吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1241-1249.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230634
雾天高速公路车辆跟驰安全分析与控制策略
- 1.重庆交通大学 交通运输学院,重庆 400074
2.生态安全屏障区交通网设施管控及循环修复技术交通运输行业重点实验室(长安大学),西安 710064
Car-following safety analysis and control strategy for foggy freeway
Yan-yan QIN1( ),Teng-fei XIAO1,Qin-zhong LUO1,Bao-jie WANG2(
),Teng-fei XIAO1,Qin-zhong LUO1,Bao-jie WANG2( )
)
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Management,Control and Cycle Repair Technology for Traffic Network Facilities in Ecological Security Barrier Area(Chang'an University),Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
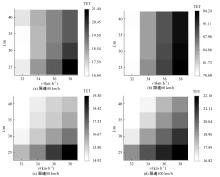
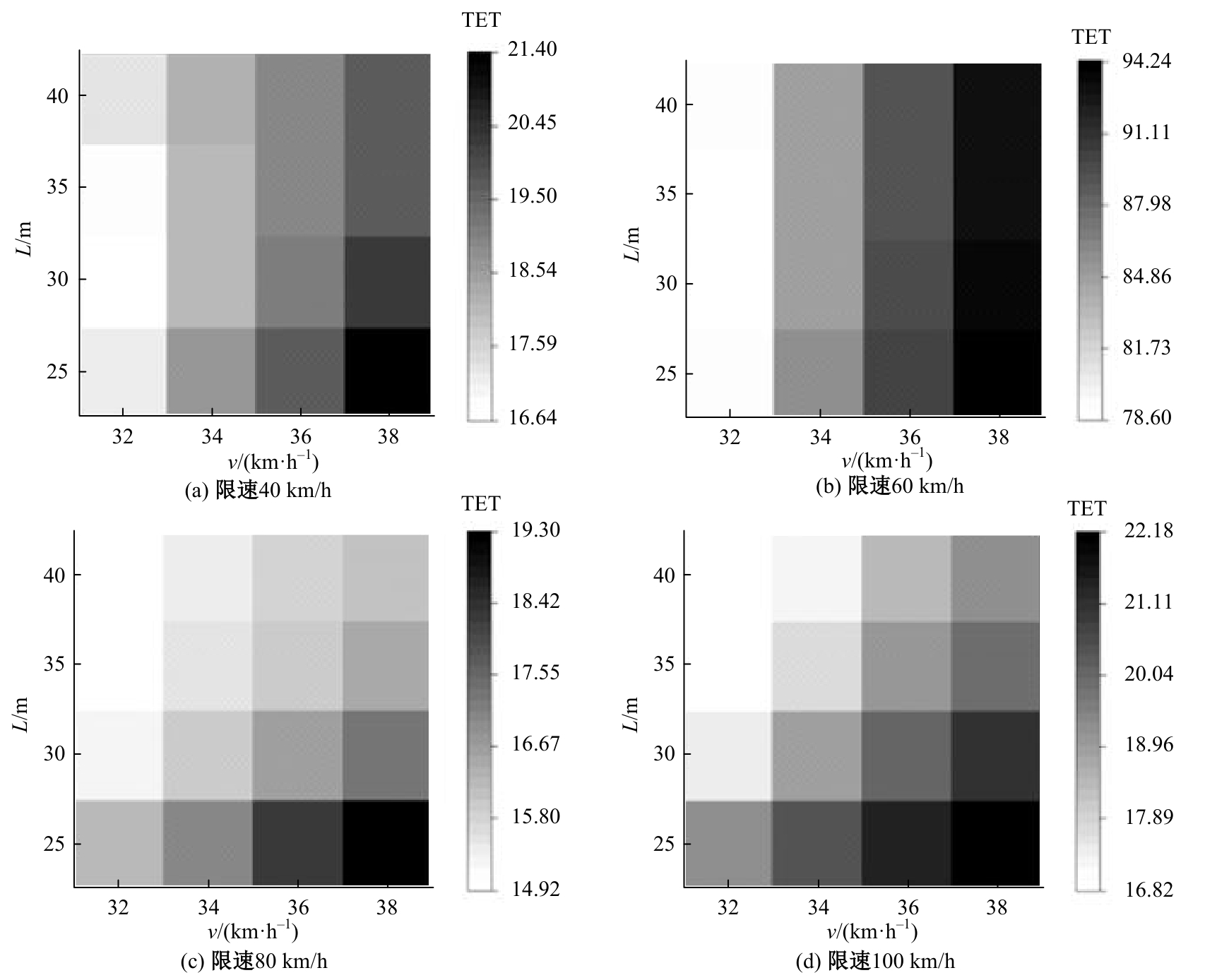
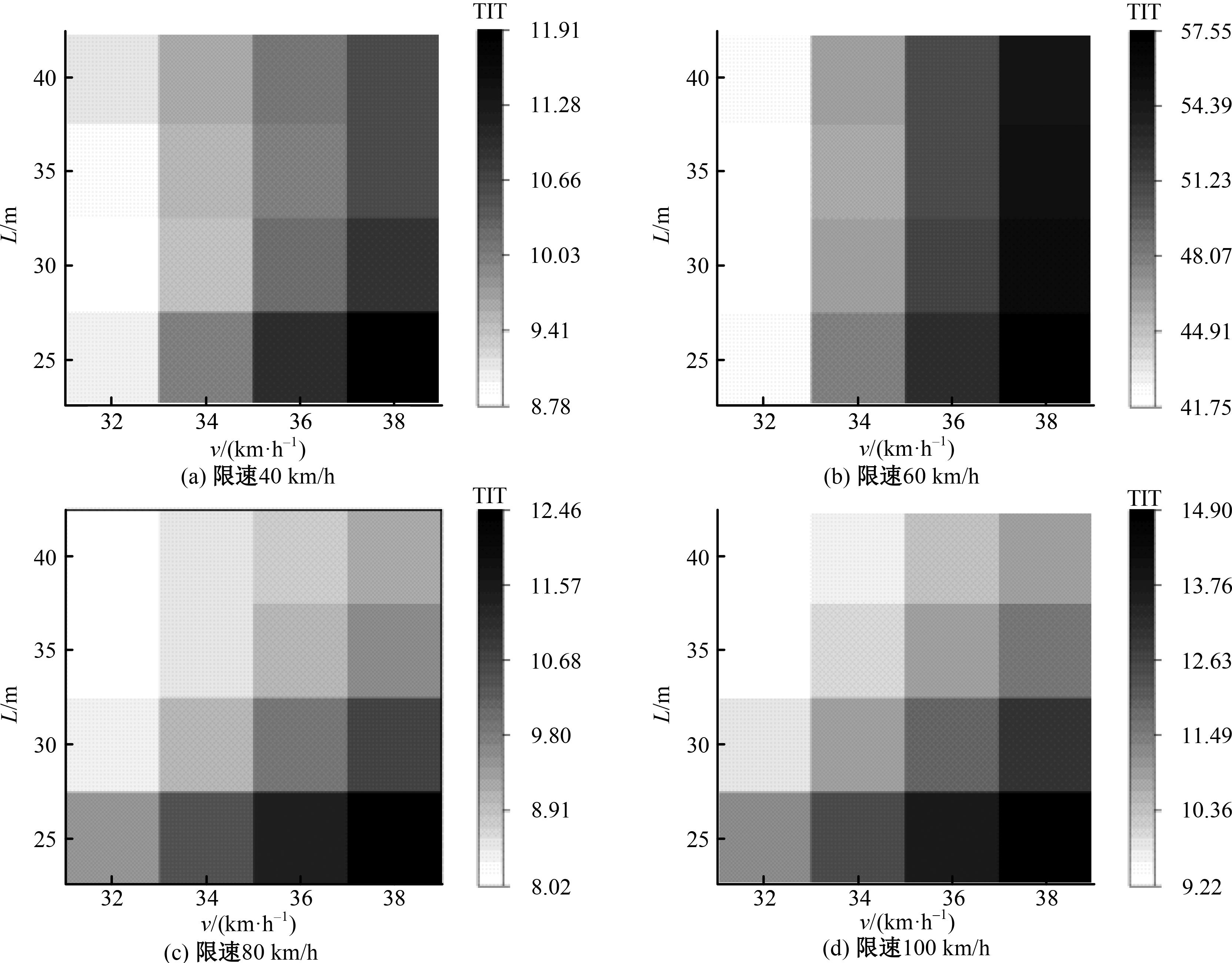
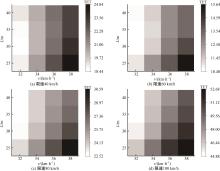
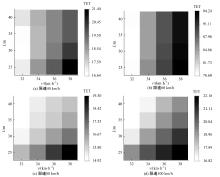
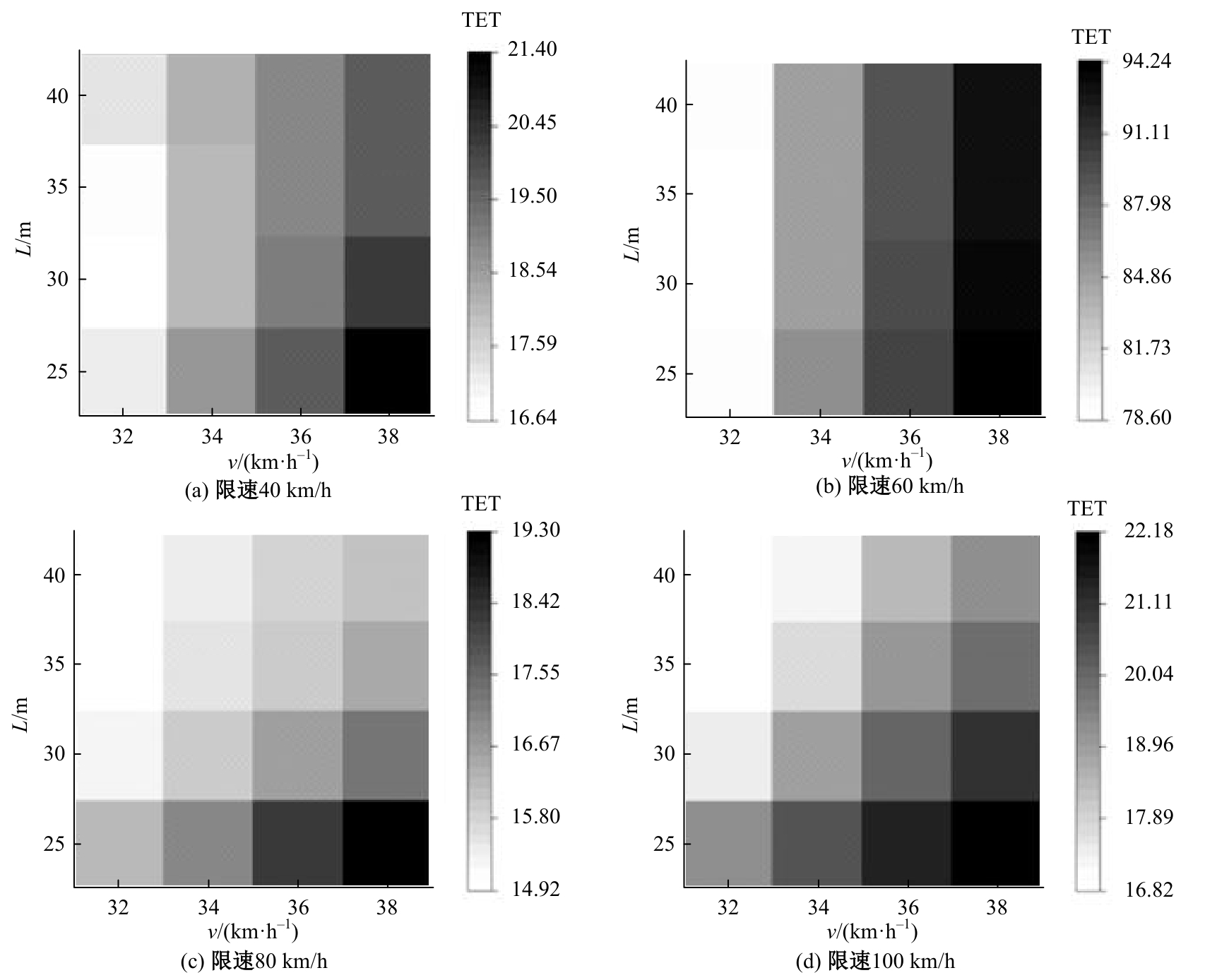
针对雾天环境高速公路车辆跟驰安全进行了研究,并提出了基于车车通信(Vehicle-to-vehicle,V2V)环境的雾天跟驰安全提升策略。首先,选取雾天跟驰模型描述雾天车辆跟驰行为,设计数值仿真实验,分析不同雾天浓度和限速条件对车辆追尾碰撞风险的影响。然后,对仿真实验中的碰撞时间阈值TTC *,车队初始速度v和头车刚观测到事故发生点时头车与事故点的距离L进行参数敏感性分析。最后,基于雾天V2V环境,考虑速度差对跟驰行为的影响作用,提出雾天场景下的高速公路跟驰安全控制策略。研究结果表明:轻雾场景和浓雾场景分别在限速60 km/h和100 km/h时车辆追尾碰撞风险最高,轻雾场景在限速40 km/h和80 km/h时车辆追尾碰撞风险最低,浓雾场景在限速60 km/h时车辆追尾碰撞风险最低。车辆追尾碰撞风险与车队初始速度v和碰撞时间阈值TTC*呈正相关,与头车刚观测到事故发生点时头车与事故点的距离L呈负相关。本文控制策略能有效降低雾天高速公路车辆追尾碰撞风险,在置信水平为95%的情况下,车辆追尾碰撞风险降低幅度显著,在不同雾天浓度和限速条件下,车辆追尾碰撞风险可降低36.70%~45.14%。