吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3209-3219.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221644
考虑定制公交及公交专用道的混合逐日均衡模型
常玉林1,2,3( ),王逸杰1,王建4,孙超1,2(
),王逸杰1,王建4,孙超1,2( ),张鹏1,徐文倩1
),张鹏1,徐文倩1
- 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2.南通理工学院 汽车工程学院,江苏 南通 226002
3.东南大学 城市智能交通江苏省重点实验室,南京 211189
4.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Day-to-day equilibrium model of mixed traffic flow considering customized bus and exclusive bus lane
Yu-lin CHANG1,2,3( ),Yi-jie WANG1,Jian WANG4,Chao SUN1,2(
),Yi-jie WANG1,Jian WANG4,Chao SUN1,2( ),Peng ZHANG1,Wen-qian XU1
),Peng ZHANG1,Wen-qian XU1
- 1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.College of Automotive Engineering,Nantong Institute of Technology,Nantong 226002,China
3.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of ITS,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
4.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
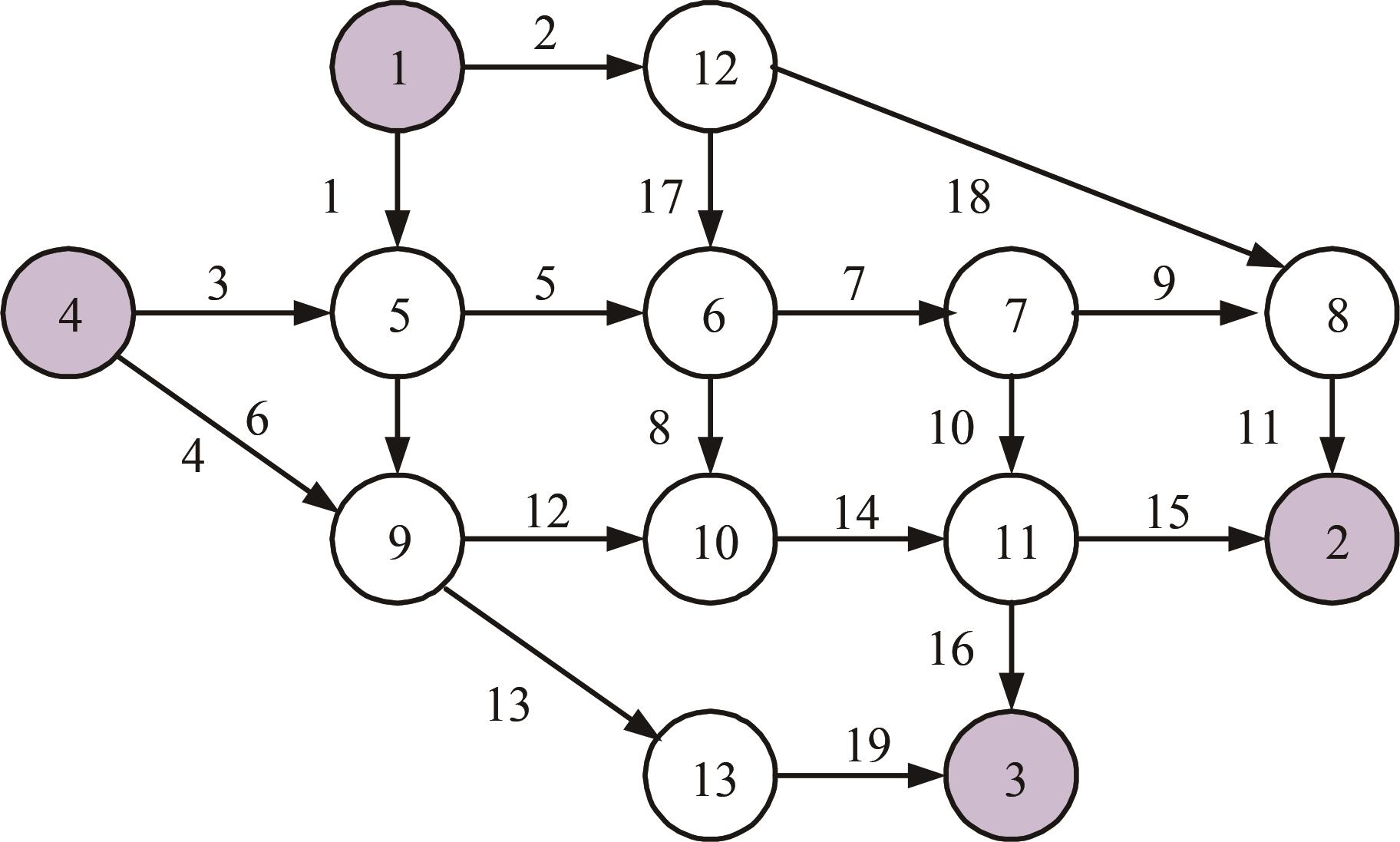
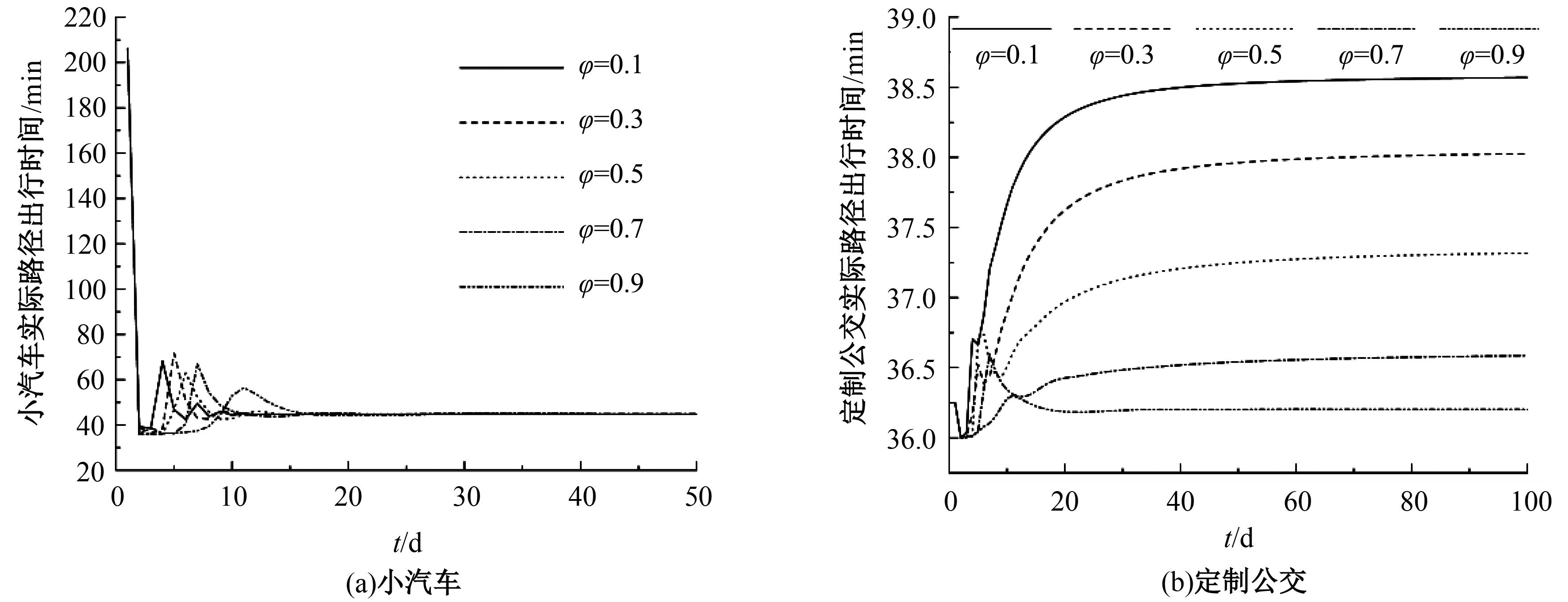
