吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 766-772.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180252
路基土抗剪强度与化学及矿物成分的关系
- 1. 吉林建筑大学 交通科学与工程学院, 长春 130118
2. 吉林大学 交通学院,长春130022
3. 吉林省高等级公路建设局, 长春 130033
Analysis of relationship between subgrade soil shear strength and chemical and minerals component
Jing WANG1( ),Xiang LYU2,Xiao⁃long QU3,Chun⁃ling ZHONG1(
),Xiang LYU2,Xiao⁃long QU3,Chun⁃ling ZHONG1( ),Yun⁃long ZHANG1
),Yun⁃long ZHANG1
- 1. School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Jilin Jianzhu University, Changchun 130118, China
2. College of Transportation, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
3. Jilin Provincial High Class Highway Construction Bureau, Changchun 130033, China
摘要:
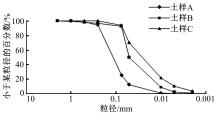
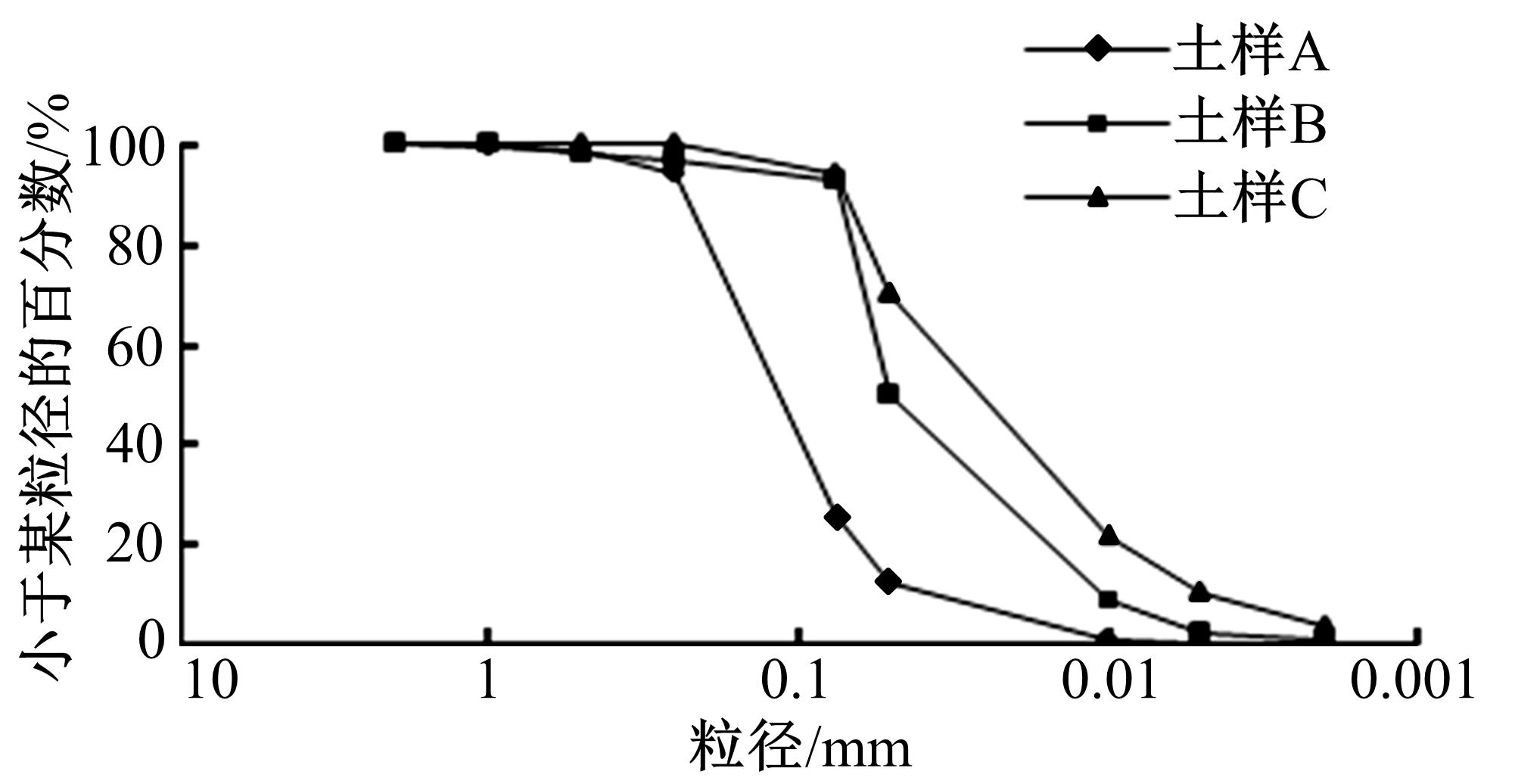
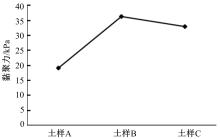
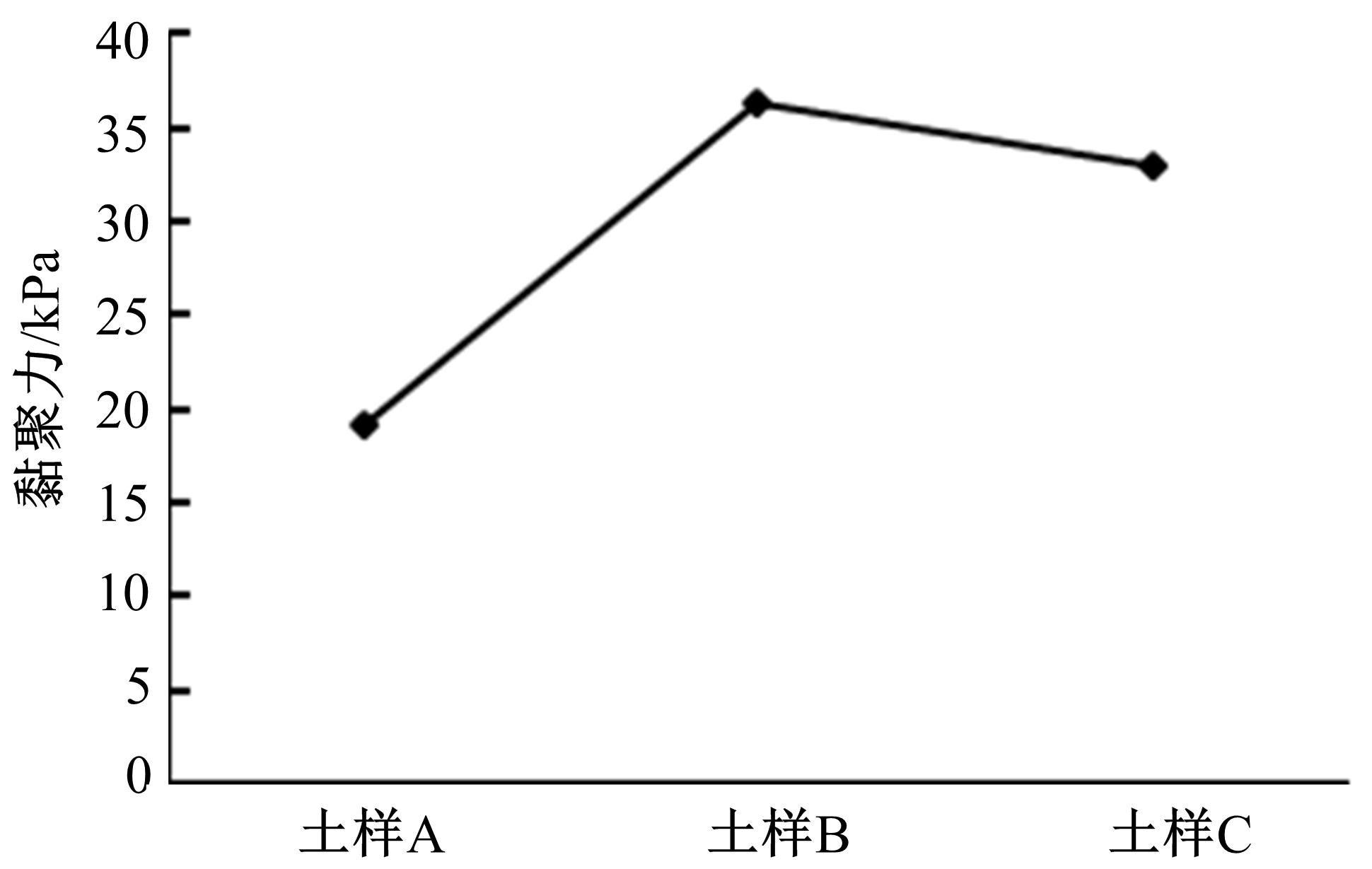
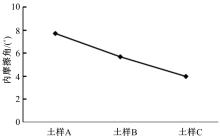
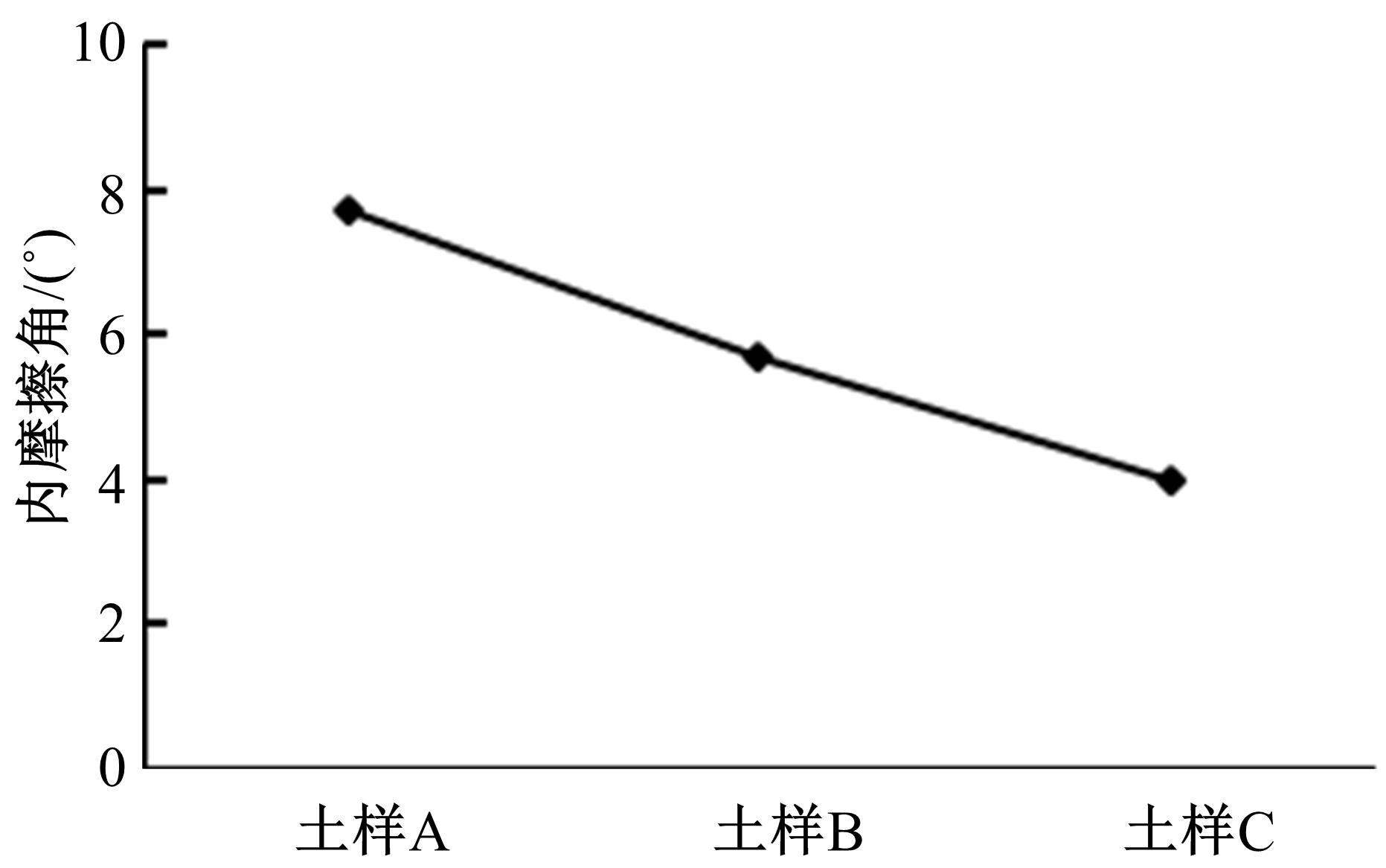
为了从矿化组成层面上揭示路基土宏观力学特性的变化规律,对不同塑性指数路基土进行了化学主次成分量测定、全岩矿物组成和黏土矿物相对含量测定,基于灰色关联理论,分析了各矿物含量与路基土抗剪强度及其参数(黏聚力和内摩擦角)的关联性。研究结果表明:在土样的化学成分中,FeO、K2O和SiO2与土样的抗剪强度关联最大,且关联度均大于0.9;P2O5与黏聚力关联最大,关联度大于0.85;Na2O、SiO2、K2O和FeO与土样的内摩擦角有较大关联,其中Na2O、SiO2与土样的关联度大于0.9,K2O、FeO的关联度大于0.8。在全岩矿物组成方面,碱性长石(fs)和石英(Q)与土样的抗剪强度、内摩擦角和黏聚力均有密切关联,关联度大于0.9;而斜长石(Pl)与土样的宏观力学特性关联度很低,可以忽略其含量对抗剪强度及其参数的影响。在黏土矿物相对含量方面,伊利石和蒙脱石混层(I/S)与土样的抗剪强度、黏聚力、内摩擦角均有密切关联;伊利石(I)在一定程度上与土样的黏聚力关联度较大;高岭石(K)与土样的抗剪强度及其参数的关联度不大,在分析土的宏观力学特性时可以不予考虑。
