吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2364-2370.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220568
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于TrAdaBoost算法为内核的行人航迹推算技术
- 桂林理工大学 信息科学与工程学院,广西 桂林 541004
Pedestrian dead reckoning technology based on TrAdaBoost algorithm
- School of Information Science and Engineering,Guilin University of Technology,Guilin 541004,China
摘要:
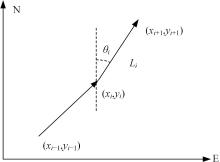
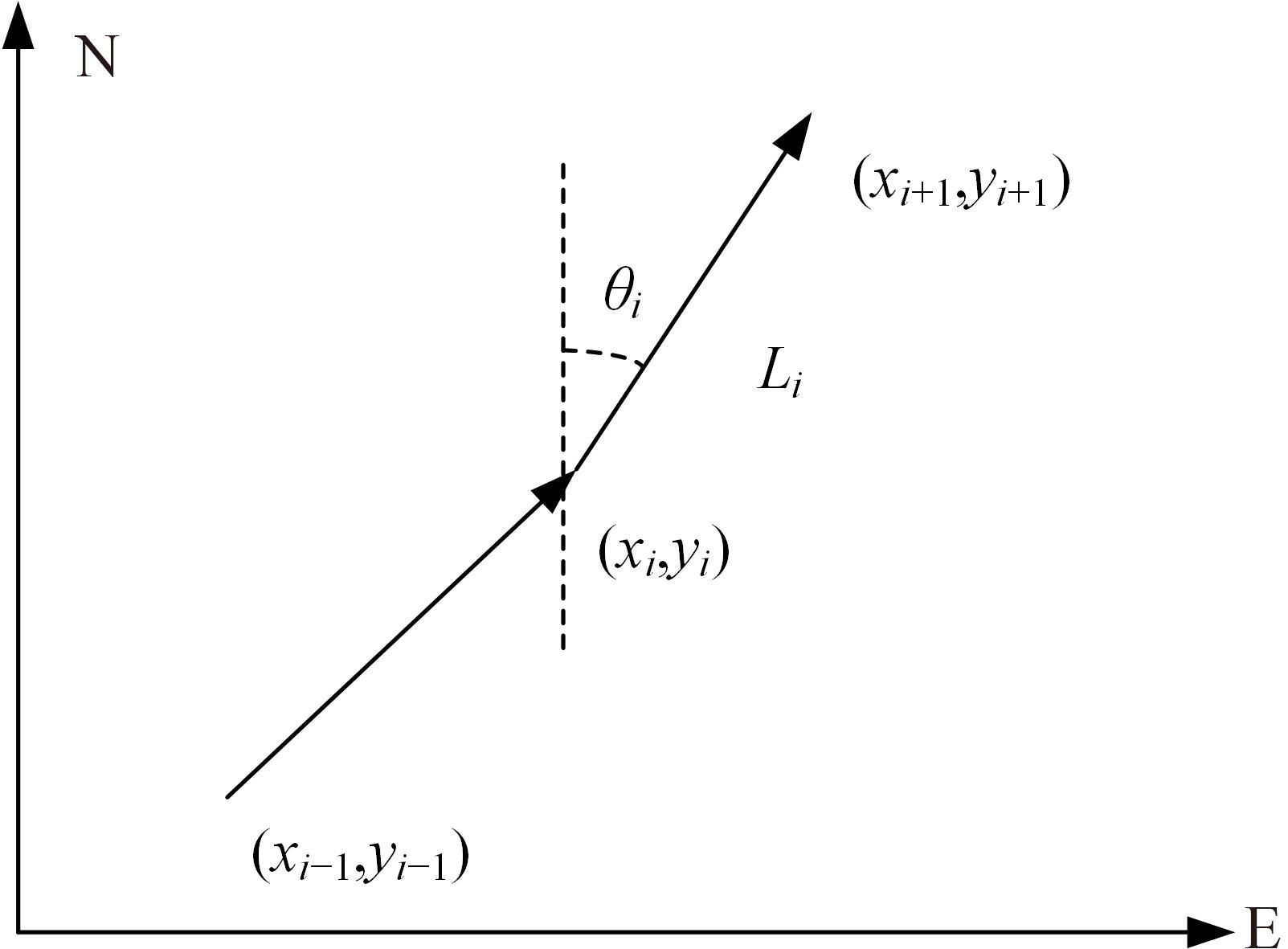
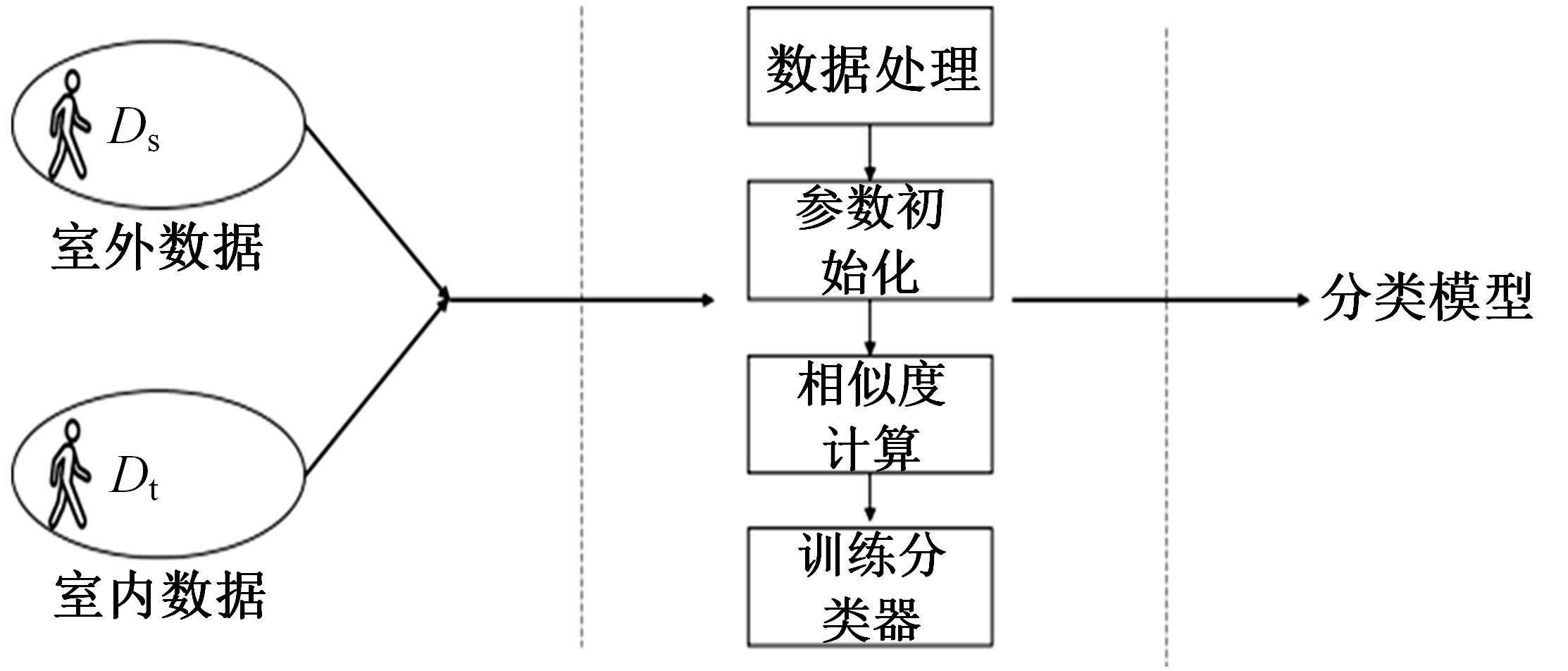
