吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1277-1284.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220755
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑驾驶员生理信息的城市交叉口风险评估方法
- 1.长安大学 运输工程学院,西安 710064
2.重庆交通职业学院 轨道交通学院,重庆 402247
A risk evaluation method for urban intersections considering drivers' physiological information
Gui-zhen CHEN1( ),Hui-ting CHENG2,Cai-hua ZHU1,Yu-ran LI1,Yan LI1(
),Hui-ting CHENG2,Cai-hua ZHU1,Yu-ran LI1,Yan LI1( )
)
- 1.College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Rail Transportation,Chongqing Vocational College of Transportation,Chongqing 402247,China
摘要:
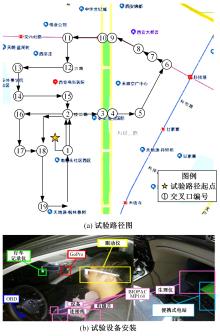
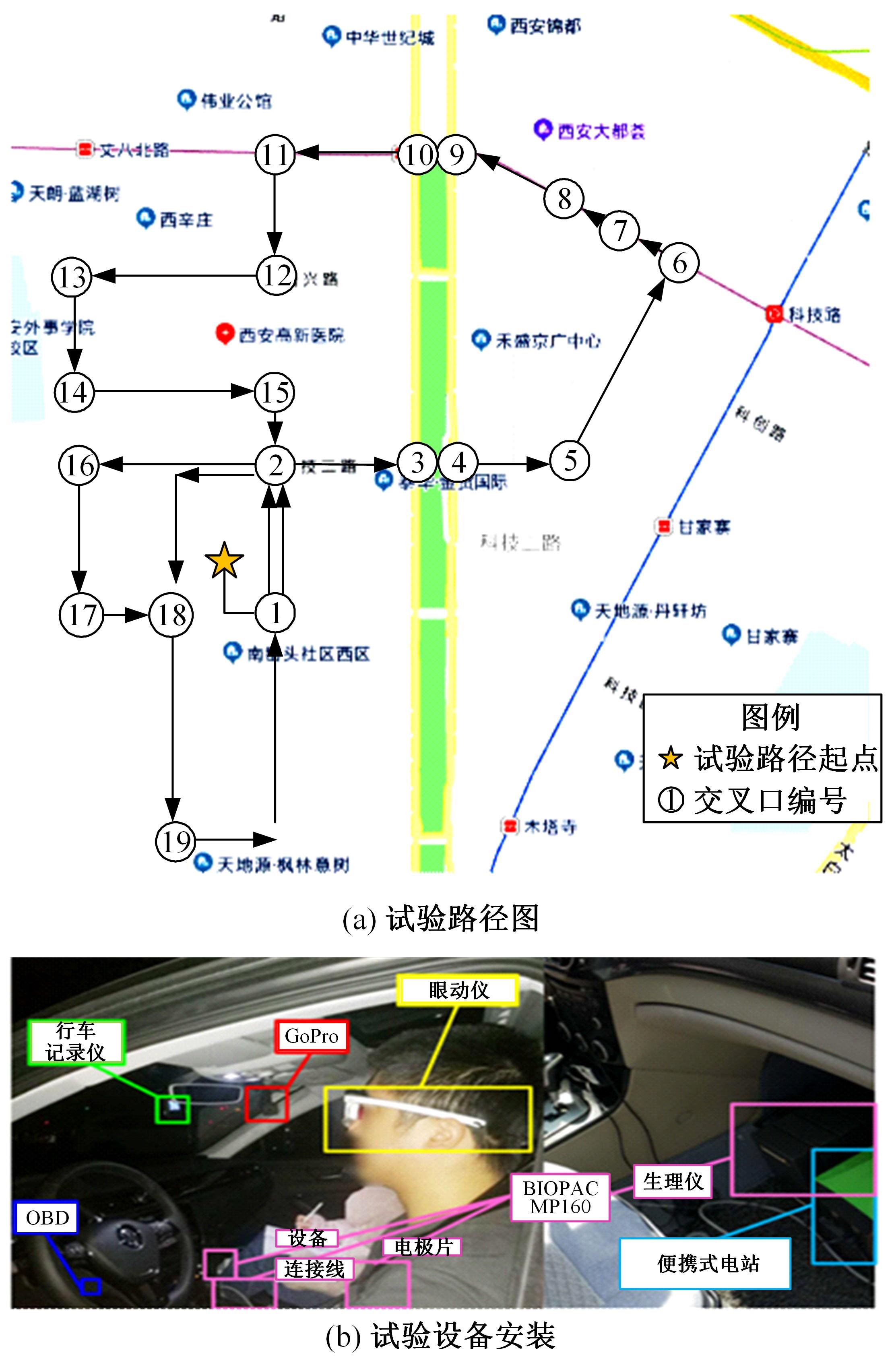
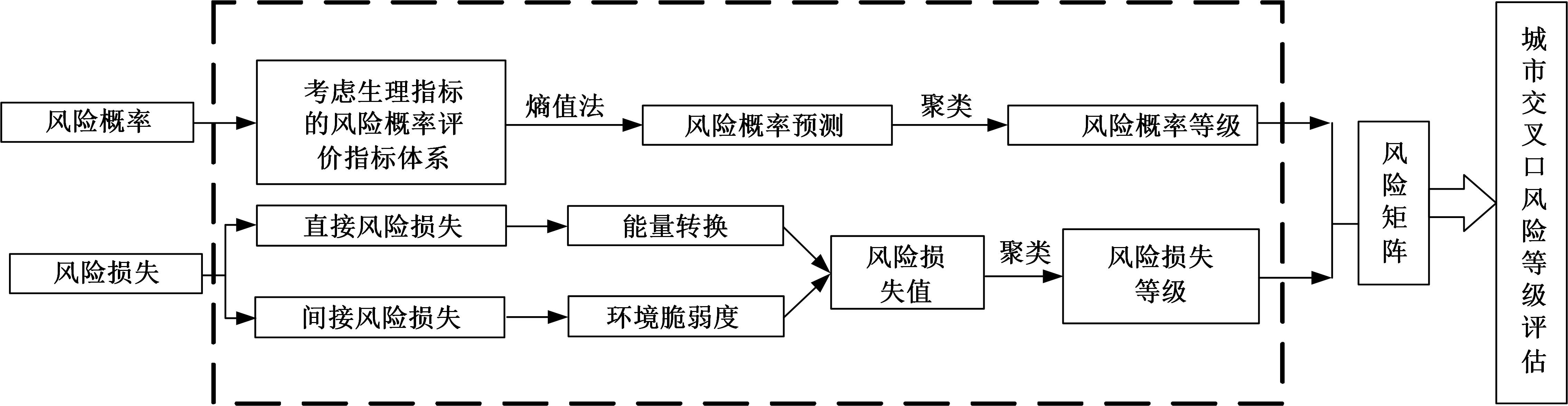
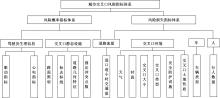
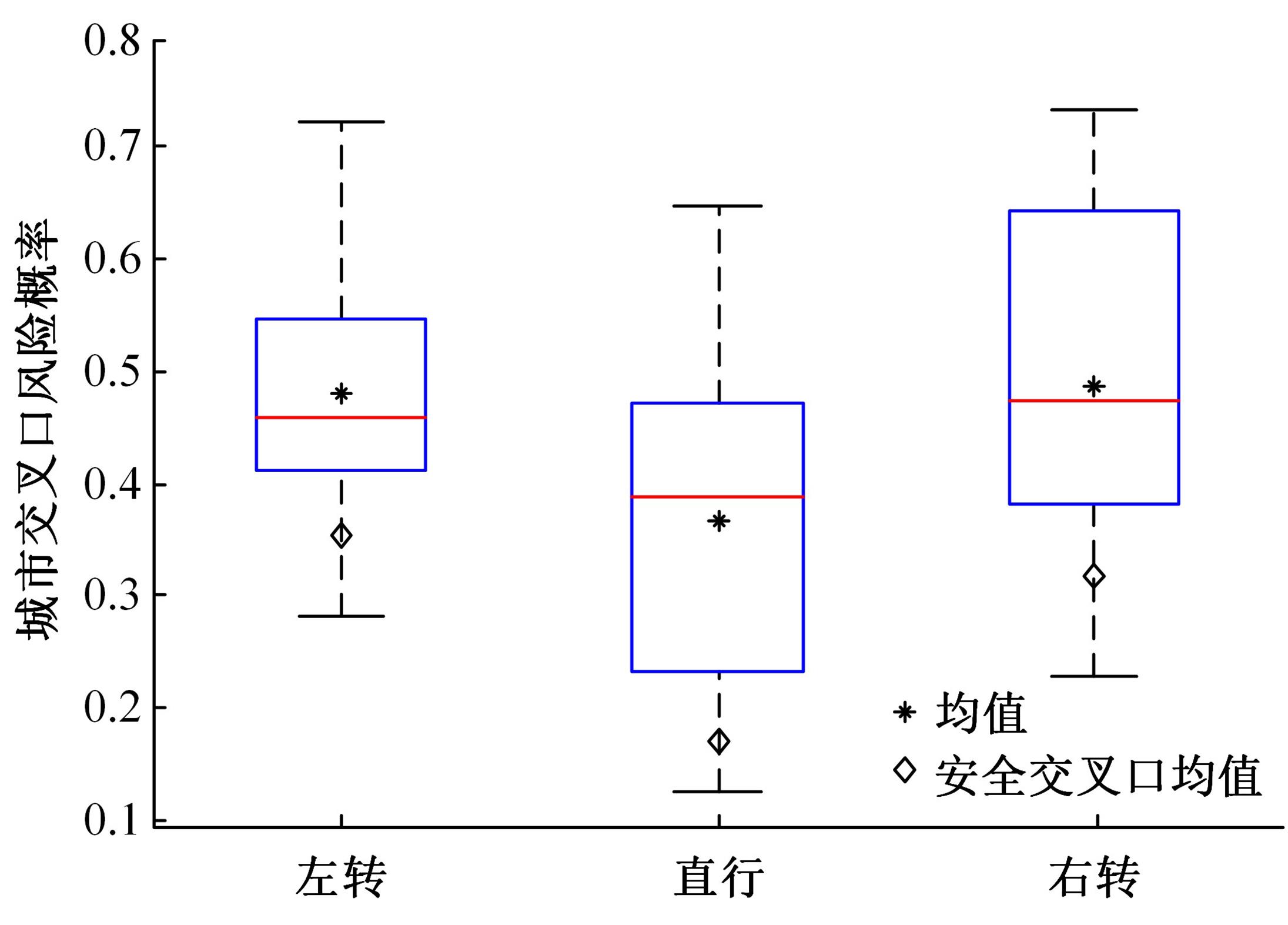
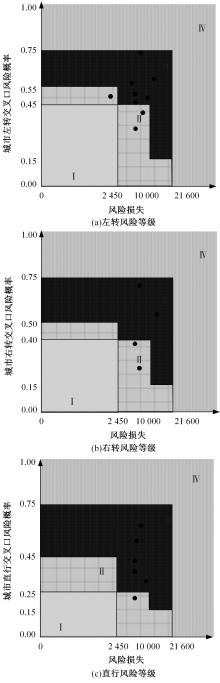
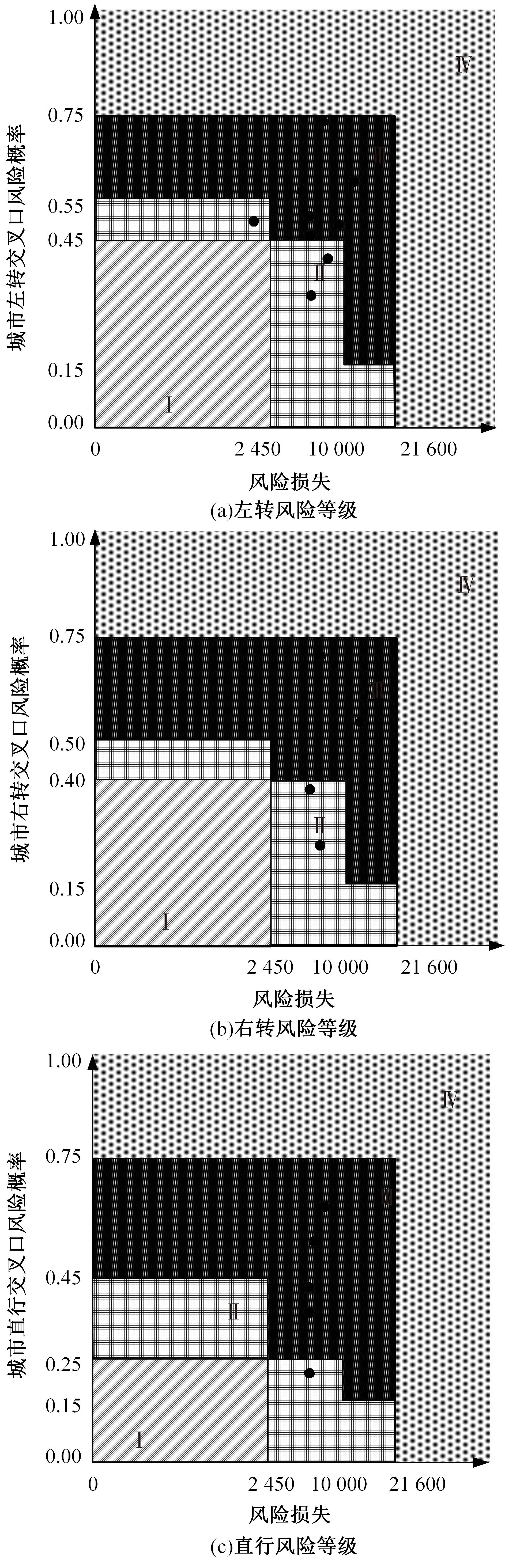
为解决交叉口风险评估未充分考虑驾驶员状态和风险损失的问题,提出了一种综合风险概率和风险损失的风险评估方法。利用熵值法得出基于驾驶员生理信息的风险概率,基于能量转换定理确定直接风险损失,提出环境脆弱度确定间接风险损失;利用聚类算法得到风险损失和风险概率的等级,进而基于风险矩阵得到交叉口风险等级。分析西安市19个交叉口试验数据得出:交叉口风险等级划分为比较安全、一般安全、比较风险和非常风险4个等级,风险等级主要集中在比较风险级别。所提出的基于驾驶员生理信息的交叉口风险评估方法与试验驾驶员的感知相符,准确度达到90%,为驾驶员风险管理提供了新方法。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Laureshyn A, Ceunynck T D, Karlsson C, et al. In search of the severity dimension of traffic events: extended Delta-V as a traffic conflict indicator[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2017, 98(1):46-56. |
| 2 | 朱彤,秦丹,董傲然,等.公交车驾驶人历史违规数据与事故责任的随机参数模型研究[J].安全与环境学报,2021,21(4):1566-1572. |