中图分类号:
- U416.1
| 1 | 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2014:114⁃116. |
| 2 | 龚晓南. 软黏土地基土体抗剪强度若干问题[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(10):1596⁃1600. |
| GongXiao⁃nan. Some problems concerning shear strength of soil in soft clay ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(10):1596⁃1600. | |
| 3 | 周波. 公路路基黄土的湿陷性评价方法研究[D].长春:吉林大学建设工程学院,2009. |
| ZhouBo. Study on collapsibility evaluation method of loess in roadbed[D]. Changchun:College of Construction Engineering,Jilin University,2009. | |
| 4 | 柏立懂. 合徐高速公路南段膨胀土矿物成分及微结构[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2005(4):13⁃16. |
| BaiLi⁃dong. Mineral composition and microstructure of expansive soil in south part of Hefei⁃Xuzhou Expressway[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2005(4):13⁃16. | |
| 5 | 柏立懂. 合徐合安高速公路膨胀土的矿物化学成分及微结构的研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学资源与环境工程学院,2005. |
| BaiLi⁃dong. Research on the composition of expansive soil of He⁃Xu and He⁃An expressway and its microstructure[D]. Hefei:School of Resources and Environment,Hefei University of Technology,2005. | |
| 6 | 闫瑞敏,桂蕾. 滑带土抗剪强度与其矿物成分典型相关性分析[J]. 人民长江,2016,47(8):47⁃50. |
