吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2994-3006.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211319
基于函数拟合AoA任意分布的MIMO信道特征分析
- 南京信息工程大学 电子与信息工程学院,南京 210044
MIMO channel Characteristics analysis of AoA arbitrary distribution based on basic function fitting
Jie ZHOU( ),Xue-ying Wang,Qian CHEN,Hong LUO,Lei XU
),Xue-ying Wang,Qian CHEN,Hong LUO,Lei XU
- School of Electronic and Information,Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology,Nanjing 210044,China
摘要:
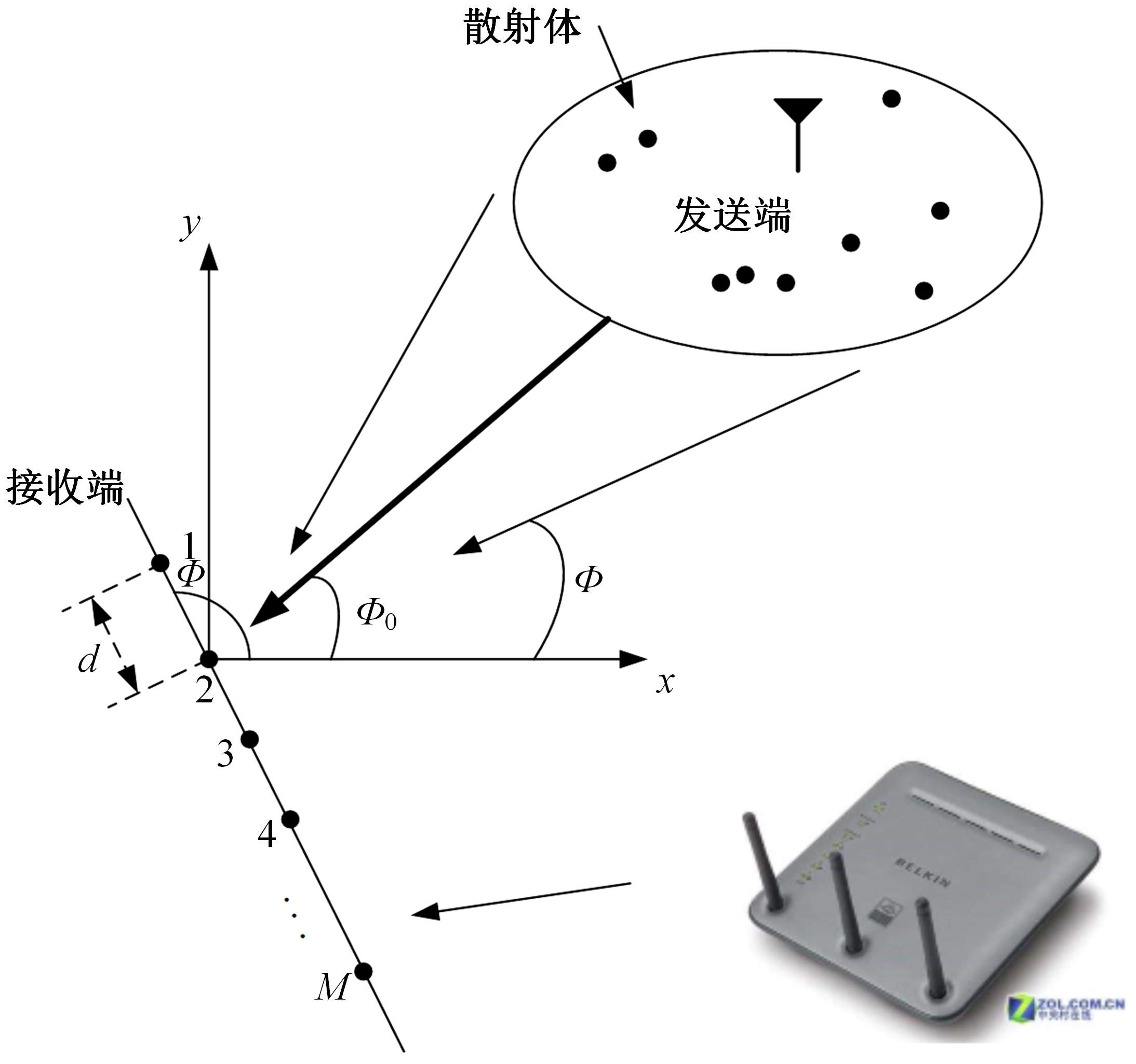
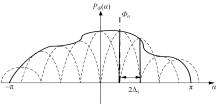
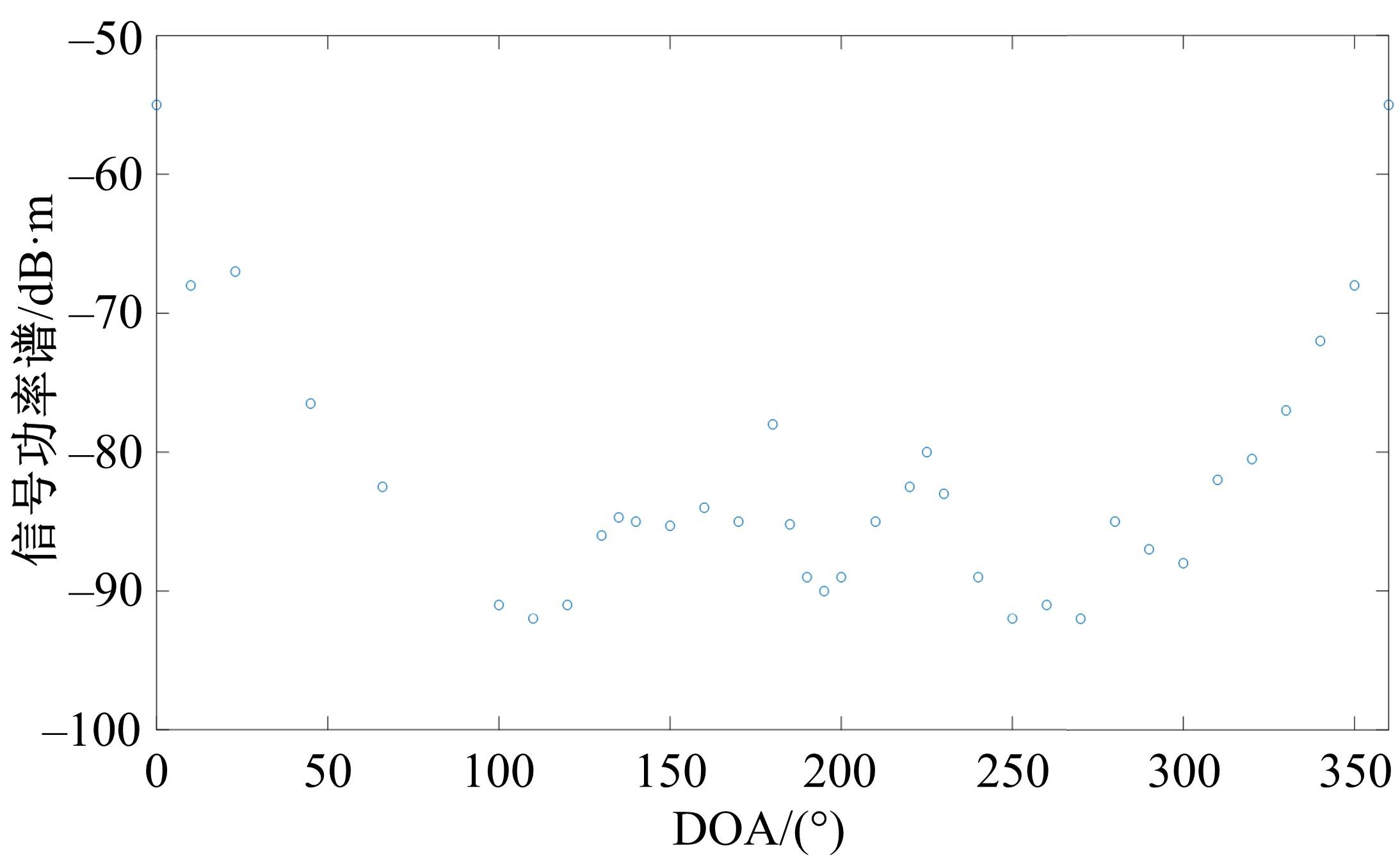
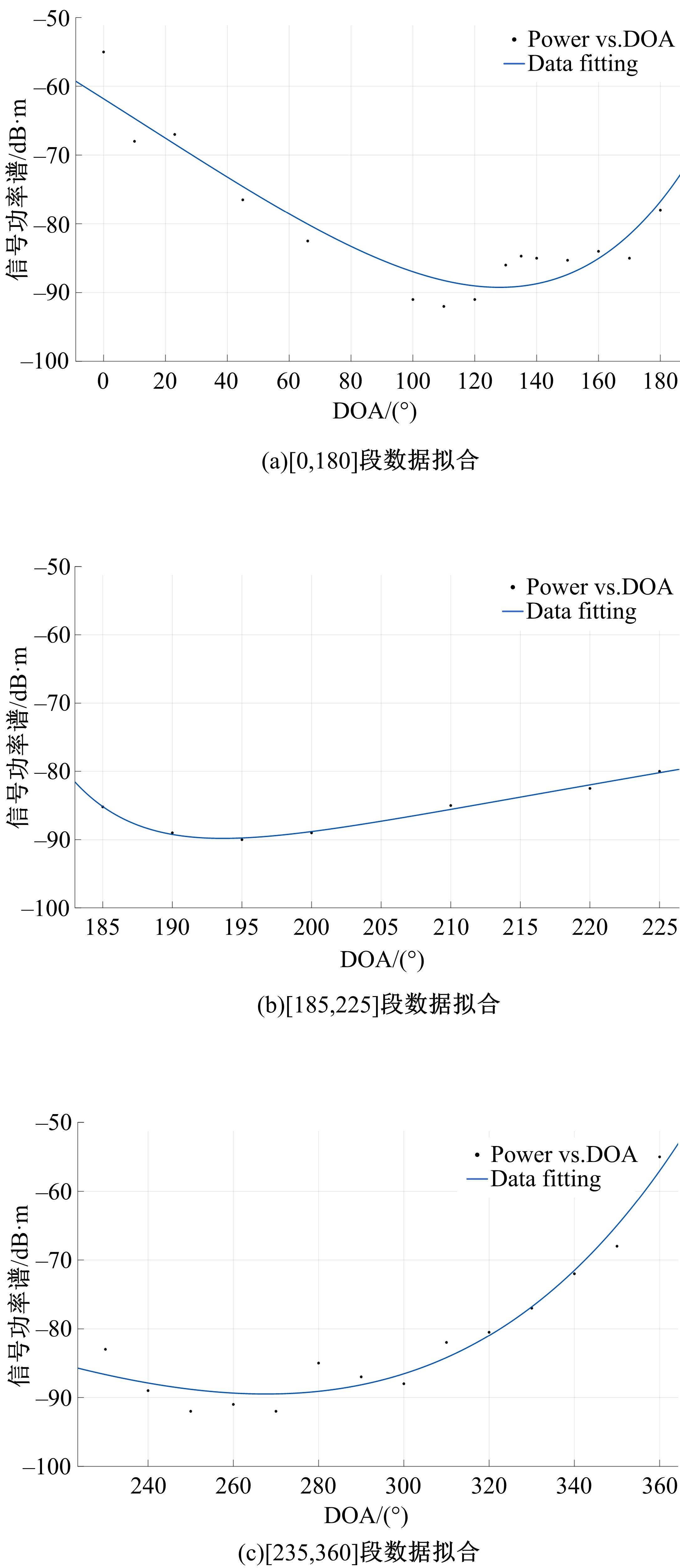
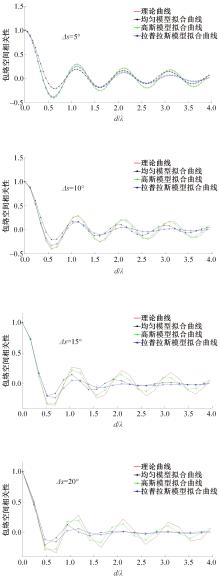
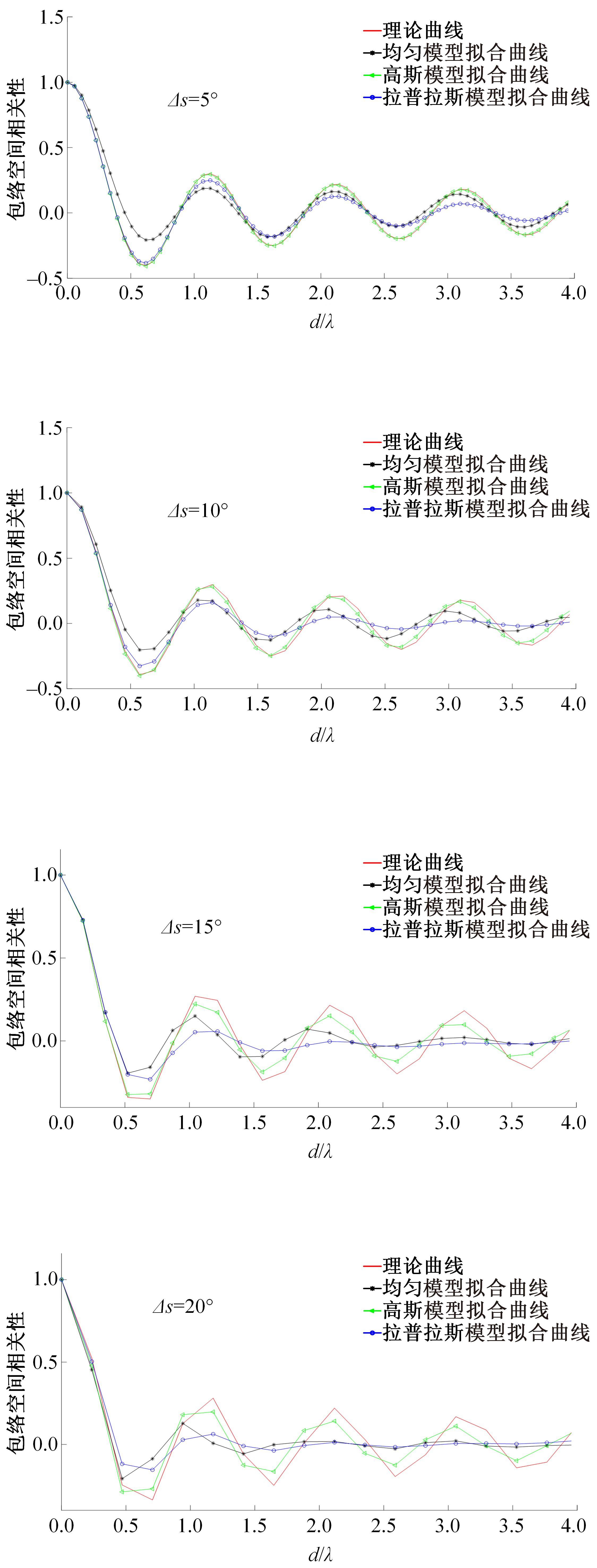
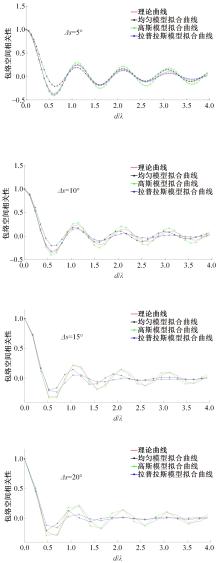
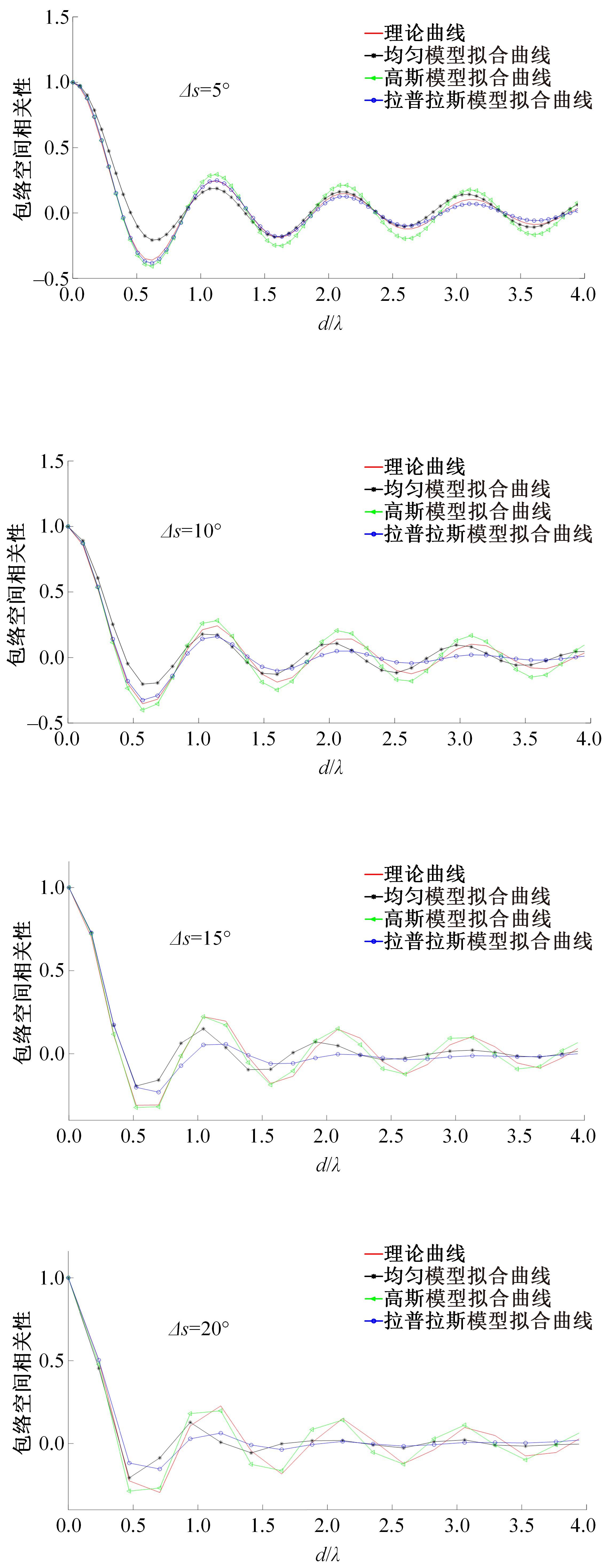
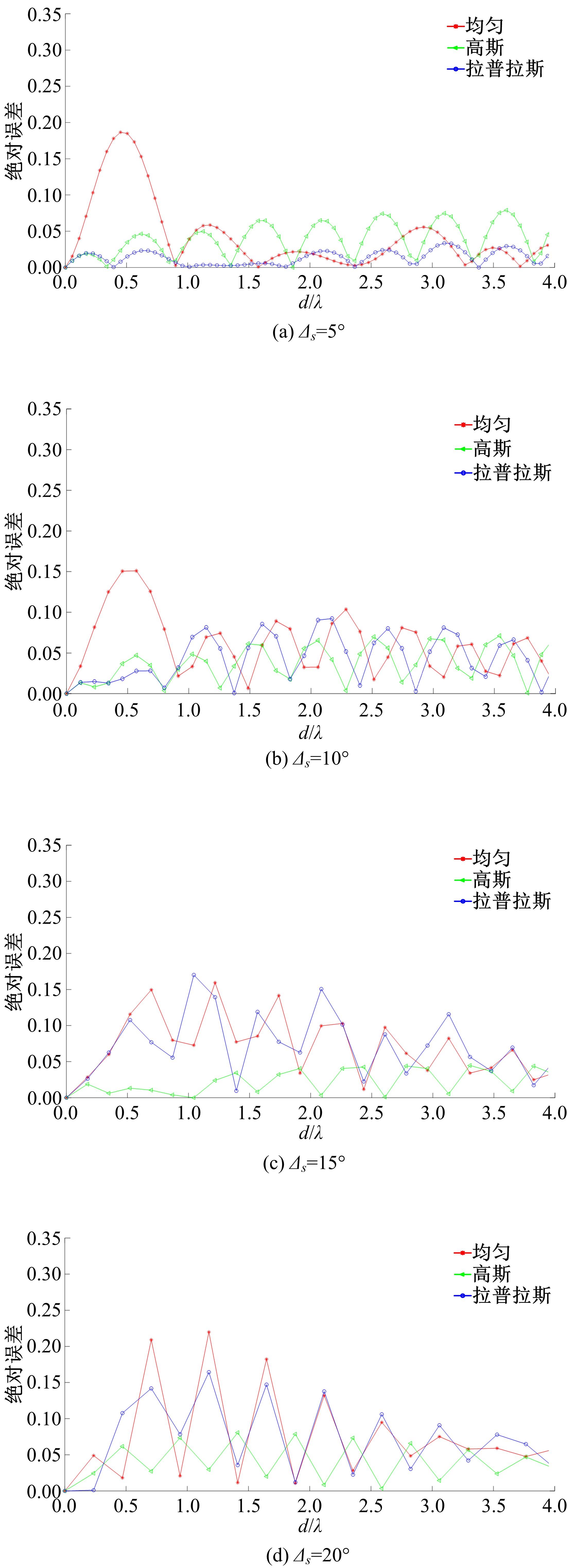
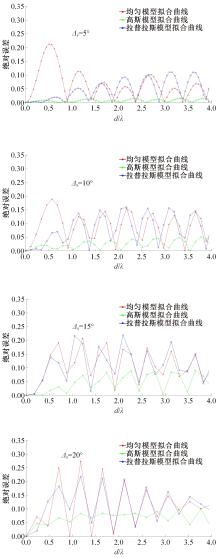
针对波达信号谱的任意性,采用角度域基函数采样法,建立多入多出(MIMO)天线衰落空间相关性(SFC)计算模型。提出了以基函数展开法,加权叠加形成符合多样无线场景波达信号近似信号到达角(AoA)复杂分布函数,导出了完整理论计算式。并对微蜂窝城市传播信道的实测数据进行了验证和分段指数非线性拟合分析,导出了实测信道下的MIMO SFC的近似拟合解,探讨了基函数采样数和加权系数的选取对计算精度的影响。研究结果表明此拟合法对任意波达信号谱分布和信道实测数据的整合有较高的拟合度,提出的近似算法可准确地拟合MIMO多天线系统的衰落相关信道特征,且能大幅度降低其计算的复杂度,提高运算效率,节省了仿真时间。此法能有效研究MIMO系统在特殊场景中的信道特征,并可推广到在多维空间域中对Massive MIMO的分析。