| Zhu Tong, Qin Dan, Dong Ao-ran, et al. Investigation on the random parameter model of bus drivers' history violation data and accident liability[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021,21(4):1566-1572. | |
| 3 | Khattak A J, Khattak A J, Council F M. Effects of work zone presence on injury and non-injury crashes [J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2002, 34(1): 19-29. |
| 4 | 潘恒彦,王永岗,李德林,等.基于交通冲突的长纵坡路段追尾风险评估及预测 [J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(5): 1355-1363. |
| Pan Heng-yan, Wang Yong-gang, Li De-lin, et al. Evaluating and forecasting rear-end collision risk of long longitudinal gradient roadway via traffic conflict[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5):1355-1363. | |
| 5 | Hirose T, Takada T, Oikawa S, et al. Validation of driver support system based on real-world bicycle and motor vehicle flows[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2021, 156(9): 106131. |
| 6 | 马艳丽, 祁首铭, 吴昊天, 等. 基于PET算法的匝道合流区交通冲突识别模型 [J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(2): 142-148. |
| Ma Yan-li, Qi Shou-ming, Wu Hao-tian, et al. Traffic conflict identification model based on post encroachment time algorithm in ramp merging area[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(2): 142-148. | |
| 7 | 郭延永, 刘攀, 吴瑶, 等. 基于贝叶斯多元泊松-对数正态分布的交通冲突模型 [J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(1): 101-109. |
| Guo Yan-yong, Liu Pan, Wu Yao,et al. Traffic conflict model based on bayesian multivariate poisson-lognormal normal distribution[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(1): 101-109. | |
