吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 614-622.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230472
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
借道左转交叉口的网联左转车辆最佳轨迹控制
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Optimal trajectory control for connected left-turn vehicles at exit lane for left-turn intersections
Yong-heng CHEN( ),Jia-wei YANG,Jing-yu SUN
),Jia-wei YANG,Jing-yu SUN
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
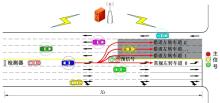
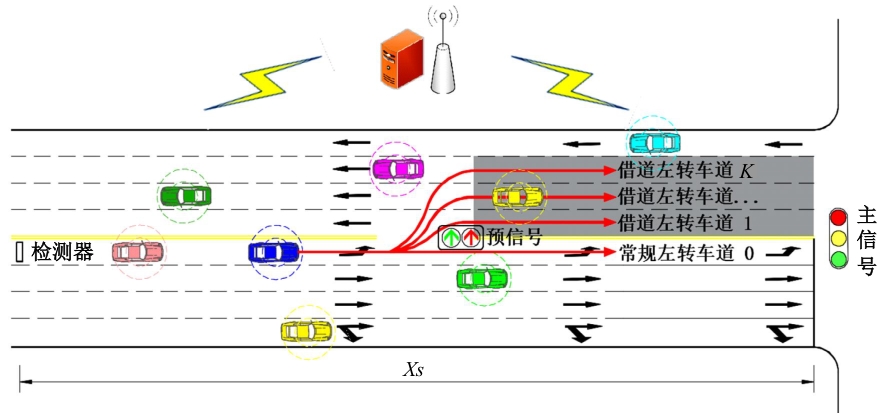
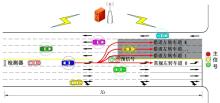
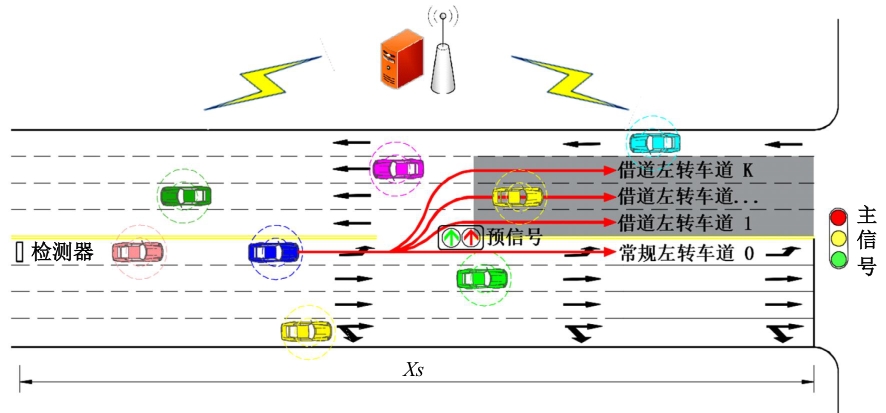
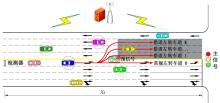
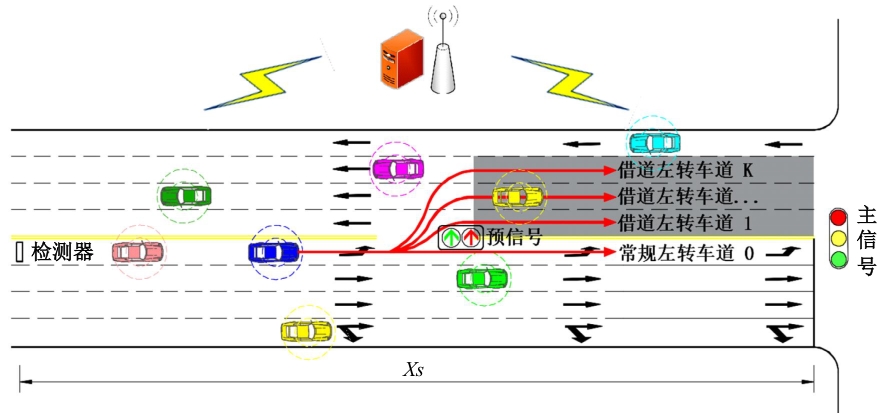
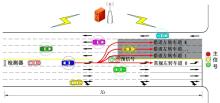
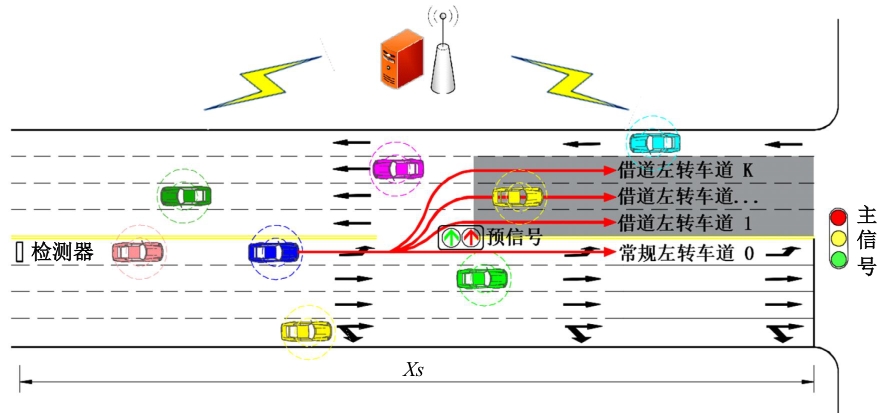
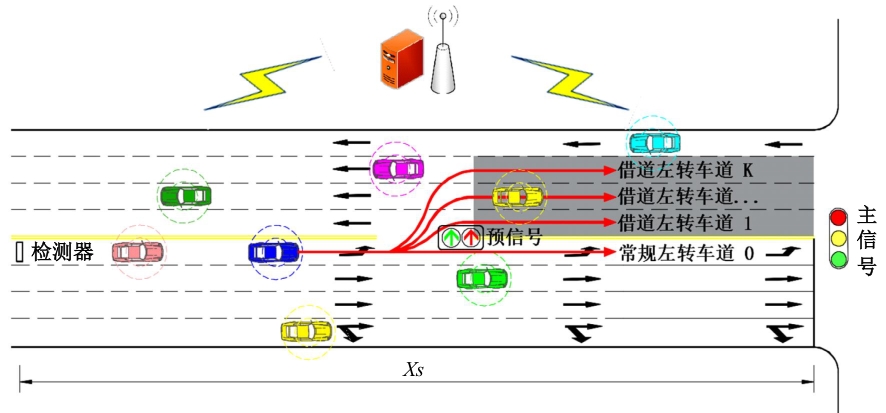
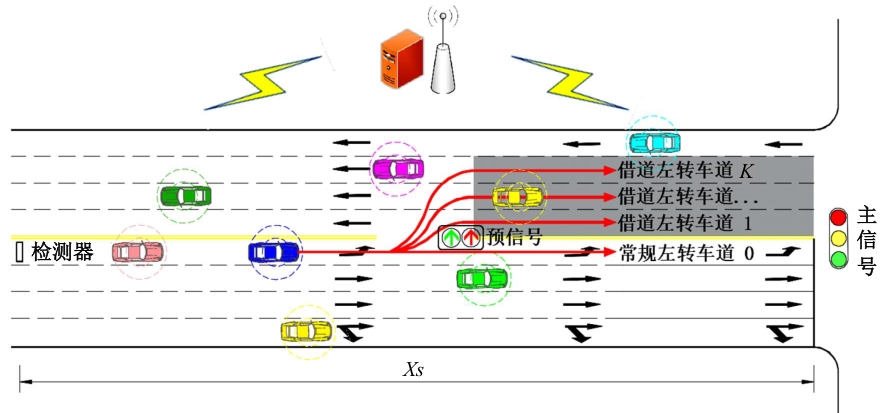
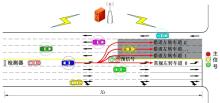
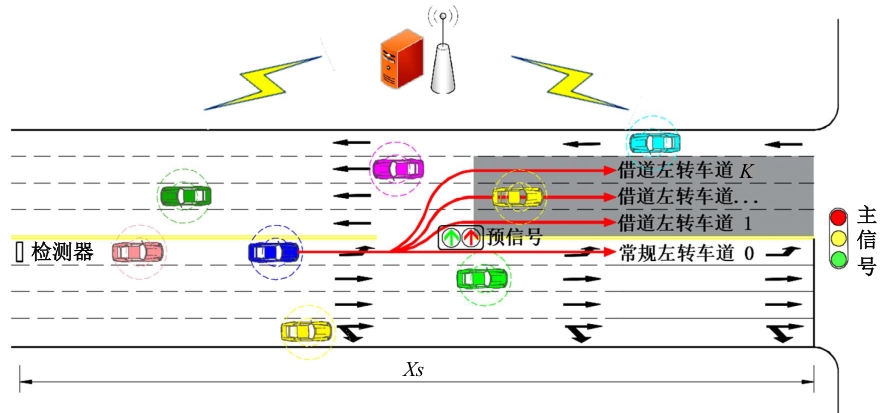
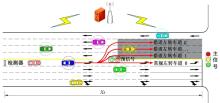
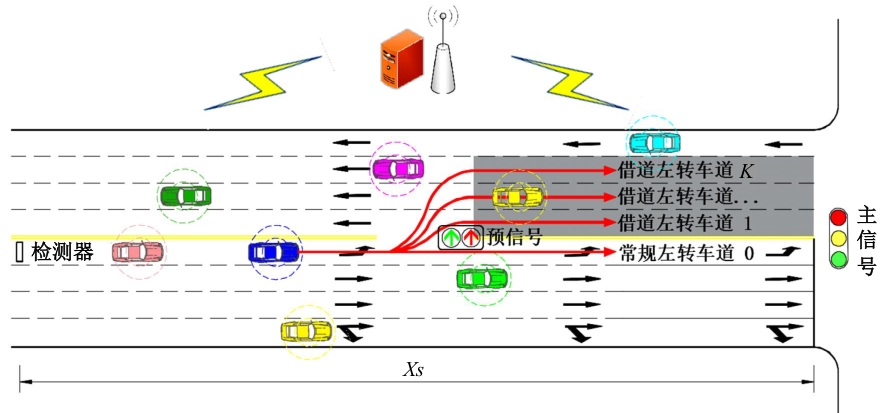
为避免车辆在借道左转交叉口频繁启停,降低车辆的延误和油耗,提出了一种智能网联车环境下借道左转交叉口左转车辆的最佳轨迹控制模型。首先,分析了考虑油耗下相较于传统交叉口,借道左转交叉口的独特之处。其次,考虑了借道左转的几何设计和交通信号,建立了相应的轨迹控制双层模型,优化车辆的车道选择和进入借道左转车道的时刻。最后,利用SUMO和Python软件进行了模型验证并设计了仿真实验分析交通量、绿信比、借道左转车道长度这些不同参数对模型效果的影响。实验结果表明:本文提出的最佳轨迹控制模型有效降低了车辆的延误和油耗,相较于Krauss控制模型,平均降低车均延误26.6%,平均降低油耗50.2%。此外,最佳轨迹控制模型在不同的借道左转车道长度下表现出鲁棒性,具有广泛的适用性。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Zhang S M, Deng W W, Zhao Q R, et al. Dynamic trajectory planning for vehicle autonomous driving[C]∥2013 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, UK, 2013: 4161-4166. |
