吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1427-1436.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200588
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
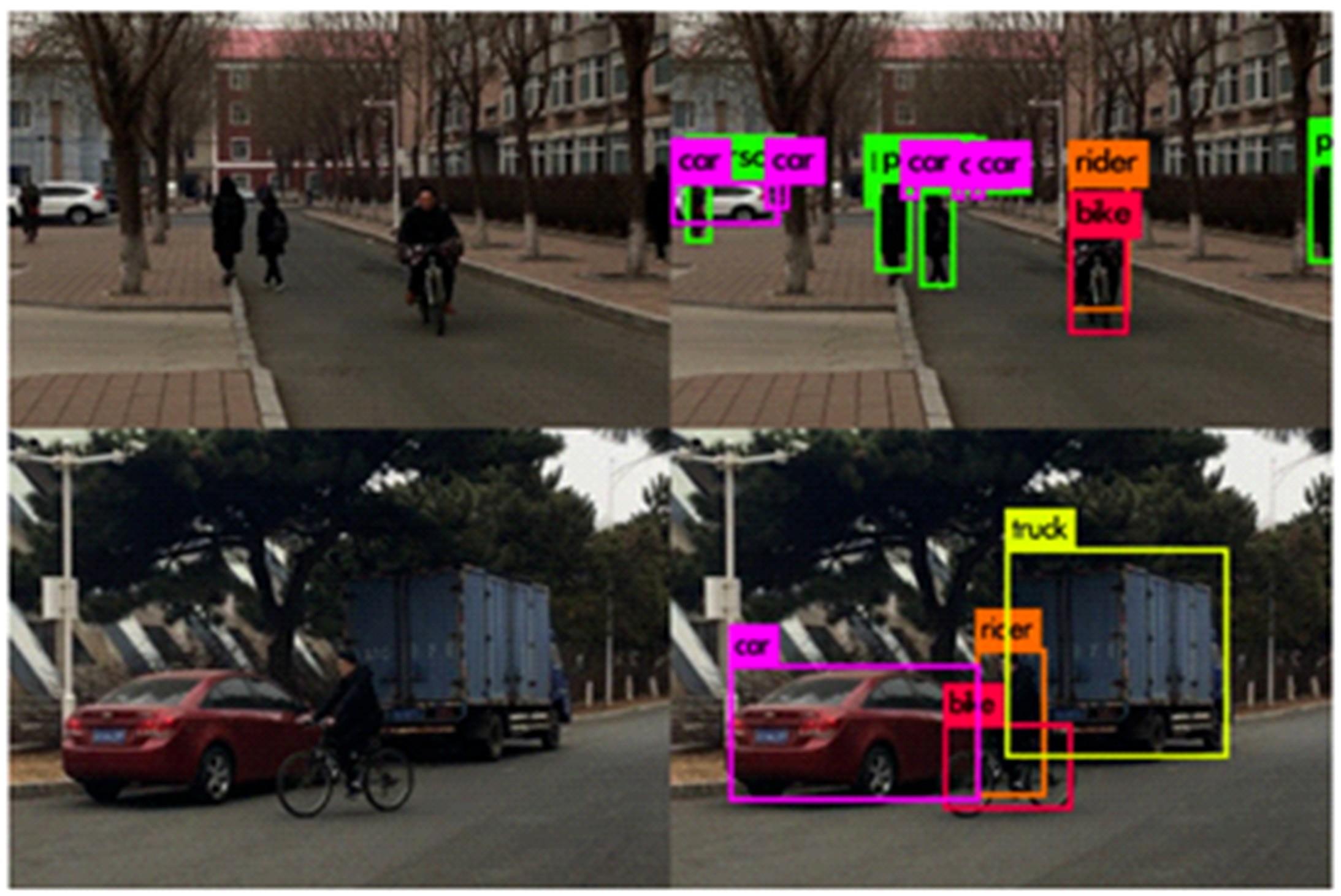
基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法
- 1.燕山大学 车辆与能源学院,河北 秦皇岛 066004
2.燕山大学 河北省特种运载装备重点实验室,河北 秦皇岛 066004
3.吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
4.北京理工大学 机械与车辆学院,北京 100081
Dynamic multiple object detection algorithm for vehicle forward based on improved YOLOv3
Li-sheng JIN1,2( ),Bai-cang GUO1,Fang-rong WANG3,Jian SHI4(
),Bai-cang GUO1,Fang-rong WANG3,Jian SHI4( )
)
- 1.School of Vehicle and Energy,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066004,China
2.Hebei Key Laboratory of Special Delivery Equipment,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066004,China
3.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
