吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1393-1400.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221338
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法
曲福恒1( ),潘曰涛1,杨勇1,2,胡雅婷3,宋剑飞1,魏成宇3
),潘曰涛1,杨勇1,2,胡雅婷3,宋剑飞1,魏成宇3
- 1.长春理工大学 计算机科学技术学院,长春 130022
2.吉林电子信息职业技术学院,吉林省 吉林市 132021
3.吉林农业大学 信息技术学院,长春 130118
An efficient global K-means clustering algorithm based on weighted space partitioning
Fu-heng QU1( ),Yue-tao PAN1,Yong YANG1,2,Ya-ting HU3,Jian-fei SONG1,Cheng-yu WEI3
),Yue-tao PAN1,Yong YANG1,2,Ya-ting HU3,Jian-fei SONG1,Cheng-yu WEI3
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.Jilin Technology College of Electronic Information,Jilin 132021 China
3.College of Information Technology,Jilin Agricultural University,Changchun 130118,China
摘要:
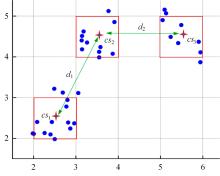
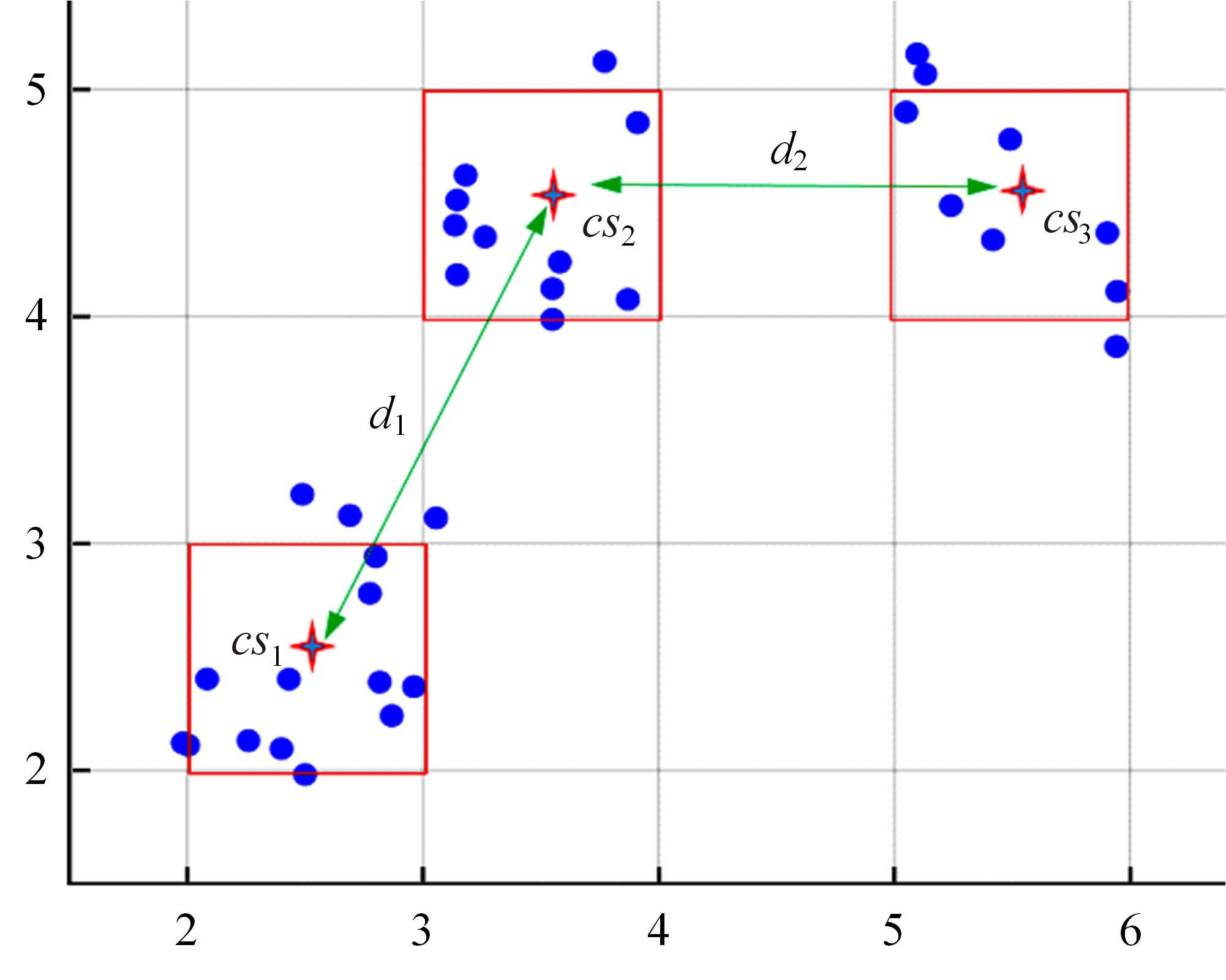
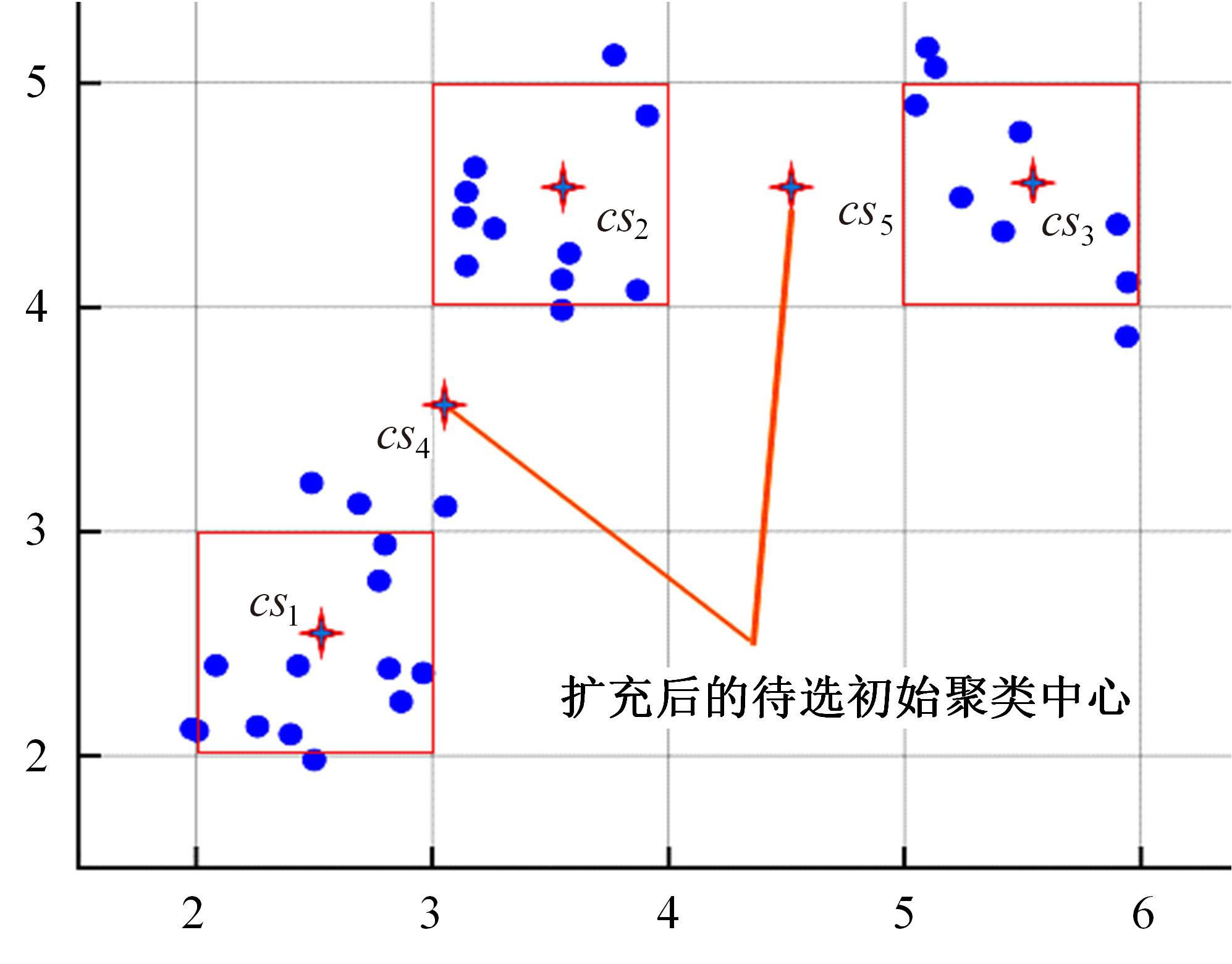
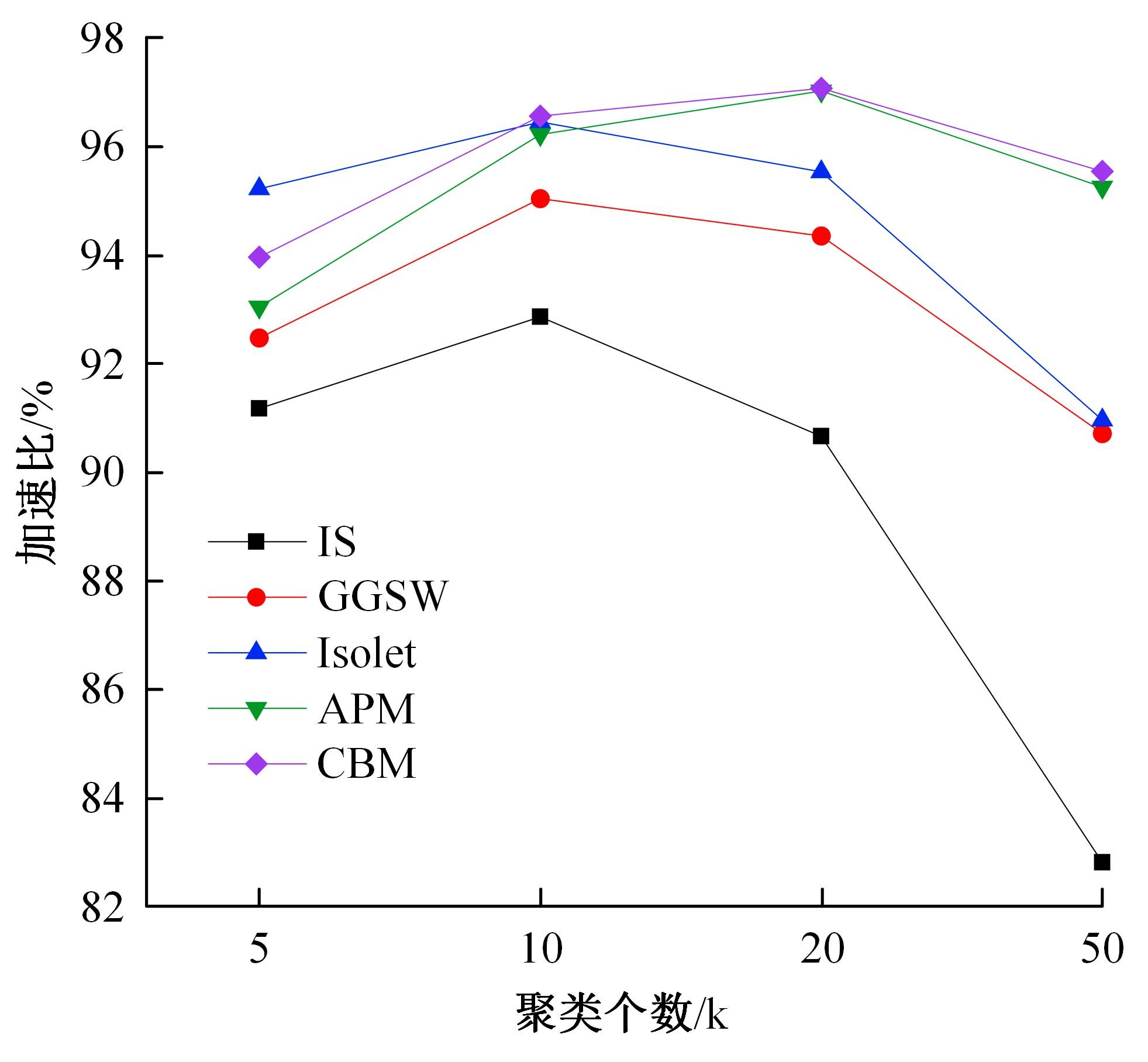
针对全局K-means聚类算法穷举样本点导致计算量大的问题,提出一种基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法。算法首先对样本空间进行网格划分,然后提出密度准则与距离准则对网格进行过滤,保留密度较大且相互距离较远的网格作为候选中心网格。为避免全局K-means算法只在样本集中选取候选中心的局限性,提出权重准则和中心迭代策略扩充候选中心,增加候选中心多样性。最后,通过增量聚类方式遍历候选中心得到最终的聚类结果。在UCI数据集上的实验结果表明:与全局K-means算法相比,新算法在保证聚类精度的前提下,计算效率平均提高了89.39%~95.79%。与K-means++、IK-+和近期提出的CD算法相比,新算法精度更高,并且克服了因随机初始化导致的聚类结果不稳定问题。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Rahman M A, Islam M Z. A hybrid clustering technique combining a novel genetic algorithm with K-means[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2014, 71: 345-365. |