| 8 | 郭伟伟, 曲昭伟, 王殿海. 交通冲突判别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2011, 41(1): 35-40. |
| Guo Wei-wei, Qu Zhao-wei, Wang Dian-hai. Traffic conflict discrimination model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(1): 35-40. | |
| 9 | Kaye S A, Lewis I, Freeman J. Comparison of self-report and objective measures of driving behavior and road safety: a systematic review[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2018, 65:141-151. |
| 10 | Minea M, Dumitrescu C M, Costea I M. Advanced e-call support based on non-intrusive driver condition monitoring for connected and autonomous vehicles [J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(24): 82723701. |
| 11 | Quddus A, Zandi A S, Prest L, et al. Using long short term memory and convolutional neural networks for driver drowsiness detection[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2021, 156(1): 106107. |
| 12 | Li Y, Wang F, Ke H, et al. A driver's physiology sensor-based driving risk prediction method for lane-changing process using hidden markov model [J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 26701105. |
| 13 | Patel M, Lal S K L, Kavanagh D, et al. Applying neural network analysis on heart rate variability data to assess driver fatigue[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(6): 7235-7242. |
| 14 | Wang J Q, Zheng Y, Li X F, et al. Driving risk assessment using near-crash database through data mining of tree-based model[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2015, 84(11): 54-64. |