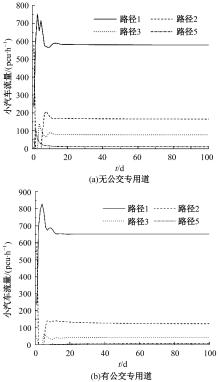
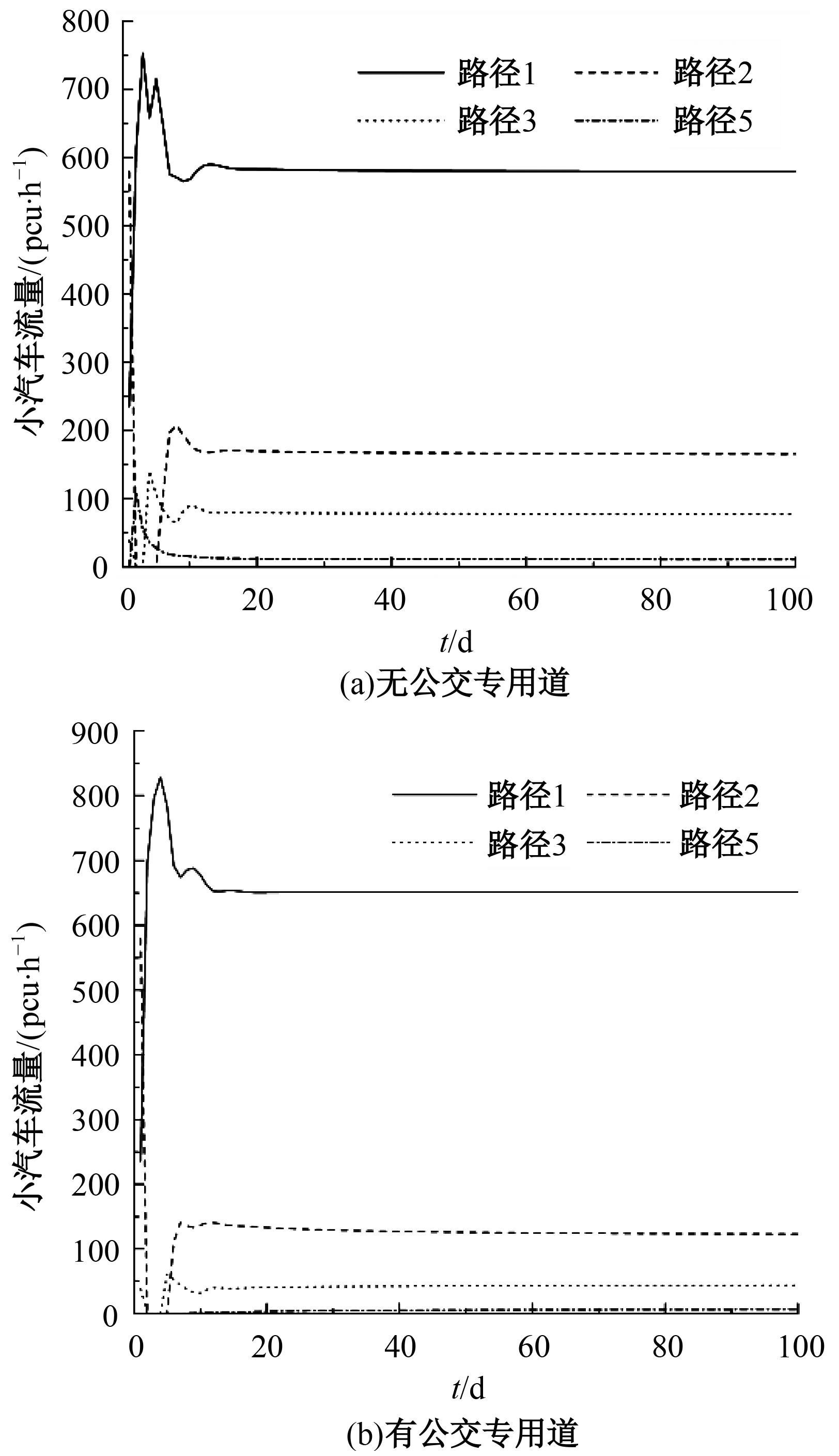
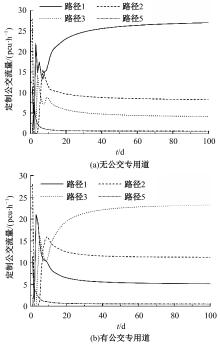
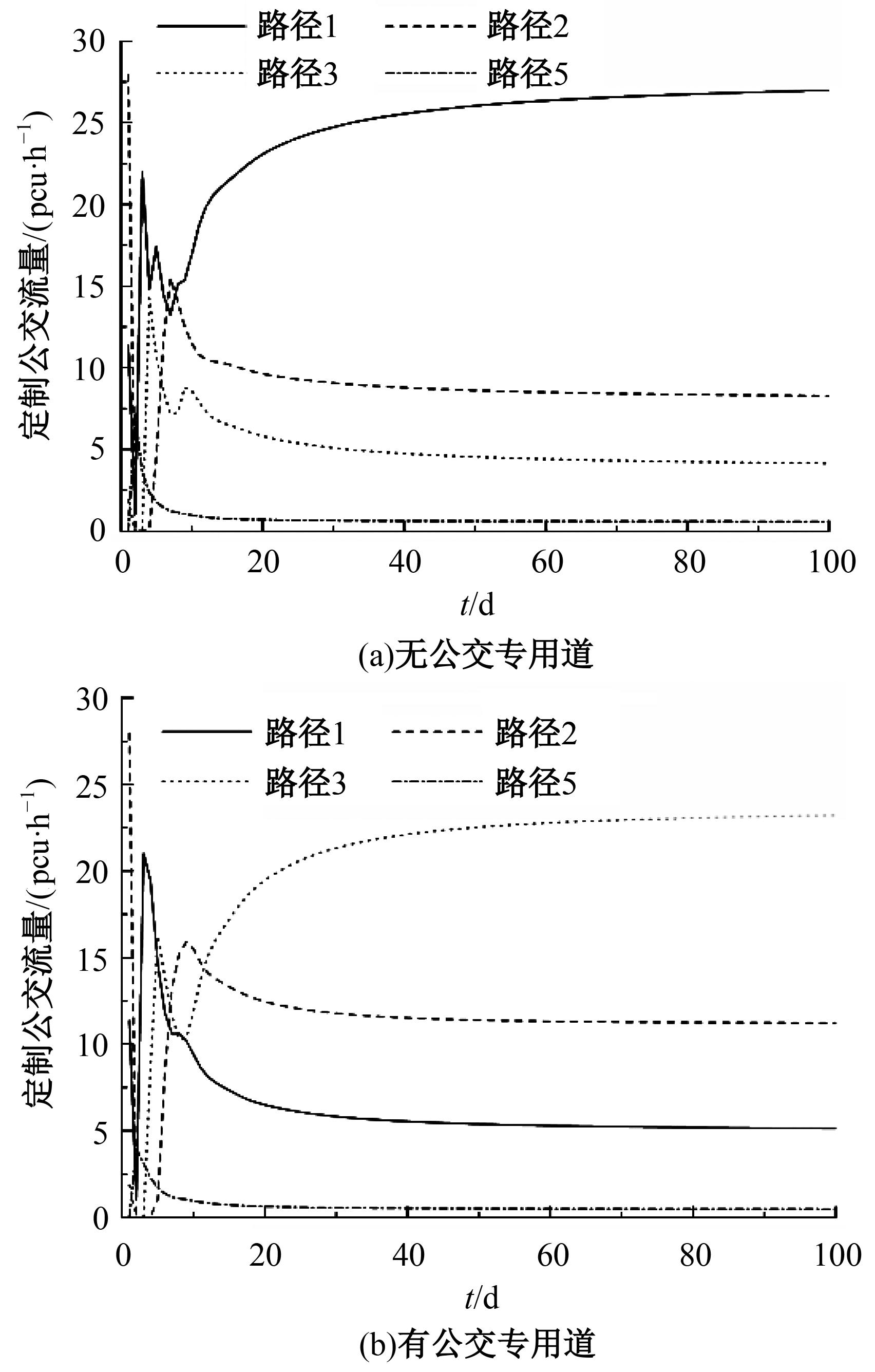
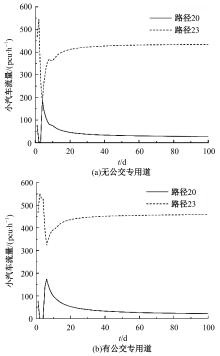
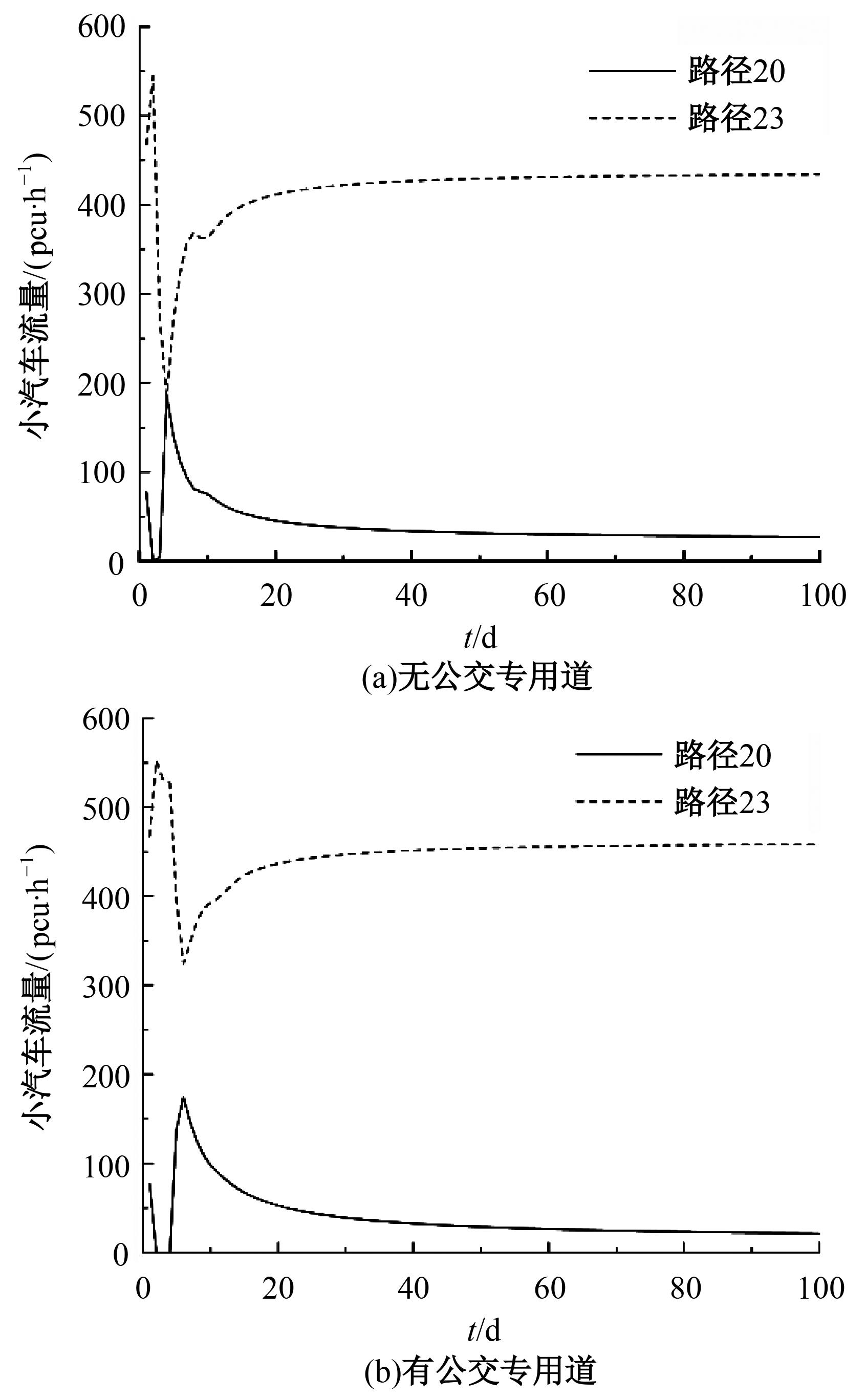
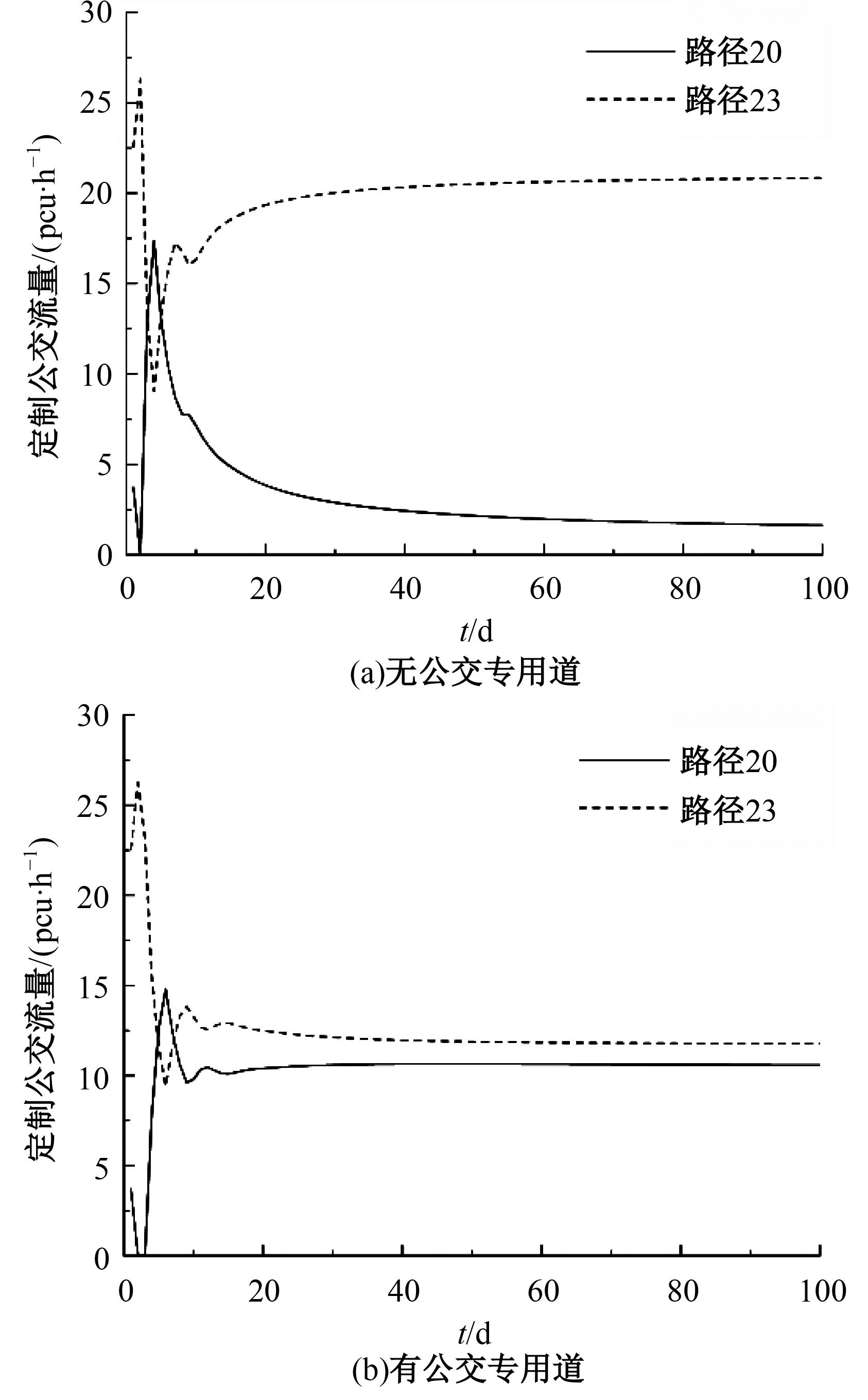
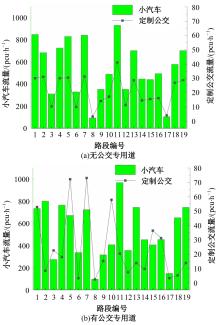
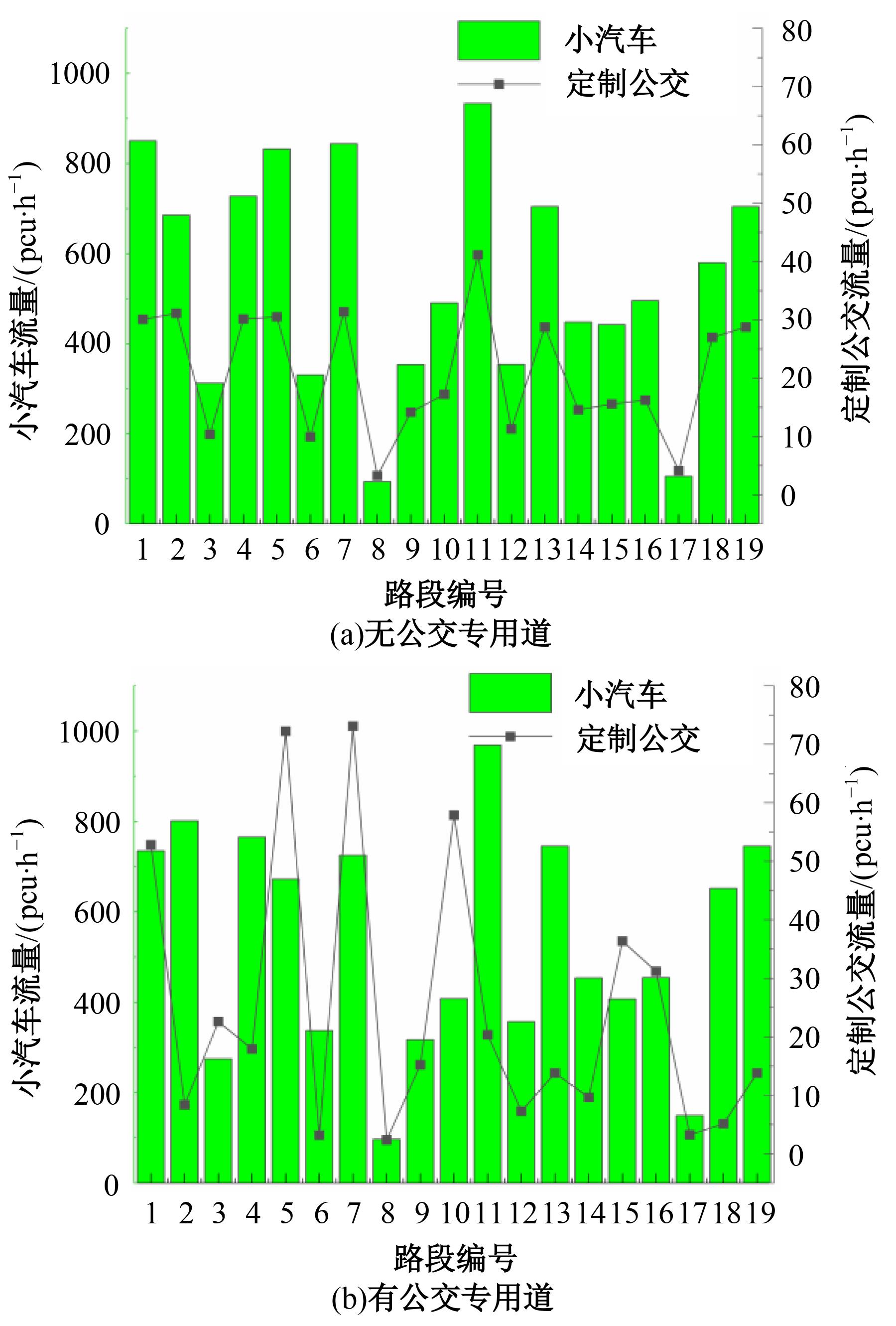
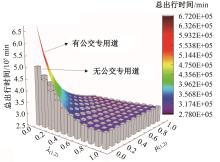
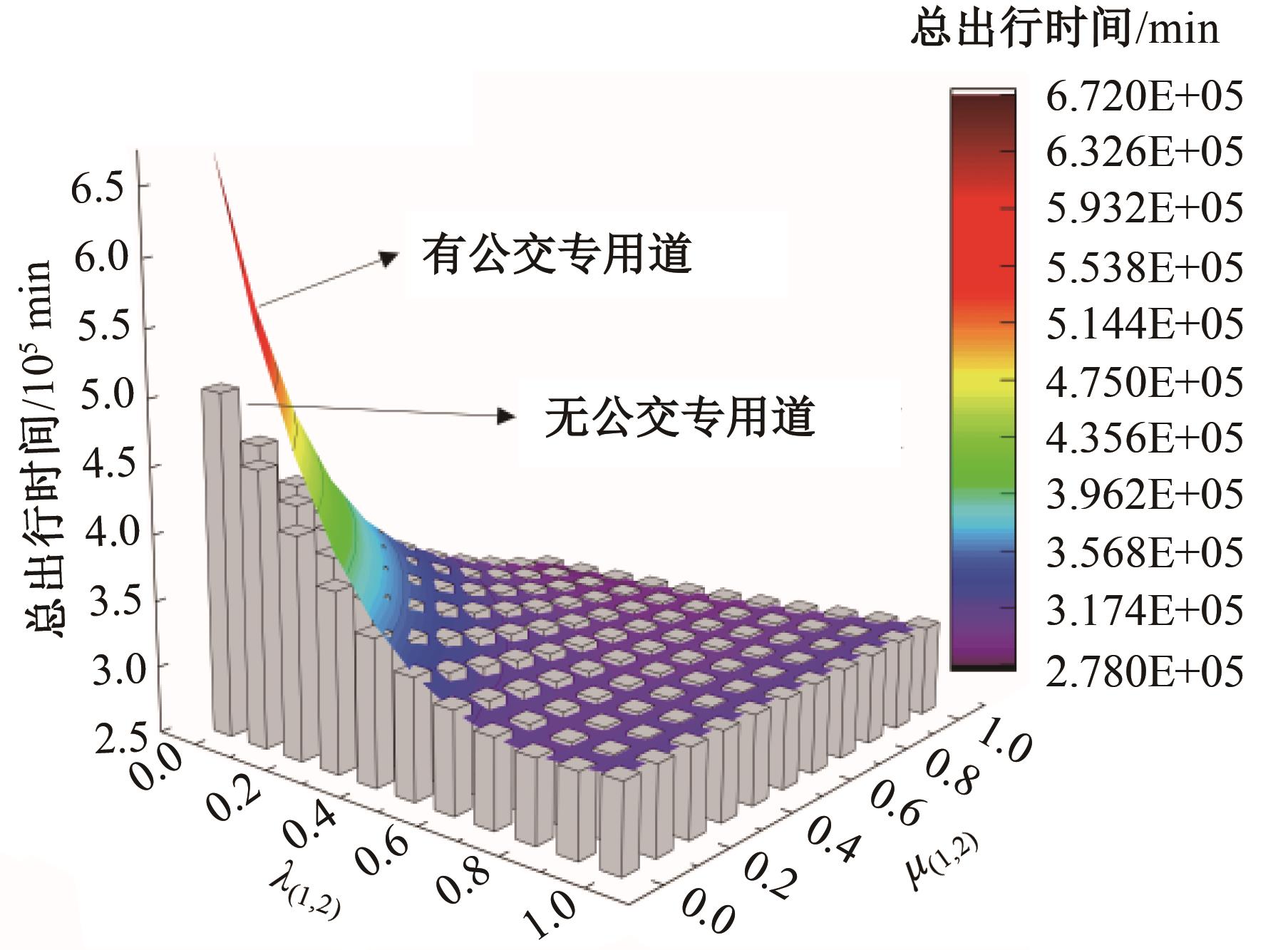
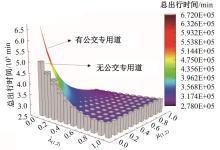
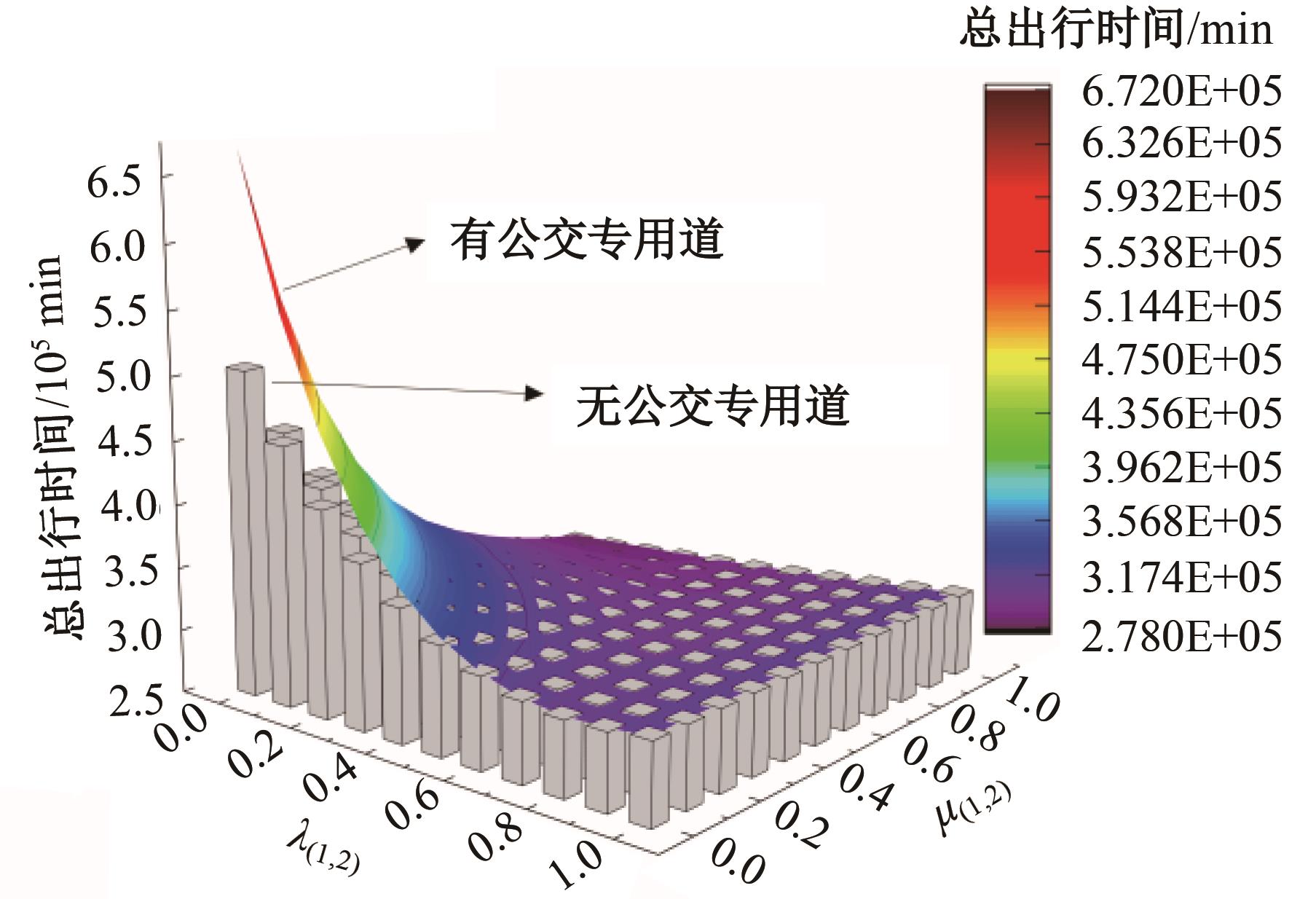
为研究小汽车、常规公交、定制公交混合交通流中出行者的逐日路径选择行为及其对路网的影响,本文首先对3种出行方式的特征进行分析,同时考虑到公交专用道这一公交优先方式,将路段分为无公交专用道的路段和有公交专用道的路段,从而构建混合交通流下的道路阻抗函数,并基于此进一步运用交通网络理论建立混合逐日均衡模型。选取含有多OD对出行需求的路网进行了数值模拟,仿真结果表明:经验依赖程度对定制公交出行者的影响大于小汽车出行者;为路径设置公交专用道会提升定制公交的路径流量,但效果的显著性具有差距;常规公交出行者比例过大时可能会增加总出行时间,而定制公交所吸引的小汽车出行者比例越大越能降低总出行时间,且设置公交专用道是否能降低总出行时间与这两项比例的大小密切相关。
中图分类号:
- U491
| [1] | 卢文慧. 基于多视角的城市交通拥堵问题研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2019. |
