吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 1086-1098.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220692
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法
- 1.江西理工大学 电气工程与自动化学院,江西 赣州 341000
2.华南理工大学 计算机科学与工程学院,广东 广州 510006
Fusion multi-scale Transformer skin lesion segmentation algorithm
Li-ming LIANG1( ),Long-song ZHOU1,Jiang YIN1,Xiao-qi SHENG2
),Long-song ZHOU1,Jiang YIN1,Xiao-qi SHENG2
- 1.School of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000,China
2.School of Computer Science and Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou,510006,China
摘要:
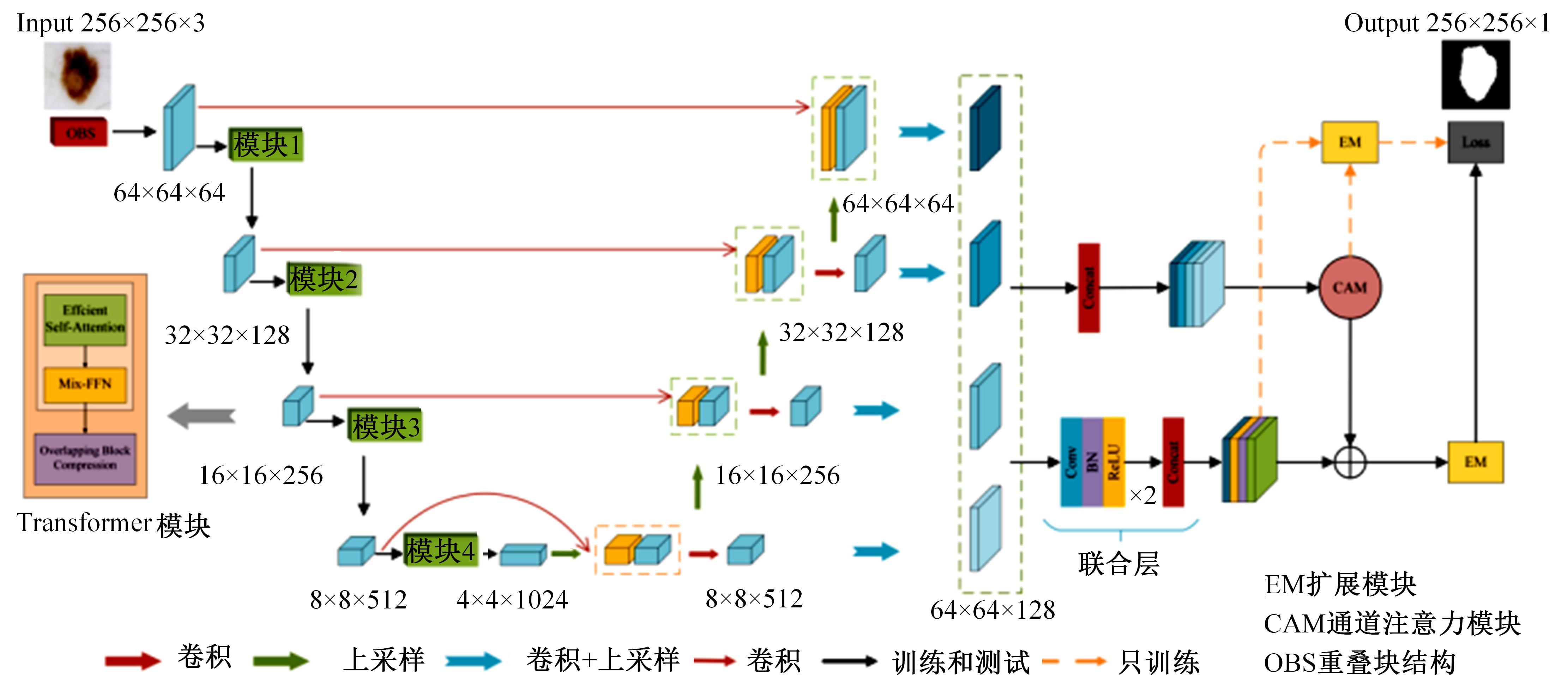
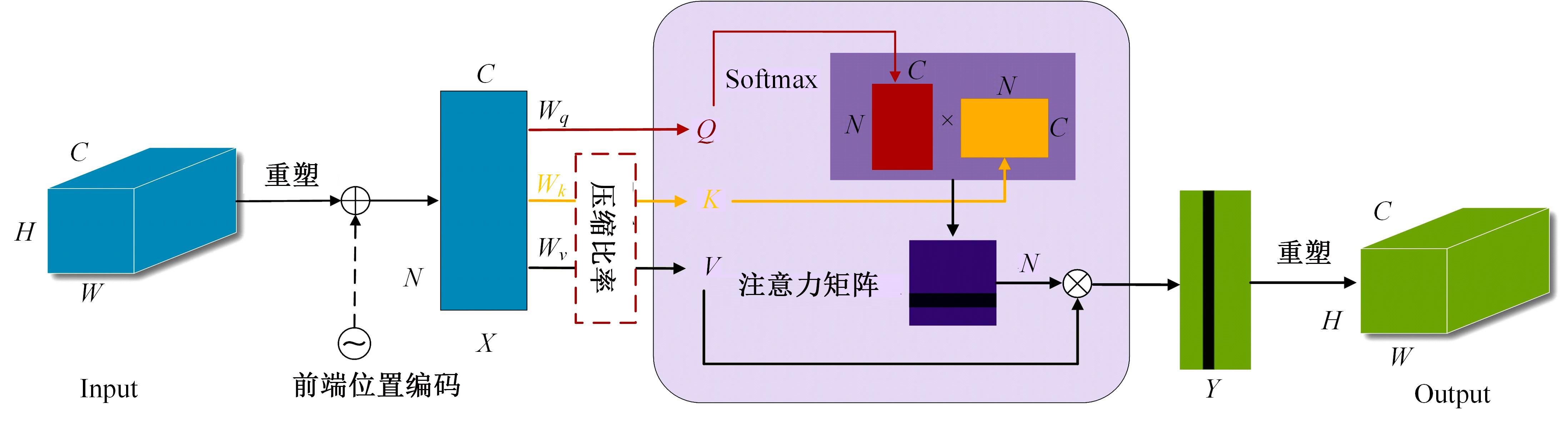
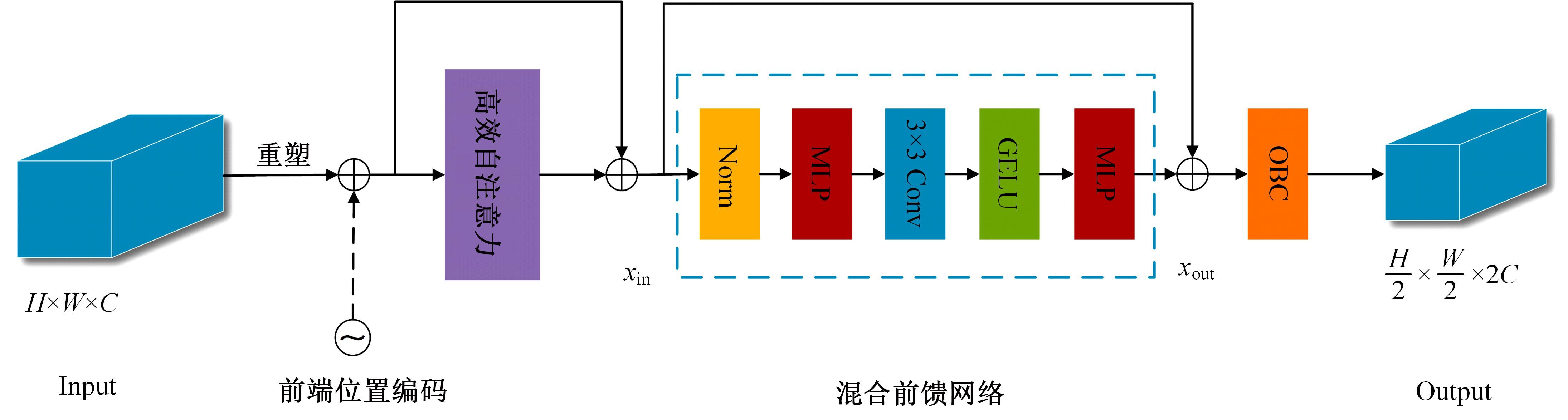
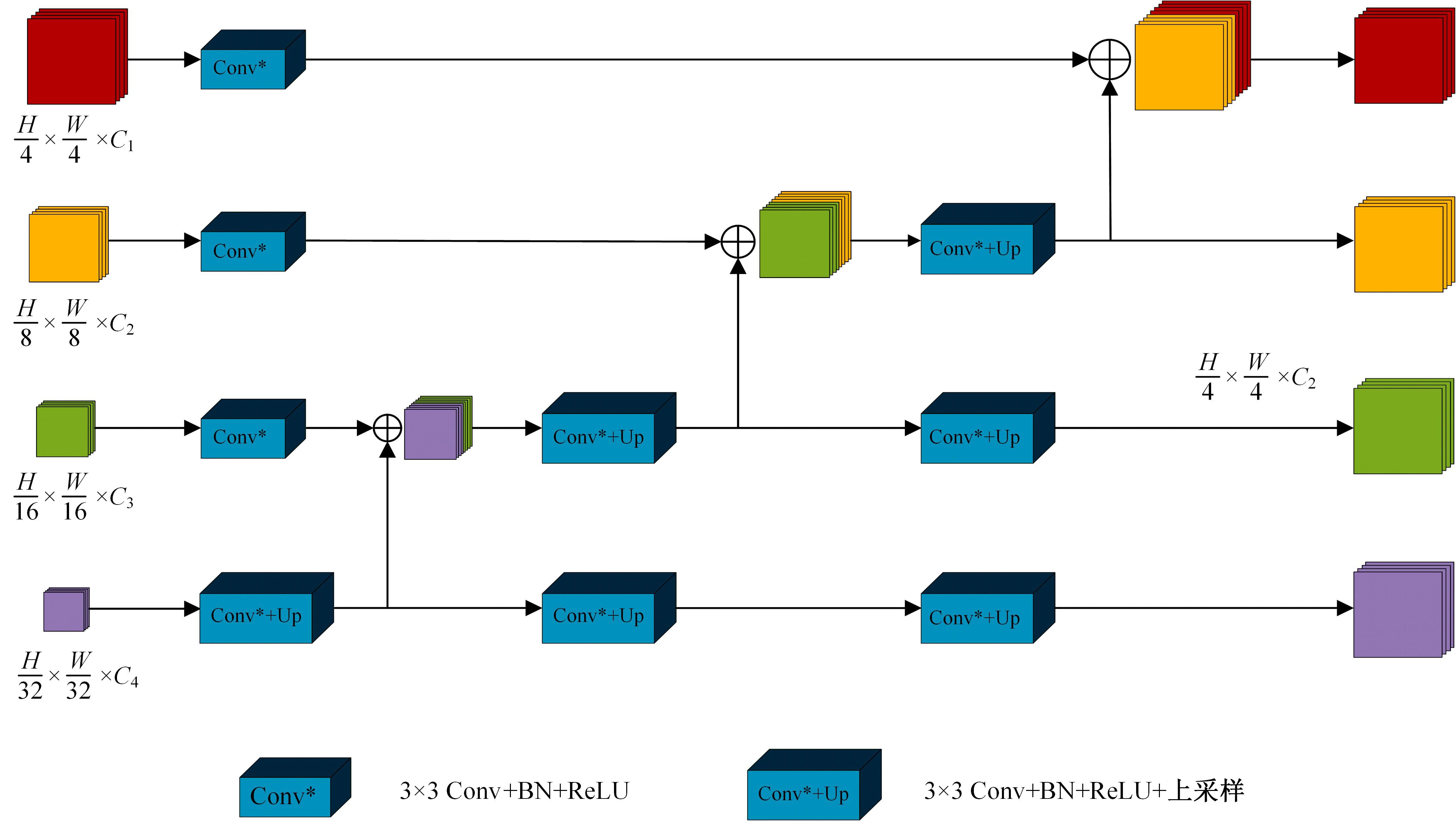
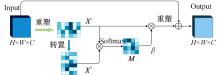