| 2 | Harjanti T W, Setiyani H, Trianto J, et al. Classification of mint leaf types based on the image using euclidean distance and K-means clustering with shape and texture feature extraction[J]. Tech-E, 2022, 5(2): 115-124. |
| 3 | 刘仲民, 李战明, 李博皓,等. 基于稀疏矩阵的谱聚类图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017,47(4): 1308-1313. |
| Liu Zhong-min, Li Zhan-ming, Li Bo-hao, et al. Spectral clustering image segmentation based on sparse matrix[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(4): 1308-1313. | |
| 4 | Lim Z Y, Ong L Y, Leow M C. A review on clustering techniques: creating better user experience for online roadshow[J]. Future Internet, 2021, 13(9): 233. |
| 5 | 张萌谡, 刘春天, 李希今, 等. 基于K-means聚类算法的绩效考核模糊综合评价系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1851-1856. |
| Zhang Meng-su, Liu Chun-tian, Li Xi-jin, et al. Design of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation system for performance appraisal based on K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1851-1856. | |
| 6 | Fränti P, Sieranoja S. How much can K-means be impr-oved by using better initialization and repeats?[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 93: 95-112. |
| 7 | 杨勇, 陈强, 曲福恒, 等. 基于模拟划分的SP-K-means-+算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1808-1816. |
| Yang Yong, Chen Qiang, Qu Fu-heng, et al. SP-K-means-+ algorithm based on simulated partition[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1808-1816. | |
| 8 | Geng X, Mu Y, Mao S, et al. An improved K-means algorithm based on fuzzy metrics[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 217416-217424. |