| YanRui⁃min,GuiLei. Canonical correlation analysis between shear strength and mineral composition of sliding zone soil [J]. Yangtze River,2016,47(8):47⁃50. | |
| 7 | 王小花,刘红军,贾永刚. 黄河口粉质土矿物成分特征及对水动力条件相应的研究[J]. 海洋科学,2008,32(2):42⁃46. |
| WangXiao⁃hua, LiuHong⁃jun, JiaYong⁃gang. The research on the mineral characteristics of sediment and the response to the hydrodynamic conditions of the tidal flat, at the northern Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Sciences,2008,32(2):42⁃46. | |
| 8 | 何蕾. 矿物成分与水化学成分对粘性土抗剪强度的控制规律及其应用[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京)水资源与环境学院,2014. |
| HeLei. Impact of mineralogical composition and water chemistry on the shear strength of clay and its application [D]. Beijing: Institute of Water Resources and Environment,China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2014. | |
| 9 | 李景阳,梁风,朱立军,等. 两种典型碳酸盐红土风化剖面的物理化学特征[J]. 中国岩溶,2005,24(1):28⁃34. |
| LiJing⁃yang,LiangFeng,ZhuLi⁃jun,et al. Physical and chemical properties of two typical weathered profiles of carbonate rocks[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2005,24(1):28⁃34. | |
| 10 | 陈积普,徐则民. 某路基边坡化学风化机理研究[J].水文地质工程地质,2014,41(6):134⁃140. |
| ChenJi⁃pu,XuZe⁃min. Study on chemical weathering mechanisms of a roadbed slope[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2014,41(6):134⁃140. | |
| 11 | JTG E40—2007.公路土工试验规程[S]. |
| 12 | JTG F10—2006.公路路基施工技术规范[S]. |