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Shangguan Q Q, Fu T, Liu S. Investigating rear-end collision avoidance behavior under varied foggy weather conditions: a study using advanced driving simulator and survival analysis[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 139:No. 105499. |
| 2 | 吴兵, 翟犇, 卢建涛, 等. 基于安全风险的恶劣天气下高速公路建议车速确定方法[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 48(11): 1570-1578. |
| Wu Bing, Zhai Ben, Lu Jian-tao, et al. Determination of freeway recommended speed based on safety risk under adverse weather conditions[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2020, 48(11): 1570-1578. | |
| 3 | Das A, Ghasemzadeh A, Ahmed M M. Analyzing the effect of fog weather conditions on driver lane-keeping performance using the SHRP2 naturalistic driving study data[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2019, 68: 71-80. |
| 4 | Hammit B E, Ghasemzadeh A, James R M, et al. Evaluation of weather-related freeway car-following behavior using the SHRP2 naturalistic driving study database[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2018, 59: 244-259. |
| 5 | Rosey F, Aillerie I, Espie S, et al. Driver behaviour in fog is not only a question of degraded visibility—a simulator study[J]. Safety Science, 2017, 95: 50-61. |
| 6 | Huang Y, Yan X D, Li X M, et al. Improving car-following model to capture unobserved driver heterogeneity and following distance features in fog condition[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2022, 10: 1-24. |