| 2 | Luo Y G, Xiang Y, Cao K, et al. A dynamic automated lane change maneuver based on vehicle-to-vehicle communication[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 62: 87-102. |
| 3 | Lu G Y, Nie Y, Liu X B, et al. Trajectory-based traffic management inside an autonomous vehicle zone[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2019, 120: 76-98. |
| 4 | 贾彦峰, 曲大义, 林璐, 等. 基于运行轨迹的网联混合车流速度协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
| Jia Yan-feng, Qu Da-yi, Lin Lu, et al. Coordinated speed control of connected mixed traffic flow based on trajectory[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. | |
| 5 | Malikopoulos A A, Beaver L, Chremos I V. Optimal time trajectory and coordination for connected and automated vehicles[J]. Automatica, 2021, 125(6):No. 109469. |
| 6 | Liu Q, Zhao J, Zhou X. Optimal trajectory control for left-turn vehicles at exit lane for left-turn intersections[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2021(10):No. 0000576. |
| 7 | Jiang H, Hu J, An S, et al. Eco approaching at an isolated signalized intersection under partially connected and automated vehicles environment[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2017, 79(6): 290-307. |
| 8 | Ma J, Li X, Zhou F, et al. Parsimonious shooting heuristic for trajectory design of connected automated traffic part II: computational issues and optimization[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2017, 95: 421-441. |
