吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 731-740.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230440
基于超连接图卷积网络的骨架行为识别方法
曹毅1,2( ),夏宇1,2,高清源1,2,叶培涛1,2,叶凡1,2
),夏宇1,2,高清源1,2,叶培涛1,2,叶凡1,2
- 1.江南大学 机械工程学院,江苏 无锡 214122
2.江南大学 江苏省食品制造装备重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
Skeleton-based action recognition based on hyper-connected graph convolutional network
Yi CAO1,2( ),Yu XIA1,2,Qing-yuan GAO1,2,Pei-tao YE1,2,Fan YE1,2
),Yu XIA1,2,Qing-yuan GAO1,2,Pei-tao YE1,2,Fan YE1,2
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,China
2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Food Manufacturing Equipment and Technology,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,China
摘要:
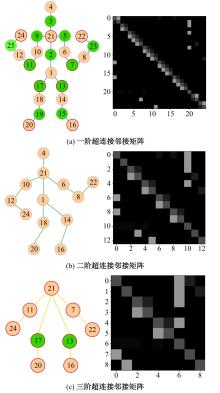
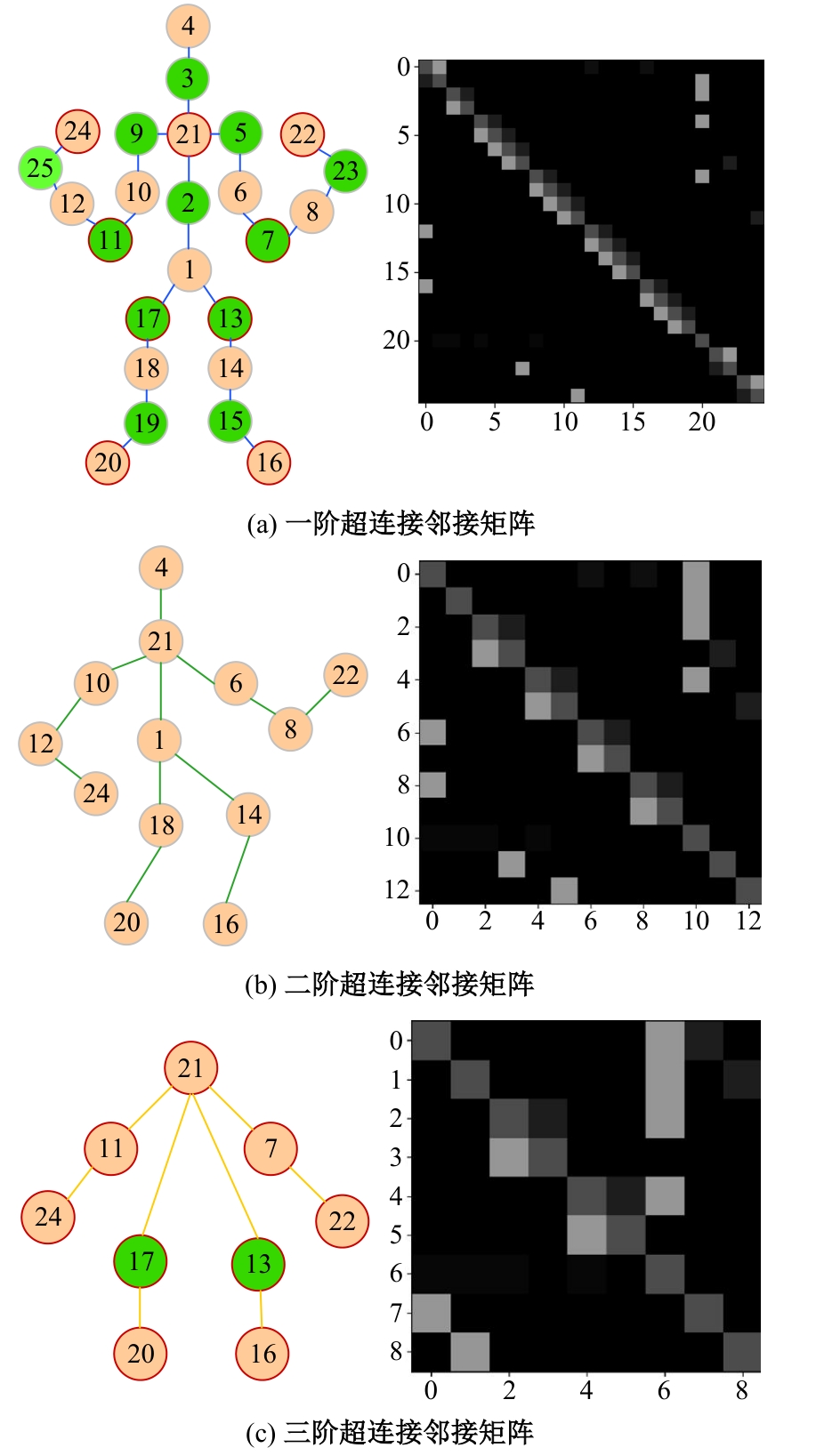
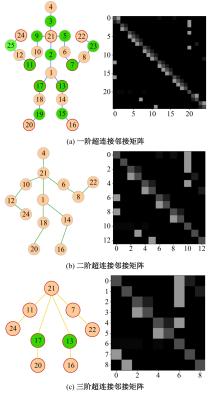
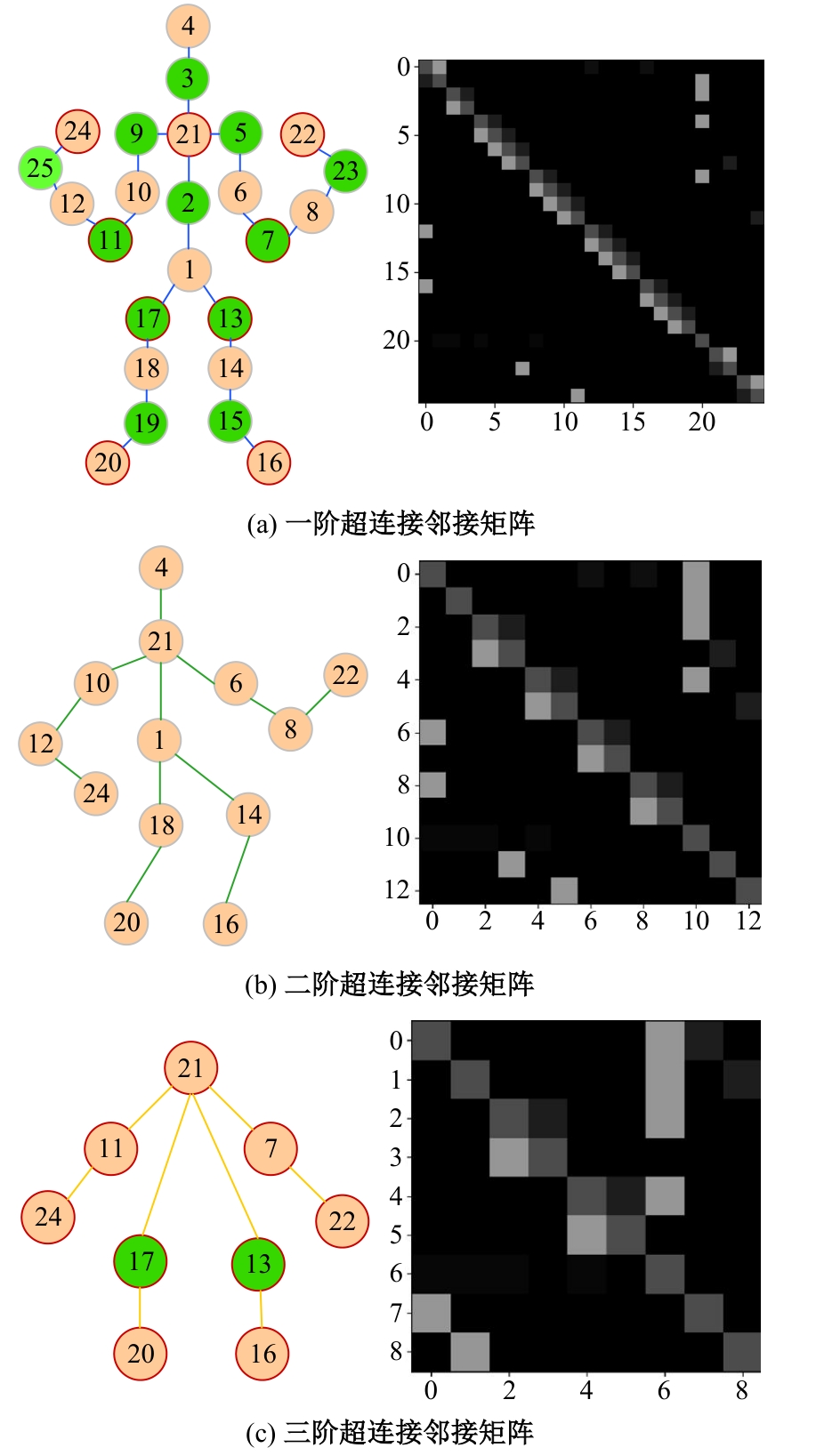
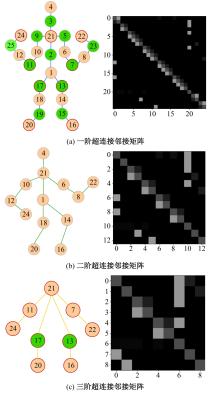
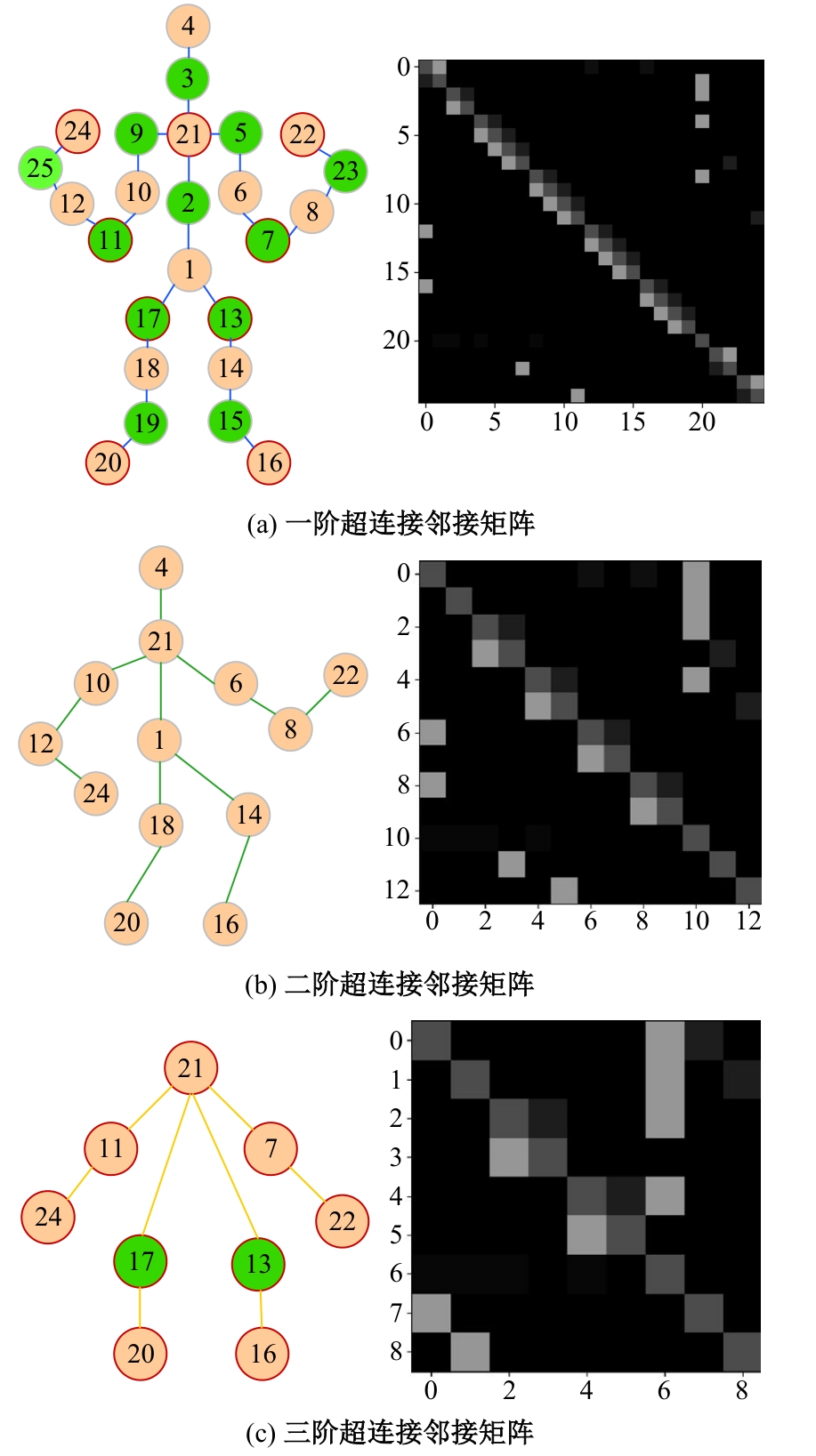