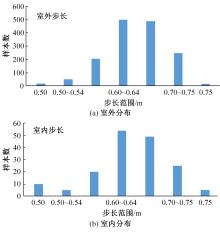
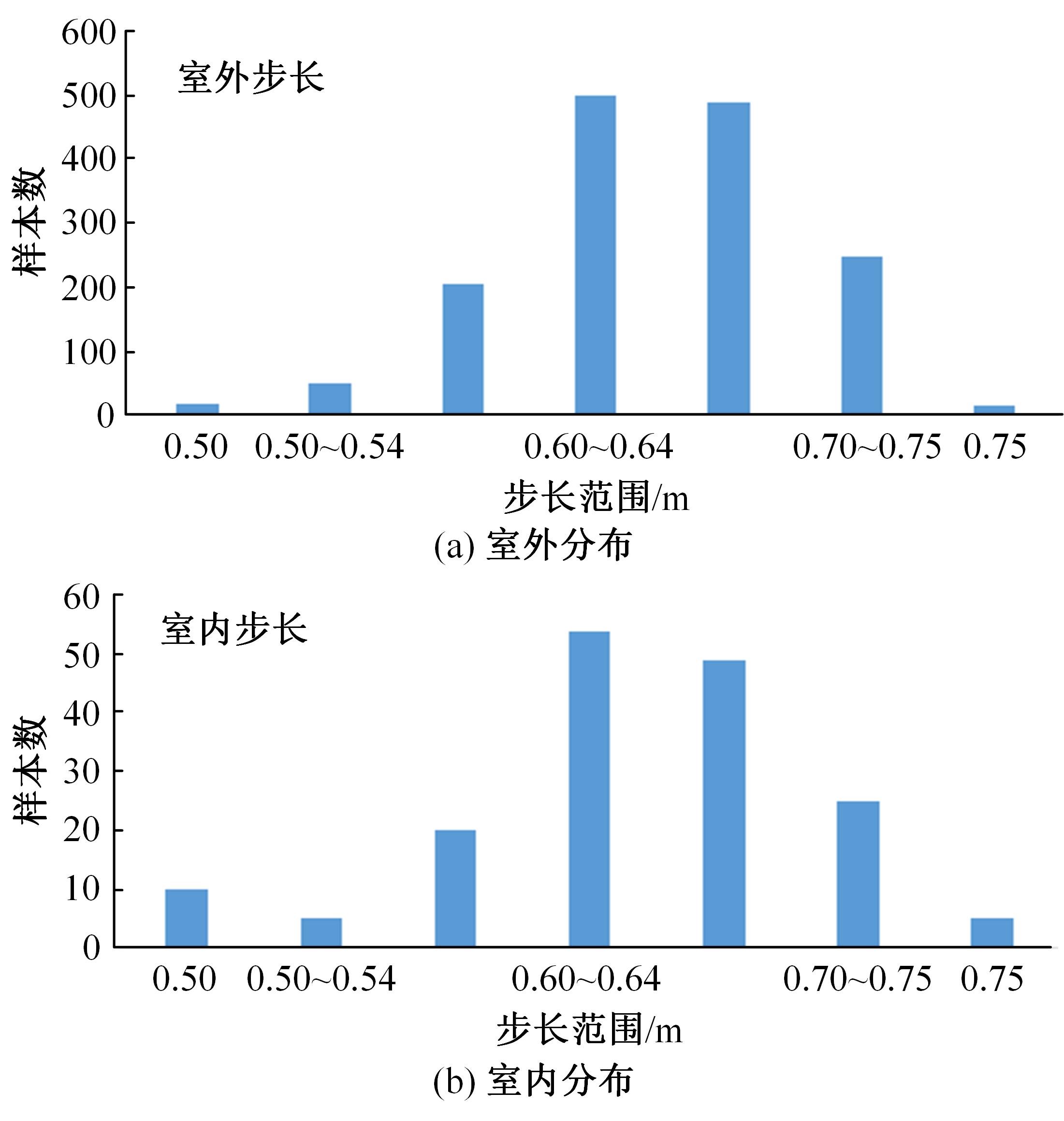
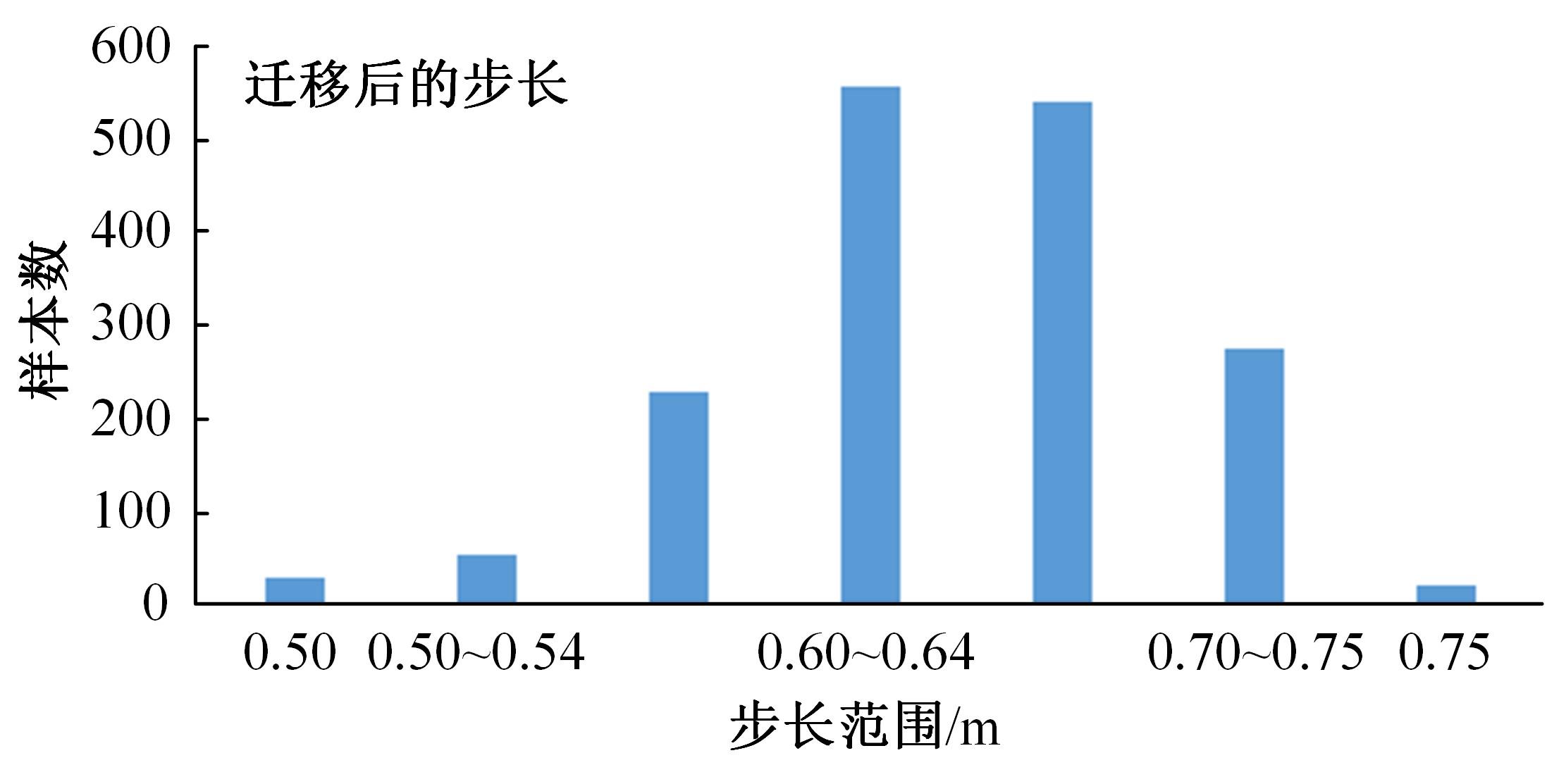
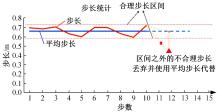
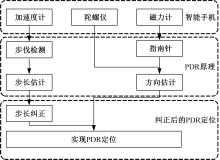
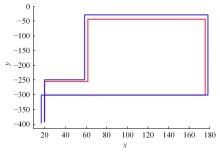
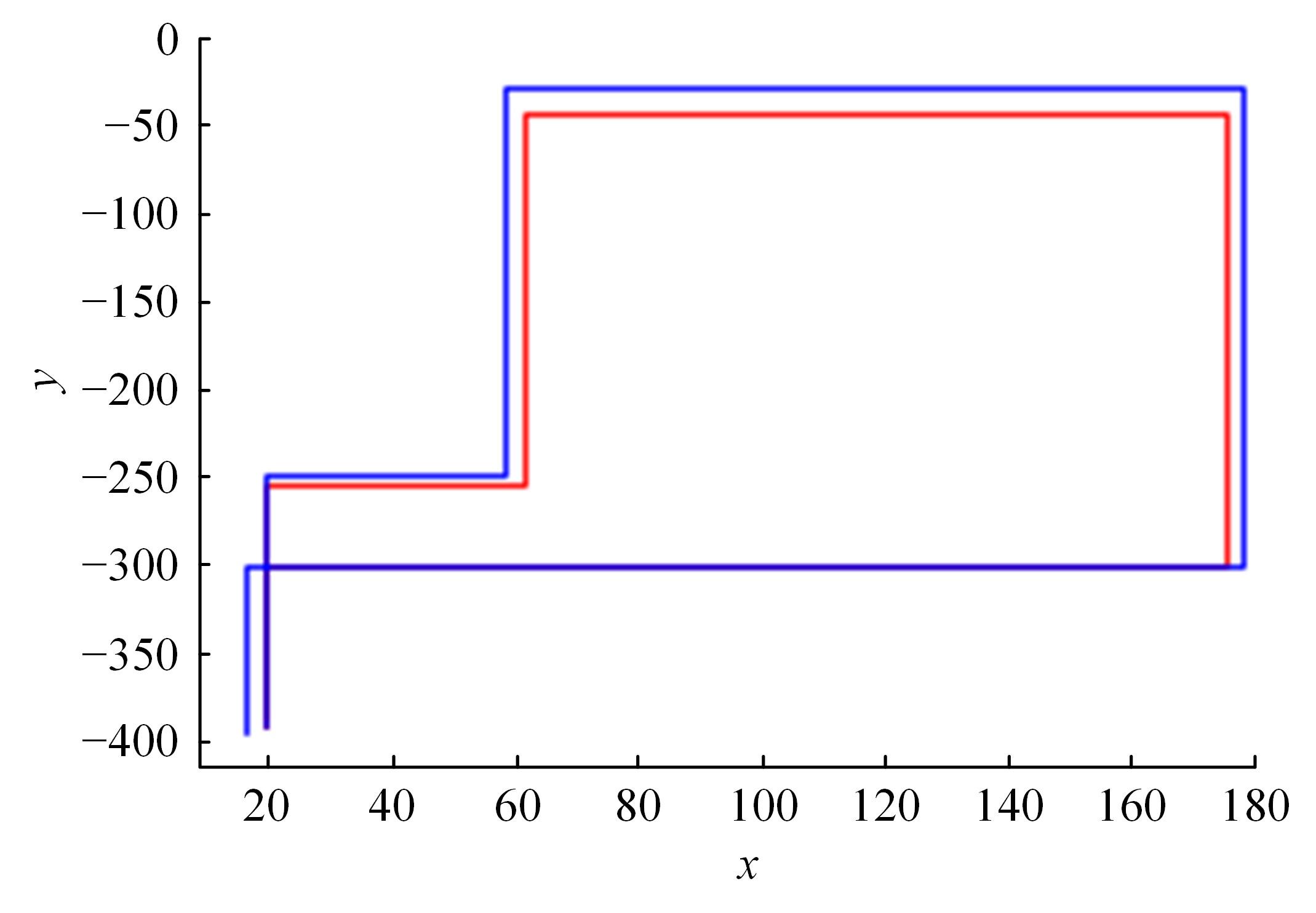
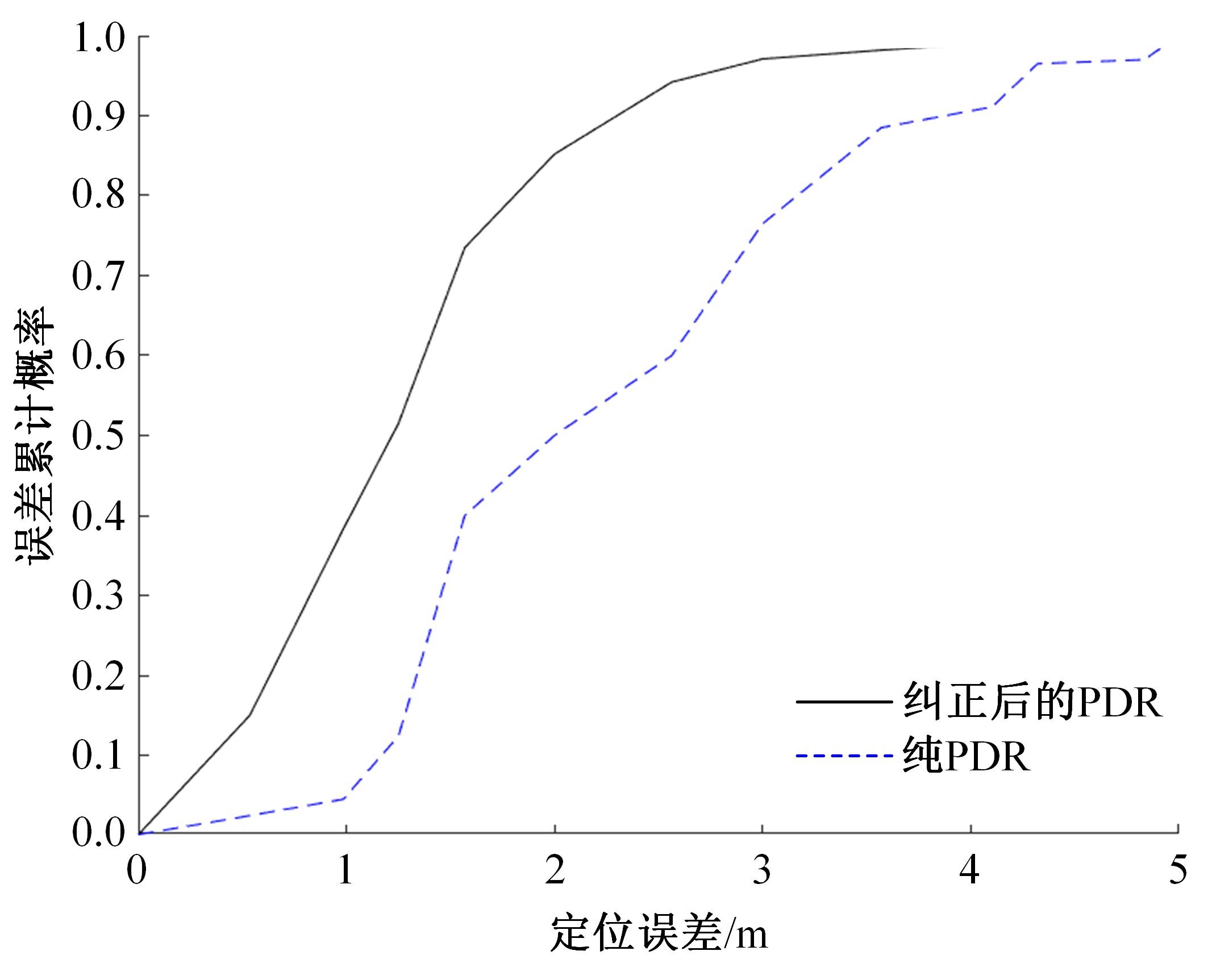
行人航迹推算(PDR)由于误差发散速度快,导致PDR定位可信时间短、累计误差大,因此,提出了基于TrAdaBoost算法为内核的行人航迹推算技术。该方法通过全球定位系统(GPS)离线收集行人室外运动信息,利用迁移学习中的TrAdaBoost算法筛选出最合适的行人运动特征,将其迁移到室内PDR定位中,纠正行人步长,实现行人航迹推算。实验结果表明:行人步长大致分布在65~75 cm内,而且经过纠正后的定位轨迹与真实定位轨迹吻合度高,不会因为惯性传感器的积累误差而出现严重偏离,平均水平误差与纯PDR定位算法相比大幅度下降,位置精度在2 m以内的概率达到了80%。