吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 897-909.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200950
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于STA⁃LSTM的自发微表情识别算法
- 1.西安邮电大学 通信与信息工程学院,西安 710121
2.西安邮电大学 电子信息现场勘验应用技术公安部重点实验室,西安 710121
Spontaneous micro-expression recognition based on STA-LSTM
Da-xiang LI1,2( ),Meng-si CHEN1,Ying LIU1,2
),Meng-si CHEN1,Ying LIU1,2
- 1.College of Communication and Information Engineering,Xi'an University of Posts and Telecommunications,Xi'an 710121,China
2.Ministry of Public Security Key Laboratory of Electronic Information Application Technology for Scene Investigation,Xi'an University of Posts and Telecommunications,Xi'an 710121,China
摘要:
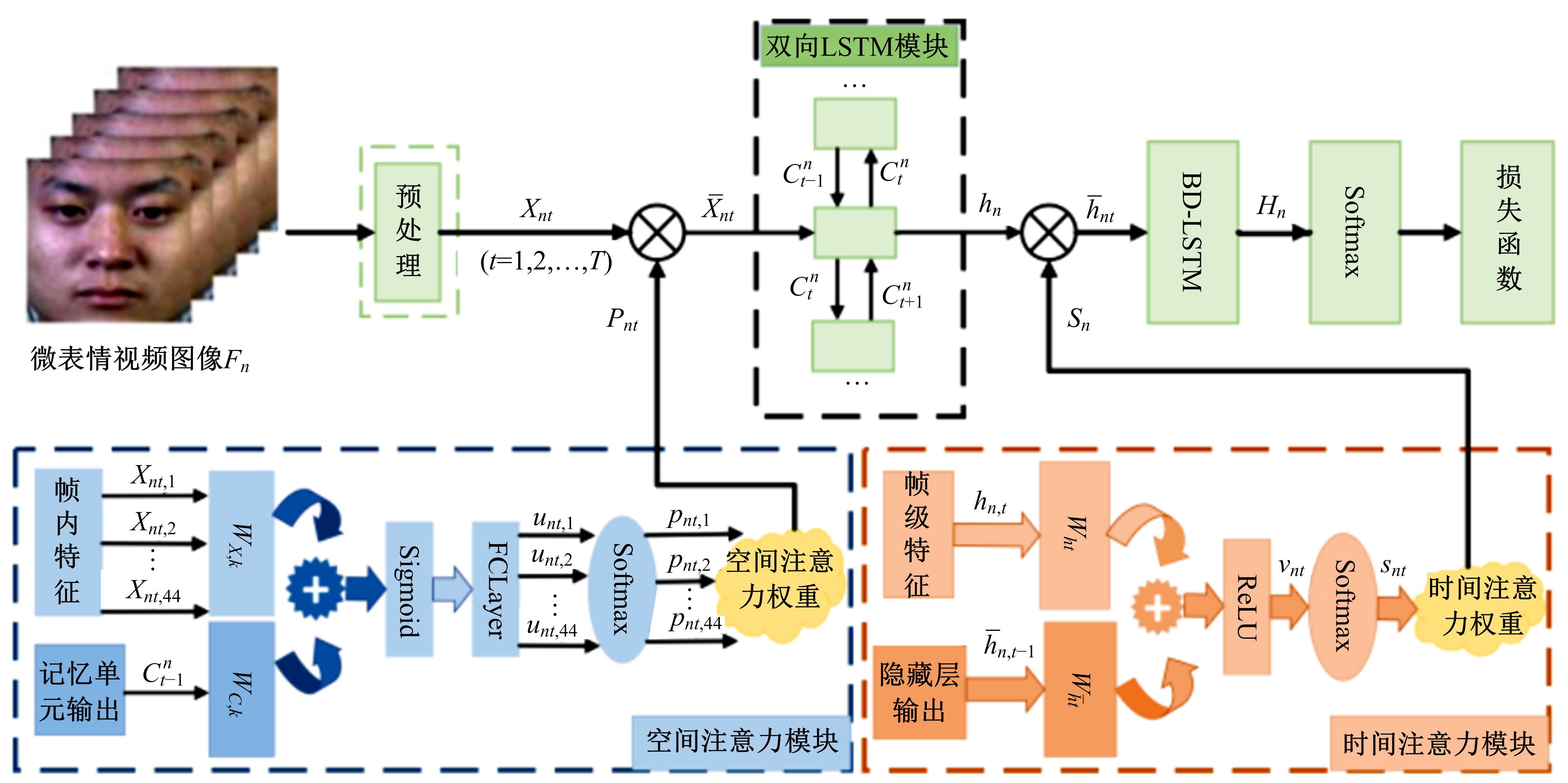
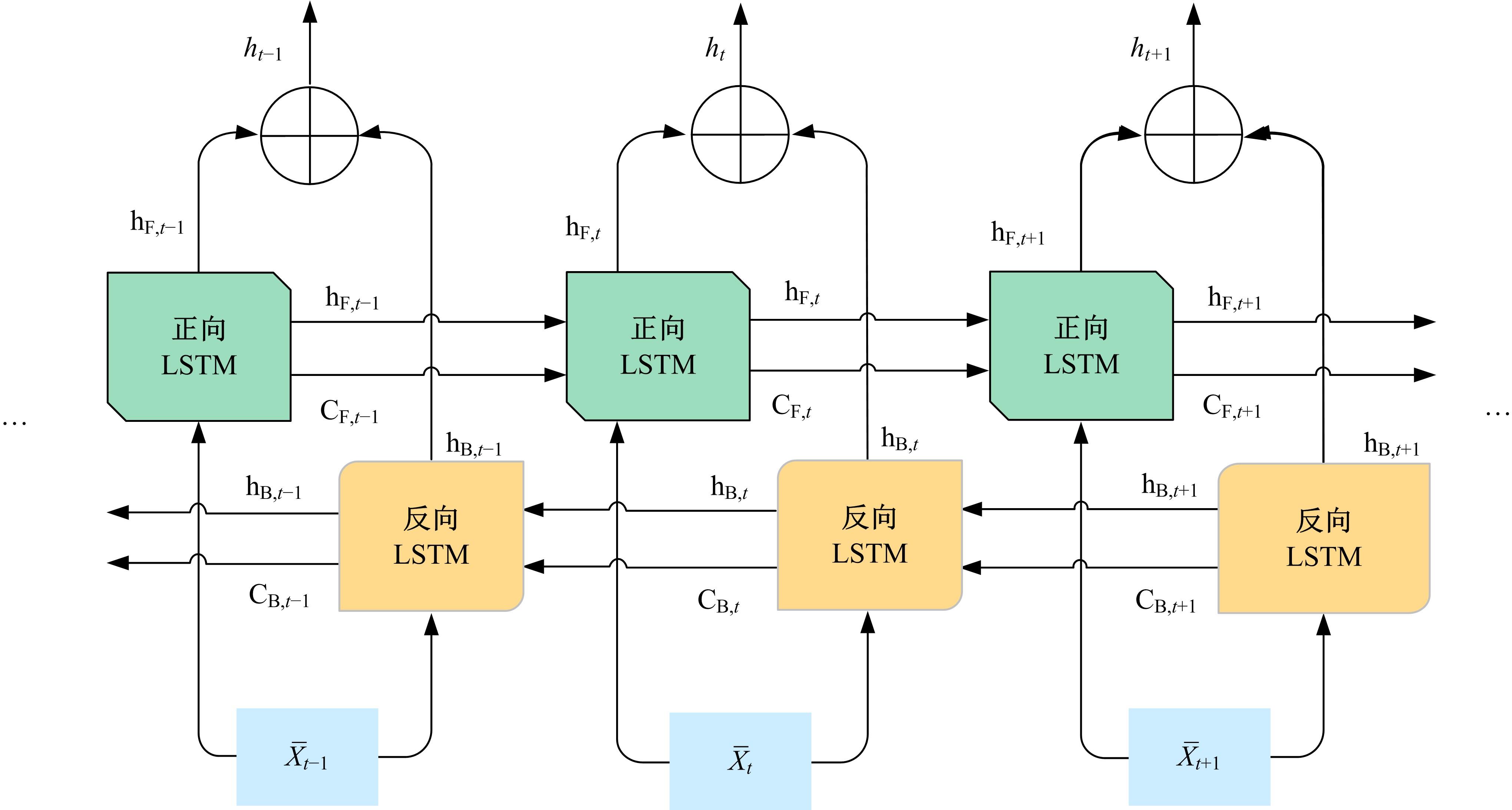
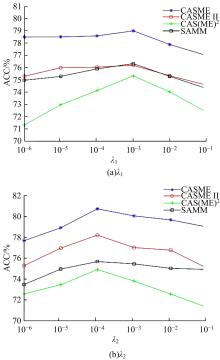
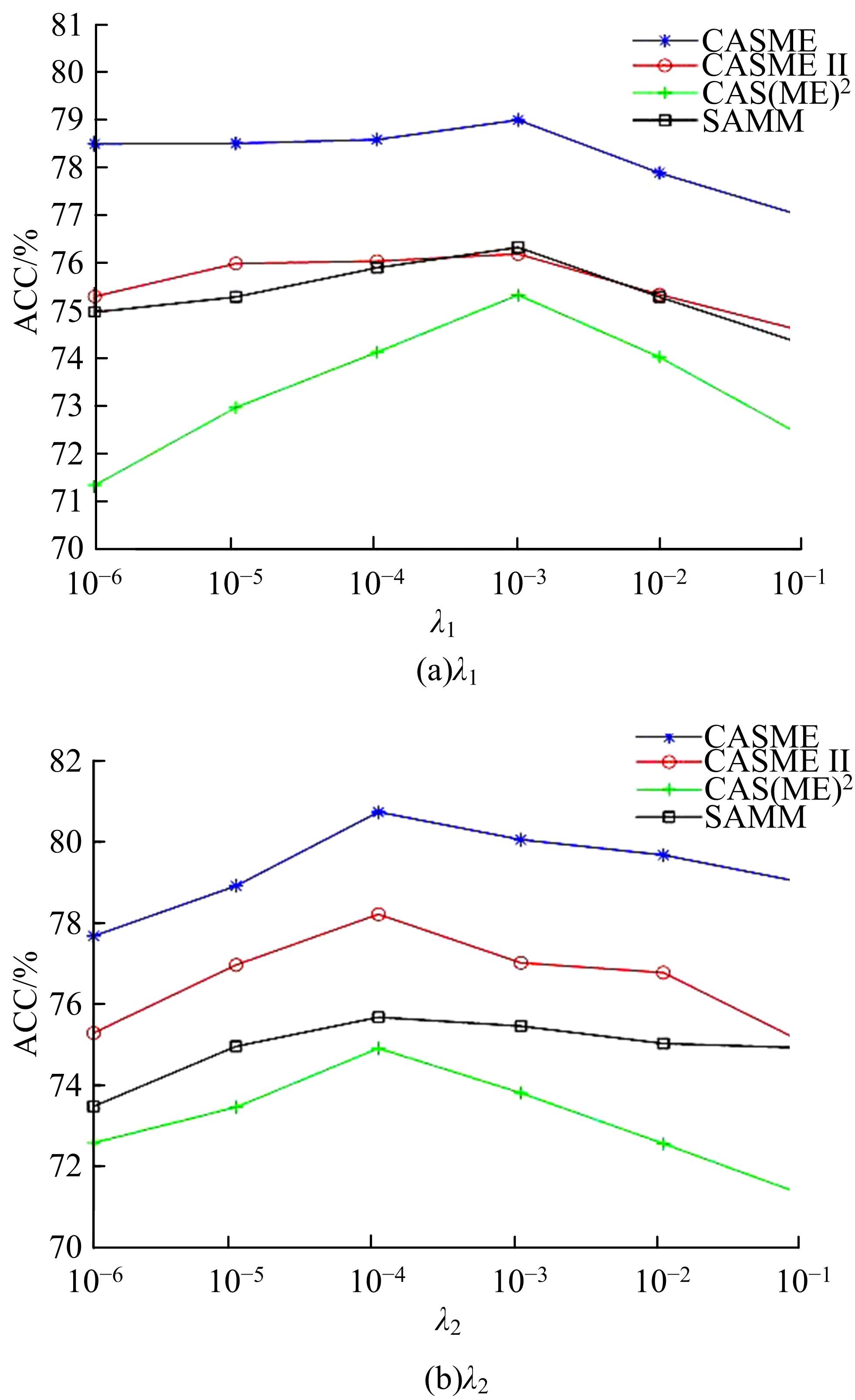
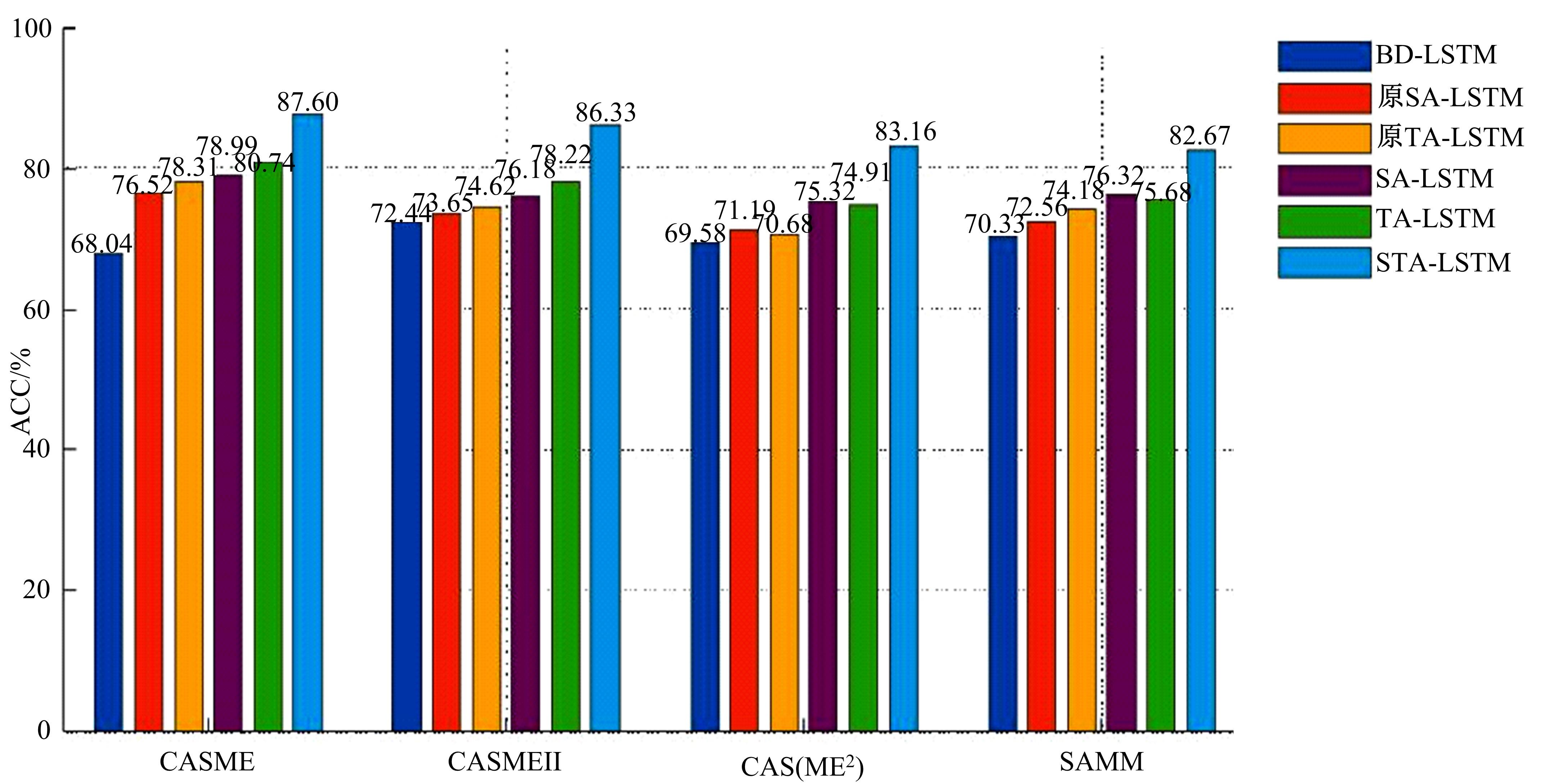
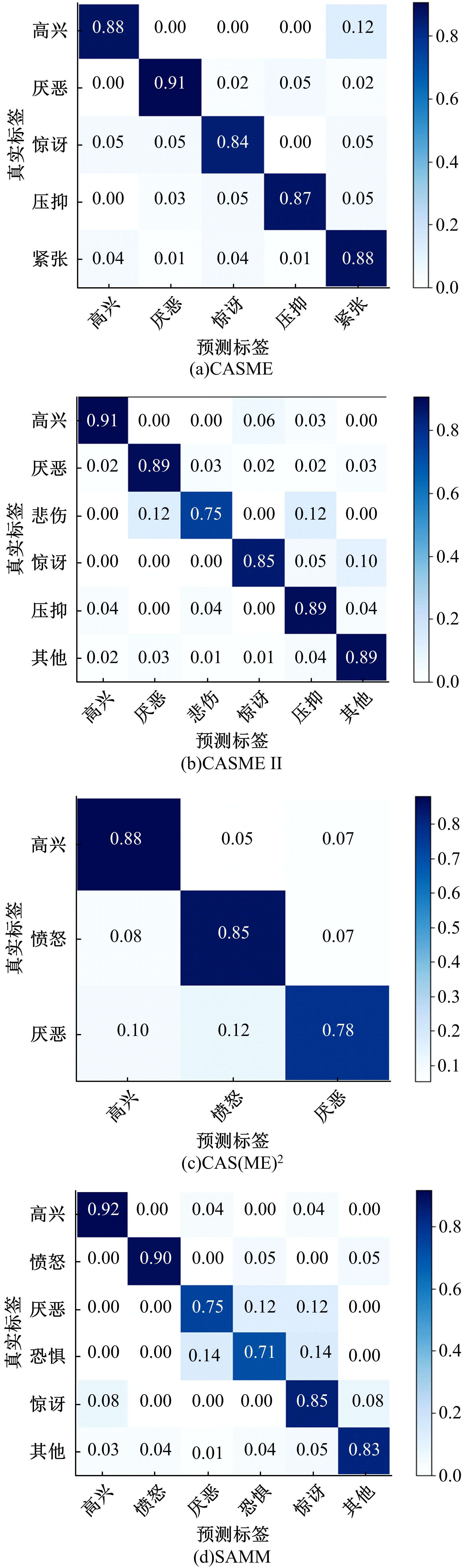
针对目前多数人心理状态处于亚健康的问题,设计了一种基于时空注意力的双向长短时记忆(LSTM)网络,以实现微表情图像特征提取及识别,从而了解人们试图掩饰的情绪。该网络由双向LSTM模块、空间注意力模块及时间注意力模块三大部分组成。将微表情视频图像作为输入,所学习的网络能够有选择性地聚焦于每帧有显著区别的动作单元,并对不同帧给予不同程度的关注度。同时,考虑到模块之间的相关性,还设计一个新的正则化的交叉熵损失函数,进一步优化网络。最后,在CASME、CASMEⅡ、CAS(ME)2、SAMM四个数据集上进行了对比实验。实验结果表明,本文方法能够提高微表情识别的精度,优于其他方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Haggard E A, Isaacs K S. Micromomentary facial expressions as indicators of ego mechanisms in psychotherapy[M]. Boston: Springer, 1966: 154-165. |
| 2 | Ekman P, Friesen W V. Nonverbal leakage and clues to deception[J]. Psychiatry-interpersonal & Biological Processes, 1969, 32(1): 88-106. |
