吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 678-684.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190623
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割
郜峰利1,2( ),陶敏1,2,李雪妍1,2,何昕3,杨帆3,王卓3,宋俊峰1,2,佟丹3(
),陶敏1,2,李雪妍1,2,何昕3,杨帆3,王卓3,宋俊峰1,2,佟丹3( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 电子科学与工程学院, 长春 130012
2.吉林大学 集成光电子学国家重点实验室, 长春 130012
3.吉林大学 第一医院 放射科, 长春 130021
Accurate segmentation of stroke in CT image based on deep learning
Feng-li GAO1,2( ),Min TAO1,2,Xue-yan LI1,2,Xin HE3,Fan YANG3,Zhuo WANG3,Jun-feng SONG1,2,Dan TONG3(
),Min TAO1,2,Xue-yan LI1,2,Xin HE3,Fan YANG3,Zhuo WANG3,Jun-feng SONG1,2,Dan TONG3( )
)
- 1.College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2.State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
3.Radiology, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
摘要:
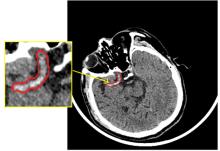
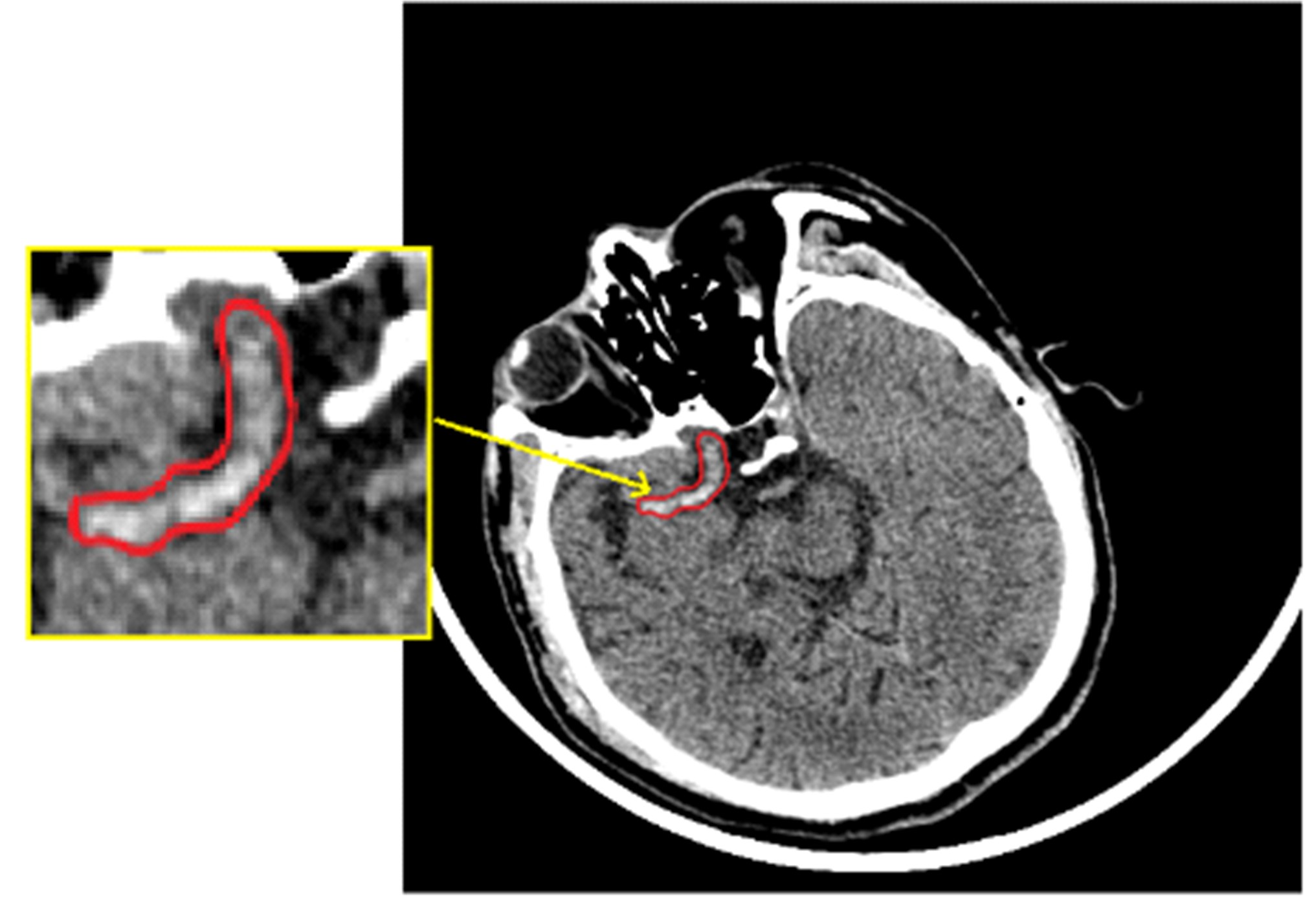
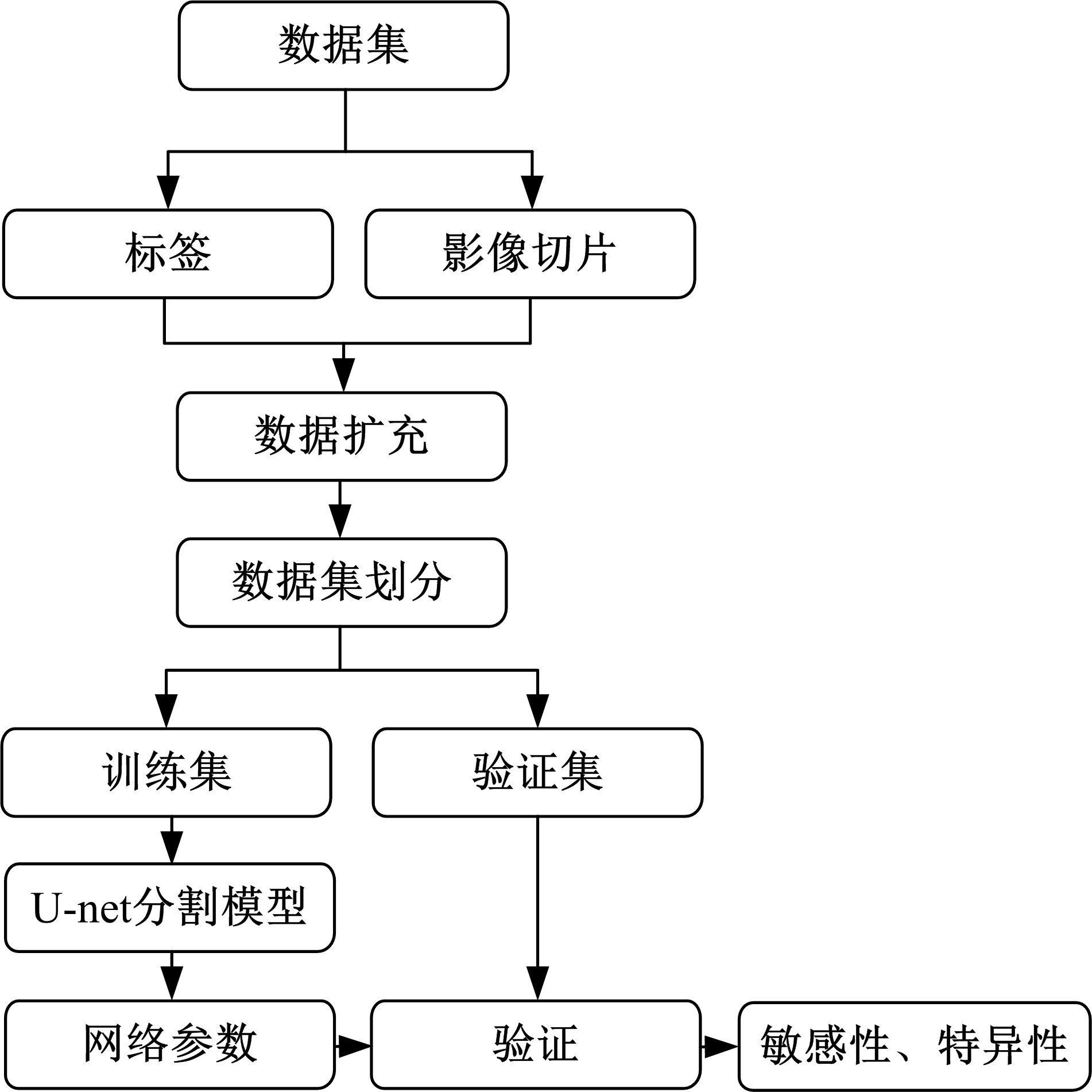
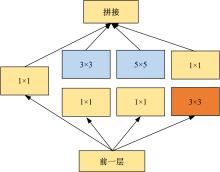
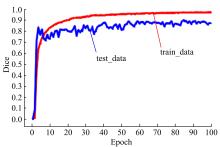
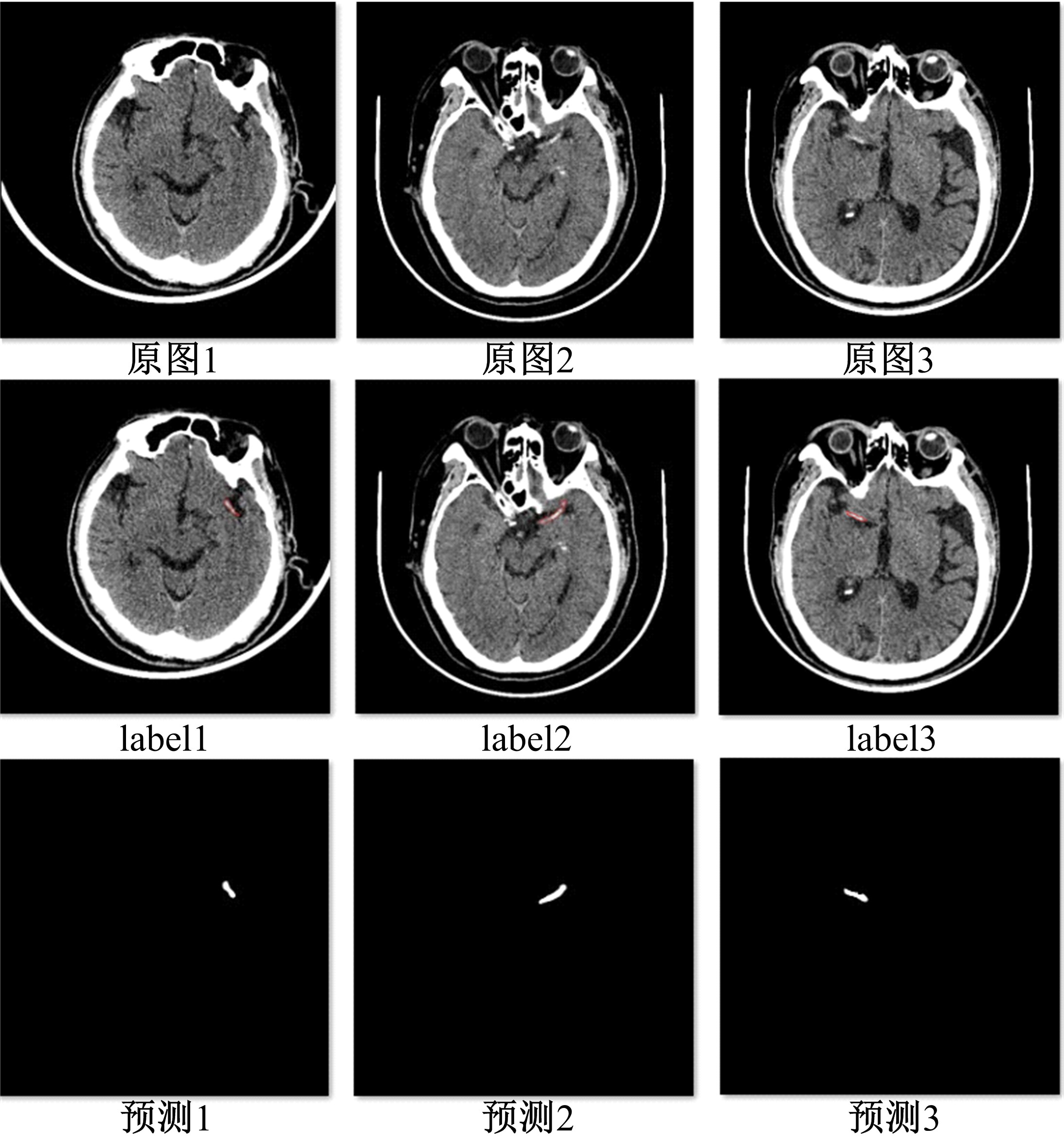
为解决脑卒中病变的人工定位和定量分析耗时且缺乏一致性的问题,提出了基于多尺度U-Net深度网络模型,从非增强计算机断层扫描影像中分割脑卒中病变的高密度征,同时使用Dice损失函数训练模型以对抗数据中类不平衡问题。实验数据表明:该模型可端到端的以数据驱动的方式自动学习高密度征显著特征,有效地分割脑部小病灶区域。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Kassebaum N J, Bertozzi-Villa A, Coggeshall M S, et al. Global, regional, and national levels and causes of maternal mortality during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013[J]. The Lancet, 2014, 384( 9947): 980- 1004. |
