吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 3736-3744.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240155
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于离散采样的多模态四足机器人路径规划
- 1.中国科学技术大学 工程科学学院,合肥 230026
2.安徽大学 电气工程与自动化学院,合肥 230601
Path planning for multimodal quadruped robots based on discrete sampling
Shuai-shuai SUN1( ),Chun-xiao FENG1,Liang ZHANG2(
),Chun-xiao FENG1,Liang ZHANG2( )
)
- 1.College of Engineering Science,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China
2.College of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
摘要:
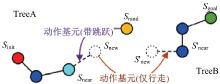
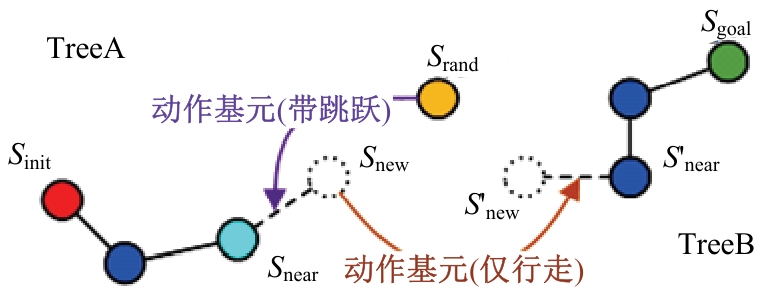
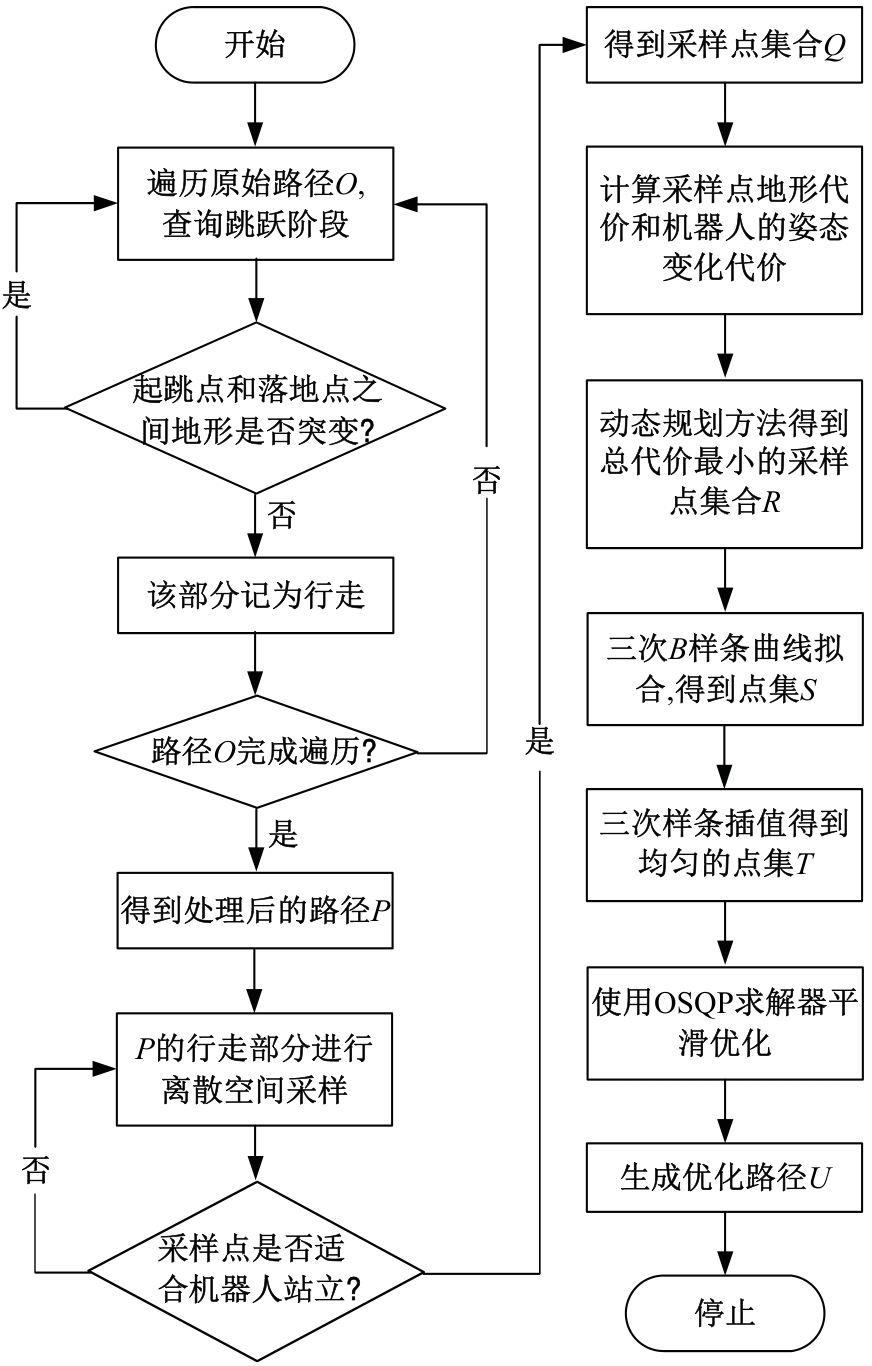
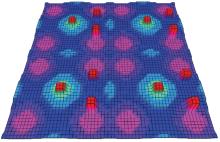
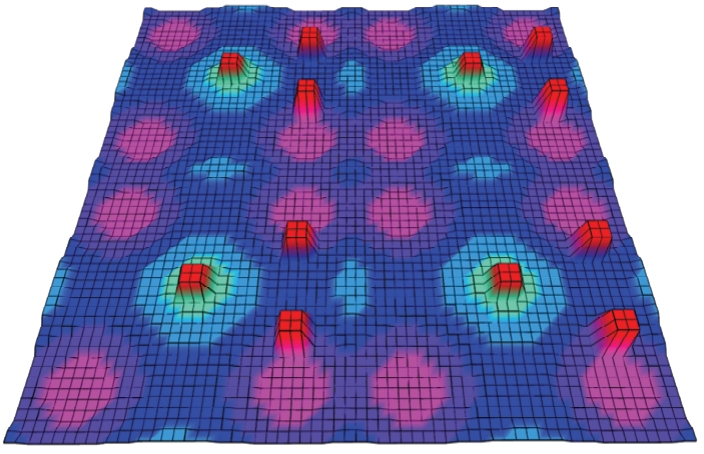
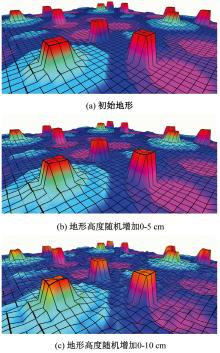
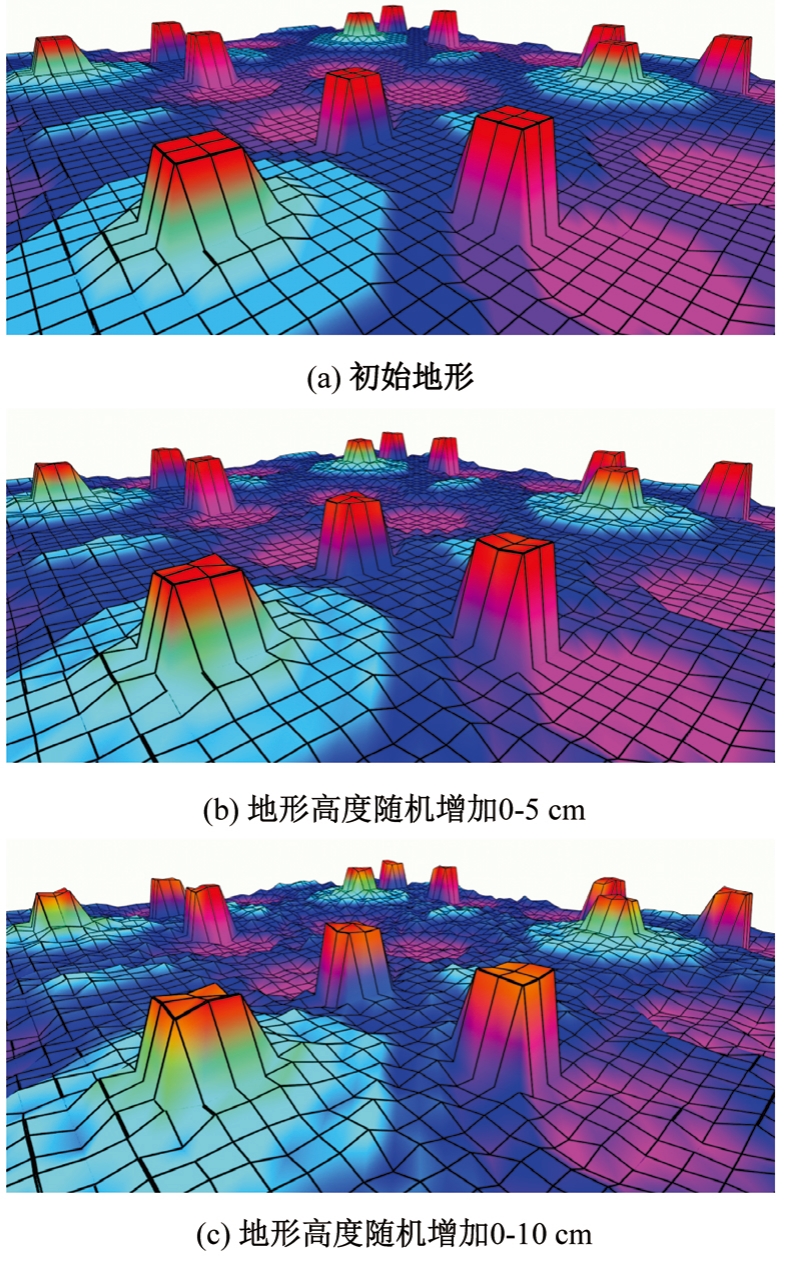
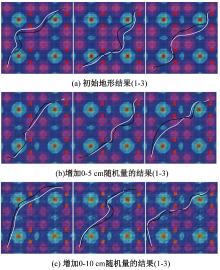
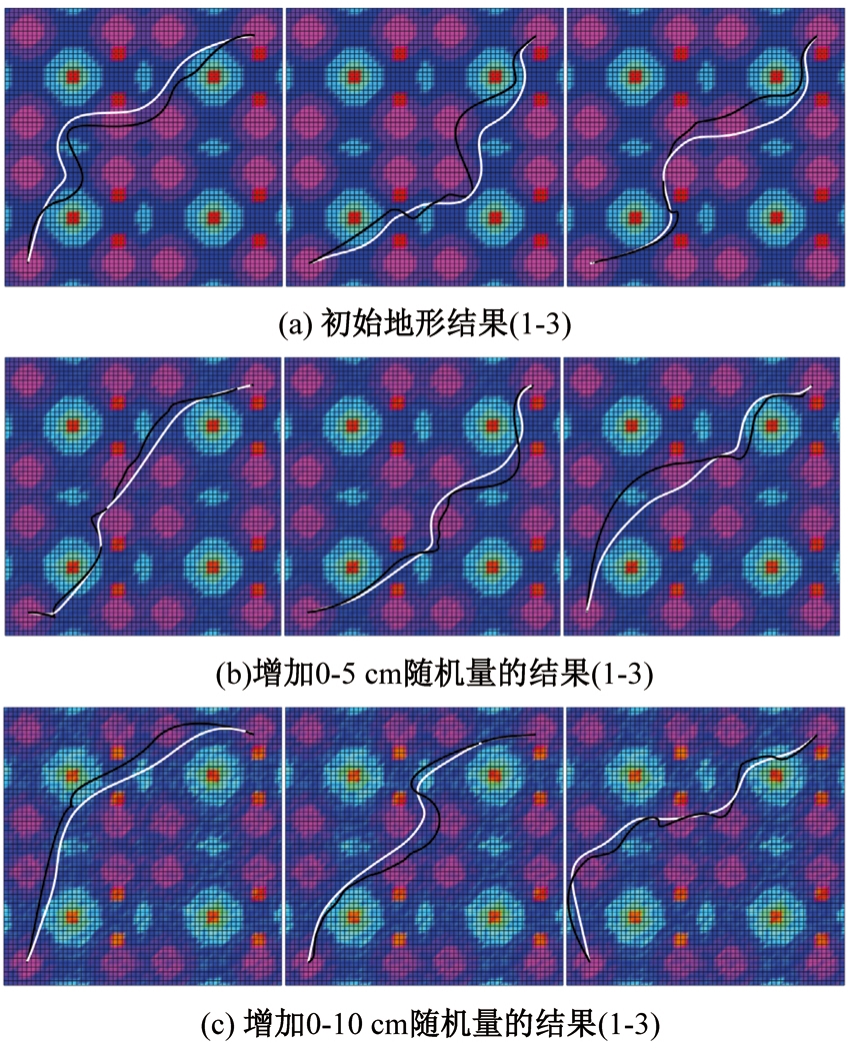
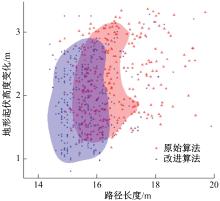
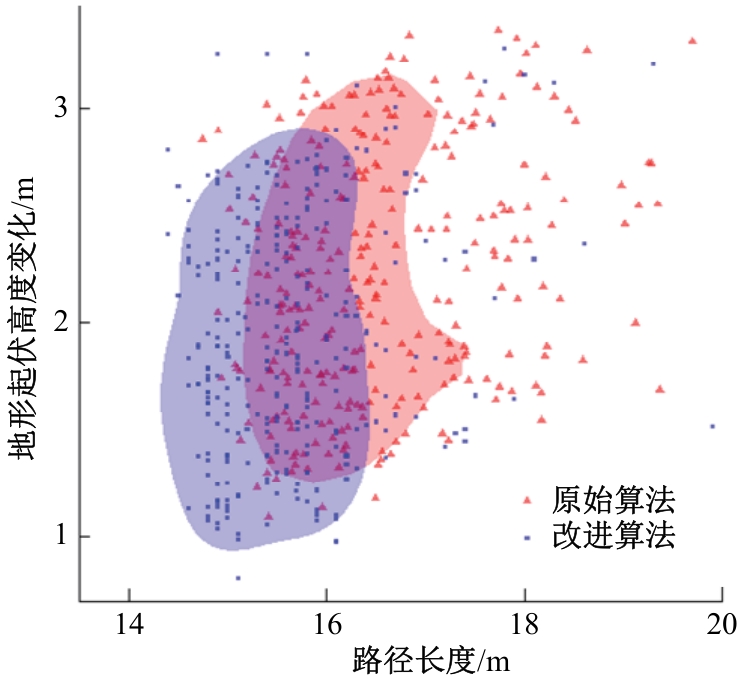
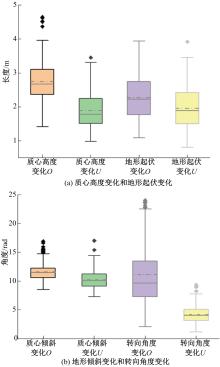
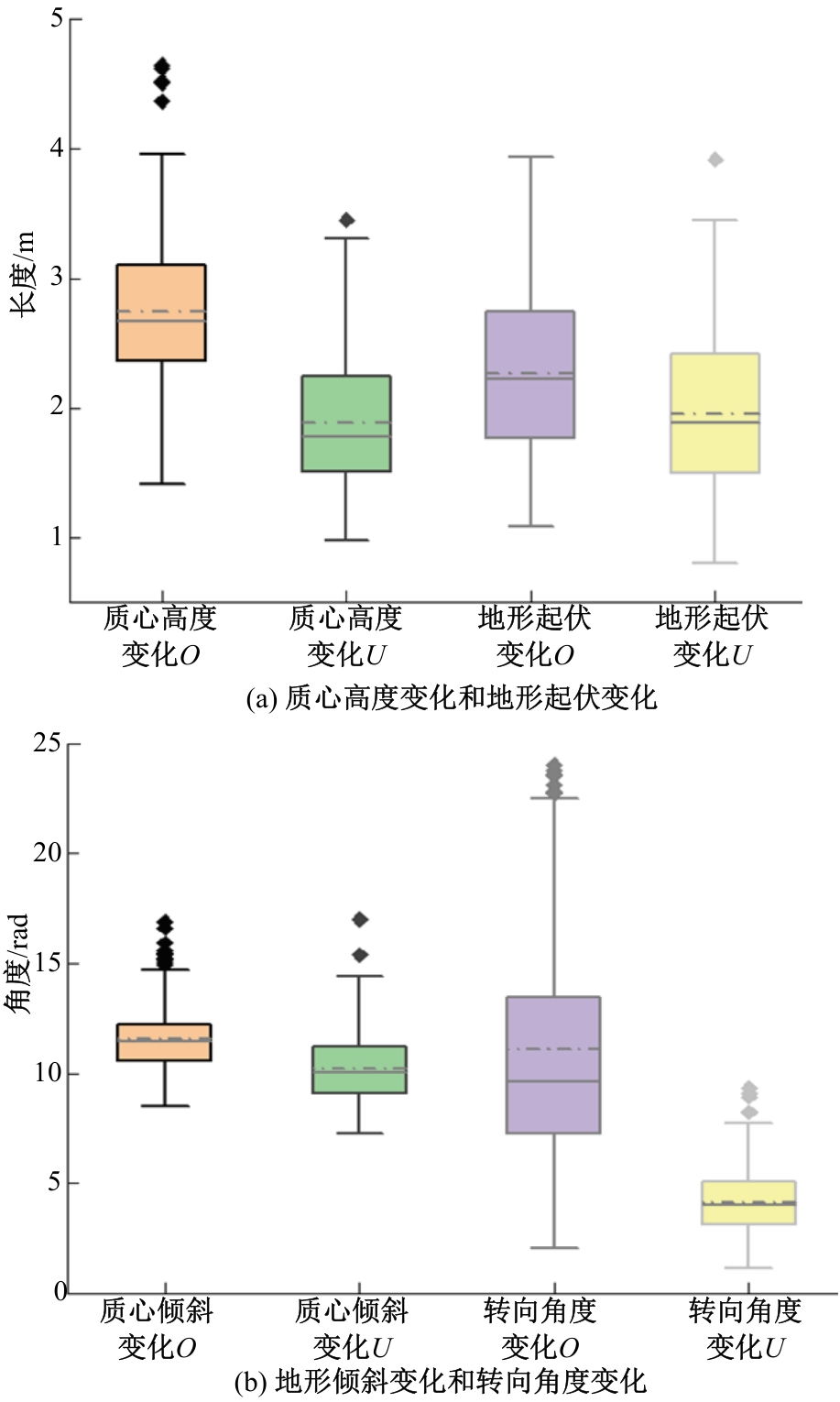