| Lu Wen-hui. A multi-perspective study of urban traffic congestion[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2019. | |
| [2] | 李彬. 定制公交与定制公交客车的研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学汽车学院, 2013. |
| Li Bin. The study of customized city bus service[D]. Xi'an: School of Automobile, Chang'an University, 2013. | |
| [3] | Liu K J, Liu J M, Zhang J W. Heuristic approach for the multiobjective optimization of the customized bus scheduling problem[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2022, 16(3): 277-291. |
| [4] | 沈旻宇. 随机用户均衡下考虑学习行为的逐日动态模型研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2016. |
| Shen Min-yu. Day-to-day flow dynamics with user learning under stochastic user equilibrium[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| [5] | Zhou B, Xu M, Meng Q, et al. A day-to-day route flow evolution process towards the mixed equilibria[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2017, 82: 210-228. |
| [6] | Zhang C, Liu T L, Huang H J, et al. A cumulative prospect theory approach to commuters' day-to-day route-choice modeling with friends' travel information[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 86: 527-548. |
| [7] | 尹子坤, 关宏志, 李涛. 逐日路径演化中出行者信息偏好的实验分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(4): 234-240. |
| Yin Zi-kun, Guan Hong-zhi, Li Tao. Experimental analysis of diver's information preference under day-to-day traffic dynamics[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2017, 17(4): 234-240. | |
| [8] | Lou X M, Cheng L, Chu Z M. Modelling travellers' en-route path switching in a day-to-day dynamical system[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2017, 5(1): 15-37. |
| [9] | 刘诗序, 王智煜, 关宏志, 等. 不同信息下的逐日路径选择行为实验与模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(6): 106-113. |
| Liu Shi-xu, Wang Zhi-yu, Guan Hong-zhi, et al. Experiment and model of day-to-day route-choice behavior under different information[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(6): 106-113. | |
