吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 576-583.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210677
用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络
- 1.天津工业大学 控制科学与工程学院,天津 300387
2.天津工业大学 电气设备智能控制重点实验室,天津 300387
Multi⁃scale attention network for brain tissue segmentation
Jin-Zhen Liu1,2( ),Guo-Hui Gao1,2,Hui Xiong1,2(
),Guo-Hui Gao1,2,Hui Xiong1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Control Science and Engineering,Tiangong University,Tianjin 300387,China
2.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Control of Electrical Equipment,Tiangong University,Tianjin 300387,China
摘要:
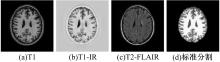
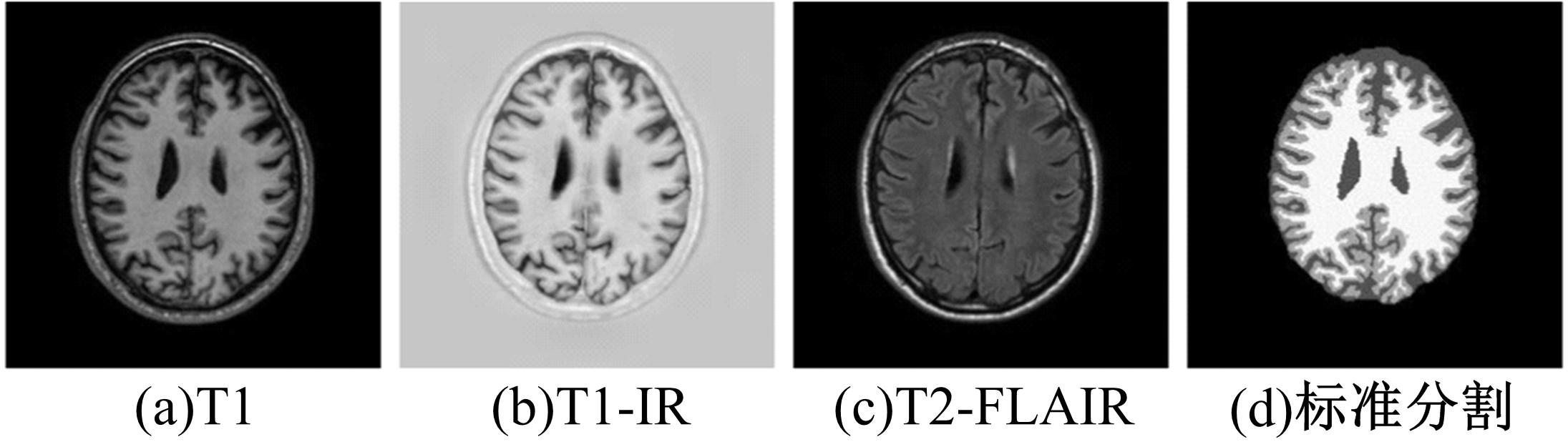
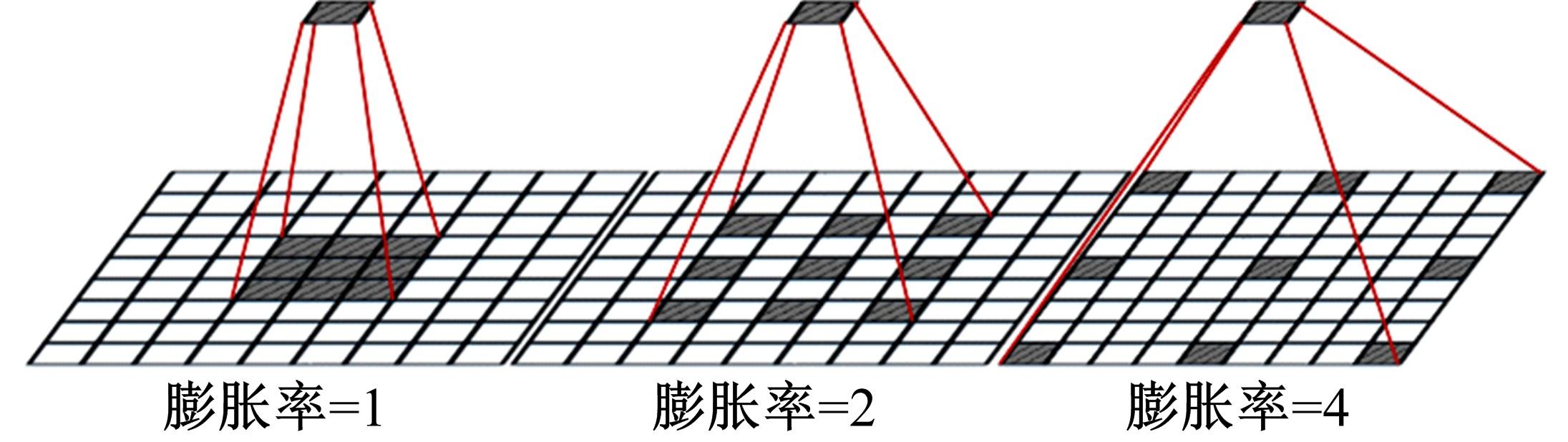
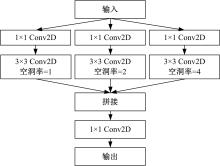
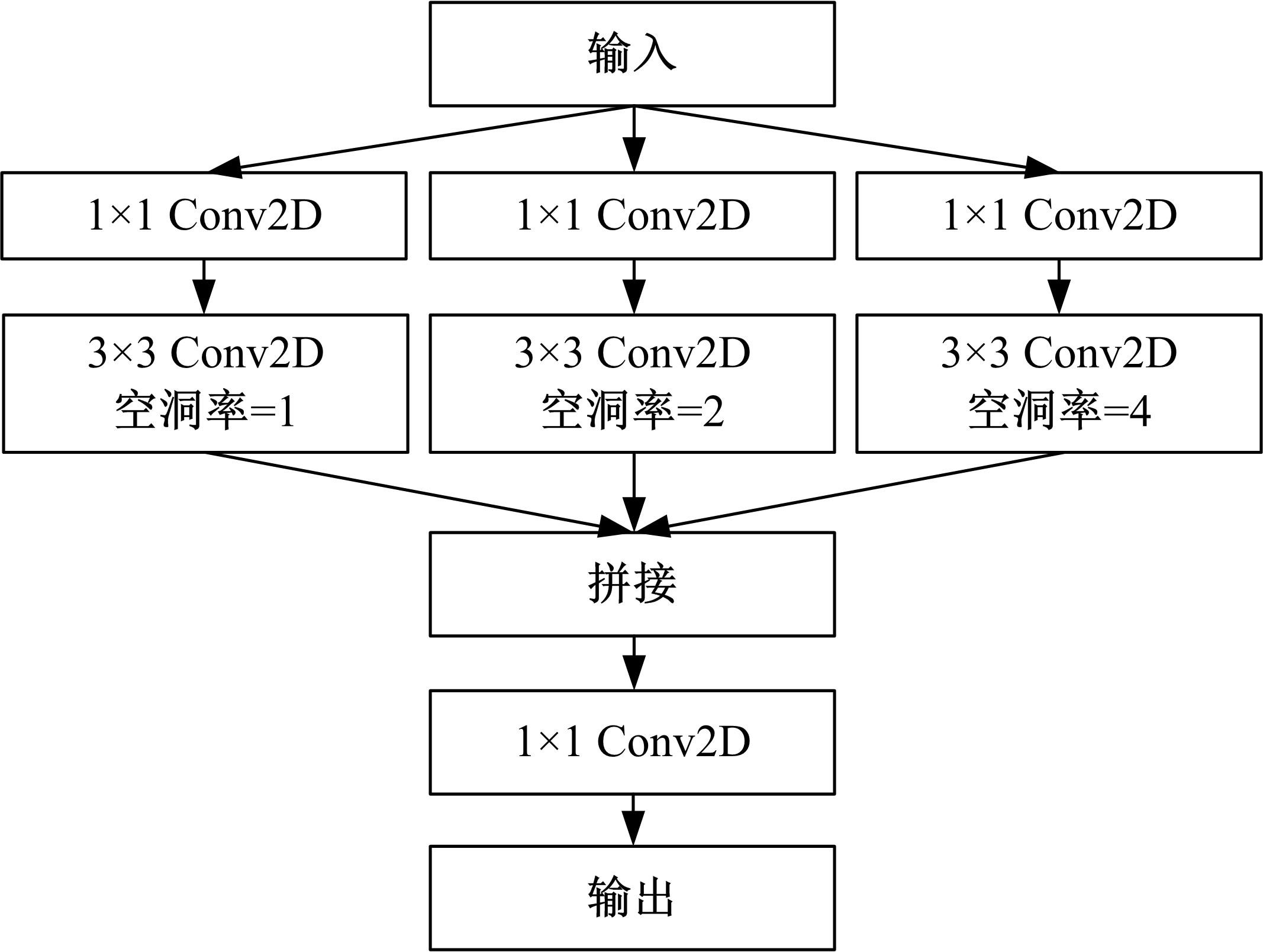
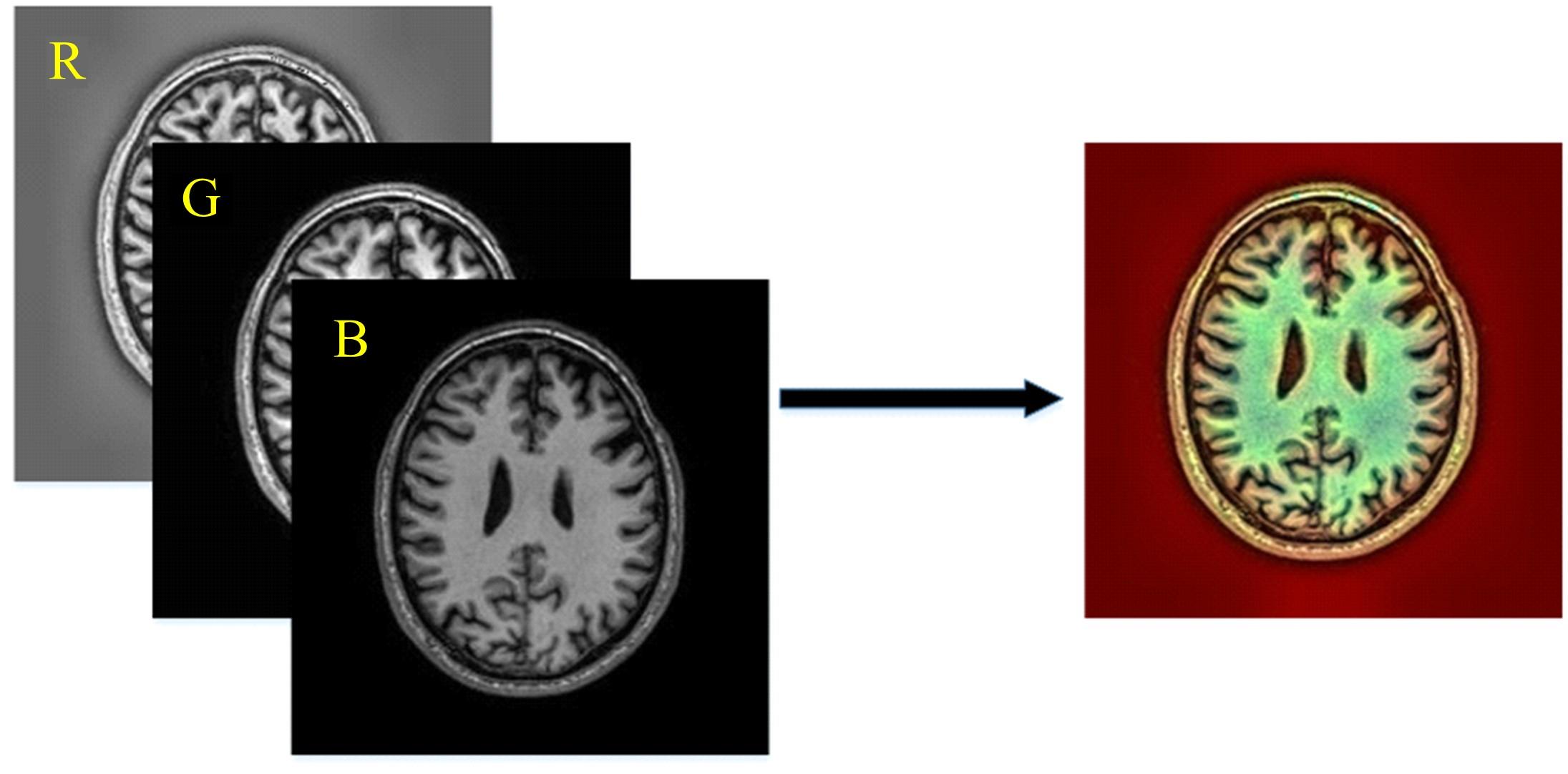
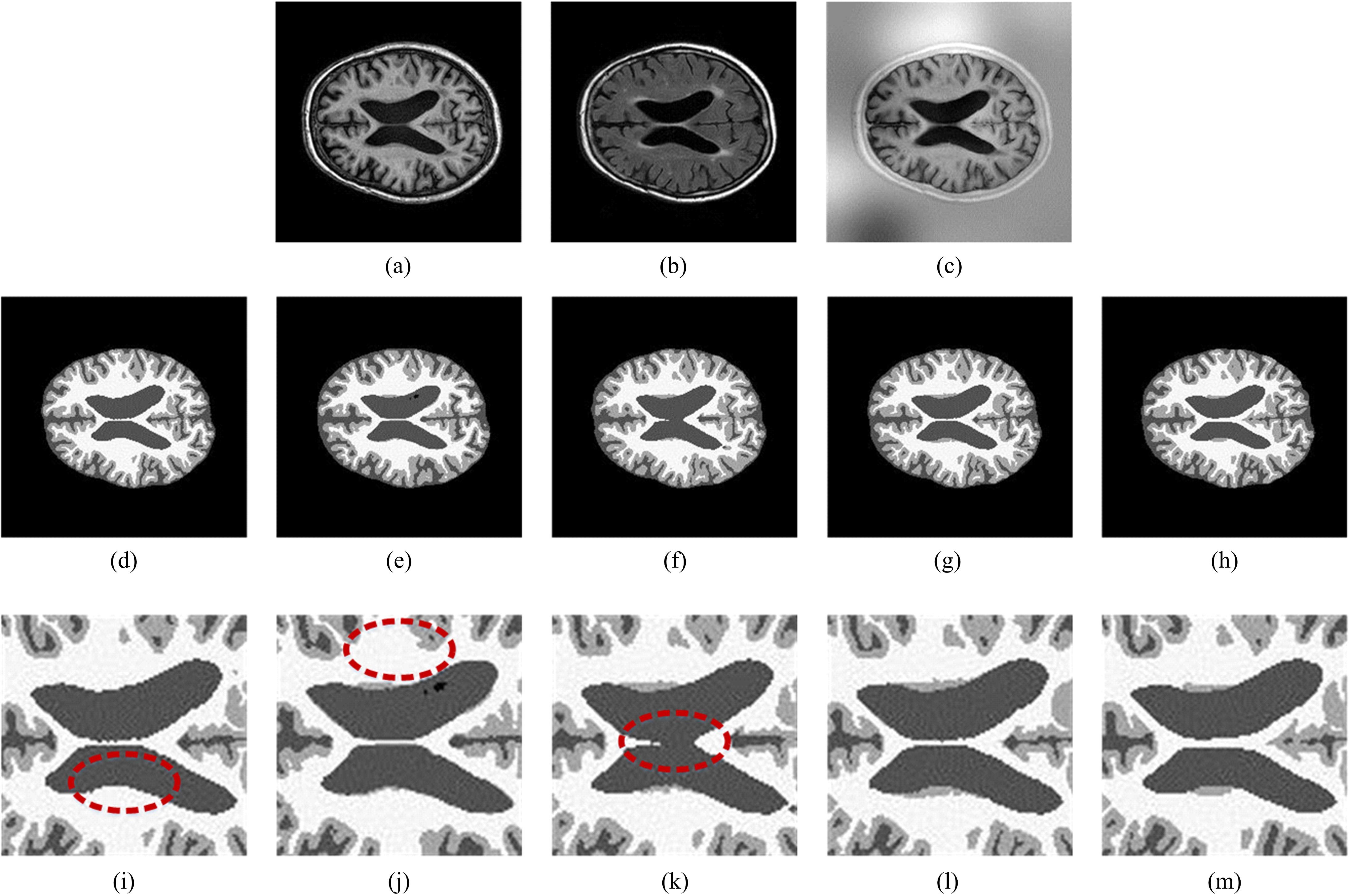
基于脑组织分割的精确头模型有助于提升经颅磁刺激的治疗效果,但由于人脑的复杂性,很难实现精确的脑组织分割。为此,本文提出了基于迁移学习的多尺度注意网络,该网络可以学习多模态数据之间的互补信息,采用迁移学习方法解决小样本数据引起的过拟合问题,利用膨胀卷积提取多尺度特征,加入注意力机制提高脑组织分割的准确性。通过MRBrainS挑战赛验证了网络的有效性,在多项指标中取得了最好成绩。多尺度注意网络可以为个性化头模型的建立提供一个较好的分割结果,进而优化经颅磁刺激的治疗效果。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Angel V P, Reza J, Sarah H L. A transcranial magnetic stimulator inducing near-rectangular pulses with controllable pulse width(cTMS)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2008, 55(1): 257-266. |