| 9 | 邵伦, 周新志, 赵成萍, 等. 基于多维网格空间的改进 K-means 聚类算法[J]. 计算机应用,2018, 38(10): 2850-2855. |
| Shao Lun, Zhou Xin-zhi, Zhao Cheng-ping, et al. Improved K-means clustering algorithm based on multidimensional grid space[J]. Computer Application, 2018,38(10): 2850-2855. | |
| 10 | Manochandar S, Punniyamoorthy M, Jeyachitra R K. Development of new seed with modified validity measures for K-means clustering[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 141: 106290. |
| 11 | Zhang S, Liu Z, Chen X, et al. Parallel implementation of improved K-means based on a cloud platform[J]. Information Technology and Control, 2019, 48(4): 673-681. |
| 12 | Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S. K-means++ the advantages of careful seeding[C]∥Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete algorithms, New Orleans, USA, 2007: 1027-1035. |
| 13 | Lattanzi S, Sohler C. A better K-means++ algorithm via local search[C]∥Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning,Long Beach,USA,2019: 3662-3671. |
| 14 | Choo D, Grunau C, Portmann J, et al. K-means++: few more steps yield constant approximation[C]∥Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2020: 1909-1917. |
| 15 | Ismkhan H. Ik-means-+: an iterative clustering algorithm based on an enhanced version of the K-means[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 79: 402-413. |
| 16 | Chowdhury K, Chaudhuri D, Pal A K. An entropy-based initialization method of K-means clustering on the optimal number of clusters[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33: 6965-6982. |