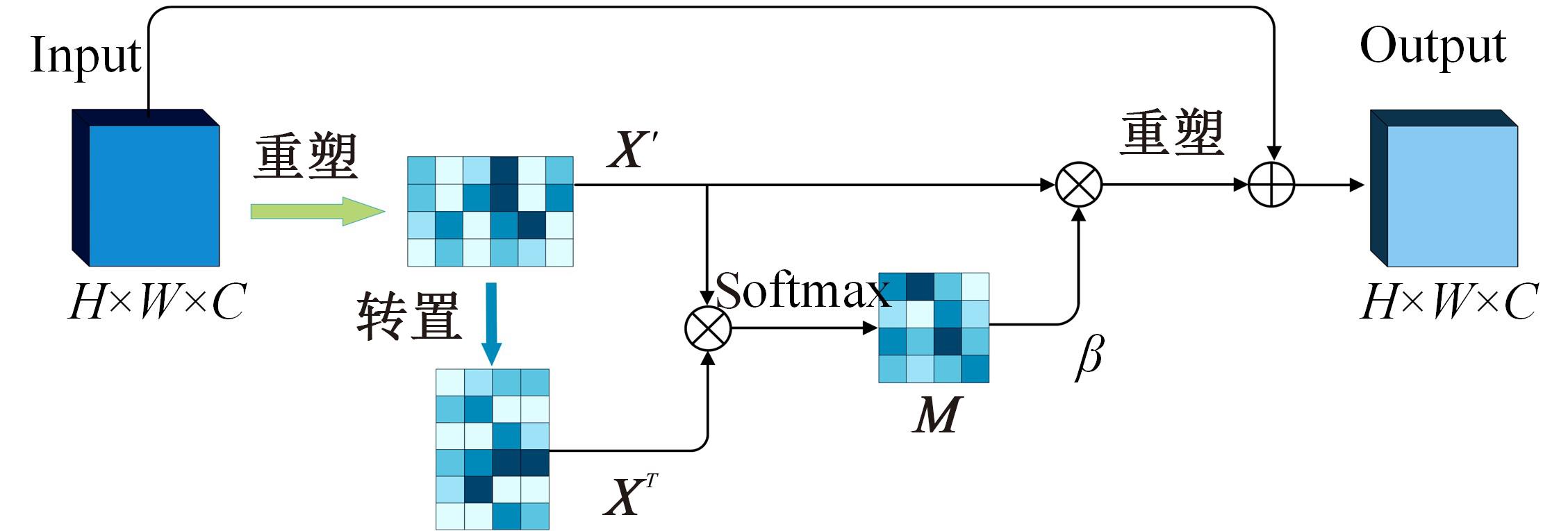
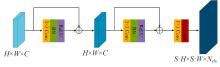
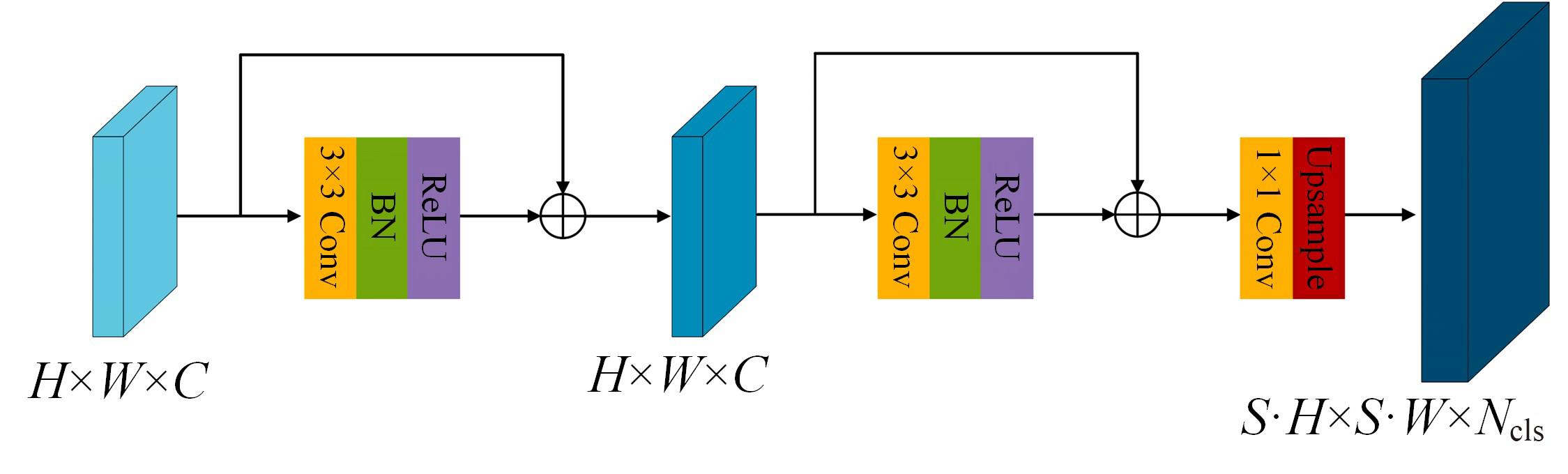
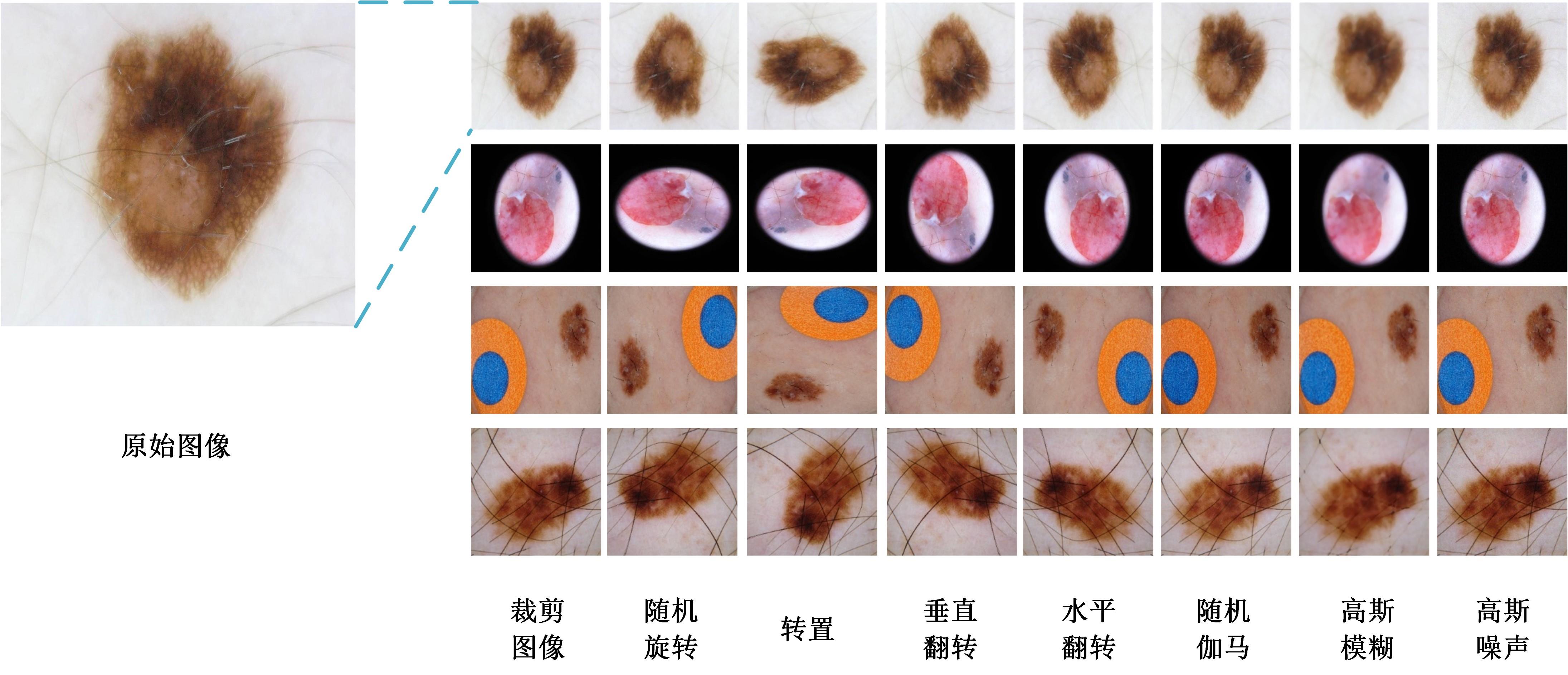
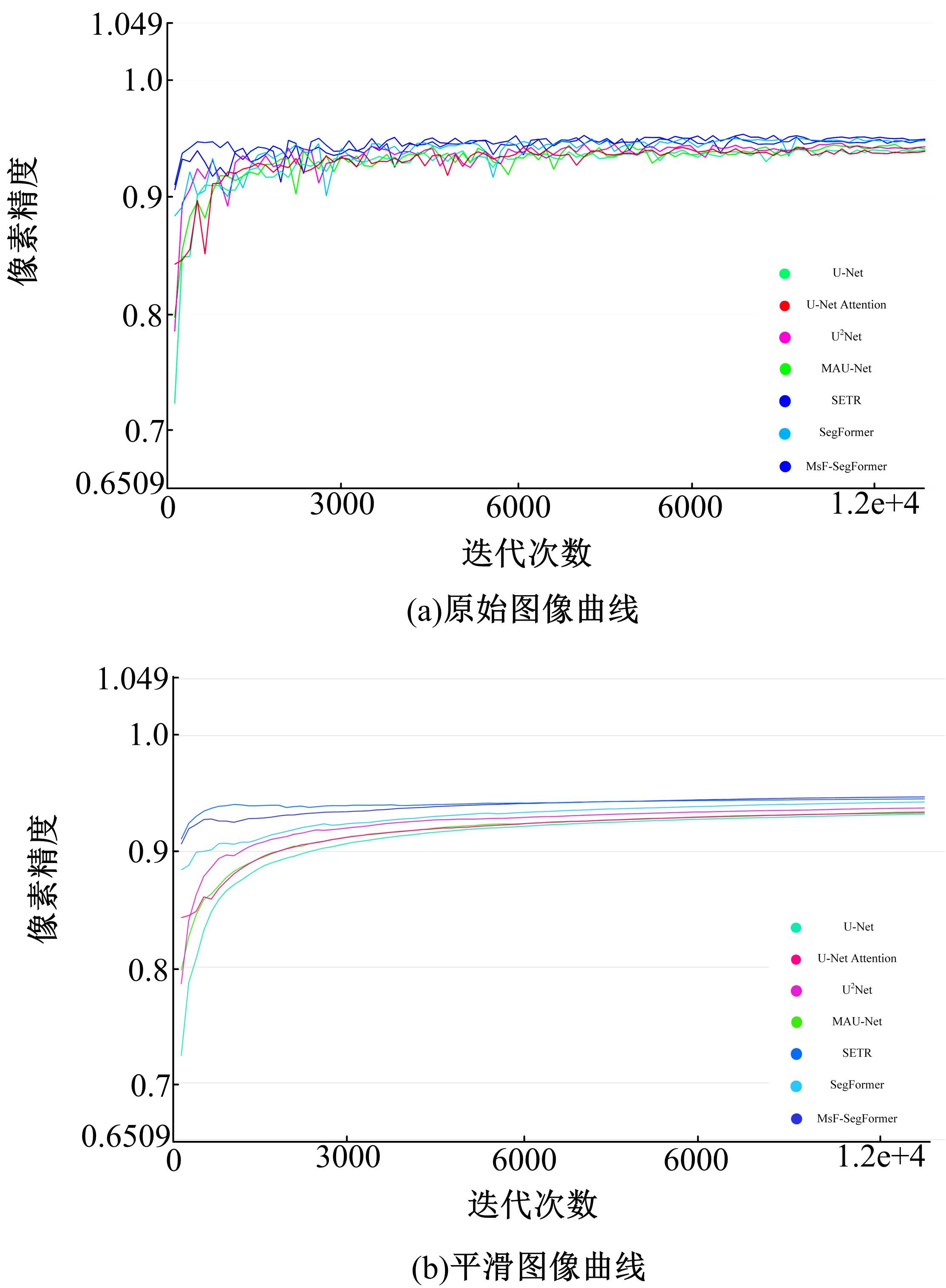
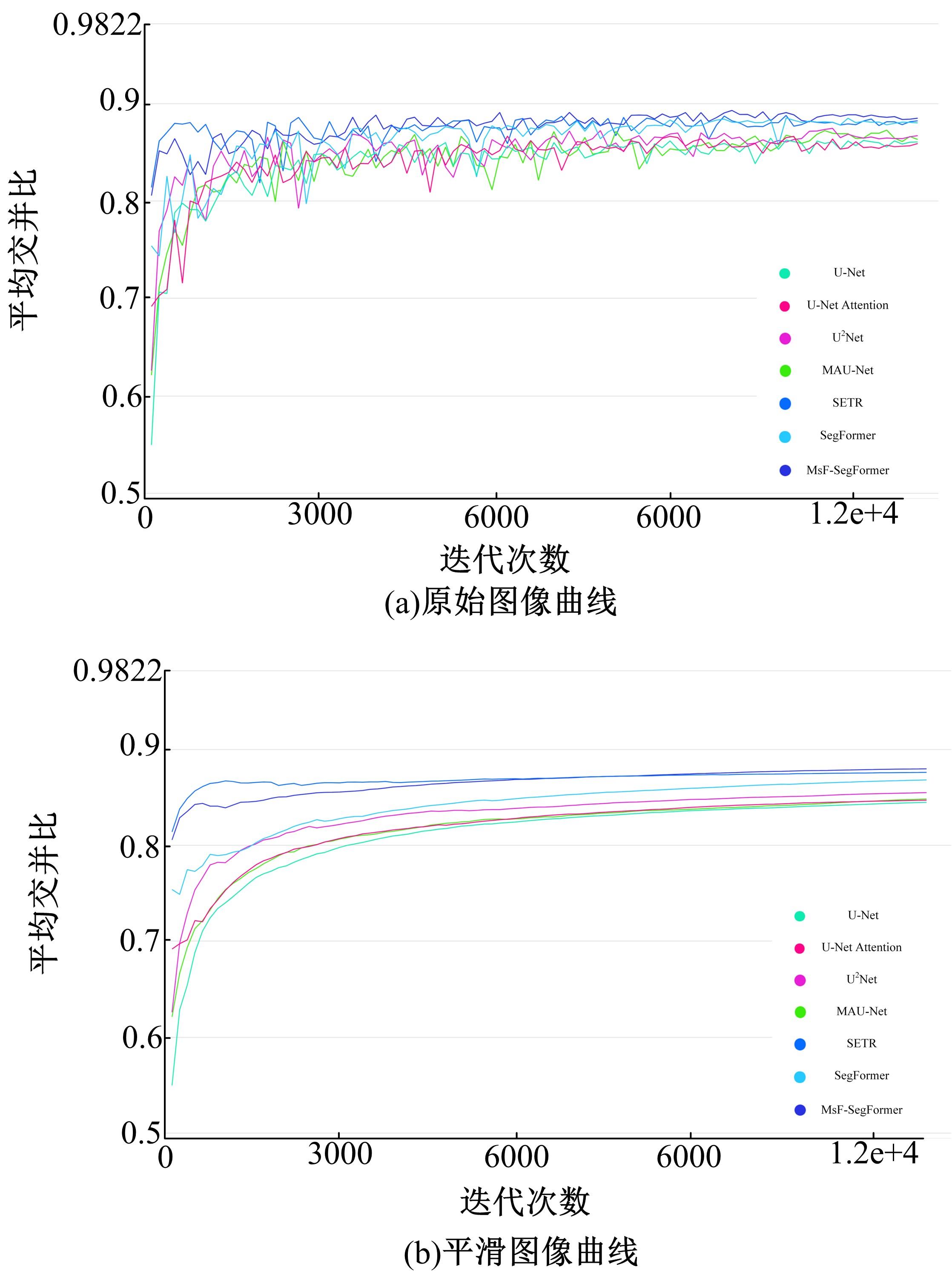
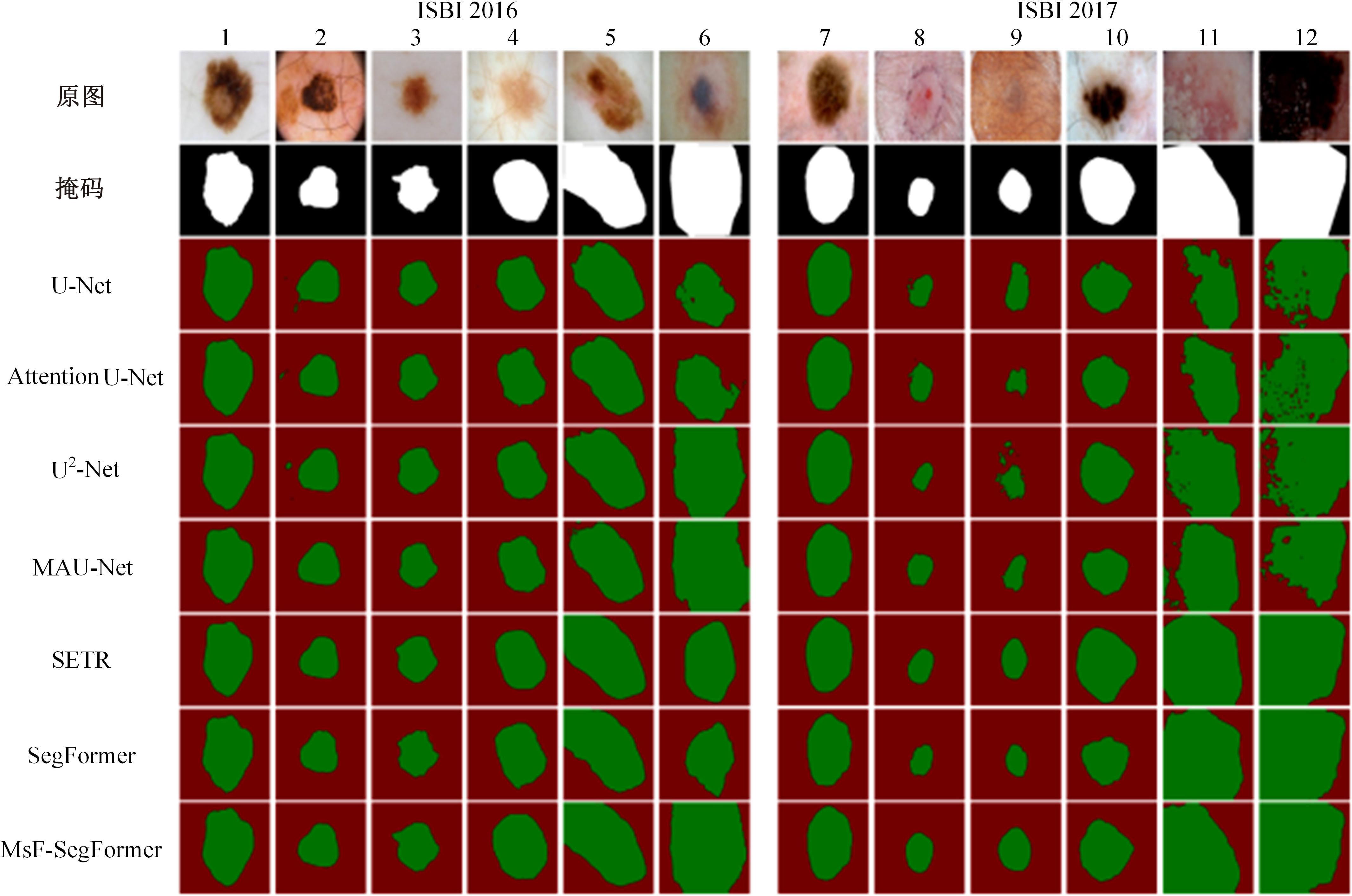
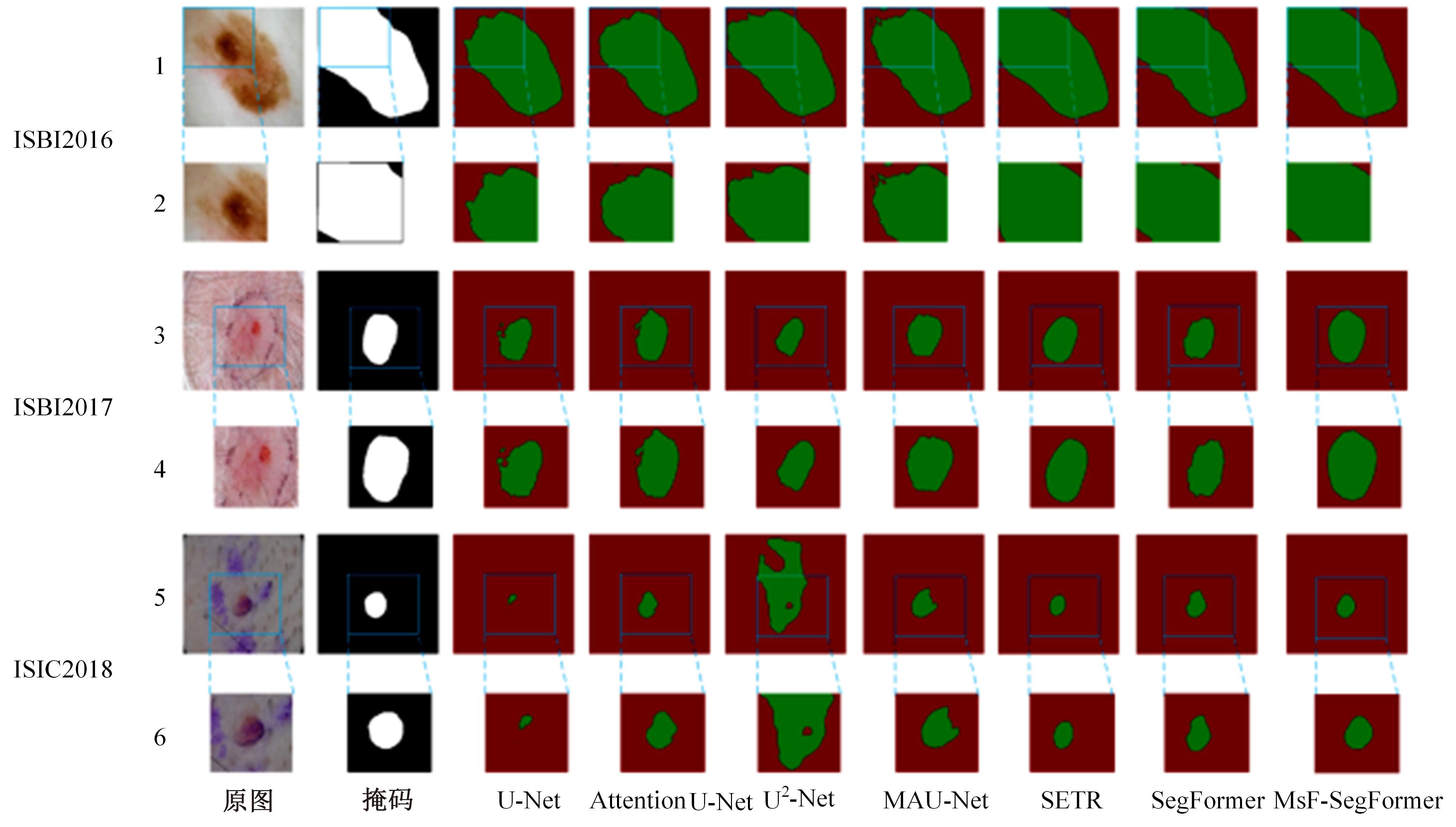
针对现有皮肤病变图像分割时缺乏多尺度特征提取,从而导致细节信息缺失和病变区域误分割的问题,本文提出一种融合多尺度Transformer的编解码网络皮肤病变分割算法。首先运用Transformer模块构建分层编码器,分层编码器从全局特征变化角度出发,多尺度分析皮肤病变区域;然后利用多尺度融合模块、通道注意力模块和联合层构建融合解码器,多尺度融合模块互补分层编码器中浅层网络信息与深层网络信息,增强空间信息和语义信息间的依赖关系,通道注意力模块能够有效识别特征丰富的通道,提高算法分割精度;最后引入扩展模块恢复图像大小以匹配实际需求。将该算法在ISBI2016、ISBI2017和ISIC2018三个公共数据集上进行实验测试,其像素精度分别为96.70%、94.50%和95.39%,平均交并比分别为91.69%、85.74%和89.29%,算法测试整体性能优于现有算法。仿真实验证明,多尺度Transformer编解码网络能够有效地分割皮肤病变图像。
中图分类号:
- TP183