| 9 | Zhou F, Li X, Ma J. Parsimonious shooting heuristic for trajectory design of connected automated traffic part I: theoretical analysis with generalized time geography[J]. Transportation Research Part B Methodological, 2016, 95(1): 394-420. |
| 10 | Zhang L G, Liang W J, Zheng X Z. Eco-driving for public transit in cyber-physical systems using v2i communication[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, 2018, 16(2): 79-89. |
| 11 | Zhao W M, Dong N. A platoon based cooperative eco-driving model for mixed automated and human-driven vehicles at a signalised intersection[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 95: 802-821. |
| 12 | 黄意然,宋国华,彭飞,等. 考虑排队长度的信号交叉口生态驾驶轨迹优化[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2022, 20(3): 43-56. |
| Huang Yi-ran, Song Guo-hua, Peng Fei, et al. Trajectory optimization for eco-driving taking into account queuing Length at signalized intersections[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2022, 20(3): 43-56. | |
| 13 | 刘显贵, 王晖年, 洪经纬, 等. 网联环境下信号交叉口车速控制策略及优化[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(2): 82-90. |
| Liu Xian-gui, Wang Hui-nian, Hong Jing-wei, et al. Speed control stsrategy and optimization of signalized intersection in network environment[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(2): 82-90. | |
| 14 | Yao H D, Li X P. Lane-change-aware connected automated vehicle trajectory optimization at a signalized intersection with multi-lane roads[J]. Transportation Research Part C Emerging Technologies, 2021, 129:No. 103182. |