4.School of Mechanical Engineering,Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing 100081,China
摘要:
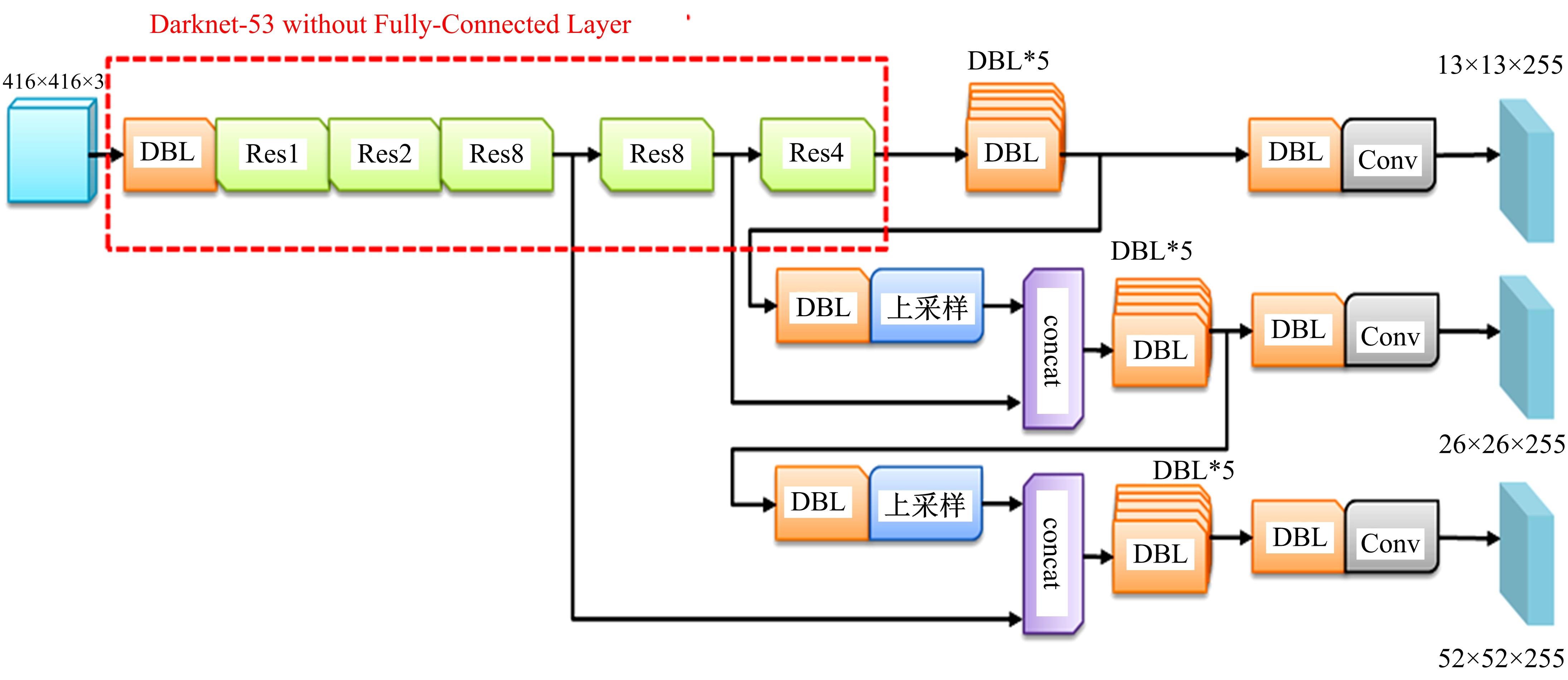
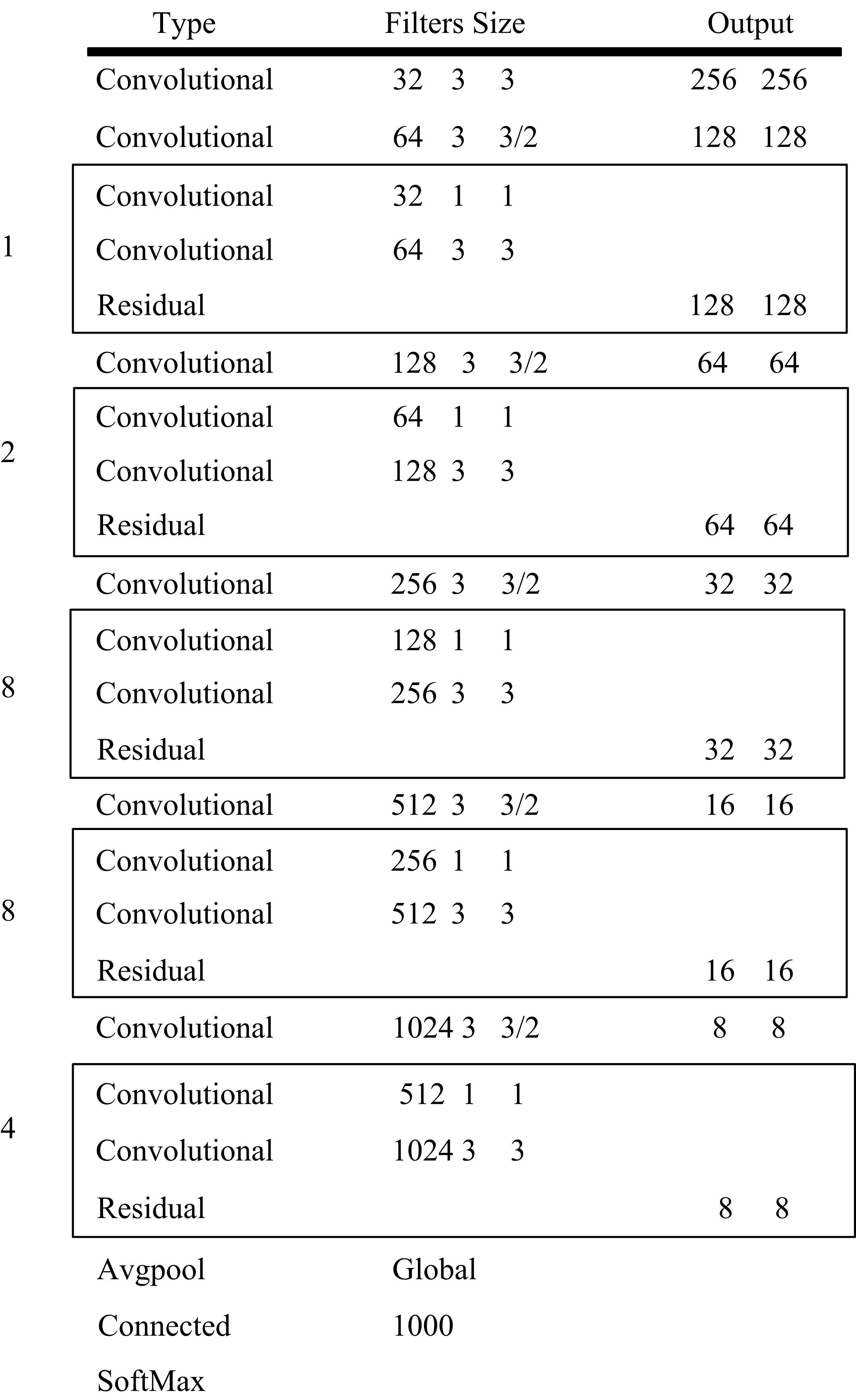
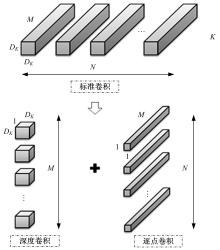
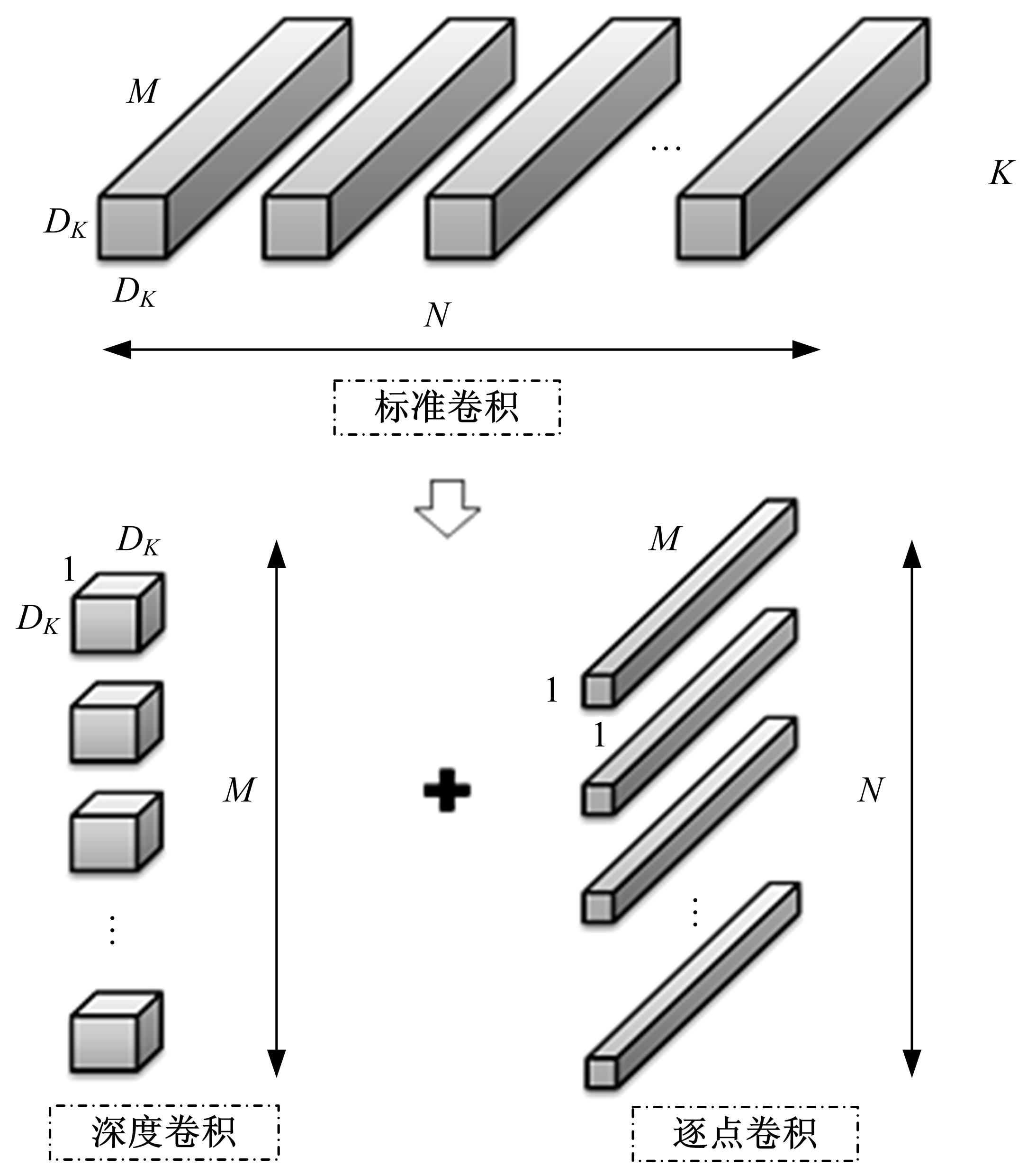
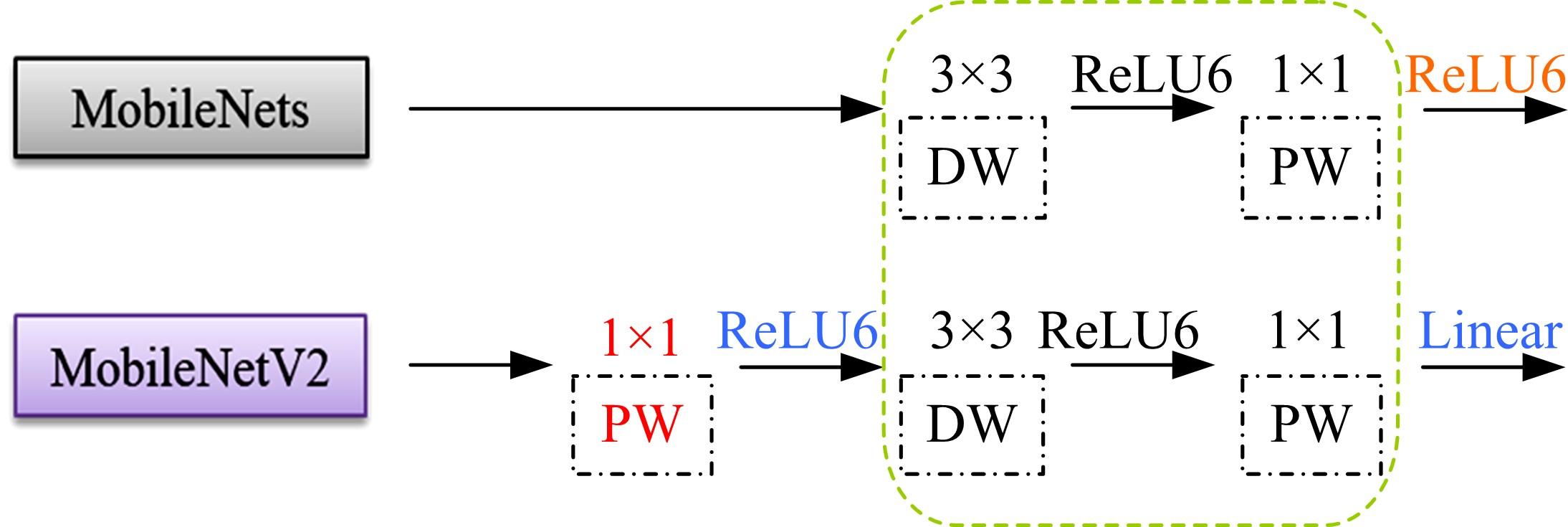
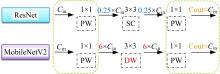
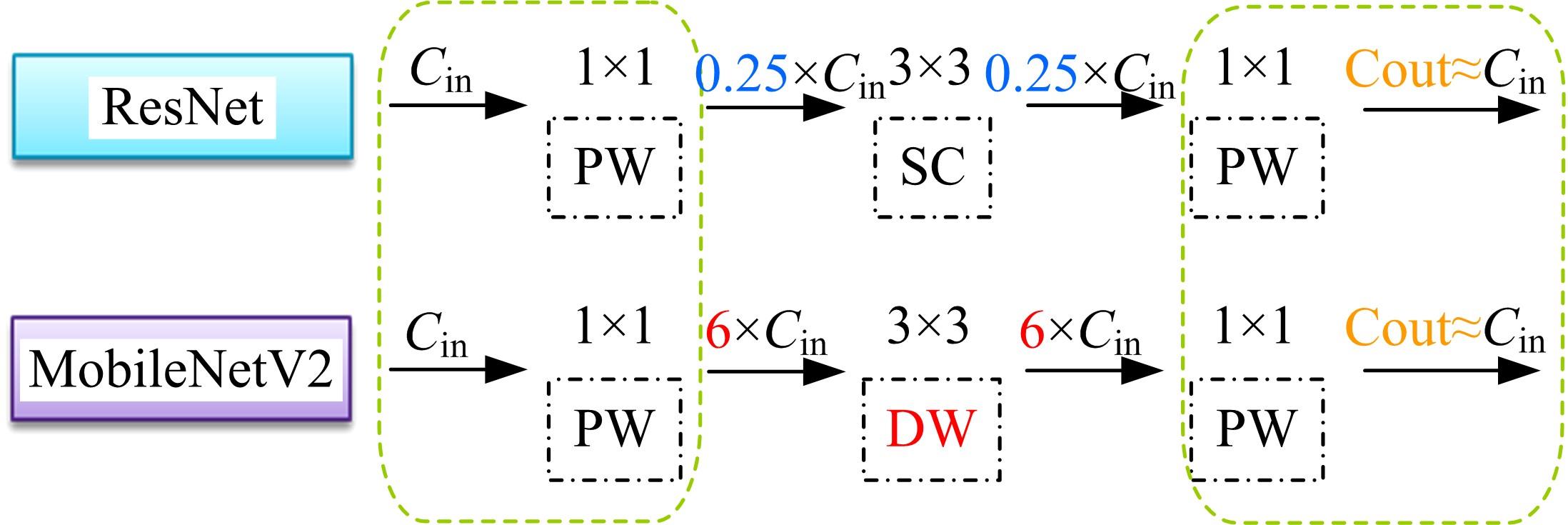
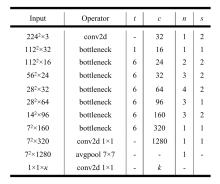
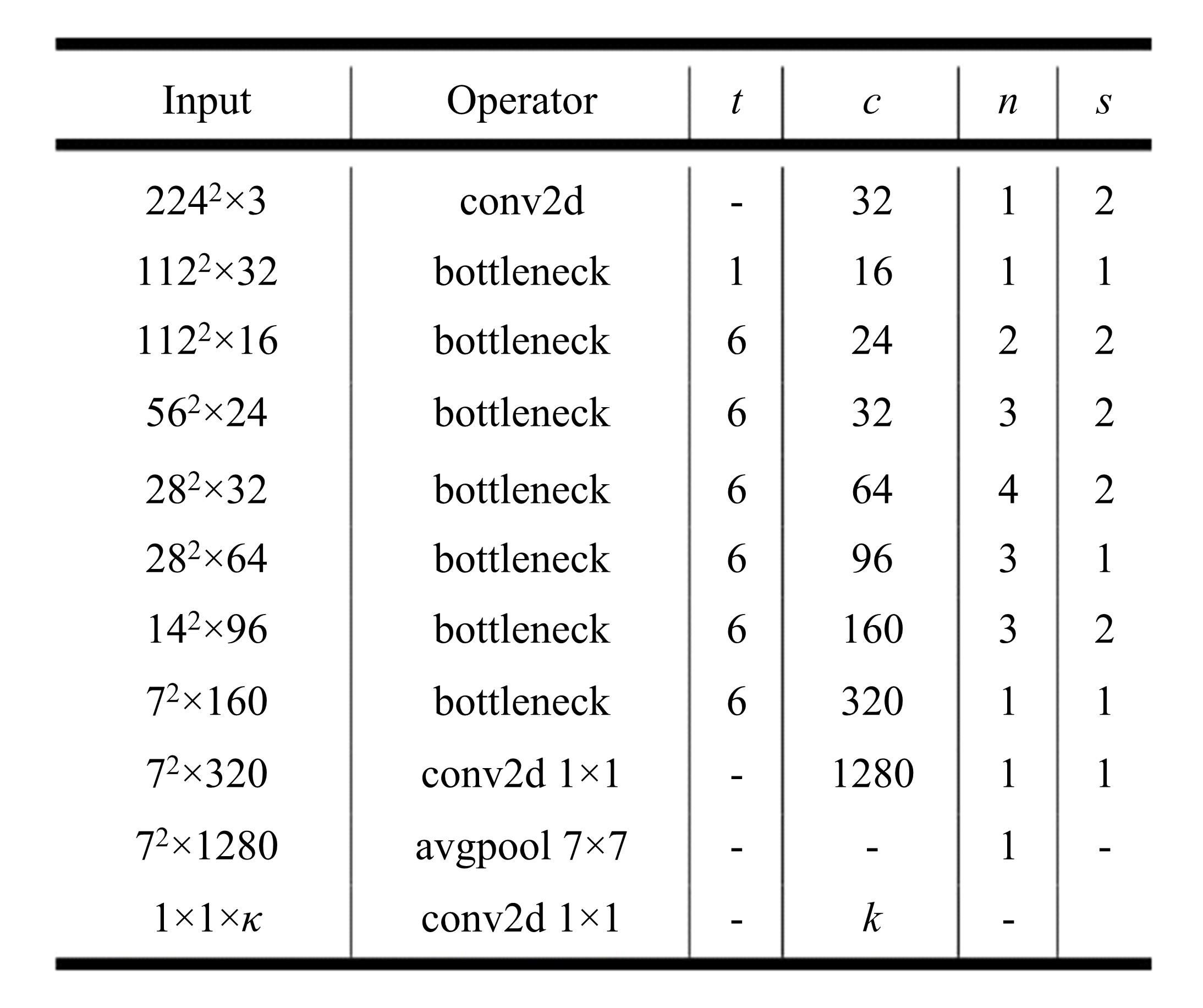
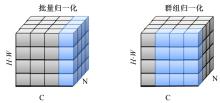
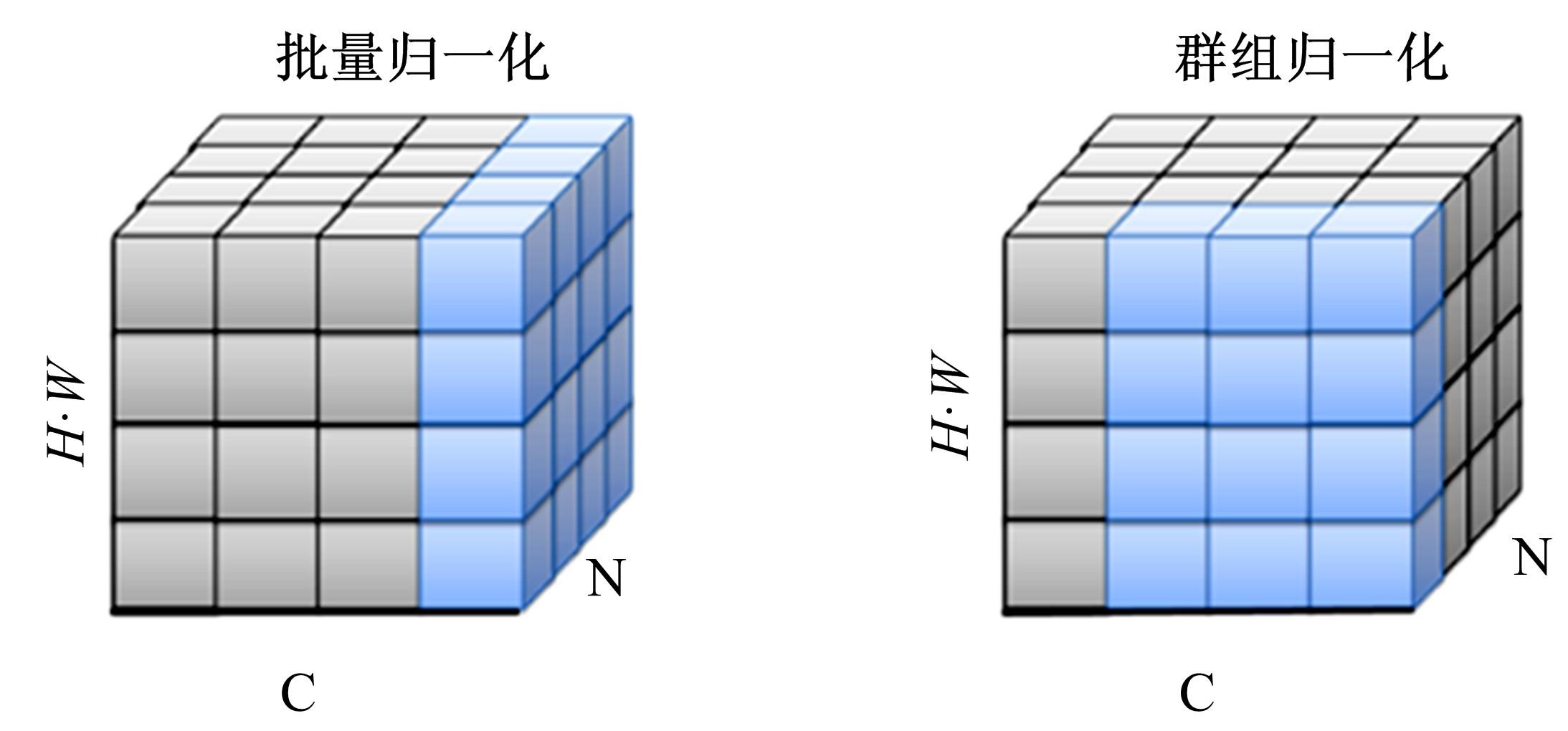
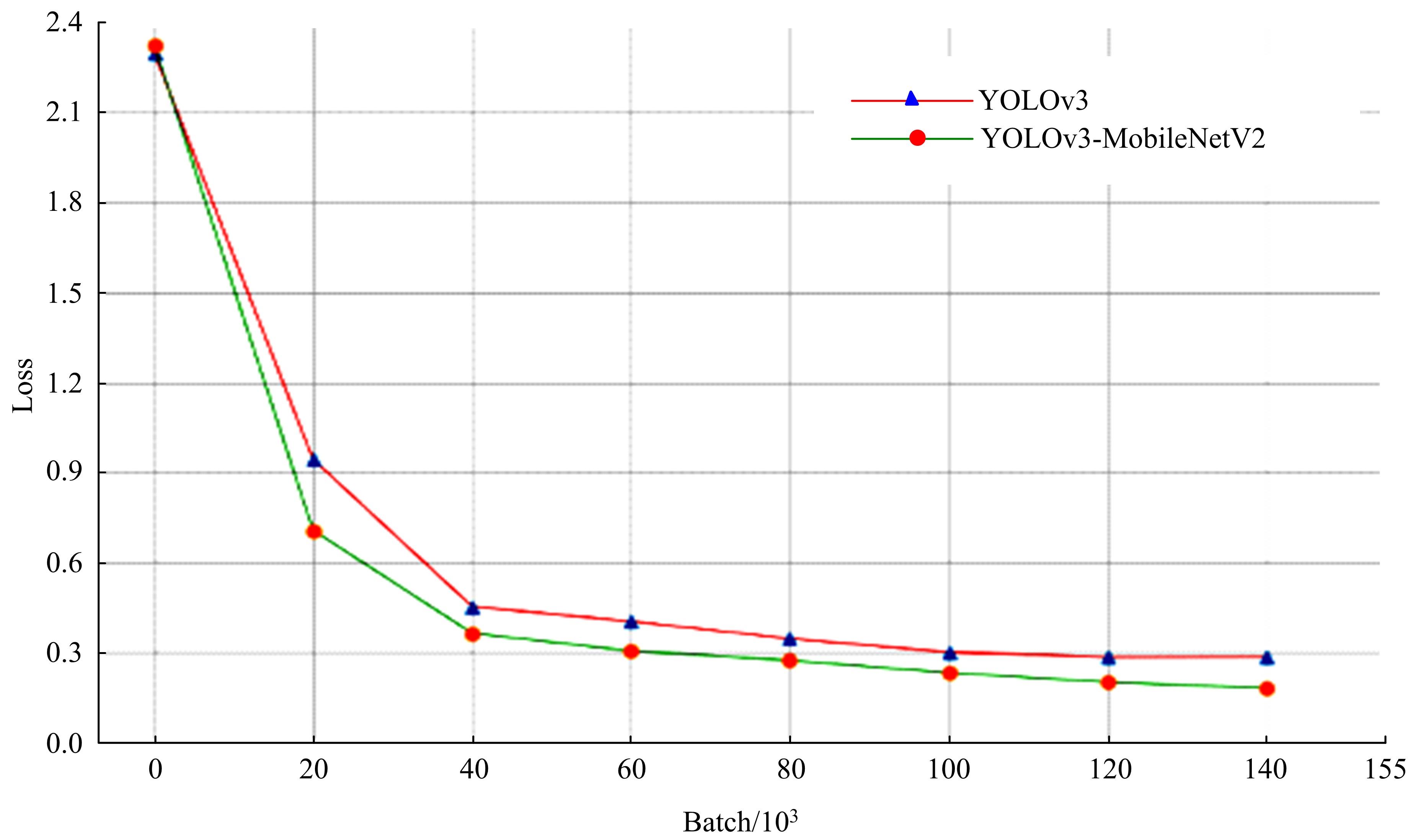
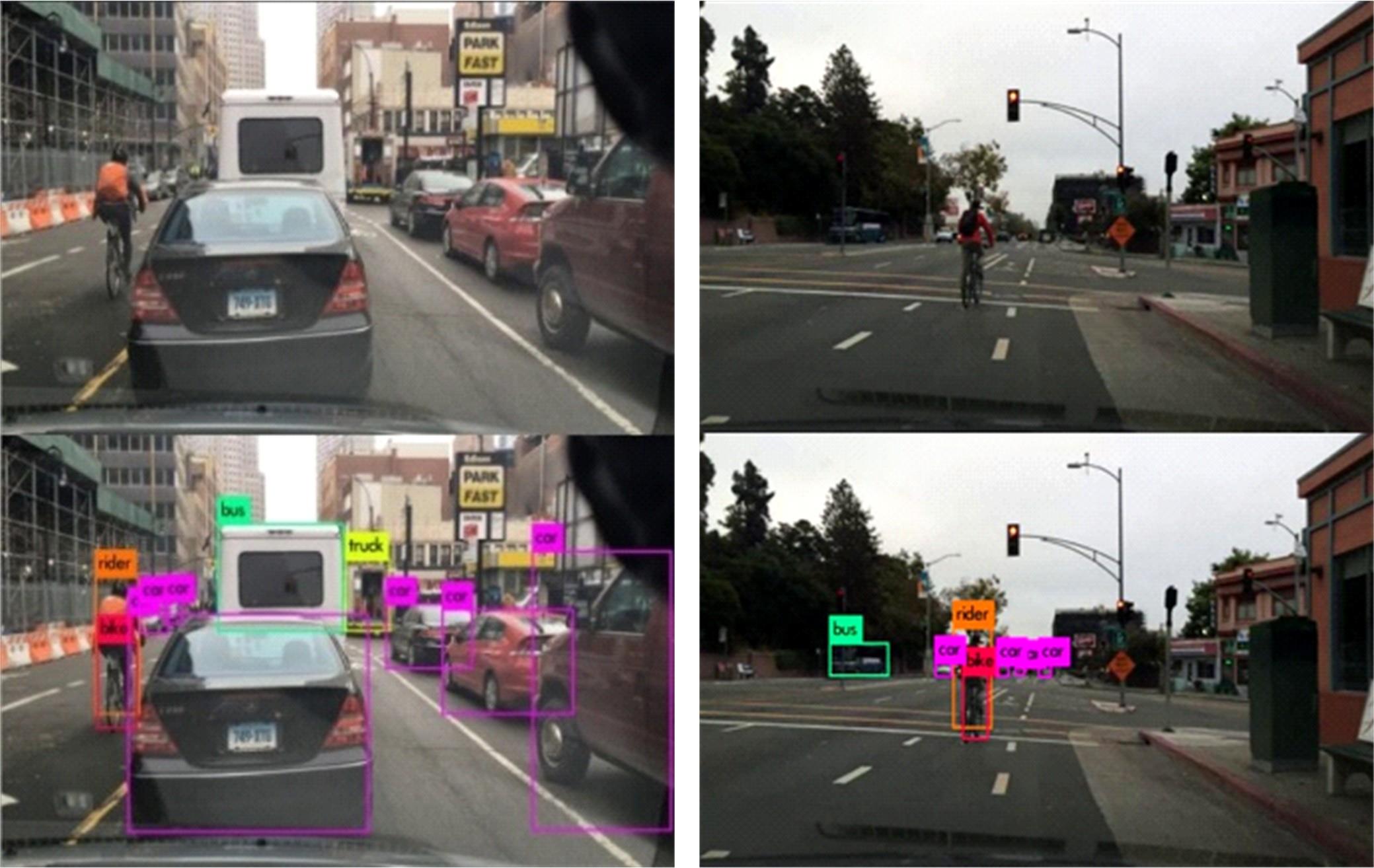
现阶段的环境感知目标检测技术多为单类目标检测,或是将一幅图像中所有目标均列为待检目标,较少有对处于车辆前方的目标进行针对性的划分和检测。为了解决以上问题,提出了将车辆前方的待检目标分为两类:一是危险性较大,随时可能发生位移的动态目标,包括四轮车辆、二轮车辆和人;二是危险性较小,不会发生位移的静态目标,包括交通信号灯和交通标识。针对危险性较大的车辆前方动态多目标,提出了一种可以移植于嵌入式端的改进YOLOv3的目标检测算法,针对原始YOLOv3算法得到模型较大,难以在嵌入式端实时检测的缺点,以轻量型骨干网络MobileNetV2替换YOLOv3原始骨干网络Darknet-53进行特征提取,在训练中加入群组归一化操作,并使用Adam作为优化器。