吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 2190-2197.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210649
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
结合黏菌觅食行为的改进多元宇宙算法
- 1.长春师范大学 高性能计算中心,长春 130032
2.吉林大学 大数据和网络管理中心,长春 130012
Improved multi⁃verse algorithm with combined slime mould foraging behavior
Li-li REN1( ),Zhi-jun WANG1,Dong-mei YAN2
),Zhi-jun WANG1,Dong-mei YAN2
- 1.High Performance Computing Center,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
2.Big Data Network Management Center,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
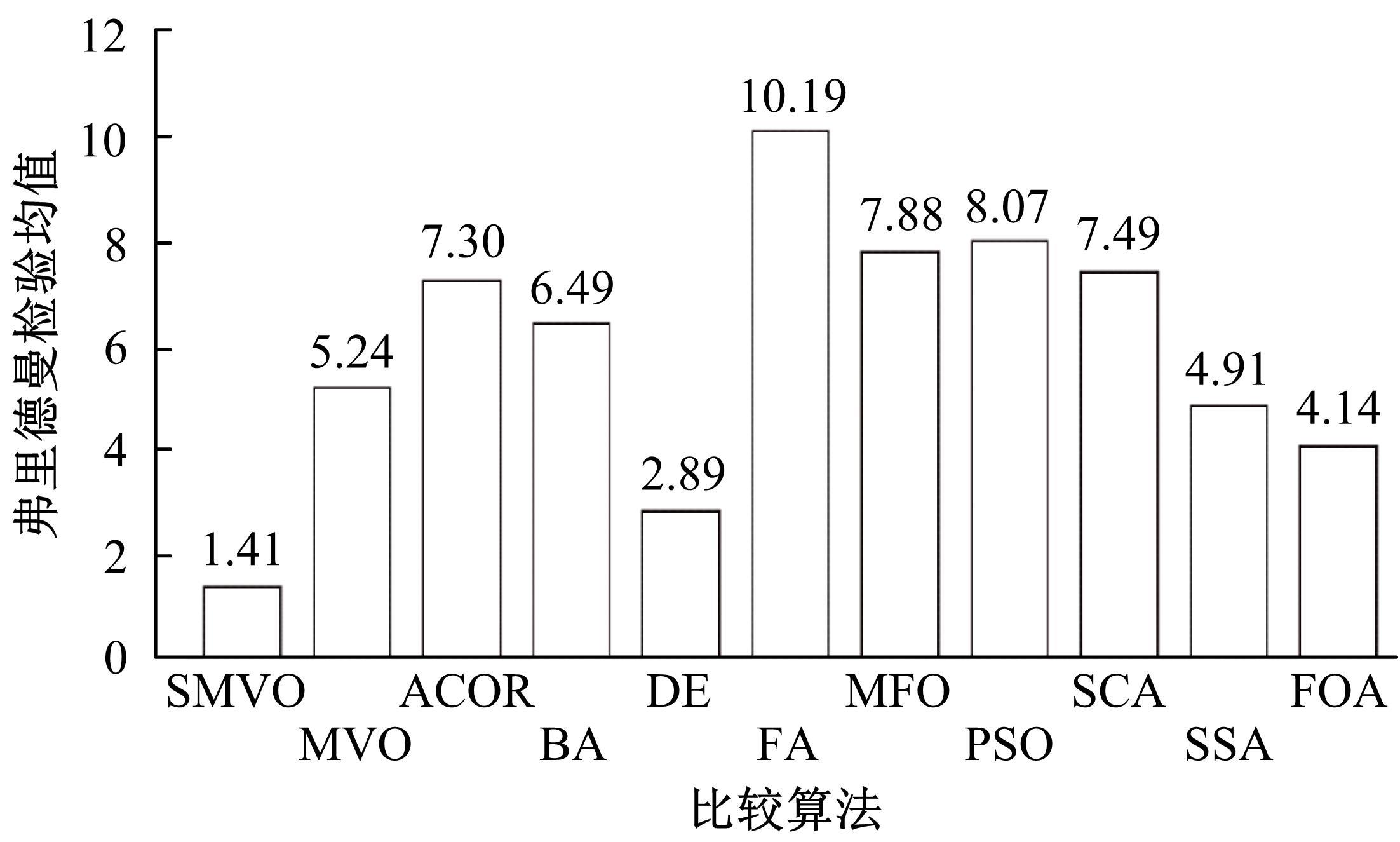
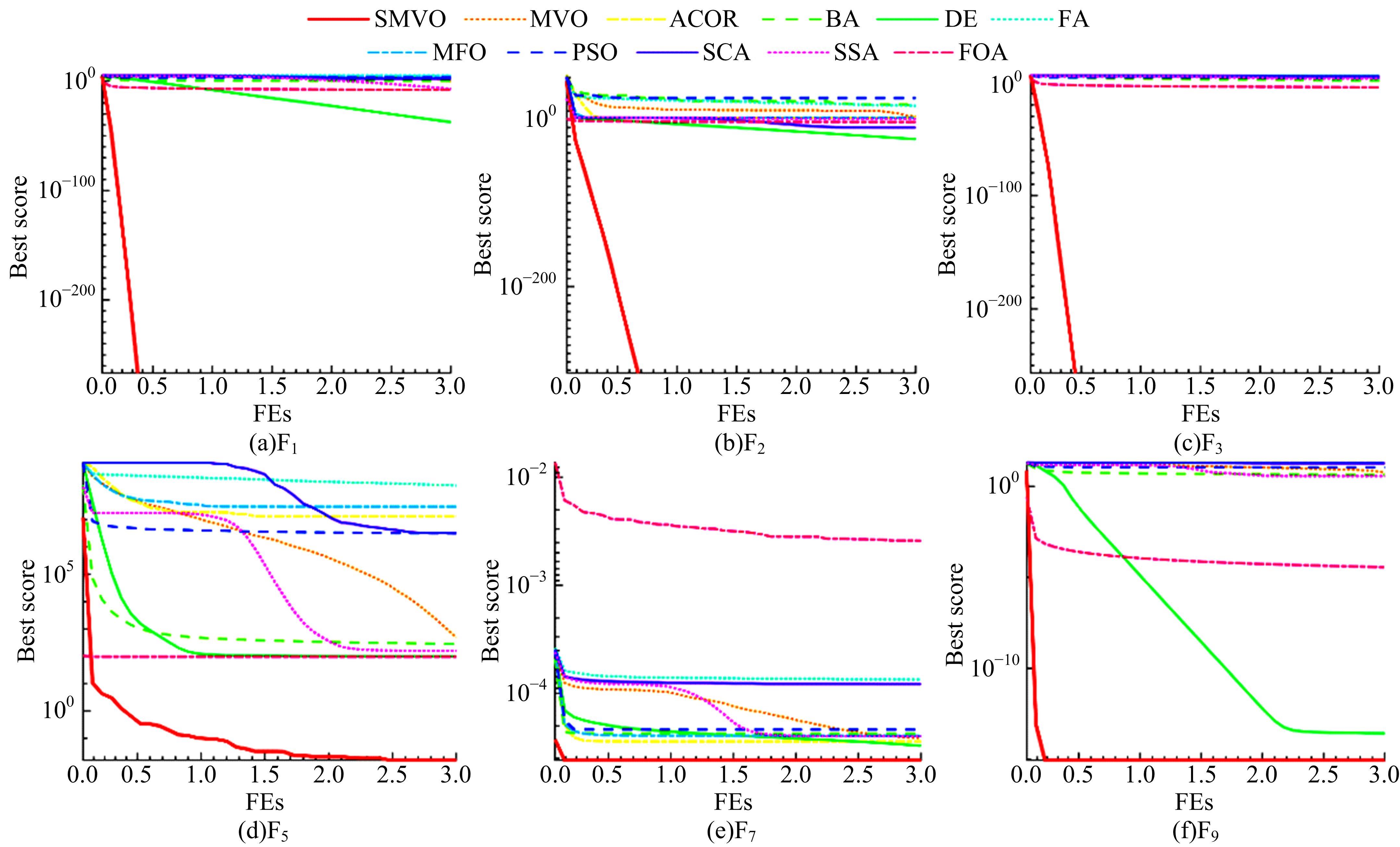
为提高多元宇宙优化算法求解实际问题的能力,提出了一种黏菌觅食的多元宇宙优化算法。该算法利用黏菌觅食行为在局部最优和全局最优之间寻求最优解。通过与其他10种同类算法在12个函数上的测试比较表明:本文算法收敛速度及解的质量优于其他算法,具有更好的求解能力和优化性能,可作为问题优化的有效工具。
中图分类号:
- TP393
| 1 | 王伟, 何东之. 基于非线性和遗传变异的灰狼优化算法[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 44(2): 199-205. |
| Wang Wei, He Dong-zhi. Gray wolf optimization algorithm based on nonlinearity and genetic variation[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 44(2): 199-205. | |
| 2 | Socha K, Dorigo M. Ant colony optimization for continuous domains[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2008, 185(3): 1155-1173. |
| 3 | Yang X S. A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm[C]∥Nature inspired cooperative strategies for optimization (NICSO 2010), Springer, , HeidelbergBerlin, 2010: 65-74. |
| 4 | Storn R, Price K. Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1997, 11(4): 341-359. |
| 5 | Yang X S. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization[C]∥International Symposium on Stochastic Algorithms, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009: 169-178. |
| 6 | Mirjalili S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 89: 228-249. |
| 7 | Poli R, Kennedy J, Blackwell T. Particle swarm optimization[J].Swarm Intelligence, 2007, 1(1): 33-57. |
| 8 | Mirjalili S. SCA: a sine cosine algorithm for solving optimization problems[J]. Knowledge-based Systems, 2016, 96: 120-133. |
| 9 | Mirjalili S, Gandomi A H, Mirjalili S Z, et al. Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2017, 114: 163-191. |
| 10 | Pan W T. A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: taking the financial distress model as an example[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2012, 26: 69-74. |