| [1] | 陈发城,鲁光泉,林庆峰,张浩东,马社强,刘德志,宋会军. 有条件自动驾驶下驾驶人接管行为综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [2] | 何永明,冯佳,魏堃,万亚楠. 超高速公路曲线路段车辆制动侧滑影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [3] | 吴娇蓉,刘旭东. 不同住房类型空间单元的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [4] | 王长帅,徐铖铖,任卫林,彭畅,佟昊. 自动驾驶接管过程中驾驶能力恢复状态对交通流振荡特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 150-161. |
| [5] | 张娜,陈峰,王剑坡,朱亚迪. 基于时空序列相似性的城轨乘客出行模式识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2588-2599. |
| [6] | 周锡浈,宫贺,李敦敦,季彦婕,严杰. 建成环境对路内停车泊位使用率的非线性影响模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [7] | 严利鑫,曾涛,贺宜,郭军华,胡鑫辉. 共驾型智能车辆人机接管行为序列编码与解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2547-2556. |
| [8] | 曲昭伟,李霖,陈永恒,吴场建. 长区间掉头车辆特性分析及其安全评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [9] | 何永明,权聪,魏堃,冯佳,万亚楠,陈世升. 超高速公路车路协同路侧单元感知融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [10] | 程国柱,盛林,王浩宇,冯天军. 考虑右转车二次冲突的信号交叉口行人过街安全评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [11] | 张明业,杨敏,黎彧,黄世玉,李清韵. 考虑有序充电策略的多车型电动公交调度优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1293-1301. |
| [12] | 秦雅琴,钱正富,谢济铭. 协同换道避障模型和轨迹数据驱动的车辆协同避障策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [13] | 严利鑫,冯进培,郭军华,龚毅轲. 不同险态情景下共驾型智能车辆接管行为特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 683-691. |
| [14] | 马潇驰,陆建. 基于基因表达式编程的高架道路事故实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 719-726. |
| [15] | 曲大义,张可琨,顾原,王韬,宋慧,戴守晨. 自动驾驶车辆换道决策行为分析及分子动力学建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 700-710. |
|
||