使用提取后的BDD100K数据集进行训练,利用未参与训练的BDD100K部分数据集和自采标注的Team_test数据集进行测试。研究结果表明,相比于原始YOLOv3算法,本文算法的漏检率可以维持在5%以内,在mAP提升0.020的基础上,本文模型在参数量上较YOLOv3基础模型减小了约89%,在CPU下的Inference Time缩小了约70%。
中图分类号:
- U491.2
| 1 | Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, USA, 2005:886-893. |
| 2 | Platt J C. A fast algorithm for training support vector machines[J]. Journal of Information Technology, 1998, 2(5):1-28. |
| 3 | Felzenszwalb P, McAllester D, Ramaman D. A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Anchorage, USA, 2008:1-8. |
| 4 | Felzenszwalb P, Girshick R, McAllester D, et al. Object detection with discriminatively trained partbased models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9):1627-1645. |
| 5 | Felzenszwalb P, Girshick R, McAllester D. Cascade object detection with deformable part models[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2241-2248. |
| 6 | Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets [J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554. |
| 7 | 李晓飞. 基于深度学习的行人及骑车人车载图像识别方法[D]. 北京:清华大学军事交通学院, 2016. |
| Li Xiao-fei. On-board pedestrian and cyclist recognition using deep learning methods[D]. Beijing: Military Transport Academy,Tsinghua University, 2016. | |
| 8 | 李珊珊. 基于深度学习的交通场景多目标检测[D]. 长沙:湖南大学会计学院,2017. |
| Li Shan-shan. The research of multi-object detection in traffic scene based on deep learning[D]. Changsha:School of Accounting, Hunan University, 2017. | |
| 9 | 杨恺, 徐友春, 安相璧, 等. 基于深度学习的车辆检测方法[J]. 计算机与网络, 2018, 44(19): 58-61. |
| Yang Kai, Xu You-chun, An Xiang-bi,et al. Vehicle detection method based on deep learning[J]. Computer & Network, 2018, 44(19): 58-61. | |
| 10 | 华夏, 王新晴, 王东, 等. 基于改进SSD的交通大场景多目标检测[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(12): 221-231. |