| 7 | 高坤, 涂辉招, 时恒, 等. 雾霾天气低能见度对不同跟驰状态驾驶行为的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1716-1727. |
| Gao Kun, Tu Hui-zhao, Shi Heng, et al. Effect of low visibility in haze weather condition on longitudinal driving behavior in different car-following stages[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1716-1727. | |
| 8 | Das A, Ahmed M M. Adjustment of key lane change parameters to develop microsimulation models for representative assessment of safety and operational impacts of adverse weather using SHRP2 naturalistic driving data[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2022, 81: 9-20. |
| 9 | Zhai B, Lu J T, Wang Y L, et al. Real-time prediction of crash risk on freeways under fog conditions[J]. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 287-298. |
| 10 | Wu Y N, Abdel A M, Cai Q, et al. Developing an algorithm to assess the rear-end collision risk under fog conditions using real-time data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 87: 11-25. |
| 11 | 黄岩, 闫学东, 李晓梦, 等. 基于多用户驾驶模拟平台的雾天高速公路跟驰模型参数标定及验证[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(8): 320-330. |
| Huang Yan, Yan Xue-dong, Li Xiao-meng, et al. Parameters calibration and validation for car-following models in freeway under foggy conditions based on multi-user driving simulator system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(8): 320-330. | |
| 12 | Minderhoud M M, Bovy P H L. Extended time-to-collision measures for road traffic safety assessment[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2001, 33(1): 89-97. |
| 13 | Hassanin O, Wang X S, Wu X B, et al. Efficiency performance and safety evaluation of the responsibility-sensitive safety in freeway car-following scenarios using automated longitudinal controls[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2022, 177:No. 106799. |
| 14 | Han Y, Yu H, Li Z B, et al. An optimal control-based vehicle speed guidance strategy to improve traffic safety and efficiency against freeway jam waves[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 163: No.106429. |
| 15 | 秦严严,刘小辉,唐热情. 交通流分析理论[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社,2023. |
| 16 | 罗瑞发, 郝慧君, 徐桃让, 等. 考虑智能网联车队强度的混合交通流基本图模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(2): 405-412. |
| Luo Rui-fa, Hao Hui-jun, Xu Tao-rang, et al. Fundamental diagram model of mixed traffic flow of connected and automated vehicles considering vehicles degradations and platooning intensity[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 405-412. | |
| 17 | 秦严严, 杨晓庆, 王昊. 智能网联混合交通流CO2排放影响及改善方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| Qin Yan-yan, Yang Xiao-qing, Wang Hao. Impacts of CO2 emissions and improving method for connected and automated mixed traffic flow[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [1] | 潘义勇,徐家聪,尤逸文,全勇俊. 网约车出行需求影响因素多尺度空间异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1567-1575. |