| 2 | Chen Y M, Gao G H, Xiong H,et al.A multi-channel parameters adjustable magnetic field generator[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 2020, 91(2): 024709. |
| 3 | 李凝, 王学义, 李小倩, 等. 重复经颅磁刺激与改良电休克治疗首发抑郁症起效时间的随机对照试验[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2015, 29(9): 667-671. |
| Li Ning, Wang Xue-yi, Li Xiao-qian, et al.A randomize controlled trial of early response between repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and modified electroconvulsive therapy in patients with first-episode depression [J]. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 2015, 29(9): 667-671. | |
| 4 | 罗明民, 张红雷.低频重复经颅磁刺激联合认知行为疗法对帕金森病患者的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(22): 5556-5559. |
| Luo Ming-min, Zhang Hong-lei. Effects of low frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with cognitive behavioral therapy on patients with Parkinson's disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2019, 39(22): 5556-5559. | |
| 5 | Oula P, Koen V L, Guilherme B S, et al. Accurate and robust whole-head segmentation from magnetic resonance images for individualized head modeling[J]. Neuroimage, 2020, 219: 117044. |
| 6 | Virginia C, Henning V, Bernhard S S, et al. Cortical thickness in primary sensorimotor cortex influences the effectiveness of paired associative stimulation[J]. Neuroimage, 2012, 60(2): 864-870. |
| 7 | Rashed E A, Gomez-Tames J, Hirata A. Development of accurate human head models for personalized electromagnetic dosimetry using deep learning[J]. Neuroimage, 2019, 202: 116132. |
| 8 | 郜峰利, 陶敏, 李雪妍, 等. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| Gao Feng-li, Tao Min, Li Xue-yan, et al. Accurate segmentation of stroke in CT image based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. | |
| 9 | 车翔玖, 董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| Che Xiang-jiu, Dong You-zheng. Improved image recognition algorithm based on multi⁃scale information fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. | |
| 10 | Chen H, Dou Q, Yu L Q, et al.VoxResNet: deep voxelwise residual networks for brain segmentation from 3D MR images[J].NeuroImage, 2018, 170: 446-455. |
| 11 | Dolz J, Gopinath K, Yuan J, et al. HyperDense-Net: a hyper-densely connected CNN for multi-modal image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(5): 1116-1126. |