| 2 | Doyle K P, Simon R P, Stenzel-Poore M P. Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2008, 55( 3): 310- 318. |
| 3 | Wang W, Wang D, Liu H, et al. Trend of declining stroke mortality in China: reasons and analysis[J]. Stroke and Vascular Neurology, 2017, 2( 3): 132- 139. |
| 4 | Ariesen M J, Claus S P, Rinkel G J E, et al. Risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage in the general population: a systematic review[J]. Stroke, 2003, 34( 8): 2060- 2066. |
| 5 | Mullins M E, Schaefer P W, Sorensen A G, et al. CT and conventional and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in acute stroke: study in 691 patients at presentation to the emergency department[J]. Radiology, 2002, 224( 2): 353- 360. |
| 6 | Chalela J A, Kidwell C S, Nentwich L M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in emergency assessment of patients with suspected acute stroke: a prospective comparison[J]. The Lancet, 2007, 369( 9558): 293- 298. |
| 7 | Rekik I, Allassonniere S, Carpenter T K, et al. Medical image analysis methods in MR/CT-imaged acute-subacute ischemic stroke lesion: Segmentation, prediction and insights into dynamic evolution simulation models. A critical appraisal[J]. Neuroimage: Clinical, 2012, 1( 1): 164- 178. |
| 8 | Barber P, Demchuk A, Zhang J, et al. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score[J]. The Lancet, 2000, 355( 9216): 1670- 1674. |
| 9 | Herweh C, Ringleb P A, Rauch G, et al. Performance of e-ASPECTS software in comparison to that of stroke physicians on assessing CT scans of acute ischemic stroke patients[J]. International Journal of Stroke, 2016, 11( 4): 438- 445. |