| 3 | Peng M, Wu Z, Zhang Z, et al. From macro to micro expression recognition: deep learning on small datasets using transfer learning[C]∥The 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Xi'an,China,2018: 657-661. |
| 4 | Yao L, Xiao X, Cao R, et al. Three stream 3d CNN with SE block for micro-expression recognition[C]∥ International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application, Guangzhou, China, 2020: 439-443. |
| 5 | 贲晛烨, 杨明强, 张鹏, 等. 微表情自动识别综述[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2014, 26(9): 1385-1395. |
| Xian-ye Ben, Yang Ming-qiang, Zhang Peng, et al. Survey on automatic micro expression recognition methods[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2014, 26(9): 1385-1395. | |
| 6 | Yan W J, Wu Q, Liu Y J, et al. CASME database: a dataset of spontaneous micro-expressions collected from neutralized faces[C]∥The 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Shanghai, China, 2013: 1-7. |
| 7 | Yan W J, Li X, Wang S J, et al. CASME II: an improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation[J]. Plos One, 2014, 9(1): No. e86041. |
| 8 | Qu F B, Wang S J, Yan W J, et al. CAS(ME)2: a database for spontaneous macro-expression and micro-expression spotting and recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2018, 9(4): 424-436. |
| 9 | Davison A K, Lansley C, Costen N, et al. SAMM: a spontaneous micro-facial movement dataset[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2018, 9(1): 116-129. |
