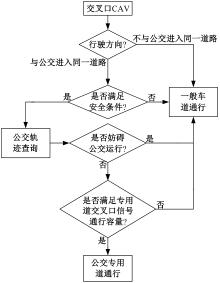
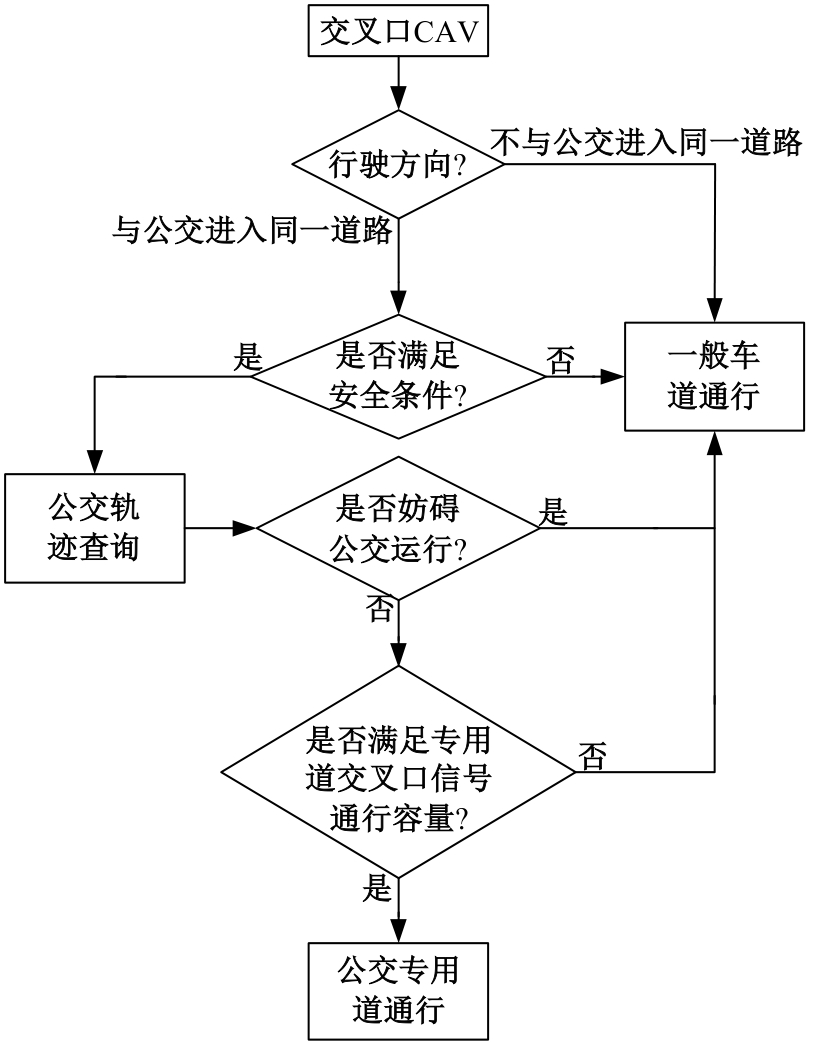
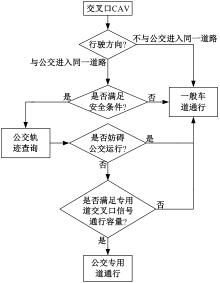
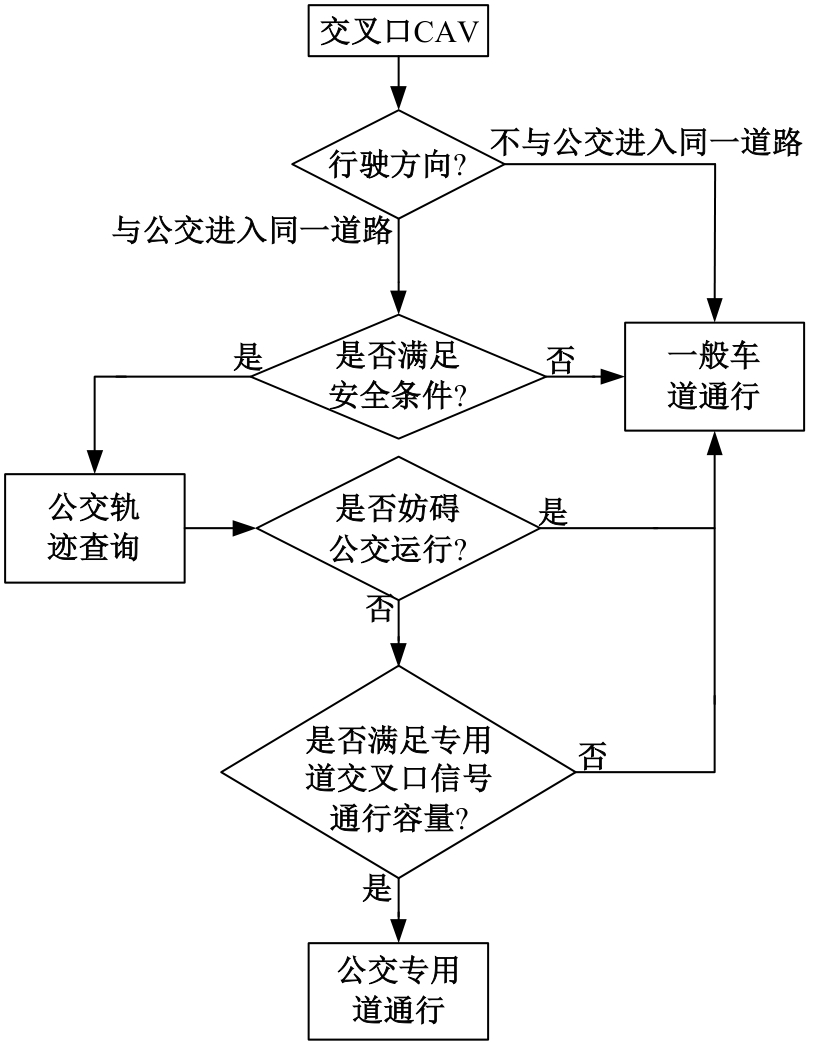
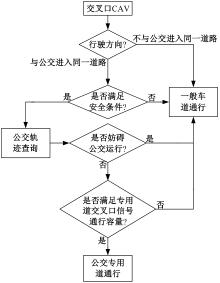
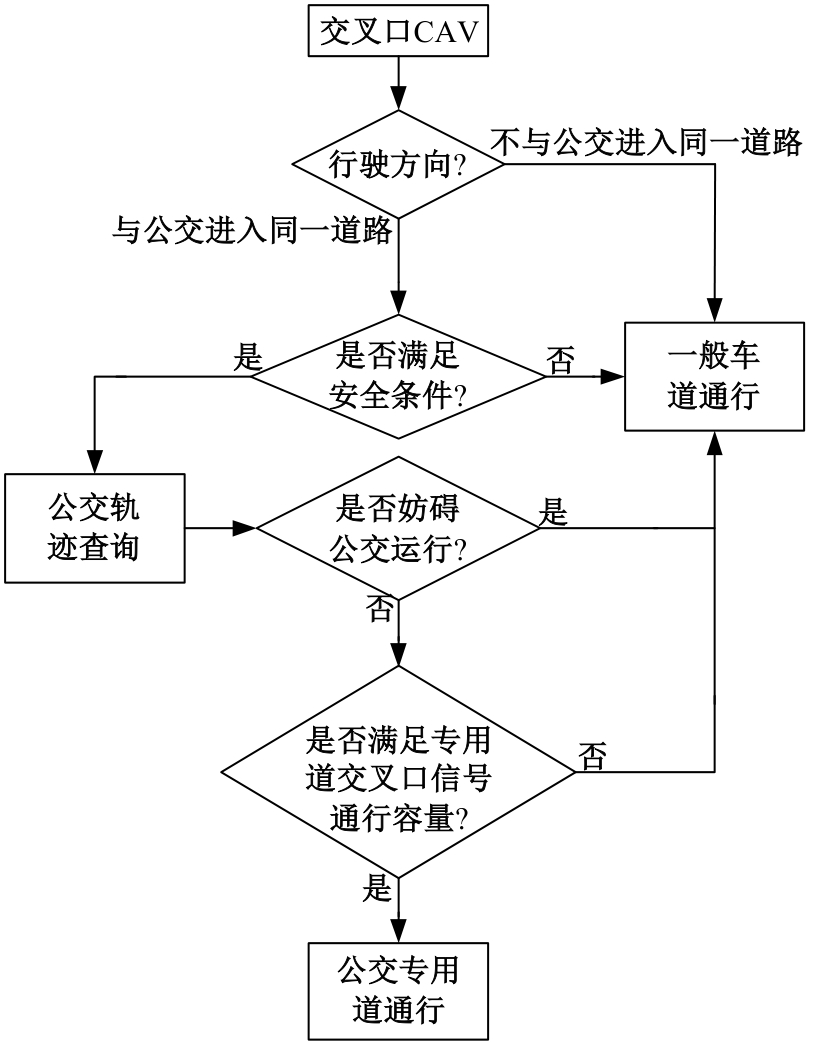
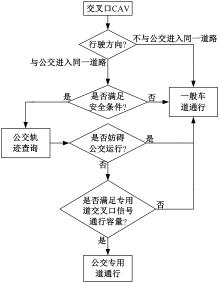
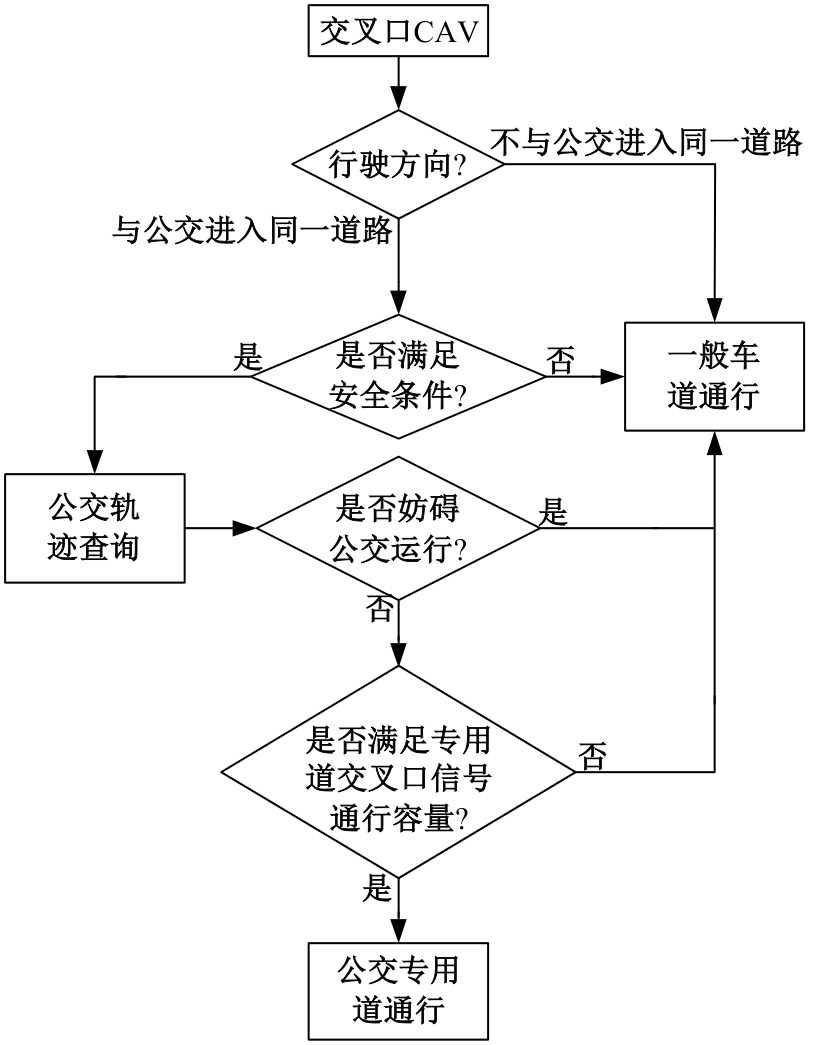
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 566-576.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230385
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
智能网联车借用公交专用道的轨迹与信号协同优化
- 1.浙江大学 智能交通研究所,杭州 310058
2.城云科技(中国)有限公司,杭州 310000
Collaborative optimization for signals and trajectories of connected automated vehicles on dedicated bus lanes
Sheng JIN1( ),Bo-lin LI1,Wei XUE2
),Bo-lin LI1,Wei XUE2
- 1.Institute of Intelligent Transportation Systems,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,China
2.City Cloud Technology (China) Co. ,Ltd. ,Hangzhou 310000,China