针对双向快速扩展随机树在多模态四足机器人路径规划中存在不必要的跳跃和行走部分路径的地形起伏程度大及转向角度变化大的问题,提出一种基于离散采样的解决方案,预处理路径去除不必要的跳跃,离散采样并动态规划获得粗解,使用B样条曲线拟合并二次规划得到最终路径。仿真结果表明:本文方法规划出的路径使机器人对质心高度的调节平均减少了31.4%,途径地形的起伏程度减小13.4%,地形倾斜角度变化降低11.4%,转向角度变化减小62.7%,证明了本文方法的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP242
| [1] | 张秀丽, 王琪, 黄森威, 等. 一种多模型融合的仿猎豹四足机器人复杂运动控制方法[J]. 机器人, 2022, 44(6): 682-693. |
| Zhang Xiu-li, Wang qi, Huang Sen-wei, et al. A multi-model fusion based complex motion control approach for a cheetah-mimicking quadruped robot[J]. Robot, 2022, 44(6): 682-693. | |
| [2] | 张帅帅, 荣学文, 李贻斌, 等. 崎岖地形环境下四足机器人的静步态规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(4): 1287-1296. |
| Zhang Shuai-shuai, Rong Xue-wen, Li Yi-bin, et al. Static gait planning method for quadruped robots on rough terrains[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(4): 1287-1296. | |
| [3] | 周坤, 李川, 李超, 等. 面向未知复杂地形的四足机器人运动规划方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(2): 210-219. |
| Zhou Kun, Li Chuan, Li Chao, et al. Motion planning method for quadruped robots walking on unknown rough terrain[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(2): 210-219. | |
| [4] | Nguyen Q, Powell M J, Katz B, et al. Optimized jump on the mit cheetah 3 robot[C]∥International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, Canada, 2019: 7448-7454. |