中图分类号:
- TN92
| 1 | Elayoubi S E, Fallgren M, Spapis P, et al. 5G Service requirements and operational use cases: analysis and METIS II vision[C]∥European Conference on Networks & Communications, Athens, Greek, 2016: 158-162. |
| 2 | 郭文祥, 余志勇, 逄晨,等. 认知无线电频谱感知技术综述[J]. 通信技术, 2018, 51(2): 261-265. |
| Guo Wen-xiang, Yu Zhi-yong, Pang Chen, et al.Overview of cognitive radio spectrum sensing technology[J]. Communication Technology,2018, 51(2):261-265. | |
| 3 | 赵水静. 大规模MIMO-OFDM系统的双稀疏信道建模与估计方法研究[D].南京: 南京邮电大学通信与信息工程学院, 2020. |
| Zhao Shui-jing. Research on double sparse channel modeling and estimation method for massive MIMO-OFDM system[D]. Nanjing: School of Communication and Information, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020. | |
| 4 | 肖大家. 5G密集网络中的干扰协调技术研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学通信工程学院, 2018. |
| Xiao Da-jia. Research on interference coordination technology in 5G dense network[D]. Nanjing: College Communication Engineering,Southeast University, 2018. | |
| 5 | 林鑫. 第5代移动通信网络的新业务及其关键技术分析[J]. 信息通信, 2018(11): 259-261. |
| Lin Xin. New business and key technology analysis of the 5th generation mobile communication network[J]. Information and Communication, 2018(11): 259-261. | |