| 10 | Nagel S, Sinha D, Day D, et al. e-ASPECTS software is non-inferior to neuroradiologists in applying the ASPECT score to computed tomography scans of acute ischemic stroke patients[J]. International Journal of Stroke, 2017, 12( 6): 615- 622. |
| 11 | Takahashi N, Lee Y, Tsai D Y, et al. An automated detection method for the MCA dot sign of acute stroke in unenhanced CT[J]. Radiological Physics and Technology, 2014, 7( 1): 79- 88. |
| 12 | Chen Y, Dhar R, Heitsch L, et al. Automated quantification of cerebral edema following hemispheric infarction: application of a machine-learning algorithm to evaluate CSF shifts on serial head CTs[J]. Neuroimage Clinical, 2016, 12: 673- 680. |
| 13 | Mitra J, Bourgeat P, Fripp J, et al. Lesion segmentation from multimodal MRI using random forest following ischemic stroke[J]. Neuroimage, 2014, 98: 324- 335. |
| 14 | 贾迪, 杨金柱, 张一飞, 等. 自适应脑组织影像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42( 1): 161- 165. |
| Jia Di, Yang Jin-zhu, Zhang Yi-fei, et al. Self-adapting segmentation for brain tissue[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42( 1): 161- 165. | |
| 15 | Shin H C, Roth H R, Gao M, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35( 5): 1285- 1298. |
| 16 | Chen L, Bentley P, Rueckert D. Fully automatic acute ischemic lesion segmentation in DWI using convolutional neural networks[J]. Neuroimage: Clinical, 2017, 15: 633- 643. |
| 17 | Zhang R, Zhao L, Lou W, et al. Automatic segmentation of acute ischemic stroke from DWI using 3D fully convolutional DenseNets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37( 9): 2149- 2160. |