| 13 | GB/T14506.28—2010. 硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第28部分:16个主次成分量测定[S]. |
| 14 | JY/T009—1996. 转靶多晶体X射线衍射方法通则[S]. |
| 15 | 王毅,岳光华,李维. 石灰岩矿物成分对其集料磨光值的灰色关联分析[J].江苏大学学报:自然科学版,2015,36(3):353⁃356,372. |
| Wang Yi Yue Guang⁃hua Li We. Analysis of grey incidence between limestone mineral composition and polishing value of aggregate[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University(Natural Science Edition), 2015,36(3):353⁃356,372. | |
| 16 | 单黎黎,何向东,钟志明,等. 基于n阶灰色补偿因子的装备维修保障费用预测模型[J]. 江苏大学学报:自然科学版,2014,35(6):685⁃692. |
| ShanLi⁃li,HeXiang⁃dong,ZhongZhi⁃ming,et al. Prediction model of equipment maintenance support cost based on n⁃order gray system theory[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University(Natural Science Edition), 2014,35(6):685⁃692. | |
| 17 | 林文玉. 岩土物理力学性质指标的关联度分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2007(2):27⁃28. |
| LinWen⁃Yu. Correlative degree analysis of physical and mechanical properties of geotechnical[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2007(2):27⁃28. |
| [1] | 黄晓明,曹青青,刘修宇,陈嘉颖,周兴林. 基于路表分形摩擦理论的整车雨天制动性能模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [2] | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军. 沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [3] | 臧国帅, 孙立军. 