| 6 | 黄俊然. 无线信道测量与建模中实测数据拟合的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学天津大学电器自动化与信息工程学院, 2010: 7-8. |
| Huang Jun-ran. Fitting of measured data in wireless channel measurement and modeling[D]. Tianjin: School of Electrical Automation and Information Engineering,Tianjin University, 2010: 7-8. | |
| 7 | 闭宇铭. 非平稳无线信道建模及其仿真技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学信息与通信工程学院,2017: 16-20. |
| Bi Yu-ming. Research on modeling of non-stationary wireless channel and its simulation technique[D]. Beijing: School of Information and Communication Engineering,Beijing University of Postsand Telecommunications, 2017: 16-20. | |
| 8 | Fleury B H. First and second-order character- ization of direction dispersion and space selectivity in the radio channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2000, 46(6): 2027-2044. |
| 9 | Ziółkowski Cezary, Kelner J M. Empirical models of the azimuthal reception angle—Part I: comparative analysis of empirical models for different propagation environments[J]. Wireless Personal Communi, 2016, 91(2): 771-791. |
| 10 | Xiao H, Nie Z. Low spatial correlation at base station uniform linear antennas[C]∥International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems, Guilin, China,2006: 785-787. |
| 11 | 李忻, 聂在平. MIMO信道中衰落信号的空域相关性评估[J]. 电子学报, 2004(12): 1949-1953. |
| Li Xin, Nie Zai-ping. Spatial correlation evaluation of fading signals in MIMO channels[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2004(12): 1949-1953. | |
| 12 | Abdul Waheed Umrani. Performance analyses of spatial diversity and beam-forming for wireless communication systems[D].Pakistan:United Arab Emirates 2008:39-65. |
| 13 | Yong S K, Honpson J S. Three dimensional spatial fading correlation model for compact MIMO receivers[J]. IEEE Trans. Wireless Communications, 2005, 4(6): 2856-2869. |
| 14 | Gutierrez C A, Patzold M. Sum of sinusoids based simulation of flat fading wireless propagation channels under non-isotropic scattering conditions[C]∥Global Telecom Conference,Washington D.C., USA, 2007: 3842-3846. |
| 15 | Forenza A, Love D J, Heath R W. Simplified spatial correlation models for clustered MIMO channels with different array configurations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2007, 56(4): 1924-1934. |
| 16 | 周杰, 邹士娇, 陈珍. 衰落相关信道近似算法及其Massive MIMO系统分析[J]. 新疆大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 35(3): 100-111. |