| [5] | Jenelten F, He J, Farshidian F, et al. DTC: deep tracking control[J]. Science Robotics, 2024, 9(86): eadh5401. |
| [6] | 崔炜, 朱发证. 机器人导航的路径规划算法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(19): 10-20. |
| Cui Wei, Zhu Fa-zheng. Review of path planning algorithms for robot navigation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(19): 10-20. | |
| [7] | Lavalle S. Rapidly-exploring random trees: a new tool for path planning[J]. The Annual Research Report, 1998, 6: 25989663. |
| [8] | Kavraki L E, Svestka P, Latombe J C, et al. Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces[J]. IEEE transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1996, 12(4): 566-580. |
| [9] | Fankhauser P, Hutter M. A universal grid map library: Implementation and use case for rough terrain navigation[J]. Robot Operating System (ROS) The Complete Reference, 2016, 1: 99-120. |
| [10] | Fankhauser P, Bloesch M, Gehring C, et al. Robot-centric elevation map with uncertainty estimates[C]∥ 17th International Conference on Climbing and Walking Robots and the Support Technologies for Mobile Machines, Poznan, Poland, 2014: 433-440. |
| [11] | 张慧, 荣学文, 李贻斌, 等. 四足机器人地形识别与路径规划算法[J]. 机器人, 2015, 37(5): 546-556. |