基于惰性弯沉点的刚性下卧层深度设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [4] | 念腾飞, 李萍, 林梅. 冻融循环下沥青特征官能团含量与流变参数灰熵分析及微观形貌[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [5] | 邱小明, 王银雪, 姚汉伟, 房雪晴, 邢飞. 基于灰色关联的DP1180/DP590异质点焊接头工艺参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1147-1152. |
| [6] | 宫亚峰, 申杨凡, 谭国金, 韩春鹏, 何钰龙. 不同孔隙率下纤维土无侧限抗压强度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [7] | 程永春, 毕海鹏, 马桂荣, 宫亚峰, 田振宏, 吕泽华, 徐志枢. 纳米TiO2/CaCO3-玄武岩纤维复合改性沥青的路用性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [8] | 张仰鹏, 魏海斌, 贾江坤, 陈昭. 季冻区组合冷阻层应用表现的数值评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [9] | 季文玉, 李旺旺, 过民龙, 王珏. 预应力RPC-NC叠合梁挠度试验及计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 129-136. |
| [10] | 马晔, 尼颖升, 徐栋, 刁波. 基于空间网格模型分析的体外预应力加固[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
| [11] | 罗蓉, 曾哲, 张德润, 冯光乐, 董华均. 基于插板法膜压力模型的沥青混合料水稳定性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1753-1759. |
| [12] | 尼颖升, 马晔, 徐栋, 李金凯. 波纹钢腹板斜拉桥剪力滞效应空间网格分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1453-1464. |
| [13] | 郑传峰, 马壮, 郭学东, 张婷, 吕丹, 秦泳. 矿粉宏细观特征耦合对沥青胶浆低温性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1465-1471. |
| [14] | 于天来, 郑彬双, 李海生, 唐泽睿, 赵云鹏. 钢塑复合筋带挡土墙病害及成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1082-1093. |
| [15] | 蔡氧, 付伟, 陶泽峰, 陈康为. 基于扩展有限元模型的土工布防荷载型反射裂缝影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 765-770. |
|