| Zhou Jie, Zou Shi-jiao, Chen Zhen. Decay correlation channel approximation algorithm and its Massive MIMO system analysis[J]. Journal of Xinjiang University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 35(3): 100-111. | |
| 17 | 周杰, 王亚林, 菊池久和. 多天线信道空间衰落相关性近似算法及其复杂性研究[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(23): 1-12. |
| Zhou Jie, Wang Ya-lin, Hisakazu Kikuchi. Spatial decay correlation approximation algorithm for multi-antenna channel and its complexity study[J]. Phys J, 2014, 63(23): 1-12. | |
| 18 | Goldsmith A, Jafar S A, Jindal N, et al. Capacity limits of MIMO channels[J]. IEEE JSAC, 2003, 21(5): 684-702. |
| 19 | 朱秋明, 徐大专, 罗艳强, 等. 多输入多输出信道空域相关性评估简化模型[J]. 电波科学学报, 2011, 26(2): 203-208. |
| Zhu Qiu-ming, Xu Da-zhuan, Luo Yan-qiang, et al. A simplified model for the evaluation of multi-input-multi-output channel airspace correlation[J]. Journal of Radio Frequency Science, 2011, 26(2): 203-208. | |
| 20 | 高凯,张尔扬. MIMO信道的空间相关特性及信道容量分析[J]. 电子与信息学报,2007, 29(7): 1542-1545. |
| Gao Kai, Zhang Er-yang. Spatial correlation characteristics and channel capacity analysis of MIMO channel[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Science, 2007, 29(7): 1542-1545. | |