| [10] | 常玉林, 徐文倩, 孙超, 等. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| Chang Yu-lin, Xu Wen-qian, Sun Chao, et al. Day-to-day equilibrium of hybrid traffic considering obedience degree under internet of vehicles environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. | |
| [11] | Wu J, Ji Y, Sun X, et al. Guidance optimization of travelers' travel mode choice based on fuel tax rate and bus departure quantity in two-mode transportation system[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020(10): 1-10. |
| [12] | 寇钊. 双模式交通逐日演化模型和逐周干预策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2021. |
| Kou Zhao. Day-to-day traffic evolution model and week-to-week intervention strategies for bi-modal networks[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| [13] | Yao J, Shi F, Shi A, et al. Evaluation of exclusive bus lanes in a bi-modal degradable road network[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 60: 36-51. |
| [14] | Zheng F, Chen J, Wang H, et al. Developing a dynamic utilisation scheme for exclusive bus lanes on urban expressways: an enhanced CTM‐based approach versus a microsimulation‐based approach[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(12): 1657-1664. |
| [15] | 四兵锋, 钟鸣, 高自友. 城市混合交通条件下路段阻抗函数的研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2008, 35(1): 68-73. |
| Si Bing-feng, Zhong Ming, Gao Zi-you. A link resistance function of urban mixed traffic network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2008, 35(1): 68-73. | |
| [16] | 陈旭, 陆丽丽, 曹祖平, 等. 道路阻抗函数研究综述[J].交通运输研究, 2020, 6(2): 30-39. |
| Chen Xu, Lu Li-li, Cao Zu-ping, et al. Review of studies on road impedance functions[J]. Transport Research, 2020, 6(2): 30-39. | |
| [17] | 陈芳, 龙建成. 基于双层规划的城市公交专用道优化设计[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 39(3): 296-302. |
| Chen Fang, Long Jian-cheng. Optimum design of city bus lane based on bi-level programming[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 39(3): 296-302. | |
| [18] | 四兵锋, 杨小宝, 高亮. 基于系统最优的城市公交专用道网络设计模型及算法[J]. 中国管理科学, 2016, 24(6): 106-114. |