| 10 | Li X, Pfister T, Huang X, et al. A spontaneous micro-expression database: inducement, collection and baseline[C]∥The 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Shanghai, China, 2013: 1-6. |
| 11 | Pfister T, Li X B, Zhao G, et al. Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1449-1456. |
| 12 | Zhao G Y, Pietikainen M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(6): 915-928. |
| 13 | Huang X, Zhao G, Hong X, et al. Spontaneous facial micro-expression analysis using spatiotemporal completed local quantized patterns[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 175(A): 564-578. |
| 14 | Wang Y, See J, Phan W, et al. LBP with six intersection points: reducing redundant information in lbp-top for micro-expression recognition[C]∥The 12th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 2014: 525-537. |
| 15 | Ben X, Zhang P, Yan R, et al. Gait recognition and micro-expression recognition based on maximum margin projection with tensor representation[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27(8): 2629-2646. |
| 16 | Xu F, Zhang J, Wang J Z. Microexpression identification and categorization using a facial dynamics map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2017: 254-267. |
| 17 | Liu Y J, Zhang J K, Yan W J, et al. A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2016, 7(4): 299-310. |
| 18 | Fu J L, Zheng H L, Mei T. Look closer to see better: recurrent attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 4476-4484. |
| 19 | Lin T Y, Roychowdhury A, Maji S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1449-1457. |
| 20 | Byeon Y H, Kwak K C. Facial expression recognition using 3d convolutional neural network [J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2014, 5(12): 107-112. |
| 21 | Kim D H, Baddar W J, Ro Y M. Micro-Expression recognition with expression-stateconstrained spatio-temporal feature representations[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York, United States, 2016: 382-386. |
| 22 | Peng M, Wang C, Chen T, et al. Dual temporal scale convolutional neural network for micro-expression recognition[J]. Frontiers in Psychology, 2017: 1745-1757. |
| 23 | Patel D, Hong X P, Zhao G Y. Selective deep features for micro-expression recognition[C]∥The 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cancun, Mexico, 2017: 2258-2263. |
| 24 | Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[C]∥ International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego USA, 2015. |
| 25 | Xiao T, Xu Y, Yang K, et al. The application of two-level attention models in deep convolutional neural network for fine-grained image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern, Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 842-850. |
| 26 | Wang F, Jiang M, Qian C, et al. Residual attention network for image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6450-6458. |
| 27 | Sharma S, Kiros R, Salakhutdinov R. Action recognition using visual attention[C]∥Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) Time Series Workshop, London,UK,2017: 1-11. |
