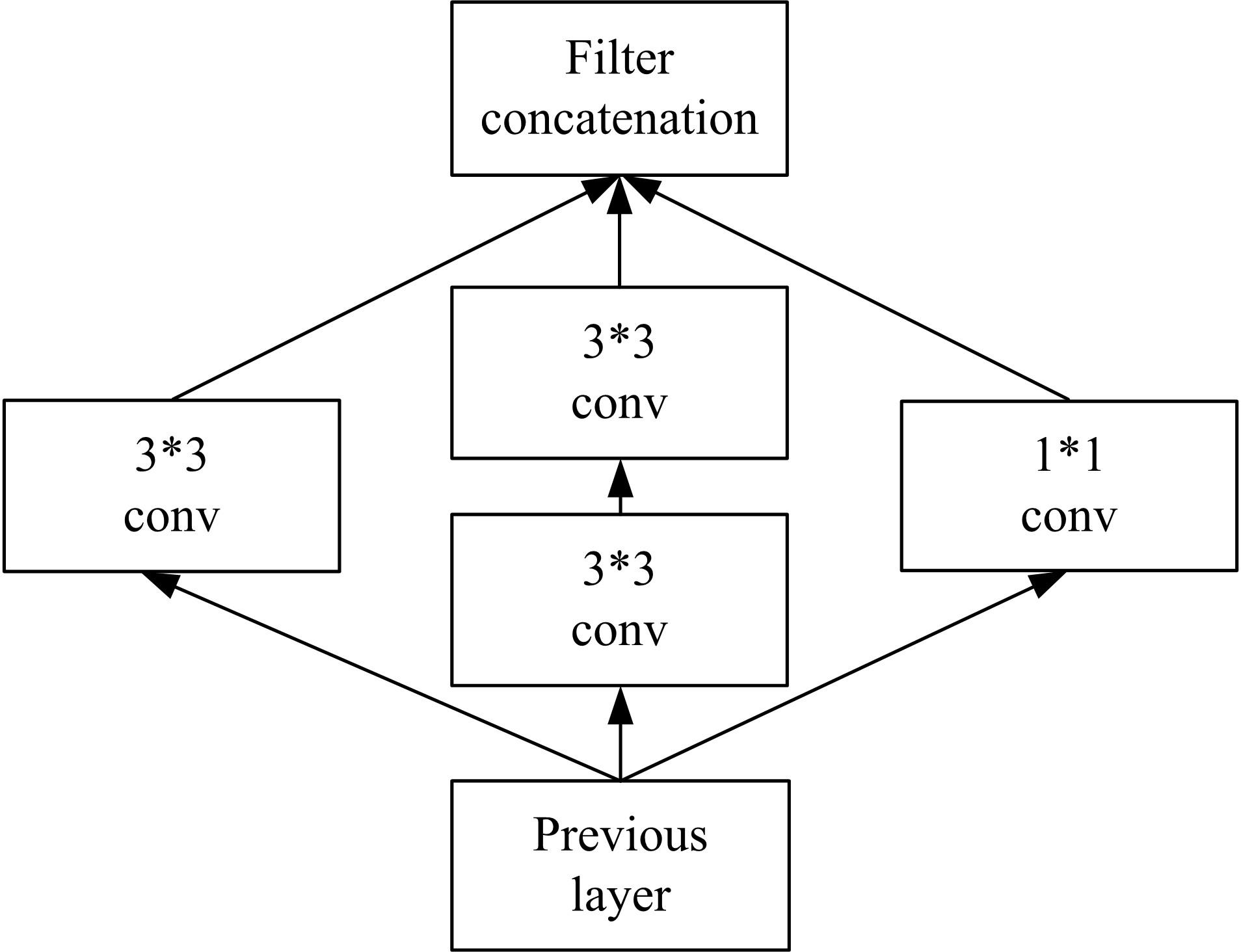
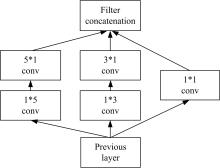
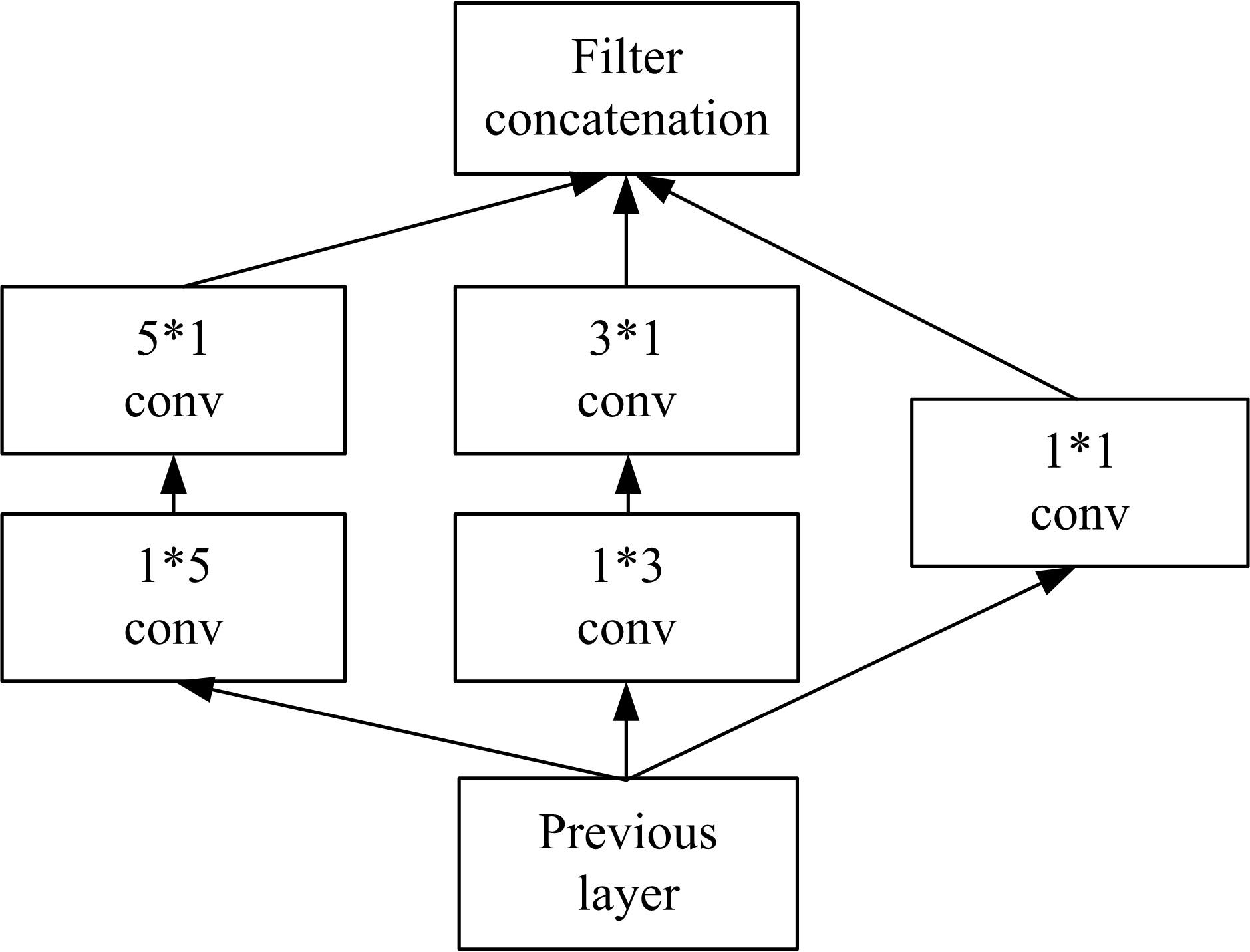
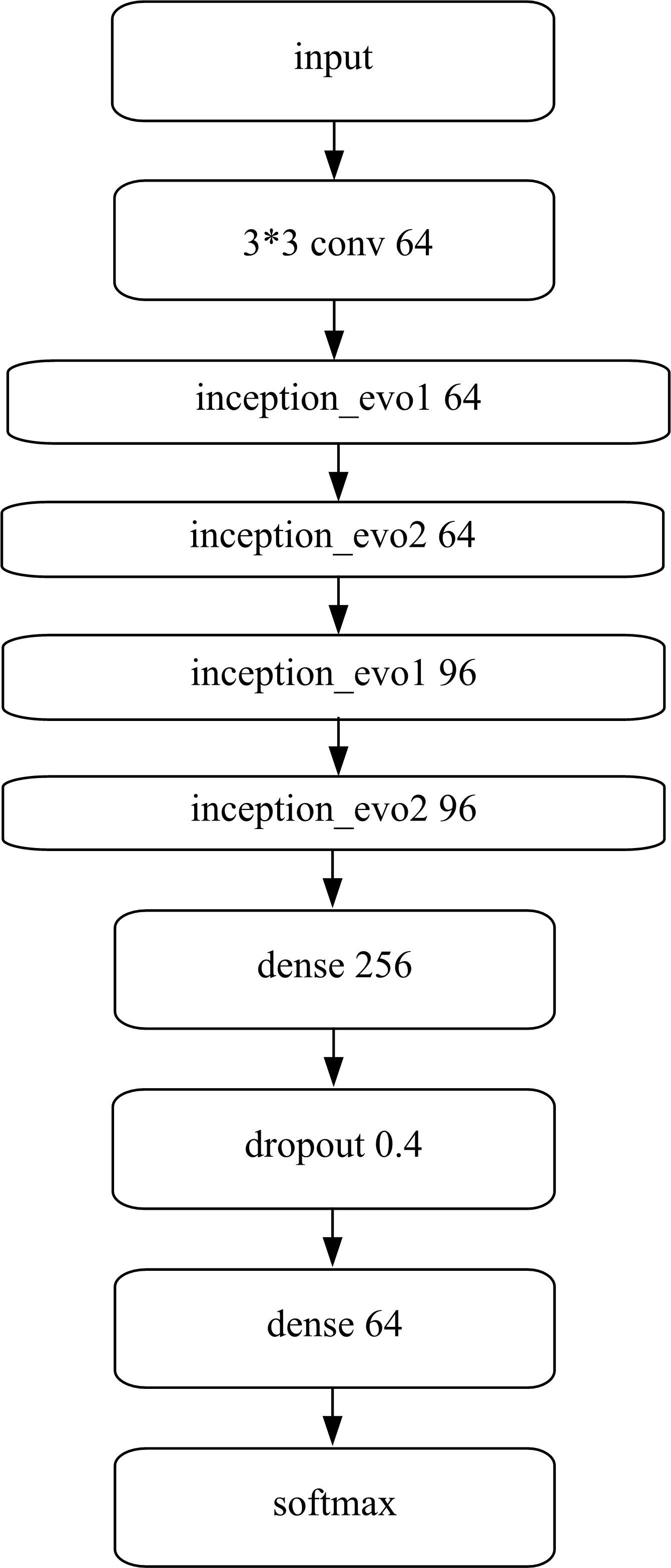
为了提高识别蛋白质-ATP结合位点预测精度,提出了基于Inception架构的深度网络模型Inception_base,同时对网络模型和训练策略进行优化和改进,提出了新的网络模型Inception_evolution。通过两组数据集在该模型上测试,获得AUC分别为0.885和0.918,均优于其他对比机器学习方法。实验结果表明,深度学习方法可以应用于蛋白质-ATP结合位点预测问题中,该模型能够更精确预测蛋白质-ATP结合位点。
中图分类号:
- TP399
| 1 | Bain F E, Fischer L A, Chen R, et al. Chapter seventeen-single-molecule analysis of replication protein A⁃DNA interactions[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2018, 600: 439-461. |
| 2 | Raphael T, Timo M, Schroda M, et al. ATP-dependent molecular chaperones in plastids — more complex than expected[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Bioenergetics, 2015, 1847(9):872-888. |
| 3 | Gerwert K, Freier E, Wolf S. The role of protein-bound water molecules in microbial rhodopsins[J]. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 2014, 1837(5): 606-613. |
| 4 | Qi W, Zhen L P, Yang Z, et al. COACH-D: improved protein⁃ligand binding sites prediction with refined ligand-binding poses through molecular docking[J]. Nuclc Acids Research,2018,46(W1):438-442. |
| 5 | Baldassi C, Zamparo M, Feinauer C, et al. Fast and accurate multivariate gaussian modeling of protein families: predicting residue contacts and protein-interaction partners[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(3): No. e92721. |
| 6 | 冉军舰. 赵瑞香 . 梁新红 ,等.基于蛋白互作网络解析甘薯渣中去氢表雄酮的生物作用机制[J]. 扬州大学学报:农业与生命科学版,2019, 40(5): 33-38. |