| 12 | Li J C, Yu Z L, Gu Z H,et al.MMAN: multi-modality aggregation network for brain segmentation from MR images[J].Neurocomputing,2019,358: 10-19. |
| 13 | Sun L Y, Ma W N, Ding X H, et al. A 3D spatially weighted network for segmentation of brain tissue from MRI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(4): 898-909. |
| 14 | Mendrik A M, Vincken K L, Kuijf H J, et al. MRBrainS challenge: online evaluation framework for brain image segmentation in 3T MRI scans[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2015, 2015: 813696. |
| 15 | Ye H J, Sheng X R, Zhan D C. Few-shot learning with adaptively initialized task optimizer: a practical meta-learning approach[J]. Machine Learning, 2020, 109(3): 643-664. |
| 16 | Wang J, Zhu H D, Wang S H, et al. A review of deep learning on medical image analysis[J]. Mobile Networks & Applications, 2021, 26(1): 351-380. |
| 17 | Tajbakhsh N, Shin J Y, Gurudu S R, et al. Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1299-1312. |
| 18 | Luo W J, Li Y J, Urtasun R, et al. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 4905-4913. |
| 19 | Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[EB/OL]. [2016-04-30]. |
| 20 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]∥15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 11211. |
| 21 | Stollenga M F, Byeon W, Liwicki M, et al. Parallel multi-dimensional LSTM, with application to fast biomedical volumetric image segmentation[C]∥29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2998-3006. |
| [1] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [2] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [3] | 张惠臻,高正凯,李建强,王晨曦,潘玉彪,王成,王靖. 基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 430-438. |
| [4] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [5] | 李永明,裴小轩,伊曙东. 混合动力汽车动力电池自适应神经网络优化控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2063-2068. |
| [6] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [7] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [8] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [9] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [10] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [11] | 宋震,柳杰. 旋转机械振动频率时间序列预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1764-1769. |
| [12] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [13] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [14] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [15] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
|