因此,该方法降低了PDR发散的速度,延长了PDR定位的可信时间,提高了短距离内的定位结果的可信度。
中图分类号:
- P228.1
| 1 | 高伟, 侯聪毅, 许万旸, 等. 室内导航定位技术研究进展与展望[J]. 导航定位学报, 2019, 7(1): 10-17. |
| Gao Wei, Hou Cong-yi, Xu Wan-yang, et al. Research progress and prospect of indoor navigation and positioning technology[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2019, 7(1): 10-17. | |
| 2 | 刘富, 权美静, 王柯. 仿蝎子振源定位机理的位置指纹室内定位方法[J] .吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6):2076-2082. |
| Liu Fu, Quan Mei-jing, Wang Ke. A position fingerprint indoor localization method based on the mechanism of simulating scorpion vibration source localization[J] Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2076-2082. | |
| 3 | 李楠, 陈家斌, 袁燕. 基于WiFi/PDR的室内行人组合定位算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2017, 25(4): 483-487. |
| Li Nan, Chen Jia-bin, Yuan Yan. Indoor pedestrianintegrated localization strategy based on WiFi/PDR[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2017, 25(4): 483-487. | |
| 4 | 金彦亮, 张晓帅, 齐崎, 等. 基于WiFi辅助的自适应步长的室内定位算法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2017, 40(12): 165-170. |
| Jin Yan-liang, Zhang Xiao-shuai, Qi Qi, et al. Indoor positioning algorithm based on adaptive step size and WiFi assisted[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2017, 40(12): 165-170. | |
| 5 | 刘庆, 关维国, 李顺康, 等. 基于扩展Kalman滤波的室内WiFi-PDR融合定位算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2019, 45(4): 66-71, 77. |
| Liu Qing, Guan Wei-guo, Li Shun-kang, et al. Indoor WiFi-PDR fusion location algorithm based on extended Kalman filter[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45(4): 66-71, 77. | |
| 6 | 郭倩倩, 崔丽珍, 杨勇, 等. 基于LSTM个性化步长估计的井下人员精准定位PDR算法[J]. 工矿自动化, 2022, 48(1): 33-39. |
| Guo Qian-qian, Cui Li-zhen, Yang Yong, et al. PDR algorithm for precise positioning of underground personnel based on LSTM personalized step size estimation[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2022, 48(1): 33-39. | |
| 7 | 宋震, 李俊良, 刘贵强. 基于深度学习和限幅模糊的变转速液压动力源恒流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| Song Zhen, Li Jun-liang, Liu Gui-qiang. A constant flow prediction method for variable speed hydraulic power source based on deep learning and limiting fuzzy control[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| [1] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [2] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [3] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [4] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [5] | 徐艳蕾,何润,翟钰婷,赵宾,李陈孝. 基于轻量卷积网络的田间自然环境杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
| [6] | 张根保,李浩,冉琰,李裘进. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. |
|
||