| 1 | Jin Q, Cui H, Sun C, et al. Cascade knowledge diffusion network for skin lesion diagnosis and segmentation[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 99:No. 106881. |
| 2 | Sarker M M K, Rashwan H A, Akram F, et al. SLSNet: skin lesion segmentation using a lightweight generative adversarial network[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 183: No.115433. |
| 3 | 欧阳继红, 郭泽琪, 刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| Ouyang Ji-hong, Guo Ze-qi, Liu Si-guang. Dual⁃branch hybrid attention decision net for diabetic retinopathy classification[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. | |
| 4 | 王雪, 李占山, 吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| Wang Xue, Li Zhan-shan, Ying-da Lyu. Medical image segmentation based on multi⁃scale context⁃aware and semantic adaptor[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. | |
| 5 | 王生生, 陈境宇, 卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| Wang Sheng-sheng, Chen Jing-yu, Lu Yi-nan. COVID⁃19 chest CT image segmentation based on federated learning and blockchain[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. | |
| 6 | 张恒良, 李锵, 关欣. 一种改进的三维双路径脑肿瘤图像分割网络[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(3): 54-61. |
| Zhang Heng-liang, Li Qiang, Guan Xin. An improved three-dimensional dual-path brain tumor image segmentation network[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 54-61. | |
| 7 | Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(4): 640-651. |