| 18 | Lecun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521( 7553): 436- 444. |
| 19 | Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2017, 39( 4): 640- 651. |
| 20 | Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2018, 40( 4): 834- 848. |
| 21 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥ International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, Cham, 2015: 234- 241. |
| 22 | Perez L, Wang J. The effectiveness of data augmentation in image classification using deep learning[J]. arXiv preprint: arXiv:1712. 04621. |
| 23 | Jiang H, Rong R, Wu J, et al. Skin lesion segmentation with improved C-UNet networks[J/OL].[ 2018-08-01]. |
| 24 | 郭继昌, 吴洁, 郭春乐, 等. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49( 5): 1726- 1734. |
| Guo Ji-chang, Wu Jie, Guo Chun-le, et al. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on residual connection convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49( 5): 1726- 1734. | |
| 25 | Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]∥ Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI Publications, 2016: 4287- 4284. |
| 26 | Perone C S, Calabrese E, Cohenadad J. Spinal cord gray matter segmentation using deep dilated convolutions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8( 1): 1- 13. |
| 27 | Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]∥3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015-Conference Track Proceedings, San Diego, 2015: 1- 13. |
| [1] | 徐谦,李颖,王刚. 基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [2] | 郭立民,陈鑫,陈涛. 基于AlexNet模型的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 1000-1008. |
| [3] | 刘仲民,王阳,李战明,胡文瑾. 基于简单线性迭代聚类和快速最近邻区域合并的图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1931-1937. |
| [4] | 肖明尧, 李雄飞, 张小利, 张刘. 基于多尺度的区域生长的图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1591-1597. |
| [5] | 刘仲民, 李战明, 李博皓, 胡文瑾. 基于稀疏矩阵的谱聚类图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1308-1313. |
| [6] | 赵夫群, 周明全, 耿国华. 基于GA-Otsu法的图像阈值分割及定量识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 959-964. |
| [7] | 肖明尧, 李雄飞. 基于高斯分解的多尺度3D Otsu阈值分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 255-261. |
| [8] | 王培智, 田地, 龙涛, 李抵非, 邱春玲, 刘敦一. 用于TOF-SIMS的锆石样品图像自动聚焦算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 308-315. |
| [9] | 申铉京, 张赫, 陈海鹏, 王玉. 快速递归多阈值分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 528-534. |
| [10] | 郑欣, 彭真明, 邢艳. 基于活跃度的图像分割算法性能评价新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 311-317. |
| [11] | 李一兵, 杨鹏, 叶方, 刘丹丹. 基于交互势函数和均场参数估计的分层MRF模型的纹理图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2075-2079. |
| [12] | 李抵非, 田地, 胡雄伟. 基于分布式内存计算的深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 921-925. |
| [13] | 李雄飞1, 2, 赵浩宇1, 陈霄3, 赵宏伟1, 2. 基于视觉特征的不规则形状目标分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1140-1144. |
| [14] | 张金果,郭海涛,吴君鹏,李依桐. 改进的最小交叉Tsallis熵的小目标声呐图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 834-839. |
| [15] | 杨扬, 戴明, 周箩鱼, 孙明超. 基于非下采样Bandelet变换的多聚焦图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 525-530. |
|
||