| 21 | Sieskul B T, Kupferschmidt C, Kaiser T. Spatial fading correlation for semicircular scattering: angular spread and spatial frequency approximations[C]∥International Conference on Communications & Electronics, Nha Trang, Vietnam, 2010: 216-221. |
| 22 | Lee W C Y. Effects on correlation between two mobile radio base-station antennas[J]. IEEE Trans Commun, 1973, 21(11): 1214-1224. |
| 23 | Eyeynis Gradsht, Kim Ryzh. Table of integrals, series and products[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1980. |
| 24 | Jie Z, Zhigang C, Kikuchi H. Analysis of MIMO antenna array based on 3D Von Mises Fisher distribution[J]. Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 2015, 22(2): 1-12. |
| 25 | Jie Z, Kenta I, Shigenobu S. Generalized spatial correlation equations for antenna arrays in wireless diversity reception: exact and approximate analyses[J]. IEICE Trans Communications, 2004, 84(5): 1-5. |
| 26 | 周杰, 曹志钢, 菊池久和. 非对称空间统计信道模型及其MIMO多天线系统[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 44(2): 232-238. |
| Zhou Jie, Cao Zhi-gang, Kikuchi Hisakazu. Asymmetric spatial statistical channel model and its MIMO multi-antenna system[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition),2014, 44(2): 232-238. | |