| 11 | Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S M, Hatamlou A. Multi-verse optimizer: a nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27(2): 495-513. |
| 12 | 熊保玉. 基于改进多元宇宙算法的零件平面度测量研究[J]. 光电子·激光, 2021, 32(3): 251-256. |
| Xiong Bao-yu. Research on part flatness measurement based on improved multiverse algorithm[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2021, 32(3): 251-256. | |
| 13 | Yang X H, Chen W K, Li A Y, et al. A Hybrid machine‐learning method for oil‐immersed power transformer fault diagnosis[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2020, 15(4): 501-507. |
| 14 | Zhu L, Lin J, Wang Z J. A discrete oppositional multi-verse optimization algorithm for multi-skill resource constrained project scheduling problem[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 85: No.105805. |
| 15 | Yildiz A R, Mirjalili S, Sait S, et al. The Harris hawks, grasshopper and multi-verse optimization algorithms for the selection of optimal machining parameters in manufacturing operations[J]. Materials Testing, 2019, 61(8): 725-733. |
| 16 | Singh A, Suhag S. Frequency regulation in an AC microgrid interconnected with thermal system employing multiverse-optimised fractional order-PID controller[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Energy, 2020, 39(3): 250-262. |
| 17 | Lin J, Zhu L, Wang Z J. A hybrid multi-verse optimization for the fuzzy flexible job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 127: 1089-1100. |
| 18 | Li L L, Wen S Y, Wang C S, et al. Renewable energy prediction: a novel short-term prediction model of photovoltaic output power[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 228: 359-375. |
| 19 | Geng K F, Ye C M, Cao L, et al. Multi-objective reentrant hybrid flowshop scheduling with machines turning on and off control strategy using improved multi-verse optimizer algorithm[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019, 2019: 1-18. |
| 20 | Chauhan U, Rani A, Kumar B, et al. A multi verse optimization based MPPT controller for drift avoidance in solar system[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 36(3): 2175-2184. |
| 21 | Buch H, Trivedi I N. On the efficiency of metaheuristics for solving the optimal power flow[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2019, 31(9): 5609-5627. |