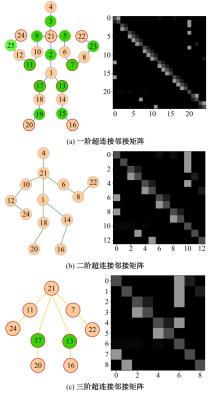
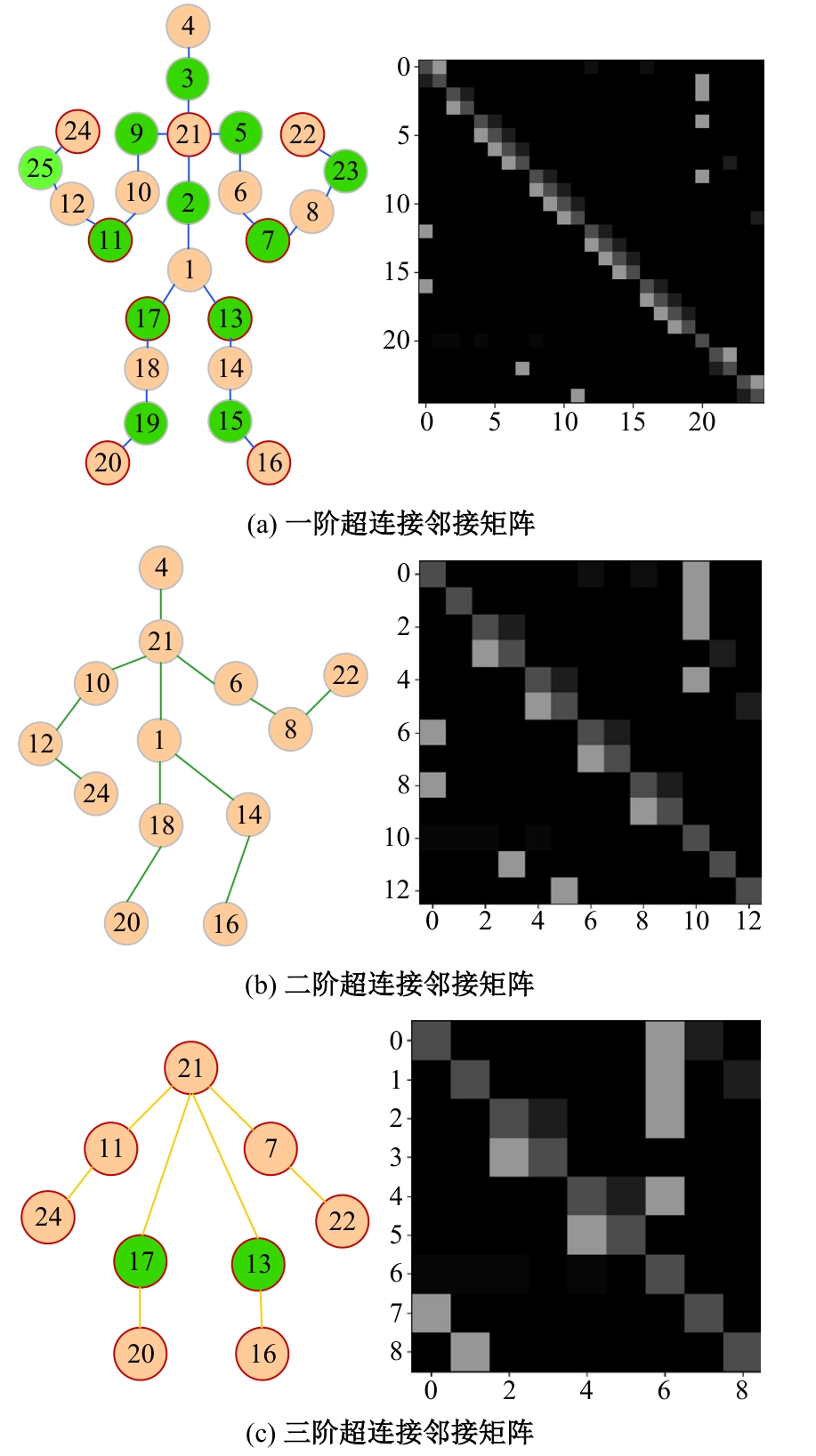
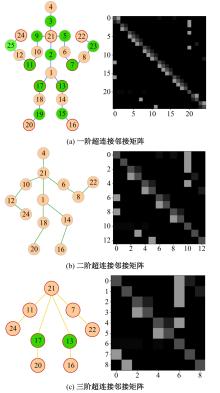
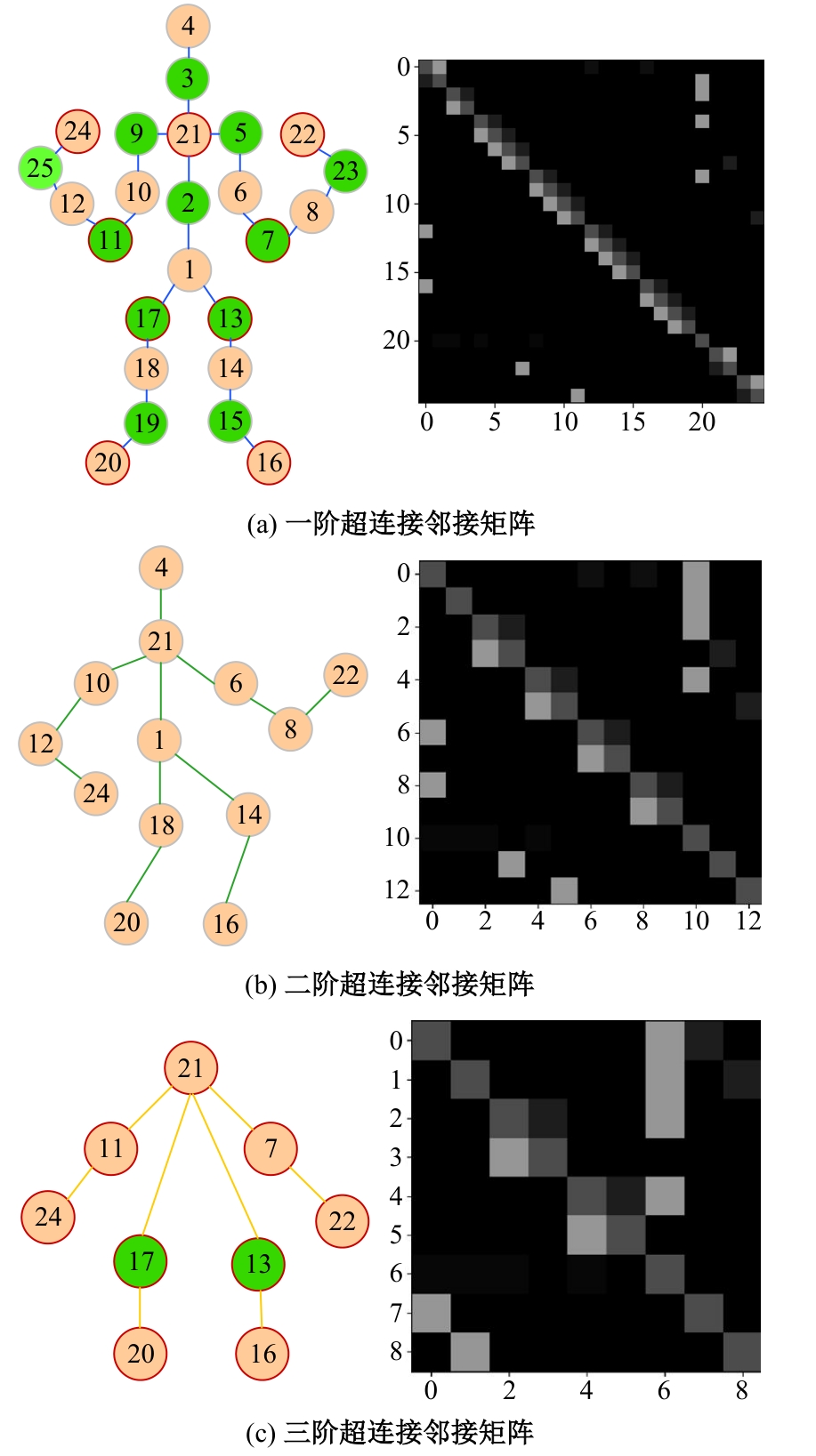
针对现有骨架行为识别方法缺乏对骨架节点长距离多维依赖关系建模且时间特征提取能力弱,导致识别准确率较低和泛化能力较差的问题,提出了一种超连接图卷积网络(HC-GCN)的行为识别模型。首先,介绍了自适应图卷积网络的基本工作原理;其次,提出超连接邻接矩阵的构造方法,并结合多维自适应图卷积模块,进而构造超连接自适应图卷积(HC-AGCN)模块;再次,基于全维动态卷积网络引入残差连接,提出残差全维动态时序卷积(ROD-TCN)模块,并结合HC-AGCN模块,进一步提出HC-GCN模型并在双流三图网络下进行训练;最后,基于NTU-RGB+D和NTU-RGB+D 120数据集开展模型的性能验证实验,实验结果表明:该模型在上述数据集的识别准确率分别为96.7%和89.0%,验证了该模型具有优异的准确率和泛化能力。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Aggarwal J K, Ryoo M S. Human activity analysis: a review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2011, 43(3): 16-28. |
| 2 | 钟忺, 王灿, 卢炎生, 等. 基于ISA网络的视频人体行为分类识别[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 47(2): 103-108. |
| Zhong Xian, Wang Can, Lu Yan-sheng, et al. Video human behavior recognition based on ISA network model[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(2): 103-108. | |