| 15 | 刘建蓓, 马小龙, 张志伟,等. 基于心电分析的青藏高原驾驶员疲劳特性[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(4): 151-158. |
| Liu Jian-bei, Ma Xiao-long, Zhang Zhi-wei, et al. Fatigue characteristics of driver in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on electrocardiogram analysis[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(4): 151-158. | |
| 16 | 徐文会, 刘开华, 王丽婷. 使用改进Welch法估计心率变异功率谱分析人体疲劳程度 [J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33(1): 67-71. |
| Xu Wen-hui, Liu Kai-hua, Wang Li-ting. Estimation of the power spectrum of heart rate variability using improved welch method to analyze the degree of fatigue[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(1): 67-71. | |
| 17 | 袁伟, 付锐, 郭应时, 等. 基于视觉特性的驾驶员换道意图识别[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(4): 132-138. |
| Yuan Wei, Fu Rui, Guo Ying-shi, et al. Drivers lane changing intention identification based on visual characteristics[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(4): 132-138. | |
| 18 | 朱才华, 孙晓黎, 李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测 [J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| Zhu Cai-hua, Sun Xiao-li, Li Yan. Forecast of urban public bicycle traffic demand by station classification[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2021, 51(2): 531-540. | |
| 19 | 潘福全, 陆键, 项乔君, 等. 公路信号平面交叉口安全服务水平研究 [J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 38(2): 298-303. |