| [2] | 卢凯明,陈艳艳,仝瑶,张健,李永行,罗莹. 数据驱动的信号交叉口排队尾车驶离状态预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1275-1286. |
| [3] | 周成栋,宋菲,赵小梅,姚俊杰. 基于多模式双动态演化的拥堵收费模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1319-1327. |
| [4] | 张河山,范梦伟,谭鑫,郑展骥,寇立明,徐进. 基于改进YOLOX的无人机航拍图像密集小目标车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [5] | 李振江,万利,周世睿,陶楚青,魏巍. 基于时空Transformer网络的隧道交通运行风险动态辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1336-1345. |
| [6] | 宋现敏,湛天舒,李海涛,刘博,张云翔. 考虑用户成本和泊位利用率的停车预约分配模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1287-1297. |
| [7] | 郭祎,魏书威,姜涛. 基于区位势能和多源数据的城市客运交通规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1328-1335. |
| [8] | 潘义勇,徐翔宇. 数据不平衡的MobileViT网络交通事故严重程度预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 947-953. |
| [9] | 陈永恒,杨家伟,孙经宇. 借道左转交叉口的网联左转车辆最佳轨迹控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 614-622. |
| [10] | 陈发城,鲁光泉,林庆峰,张浩东,马社强,刘德志,宋会军. 有条件自动驾驶下驾驶人接管行为综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [11] | 何永明,冯佳,魏堃,万亚楠. 超高速公路曲线路段车辆制动侧滑影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [12] | 吴娇蓉,刘旭东. 不同住房类型空间单元的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [13] | 王长帅,徐铖铖,任卫林,彭畅,佟昊. 自动驾驶接管过程中驾驶能力恢复状态对交通流振荡特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | 张娜,陈峰,王剑坡,朱亚迪. 基于时空序列相似性的城轨乘客出行模式识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2588-2599. |
| [15] | 商蕾,杨萍,杨祥国,潘建欣,杨军,张梦如. 基于APSO-BP-PID控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2401-2413. |
|