| Si Bing-feng, Yang Xiao-bao, Gao Liang. System optimization based bus-lane network design model and algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2016, 24(6): 106-114. | |
| [19] | 刘诗序, 陈文思, 池其源, 等. 弹性需求下的网络交通流逐日动态演化[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(6): 12-26. |
| Liu Shi-xu, Chen Wen-si, Chi Qi-yuan, et al. Day-to-day dynamical evolution of network traffic flow with elastic demand[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(6): 12-26. | |
| [20] | . 城市道路工程设计规范 [S]. |
| [1] | 潘义勇,徐家聪,尤逸文,全勇俊. 网约车出行需求影响因素多尺度空间异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1567-1575. |
| [2] | 卢凯明,陈艳艳,仝瑶,张健,李永行,罗莹. 数据驱动的信号交叉口排队尾车驶离状态预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1275-1286. |
| [3] | 周成栋,宋菲,赵小梅,姚俊杰. 基于多模式双动态演化的拥堵收费模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1319-1327. |
| [4] | 张河山,范梦伟,谭鑫,郑展骥,寇立明,徐进. 基于改进YOLOX的无人机航拍图像密集小目标车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [5] | 秦严严,肖腾飞,罗钦中,王宝杰. 雾天高速公路车辆跟驰安全分析与控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1241-1249. |