| Ran Jun-jian, Zhao Rui-xiang, Liang Xin-hong, et al. Biological mechanism analysis of DHEA from sweet potato residue based on protein-protein interaction network[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2019, 40(5): 33-38. | |
| 7 | Carrano A, Snkhchyan H, Kooij G, et al. ATP-binding cassette transporters P-glycoprotein and breast cancer related protein are reduced in capillary cerebral amyloid angiopathy[J]. Neurobiology of Aging, 2014, 35(3): 565-575. |
| 8 | Christian S, Christoph W, Walter M. ATP- and ADP-dnaA protein, a molecular switch in gene regulation[J]. Embo Journal, 1999, 18(21): 6169-6176. |
| 9 | Chauhan J S, Mishra N K, Raghava G P. Identification of ATP binding residues of a protein from its primary sequence[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2009, 10(1): 434. |
| 10 | Chen K, Mizianty M J, Kurgan L. ATPsite: sequence-based prediction of ATP-binding residues[J]. Proteome Science, 2011, 9(S1):235-242. |
| 11 | Kurgan L, Chen K, Mizianty M J. Prediction and analysis of nucleotide binding residues using sequence and sequence-derived structural descriptors[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 28(3):331-341. |
| 12 | Yu Dong-Jun, Hu jun, Tang Zhen-min, et al. Improving protein-ATP binding residues prediction by boosting SVMs with random under-sampling[J]. Neurocomputing, 2013, 104: 180-190. |
| 13 | Yu Dong-jun, Hu Jun, Huang Yan, et al. TargetATPsite: a template‐free method for ATP‐binding sites prediction with residue evolution image sparse representation and classifier ensemble[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2013, 34(11): 974-985. |