| Zhang hui, Rong Xue-wen, Li Yi-bin, et al. Terrain recognition and path planning for quadruped robot[J]. Robot, 2015, 37(5): 546-556. | |
| [12] | Wermelinger M, Fankhauser P, Diethelm R, et al. Navigation planning for legged robots in challenging terrain[C]∥IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Daejeon, South Korea, 2016: 1184-1189. |
| [13] | Karaman S, Frazzoli E. Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning[J]. The International journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(7): 846-894. |
| [14] | Norby J, Johnson A M. Fast global motion planning for dynamic legged robots[C]∥IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and System, Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 3829-3836. |
| [15] | Kuffner J J, LaValle S M. RRT-connect: an efficient approach to single-query path planning[J]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings, 2000, 2: 995-1001. |
| [16] | Wellhausen L, Hutter M. Rough terrain navigation for legged robots using reachability planning and template learning[C]∥IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2021: 6914-6921. |
| [17] | Fernbach P, Tonneau S, Del Prete A, et al. A kinodynamic steering-method for legged multi-contact locomotion[C]∥IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 3701-3707. |
| [18] | 吴振宇, 刘小飞, 王义普. 基于DKRRT*-APF算法的无人系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(3): 781-791. |
| Wu Zhen-yu, Liu Xiao-fei, Wang Yi-pu. Trajectory planning of unmanned system based on DKRRT*⁃APF algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 781-791. | |
| [19] | Deboor C. On calculating with B-splines[J]. Journal of Approximation Theory, 1972, 6(1): 50-62. |
| [20] | Steinbeck M, Koschke R. Tinyspline: a small, yet powerful library for interpolating, transforming, and querying nurbs, b-splines, and bézier curves[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering, Honolulu, USA, 2021: 572-576. |
| [21] | Stellato B, Banjac G, Goulart P, et al. OSQP: an operator splitting solver for quadratic programs[J]. Mathematical Programming Computation, 2020, 12(4): 637-672. |
| [1] | 郭艳萍,高云,周建慧. 基于链路状态的卫星通信多模态动态拥塞控制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2026, 56(1): 257-264. |
| [2] | 兰巍,周政,王冠宇,王伟,张苗苗. 基于机器学习的汽车设计智能拟合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(9): 2858-2863. |
| [3] | 张伏,韩伟东,鲍若飞,张亚坤,王亚飞,付三玲. 融合改进A*与DWA算法的车间移动机器人路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(9): 3020-3031. |