| 27 | 陈钱, 周杰, 邵根富. 角度域任意功率谱MIMO信道特征计算[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(6): 271-275. |
| Chen Qian, Zhou Jie, Shao Gen-fu. MIMO channels with arbitrary AoA power spectrum for various wireless environments[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(6): 271-275. | |
| 28 | Ghoraishi M, Takada J I, Imai T. A pseudo-geometrical channel model for dense urban line-of-sight street microcell[C]∥The 17th IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Helsinki, Finland, 2006:1-5. |
| 29 | Ghoraishi H, Jun-ichi J, Takada J, et al. A single bounce channel model for dense urban street microcell[C]∥URSI-Japan Radio Science Meeting, Tokyo,Japan, 2006:1-5. |
| [1] | 国强,崔玉强,王勇. 无线传感器网络中基于动态簇的节点调度算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1466-1476. |
| [2] | 李建坡,李美霖,杨涛,薛鹏. 大规模MIMO⁃OFDM系统中低复杂度维纳滤波信道估计算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 211-218. |
| [3] | 孙大洋,王雪莹,韩双雪,钟辉,戴江南. 虚拟锚点高维坐标的非视距识别及定位优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2207-2215. |
| [4] | 李建坡,薛鹏,杨涛,李美霖. 基于分组导频复用的大规模多输入多输出系统导频污染抑制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2225-2236. |