| 8 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Berlin,Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| 9 | Sarker M, Kamal M, Rashwan H A, et al. SLSDeep: skin lesion segmentation based on dilated residual and pyramid pooling networks[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 2018: 21-29. |
| 10 | Gu R, Wang L, Zhang L. DE-Net: a deep edge network with boundary information for automatic skin lesion segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 468: 71-84. |
| 11 | Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[J/OL]. [2020-09-23].. |
| 12 | Cao H, Wang Y, Chen J, et al. Swin-Unet: Unet-like pure Transformer for medical image segmentation[J/OL]. [2021-11-10]. . |
| 13 | Wang W, Xie E, Li X, et al. Pyramid vision Transformer: a Versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 568-578. |
| 14 | Xie E, Wang W, Yu Z, et al. SegFormer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers[J/OL]. [2021-09-16].. |
| 15 | Petit O, Thome N, Rambour C, et al. U-net Transformer: self and cross attention for medical image segmentation[C]∥International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Nagoya, Japan, 2021: 267-276. |
| 16 | Islam M A, Jia S, Bruce N D B. How much position information do convolutional neural networks encode?[J/OL]. [2020-08-17]. . |
| 17 | Chu X, Tian Z, Zhang B, et al. Conditional positional encodings for vision transformers[J/OL]. [2021-07-26]. . |
| 18 | Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3146-3154. |
| 19 | Gutman D, Codella N C F, Celebi E, et al. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC)[J/OL].[2016-08-24]. . |