| 3 | 曹毅, 刘晨, 黄子龙, 等. 一种基于DenseNet网络与帧差法特征输入的人体行为识别方法[P]. 中国专利: ZL201910332644.3, 2023-04-07. |
| 4 | 詹健浩, 吴鸿伟, 周成祖, 等. 基于深度学习的行为识别多模态融合方法综述[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2023, 32(1): 41-49. |
| Zhan Jian-hao, Wu Hong-wei, Zhou Cheng-zu, et al. Survey on multi-modality fusion methods for action recognition based on deep learning[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2023, 32(1): 41-49. | |
| 5 | 刘云, 薛盼盼, 李辉, 等. 基于深度学习的节点行为识别综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1789-1802. |
| Liu Yun, Xue Pan-pan, Li Hui, et al. A review of action recognition using joints based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1789-1802. | |
| 6 | Si C, Chen W, Wang W, et al. An attention enhanced graph convolutional LSTM network for skeleton-based action recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1227-1236. |
| 7 | Liu J, Wang G, Hu P, et al. Global context-aware attention LSTM networks for 3D action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3671-3680. |
| 8 | Shi L, Zhang Y, Cheng J, et al. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12018-12027. |
| 9 | 曹毅, 刘晨, 黄子龙, 等. 时空自适应图卷积神经网络的骨架行为识别[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(11): 5-10. |
| Cao Yi, Liu Chen, Huang Zi-long, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition based on spatio-temporal adaptive graph convolutional neural-network[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 5-10. | |
| 10 | Xing Y, Zhu J, Li Y, et al. An improved spatial temporal graph convolutional network for robust skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53: 4592-4608. |
| 11 | 曹毅, 吴伟官, 李平, 等. 基于时空特征增强图卷积网络的骨架行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 3022-3031. |
| Cao Yi, Wu Wei-guan, Li Ping, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition based on spatio-temporal feature enhanced graph convolutional network[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information, 2023, 45(8): 3022-3031. | |