摘要:
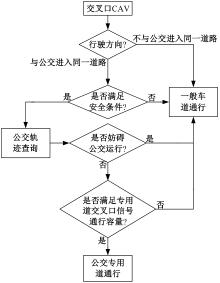
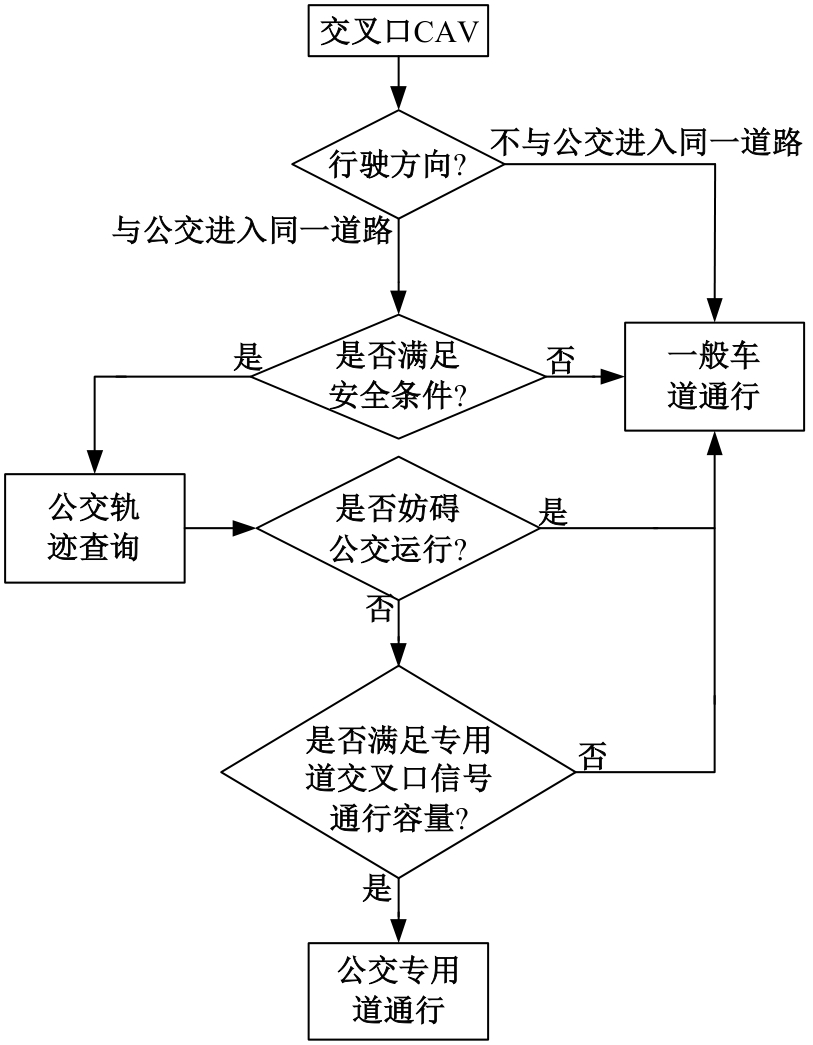
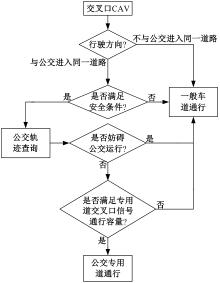
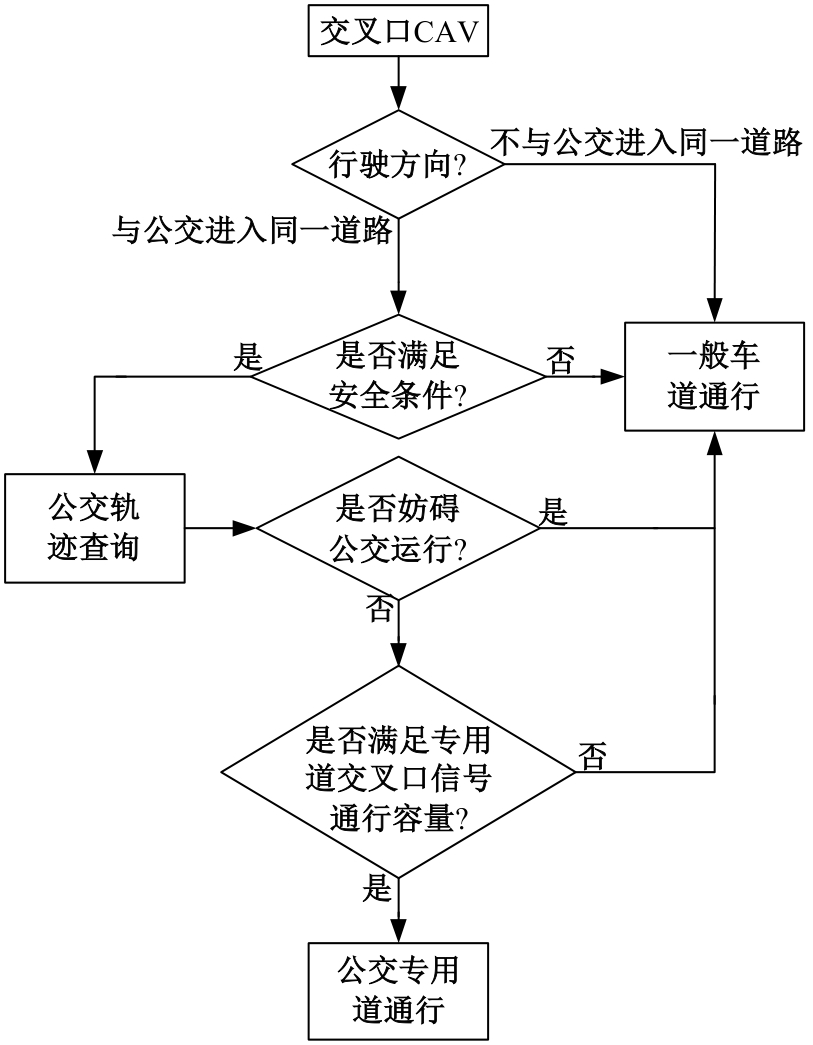
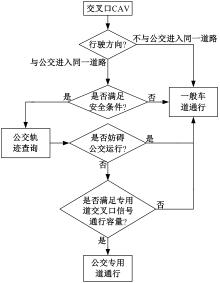
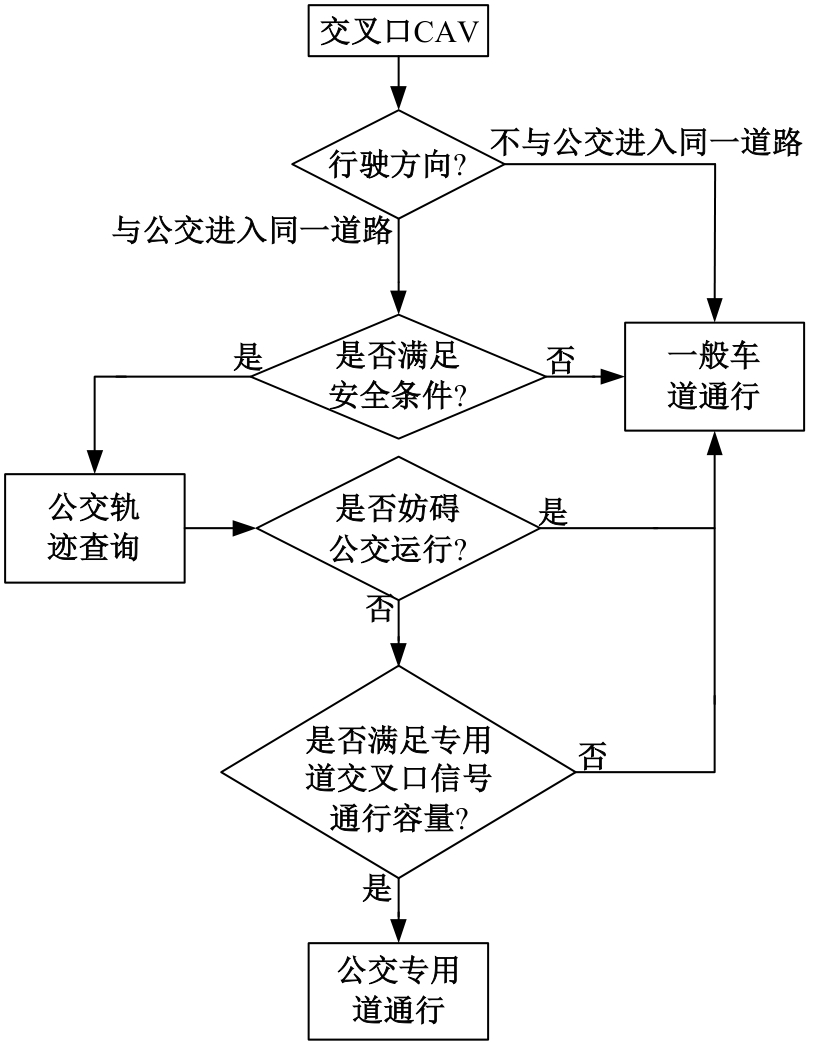
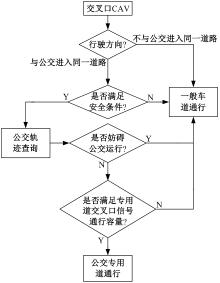
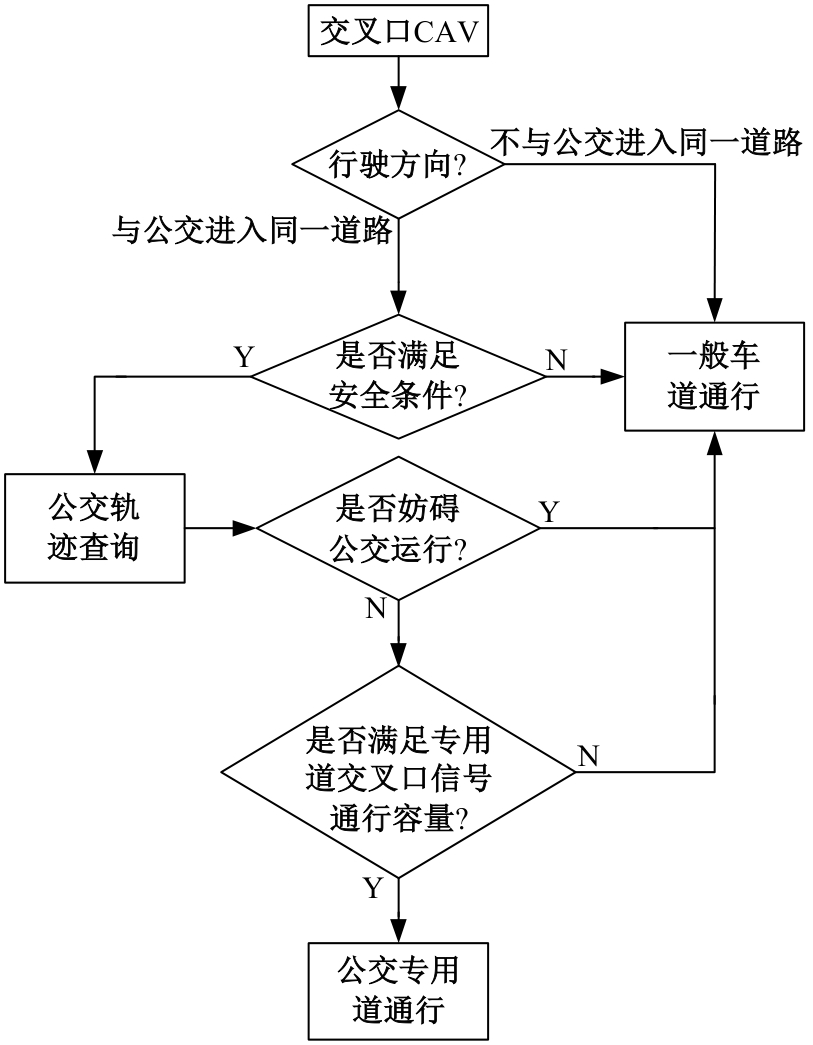
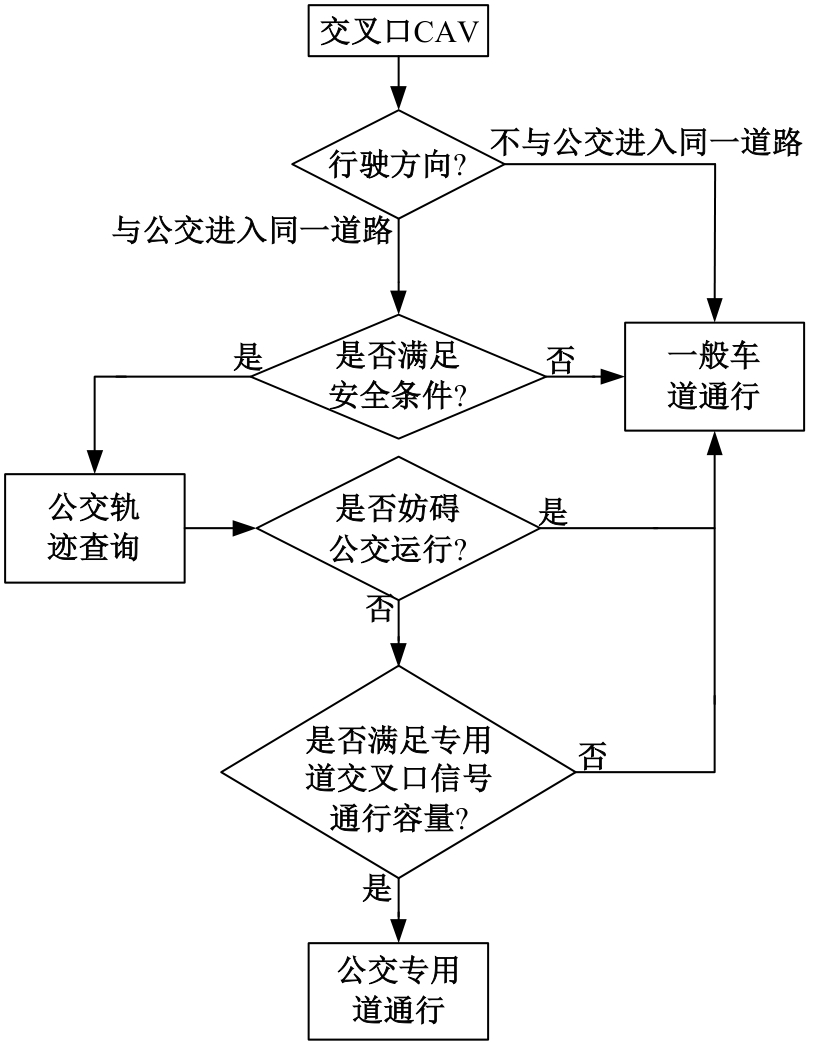
为改善智能网联车与人工驾驶汽车的混行交通流运行状态,本文提出了一种智能网联车借用公交专用道通行的轨迹与信号的协同优化方法。先在信号和轨迹双层优化模型中,为轨迹变量与信号变量建立线性数学关系,并对整体模型进行时空上的分段求解。然后应用于实际数值案例,对模型进行可行性分析,对比协同优化与非协同优化的数值结果,证明了协同优化相比于非协同优化对于智能网联车的运行效率平均有7.7%的提升。
中图分类号:
- U491.5
| 1 | Ye L, Yamamoto T. Impact of dedicated lanes for connected and autonomous vehicle on traffic flow throughput[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 512: 588-597. |
| 2 | Almeida C G H, Menendez M. Automated and connected vehicles: effects on traffic, mobility and urban design[J]. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 2017, 6(1): 3-4. |