| 28 | Stollenga M, Masci J, Gomez F, et al. Deep networks with internal selective attention through feedback connections[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Manno-Lugano, Switzerland, 2014: 3545-3553. |
| 29 | Paul Ekman, Friesen Wallace V. Facial Action Coding System:a Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement[M]. Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1978. |
| 30 | Deng W H, Hu J N, Guo J. Compressive binary patterns: designing a robust binary face descriptor with random-field eigenfilters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(3): 758-767. |
| 31 | King D E. Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit[J]. Machine Learning Research, 2009, 10: 1755-1758. |
| 32 | Zhou Z H, Zhao G Y, Guo Y M, et al. An image-based visual speech animation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2012, 22(10): 1420-1432. |
| 33 | Li X, Pfister T, Huang X, et al. A Spontaneous micro-expression database: inducement, collection and baseline[C]∥The 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Shanghai, China, 2013. |
| 34 | See J, Yap M H, Li J, et al. MEGC 2019 – the second facial micro-expressions grand challenge[C]∥The 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Lille, France, 2019. |
| 35 | Wang Y, See J, Phan W, et al. LBP with Six intersection points: reducing redundant information in LBP-TOP for micro-expression recognition[C]∥ACCV, Singapore,2014: 525-537. |
| 36 | Chan C H, Goswami B, Kittler J, et al. Local ordinal contrast pattern histograms for spatiotemporal, lip-based speaker authentication[C]∥The 4th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 2012: 602-612. |
| 37 | Chaudhry R, Ravichandran A, Hager G, et al. Histograms of oriented optical flow and Binet-Cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions[C]∥IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 1932-1939. |
| 38 | Xu F, Zhang J P, Wang J Z. Microexpression identification and categorization using a facial dynamics map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2017, 8(2): 254-267. |
| 39 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]∥Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Singapore,2015: 1-14. |
| 40 | He K H, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 41 | Zhao G Y, Pietikainen M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(6): 915-928. |
| 42 | Liong S T, See J, Wong K S, et al. Less is more: micro-expression recognition from video using apex frame[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2018, 62: 82-92. |
| 43 | Zhou L, Mao Q, Xue L. Dual-inception network for cross-database micro-expression recognition[C]∥The 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Lille, France, 2019. |
| 44 | Peng M, Wang C, Bi T, et al. A novel apex-time network for cross-dataset micro-expression recognition[C]∥The 8th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Cambridge, UK, 2019. |
| 45 | Quang N V, Chun J, Tokuyama T. CapsuleNet for Micro-Expression Recognition[C]∥The 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Lille, France, 2019. |
| 46 | Liong S T, Gan Y S, See J, et al. Shallow triple stream three-dimensional CNN (STSTNET) for micro-expression recognition[C]∥The 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Lille, France, 2019. |
| 47 | Wang C Y, Peng M, Bi T, et al. Micro-attention for micro-expression recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 410: 354-362. |
| [1] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [2] | 魏晓辉,苗艳微,王兴旺. Rhombus sketch:自适应和准确的流数据sketch[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 874-884. |
| [3] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [4] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [5] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [6] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [7] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [8] | 毛琳,任凤至,杨大伟,张汝波. 双向特征金字塔全景分割网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 657-665. |
| [9] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [10] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [11] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [12] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [13] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [14] | 林俊聪,雷钧,陈萌,郭诗辉,高星,廖明宏. 基于电影视觉特性的动态多目标实时相机规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2154-2163. |
| [15] | 任丽莉,王志军,闫冬梅. 结合黏菌觅食行为的改进多元宇宙算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2190-2197. |
|
||