| [5] | 马彦,黄健飞,赵海艳. 基于车间通信的车辆编队控制方法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 711-718. |
| [6] | 刘毅,肖玲玲,王改静,张武军. 基于联合优化的D2D资源分配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 306-314. |
| [7] | 李翠然,于永生,谢健骊. 基于次用户优先级的频谱共享动态博弈算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 315-323. |
| [8] | 王金鹏,叶政鹏,曹帆,邹念育. 5G移动通信中基于同频干扰分布的协同分布式天线传输系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 333-341. |
| [9] | 李文军,华强,谭立东,孙悦. DV⁃HOP和接收信号强度指示结合的改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1689-1695. |
| [10] | 王洪雁,房云飞,朱圣棋,裴炳南. 非均匀噪声条件下考虑互耦效应的DOA估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1706-1714. |
| [11] | 刘勇,邓方顺,刘小林,闵思婕,王鹏. 基于双混沌振子的最小频移键控信号频率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1357-1362. |
| [12] | 王宏志,姜方达,周明月. 基于遗传粒子群优化算法的认知无线电系统功率分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1363-1368. |
| [13] | 周彦果,张海林,陈瑞瑞,周韬. 协作网络中采用双层博弈的资源分配方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1879-1886. |
| [14] | 孙晓颖, 扈泽正, 杨锦鹏. 基于分层贝叶斯网络的车辆发动机系统电磁脉冲敏感度评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1254-1264. |
| [15] | 董颖, 崔梦瑶, 吴昊, 王雨后. 基于能量预测的分簇可充电无线传感器网络充电调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1265-1273. |
|
||