| 3 | NHTSA. Preliminary statement of policy concerning automated vehicles[R]. Washington: NHTSA, 2013. |
| 4 | Zhou J, Zhu F. Modeling the fundamental diagram of mixed human-driven and connected automated vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 115: 102614. |
| 5 | Mohajerpoor R, Ramezani M. Mixed flow of autonomous and human-driven vehicles: analytical headway modeling and optimal lane management[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 109: 194-210. |
| 6 | Chen Z, He F, Zhang L H, et al. Optimal deployment of autonomous vehicle lanes with endogenous market penetration[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 72: 143-156. |
| 7 | Conceição L, Correia G, Tavares J P. The deployment of automated vehicles in urban transport systems: a methodology to design dedicated zones[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2017, 27: 230-237. |
| 8 | 毛向阳, 尚世亮, 崔海峰. 自动驾驶汽车安全影响因素分析与应对措施研究[J]. 上海汽车, 2018, 2018(1): 33-37. |
| Mao Xiang-yang, Shang Shi-liang, Cui Hai-feng. Analysis of safety influencing factors and countermeasures of autonomous vehicles[J]. Shanghai Auto, 2018, 2018(1): 33-37. | |
| 9 | Wirasinghe S C, Kattan L, Rahman M, et al. Bus rapid transit-a review[J]. International Journal of Urban Sciences, 2013, 17(1): 1-31. |
| 10 | Hoonsiri C, Chiarakorn S, Kiattikomol V. Using combined bus rapid transit and buses in a dedicated bus lane to enhance urban transportation sustainability[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(6): No. 13063052. |
| 11 | He S L, Ding F, Lu C R, et al. Impact of connected and autonomous vehicle dedicated lane on the freeway traffic efficiency[J]. European Transport Research Review, 2022, 14(1): 102374. |
| 12 | 陆化普, 孙煦, 吴娟. 公交专用道优化设计的双层规划模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2015, 28(2): 87-94. |