| Hua Xia, Wang Xin-qing, Wang Dong, et al. Multi-objective detection of traffic scenes based on improved SSD[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 221-231. | |
| 11 | Dhall A, Dai D, van Gool L. Real-time 3D traffic cone detection for autonomous driving[C]∥The 30th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Paris, France, 2019: 494-501. |
| 12 | 李大华, 汪宏威, 高强, 等. 一种卷积神经网络的车辆和行人检测算法[J]. 激光杂志, 2020, 41(4):70-75. |
| Li Da-hua, Wang Hong-wei, Gao Qiang, et al. Vehicle and pedestrian detection algorithm based on convolutional neural network[J]. Laser Journal, 2020, 41(4):70-75. | |
| 13 | 新华网. 报告显示:2019年我国外卖行业交易额预计超6000亿元[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(1):157. |
| net Xinhua. Report shows: in 2019, China's foreign sales industry transactions are expected to exceed 600 billion yuan[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(1):157. | |
| 14 | Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrelland T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for object detection and semantic segmentation[C]∥The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, USA, 2014: 580-587. |
| 15 | Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]∥The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779-788. |
| 16 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517-6525. |
| 17 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018. |
| 18 | Lin T Y, Dollar P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936-944. |
| 19 | Mark Sandler, Andrew Howard, Zhu Meng-long, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510-4520. |
| 20 | Howard A G, Zhu M, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[Z]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2017. |
| 21 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 22 | Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]∥International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lile, France, 2015: 448-456. |