| 14 | Fang C, Noguchi T, Yamana H. Simplified sequence-based method for ATP-binding prediction using contextual local evolutionary conservation[J]. Algorithms for Molecular Biology, 2014, 9(1): 7. |
| 15 | Andrews B J, Hu J. TSC_ATP: a two-stage classifier for predicting protein-ATP binding sites from protein sequence[C]∥ Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 2015: 1-5. |
| 16 | Hu Jun, Li Yang, Zhang Yang,et al. ATPbind: accurate protein⁃ATP binding site prediction by combining sequence-profiling and structure-based comparisons[J]. Journal of Chemical Information & Modeling, 2018,58:501-510. |
| 17 | Zhou J, Lu Q, Xu R, et al. CNNsite: prediction of DNA-binding residues in proteins using convolutional neural network with sequence features[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 2016: 78-85. |
| 18 | Pan Xiao-yong, Peter R, Yan Jun-chi, et al. Prediction of RNA-protein sequence and structure binding preferences using deep convolutional and recurrent neural networks[J]. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1):511. |
| 19 | Zhang Yu, Yu Dong-jun. Protein-ATP binding site prediction based on 1D-convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(11): 3146-3150. |
| 20 | Mcguffin L J, Kevin B, Jones D T. The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server[J]. Bioinformatics, 2000,16(4): 2. |
| 21 | Faraggi E, Zhou Yao-qi, Kloczkowski A. Accurate single-sequence prediction of solvent accessible surface area using local and global features[J]. Protns Structure Function & Bioinformatics, 2015, 82(11): 3170-3176. |
| 22 | Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, et al. Going Deeper with Convolutions[C]∥ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2015:1-9. |