| Lu Hua-pu, Sun Xu, Wu Juan. Bi-level programming model for optimization design of eclusive bus lane[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(2): 87-94. | |
| 13 | 徐志刚, 李金龙, 赵祥模, 等. 智能公路发展现状与关键技术[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(8): 1-24. |
| Xu Zhi-gang, Li Jin-long, Zhao Xiang-mo, et al. A review on intelligent road and its related key technologies[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport. 2019, 32(8): 1-24. | |
| 14 | Eichler M, Daganzo C F. Bus lanes with intermittent priority: strategy formulae and an evaluation[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2006, 40(9): 731-744. |
| 15 | 赵鑫. 基于元胞自动机的联网车辆专用车道设置研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2020. |
| Zhao Xin. Researchon dedicated lane setting ointernet of vehicles based oncellular automata[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. | |
| 16 | Winsor M. Influence of networked and cooperative vehicles on virtual right-of-way performance in mixed traffic[D]. Munich: Technical University of Munich, 2020. |
| 17 | Chen X D, Lin X, He F, et al. Modeling and control of automated vehicle access on dedicated bus rapid transit lanes[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 120: 102795. |
| 18 | 庞明宝, 柴紫欣, 巩丹阳. 混合交通下智能网联车借道公交专用车道控制[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(4): 118-124. |
| Pang Ming-bao, Chai Zi-xin, Gong Dan-yang. Control of connected and automated vehicles driving on dedicated bus lane under mixed traffic[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(4): 118-124. | |
| 19 | Brociek R, Wajda A, Słota D. Comparison of heuristic algorithms in identification of parameters of anomalous diffusion model based on measurements from sensors[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(3): 23031722. |