| [4] | 孙佩铭,王喆. 基于导向差分进化算法的党务活动调度优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(8): 2761-2770. |
| [5] | 刘元宁,王星喆,黄子彧,张家晨,刘震. 基于多模态数据融合的胃癌患者生存预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(8): 2693-2702. |
| [6] | 王旭. 四足机器人运动及稳定控制关键技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1483-1496. |
| [7] | 袁杰,王军博,陈歆,黄馨,张傲翔,崔安琪. 人工智能在超高性能混凝土中的应用研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 771-789. |
| [8] | 曹毅,夏宇,高清源,叶培涛,叶凡. 基于超连接图卷积网络的骨架行为识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 731-740. |
| [9] | 黄汉英,李鹏飞. 边缘服务器计算资源分配方法与仿真实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 316-324. |
| [10] | 李健,孙晓海,廖昌义,杨建平. 基于双起点蚁群算法的机器人路径规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 325-332. |
| [11] | 杨楠,肖军. 序列二次规划算法下城市智能交通运行节能优化控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2223-2228. |
| [12] | 朱瑾,黄琦. 路网资源分配下自动化码头水平运输调度与路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2245-2255. |
| [13] | 井佩光,田雨豆,汪少初,李云,苏育挺. 基于动态扩散图卷积的交通流量预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1582-1592. |
| [14] | 曲福恒,潘曰涛,杨勇,胡雅婷,宋剑飞,魏成宇. 基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [15] | 金志刚,苏仁鋆,赵晓芳. 基于异质图网络的心理评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
|