| 17 | Nie F, Xue J, Wu D, et al. Coordinate descent meth-od for k-means[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021,44(5): 2371-2385. |
| 18 | Likas A, Vlassis N, Verbeek J J. The global k-means clustering algorithm[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2003,36(2): 451-461. |
| [1] | 孙帅帅,冯春晓,张良. 基于离散采样的多模态四足机器人路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [2] | 金志刚,苏仁鋆,赵晓芳. 基于异质图网络的心理评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
| [3] | 高敬鹏,王国轩,高路. 基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [4] | 刘浏,丁鲲,刘姗姗,刘茗. 基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [5] | 傅丽芳,陈卓,敖长林. 基于分类和回归树决策树的网络大数据集离群点动态检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2620-2625. |
| [6] | 宋世军,樊敏. 基于随机森林算法的大数据异常检测模型设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2659-2665. |
| [7] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [8] | 谢波,高榕,许富强,田彦涛. 低附着路况条件下人车共享转向系统稳定控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 713-725. |
| [9] | 马月坤,郝益锋. 考虑特征稀疏特性的短文本命名实体快速识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3529-3535. |
| [10] | 刘春晖,王思长,郑策,陈秀连,郝春蕾. 基于深度学习的室内导航机器人避障规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [11] | 白丽丽,姜封国,周玉明,曾枭. 基于改进鲸鱼算法的结构可靠性优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3160-3165. |
| [12] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [13] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [14] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [15] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
|
||