| 23 | Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016:2818-2826. |
| 24 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2017,42(2): 318-327. |
| 25 | Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2016: arXiv:. |
| [1] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [2] | 张杰,景雯,陈富. 基于被动分簇算法的即时通信网络协议漏洞检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2253-2258. |
| [3] | 刘远红,郭攀攀,张彦生,李鑫. 基于黎曼流形的稀疏图保持投影的特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2268-2279. |
| [4] | 董丽丽,杨丹,张翔. 基于深度学习的大规模语义文本重叠区域检索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1817-1822. |
| [5] | 钟辉,康恒,吕颖达,李振建,李红,欧阳若川. 基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. |
| [6] | 金立生,郭柏苍,王芳荣,石健. 基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [7] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于海量文本数据的知识图谱自动构建算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1358-1363. |
| [8] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [9] | 李锦青,周健,底晓强. 基于循环生成对抗网络的学习型光学图像加密方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1060-1066. |
| [10] | 袁哲明,袁鸿杰,言雨璇,李钎,刘双清,谭泗桥. 基于深度学习的轻量化田间昆虫识别及分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [11] | 彭博,张媛媛,王玉婷,唐聚,谢济铭. 基于自动编码机-分类器的视频交通状态自动识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [12] | 宋震,李俊良,刘贵强. 基于深度学习和限幅模糊的变转速液压动力源恒流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| [13] | 徐涛,马克,刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [14] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [15] | 谌华,郭伟,闫敬文,卓文浩,吴良斌. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1778-1787. |
|
||