| Pan Fu-quan, Lu Jian, Xiang Qiao-jun, et al. Level of safety service for highway signalized intersections [J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 38(2): 298-303. | |
| 20 | 张志刚. 道路因素、交通环境与交通事故分析 [J]. 公路交通科技, 2000, 17(6): 56-59. |
| Zhang Zhi-gang. Road conditions, traffic environment and traffic accident analysis[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2000, 17(6): 56-59. |
| [1] | 赵晓华,刘畅,亓航,欧居尚,姚莹,郭淼,杨海益. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [2] | 杨秀建,贾晓寒,张生斌. 考虑汽车队列动态特性的混合交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [3] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [4] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [5] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [6] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [7] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [8] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [9] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [10] | 杨敏,张聪伟,李大韦,马晨翔. 基于贝叶斯网的空铁联程乘客出行满意度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2839-2846. |
| [11] | 曹倩,李志慧,陶鹏飞,马永建,杨晨曦. 考虑风险异质特性的路网交通事故风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2817-2825. |
| [12] | 秦严严,杨晓庆,王昊. 智能网联混合交通流CO2排放影响及改善方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [13] | 彭浩楠,唐明环,查奇文,王伟忠,王伟达,项昌乐,刘玉龙. 自动驾驶汽车双车道换道最优轨迹规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2852-2863. |
| [14] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,李剑. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| [15] | 户佐安,夏一鸣,蔡佳,薛锋. 延误条件下综合多种策略的城轨列车运行调整优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1664-1672. |
|
||