| [6] | 岳昊,常笑,刘建业,曲秋莳. 引入车辆窗的定制公交线路优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1266-1274. |
| [7] | 宋现敏,湛天舒,李海涛,刘博,张云翔. 考虑用户成本和泊位利用率的停车预约分配模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1287-1297. |
| [8] | 郭祎,魏书威,姜涛. 基于区位势能和多源数据的城市客运交通规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1328-1335. |
| [9] | 潘义勇,徐翔宇. 数据不平衡的MobileViT网络交通事故严重程度预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 947-953. |
| [10] | 陈永恒,杨家伟,孙经宇. 借道左转交叉口的网联左转车辆最佳轨迹控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 614-622. |
| [11] | 陈发城,鲁光泉,林庆峰,张浩东,马社强,刘德志,宋会军. 有条件自动驾驶下驾驶人接管行为综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [12] | 何永明,冯佳,魏堃,万亚楠. 超高速公路曲线路段车辆制动侧滑影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [13] | 吴娇蓉,刘旭东. 不同住房类型空间单元的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [14] | 金盛,李博林,薛炜. 智能网联车借用公交专用道的轨迹与信号协同优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 566-576. |
| [15] | 王长帅,徐铖铖,任卫林,彭畅,佟昊. 自动驾驶接管过程中驾驶能力恢复状态对交通流振荡特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 150-161. |
|