| 23 | Wu Yu-xin, He Kai-ming. Group normalization[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany,2018: 3-19. |
| 24 | Qian N. On the momentum term in gradient descent learning algorithms[J]. Neural Networks, 1999, 12(1):145-151. |
| 25 | Duchi J, Hazan E, Singer Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12(7):257-269. |
| 26 | Kingma D, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[DB/OL]. [2018-10-22]. . |
| 27 | Yu F, Xian W, Chen Y, et al. BDD100K: a diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2633-2642. |
| [1] | 于向军,槐元辉,姚宗伟,孙中朝,俞安. 工程车辆无人驾驶关键技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. |
| [2] | 李锦青,周健,底晓强. 基于循环生成对抗网络的学习型光学图像加密方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1060-1066. |
| [3] | 宋震,李俊良,刘贵强. 基于深度学习和限幅模糊的变转速液压动力源恒流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| [4] | 袁哲明,袁鸿杰,言雨璇,李钎,刘双清,谭泗桥. 基于深度学习的轻量化田间昆虫识别及分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [5] | 彭博,张媛媛,王玉婷,唐聚,谢济铭. 基于自动编码机-分类器的视频交通状态自动识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [6] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [7] | 谌华,郭伟,闫敬文,卓文浩,吴良斌. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1778-1787. |
| [8] | 郜峰利,陶敏,李雪妍,何昕,杨帆,王卓,宋俊峰,佟丹. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| [9] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [10] | 郭立民,陈鑫,陈涛. 基于AlexNet模型的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 1000-1008. |
| [11] | 王新竹, 李骏, 李红建, 尚秉旭. 基于三维激光雷达和深度图像的自动驾驶汽车障碍物检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 360-365. |
| [12] | 李抵非, 田地, 胡雄伟. 基于分布式内存计算的深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 921-925. |
| [13] | 王荣本;李琳辉;郭烈;金立生;张明恒 . 基于立体视觉的越野环境感知技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(03): 520-0524. |
|
||