| 22 | Al-qaness M A A, Elaziz M A, Ewees A A, et al. A modified adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system using multi-verse optimizer algorithm for oil consumption forecasting[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(10): 1071. |
| 23 | Liu Xiao-long. Application of improved multiverse algorithm to large scale optimization problems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1666-1673. |
| 24 | Ewees A A, Abd El Aziz M, Hassanien A E. Chaotic multi-verse optimizer-based feature selection[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2019, 31(4): 991-1006. |
| 25 | Li S M, Chen H L, Wang M J. et al. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 111: 300-323. |
| 26 | García S, Fernández A, Luengo J, et al. Advanced nonparametric tests for multiple comparisons in the design of experiments in computational intelligence and data mining: Experimental analysis of power[J]. Information Sciences, 2010, 180(10): 2044-2064. |
| 27 | Derrac J, García S, Molina D, et al. A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 1(1): 3-18. |
| [1] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [2] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [3] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [4] | 林俊聪,雷钧,陈萌,郭诗辉,高星,廖明宏. 基于电影视觉特性的动态多目标实时相机规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2154-2163. |
| [5] | 姚引娣,贺军瑾,李杨莉,谢荡远,李英. 自构建改进型鲸鱼优化BP神经网络的ET0模拟计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1798-1807. |
| [6] | 赵宏伟,张子健,李蛟,张媛,胡黄水,臧雪柏. 基于查询树的双向分段防碰撞算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1830-1837. |
| [7] | 张萌谡,刘春天,李希今,黄永平. 基于K⁃means聚类算法的绩效考核模糊综合评价系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1851-1856. |
| [8] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [9] | 杨勇,陈强,曲福恒,刘俊杰,张磊. 基于模拟划分的SP⁃k⁃means-+算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1808-1816. |
| [10] | 孙小雪,钟辉,陈海鹏. 基于决策树分类技术的学生考试成绩统计分析系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1866-1872. |
| [11] | 王春波,底晓强. 基于标签分类的云数据完整性验证审计方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1364-1369. |
| [12] | 欧阳丹彤,刘扬,刘杰. 故障响应指导下基于测试集的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
| [13] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [14] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于机器学习的地理空间数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1011-1016. |
| [15] | 孙宝凤,任欣欣,郑再思,李国一. 考虑工人负荷的多目标流水车间优化调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 900-909. |
|
||