| 20 | Luo Q, Rao Y Q. Heuristic algorithms for the special knapsack packing problem with defects arising in aircraft arrangement[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 215: 119392. |
| [1] | 范国伟,高宇,刘泉志,肖阳,吕雪莹,张乐,张刘. 基于改进自适应伪谱法的遥感卫星姿态机动规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 355-365. |
| [2] | 才华,寇婷婷,杨依宁,马智勇,王伟刚,孙俊喜. 基于轨迹优化的三维车辆多目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2338-2347. |
| [3] | 蒲云,徐银,刘海旭,谭一帆. 考虑多车影响的智能网联车跟驰模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1285-1292. |
| [4] | 赵新刚,王桢. 基于改进MOEA/D算法的含可再生能源系统协同优化调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1129-1135. |
| [5] | 吴娇蓉,林清凯,邓泳淇. 基于公交线路运行稳定性的潜在公交专用道需求识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 692-699. |
| [6] | 宋成举,贾洪飞,秦昊溥. 网联车混入条件下混合交通流跟驰稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 419-426. |
| [7] | 张蕾,李子牧,鄢永耀,豆飞,刘宏杰. 面向虚拟编组的多列车协同制动控制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 3027-3036. |
| [8] | 冯爽,洪伟,李小平,解方喜. 柴油机瞬变工况喷射参数及田口法协同优化对微粒排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2483-2492. |
| [9] | 焦玉玲,邓雪,李琳,刘文佳,张天泽,曹楠. 多约束条件下双边U型装配线平衡与协同优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2053-2060. |
| [10] | 刘洋,刘吉成. 基于大数据与粒子群的清洁能源协同优化调度方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1443-1448. |
| [11] | 罗瑞发,郝慧君,徐桃让,顾秋凡. 考虑智能网联车队强度的混合交通流基本图模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 405-412. |
| [12] | 魏路,高磊,李晋宏,杨建,田玉林. 基于密度峰值聚类的交通控制子区划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 124-131. |
| [13] | 马苗苗,刘立成,王鑫,杨茂. 风光发电与新能源汽车协同优化调度策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2096-2106. |
| [14] | 刘东波,沈莉潇,代磊磊,陆建. 基于多目标雷达数据的单点交通信号控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2456-2465. |
| [15] | 贾超,徐洪泽,王龙生. 基于多质点模型的列车自动驾驶非线性模型预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1913-1922. |
|
||