| 12 | Ding C, Wen S, Ding W, et al. Temporal segment graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 110: 104675. |
| 13 | Alsarhan T, Ali U, Lu H. Enhanced discriminative graph convolutional network with adaptive temporal modelling for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2022, 216: 103348. |
| 14 | Yang H, Yan D, Zhang L, et al. Feedback graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 164-175. |
| 15 | Cheng K, Zhang Y, He X, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 180-189. |
| 16 | Li C, Zhong Q, Xie D, et al. Co-occurrence feature learning from skeleton data for action recognition and detection with hierarchical aggregation[C]∥Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 786-792. |
| 17 | Tae S K, Austin R. Interpretable 3D human action analysis with temporal convolutional networks[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, New York, USA, 2017: 1623-1631. |
| 18 | Zhang P, Lan C, Zeng W, et al. Semantics-guided neural networks for efficient skeleton-based human action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1109-1118. |
| 19 | Henaff M, Bruna J, Le C Y. Deep convolutional networks on graph structured data[J/OL]. [2023-04-15]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: . |
| 20 | 曹毅, 夏宇, 高清源, 等. 基于动态时序多维自适应图卷积网络的骨架行为识别方法[P]. 中国专利: ZL115661861A, 2022-01-31. |
| 21 | Li C, Zhou A, Yao A. Omni-dimensional dynamic convolution[J/OL]. [2023-04-16]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2209.07947v1. |
| 22 | Amir S, Liu J, Ng T T, et al. NTU RGB+D: a large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2016: 1010-1019. |
| 23 | Liu J, Shahroudy A, Perez M, et al. NTU RGB+D 120: a large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2684-2701. |
| [1] | 井佩光,田雨豆,汪少初,李云,苏育挺. 基于动态扩散图卷积的交通流量预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1582-1592. |
| [2] | 曲福恒,潘曰涛,杨勇,胡雅婷,宋剑飞,魏成宇. 基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [3] | 孙帅帅,冯春晓,张良. 基于离散采样的多模态四足机器人路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [4] | 金志刚,苏仁鋆,赵晓芳. 基于异质图网络的心理评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
| [5] | 高敬鹏,王国轩,高路. 基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [6] | 刘浏,丁鲲,刘姗姗,刘茗. 基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [7] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [8] | 刘春晖,王思长,郑策,陈秀连,郝春蕾. 基于深度学习的室内导航机器人避障规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [9] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [10] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [11] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [12] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [13] | 王秀芳,孙双,丁春阳. 基于1D⁃RSCNN的嵌入式轴承故障实时检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 310-317. |
| [14] | 雷景佩,欧阳丹彤,张立明. 基于知识图谱嵌入的定义域值域约束补全方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 154-161. |
| [15] | 李志华,张烨超,詹国华. 三维水声海底地形地貌实时拼接与可视化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 180-186. |
|
||