| 20 | Codella N C F, Gutman D, Celebi M E, et al. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic)[C]∥IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging(ISBI 2018), WashingtonDC, USA, 2018: 168-172. |
| 21 | Tschandl P, Rosendahl C, Kittler H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions[J]. Scientific Data, 2018, 5(1): 1-9. |
| 22 | Mendonça T, Ferreira P M, Marques J S, et al. PH 2-A dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking[C]∥The 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society(EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 2013: 5437-5440. |
| 23 | Loshchilov I, Hutter F. Decoupled weight decay regularization[J/OL].[2017-06-24]. . |
| 24 | Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc L L, et al. Attention U-net: learning where to look for the pancreas[J/OL]. [2018-10-22]. . |
| 25 | Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, et al. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106: No.107404. |
| 26 | 梁礼明, 尹江, 彭仁杰, 等. 基于多尺度注意力的皮肤镜图像自动分割算法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021,21(34): 14644-14650. |
| Liang Li-ming, Yin Jiang, Peng Ren-jie, et al. Automatic segmentation algorithm of dermoscopy images based on multi-scale attention[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(34): 14644-14650. | |
| 27 | Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H, et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashvill, USA, 2021: 6881-6890. |
| [1] | 王德兴,高凯,袁红春,杨钰锐,王越,孔令栋. 基于色彩校正和TransFormer细节锐化的水下图像增强[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 785-796. |
| [2] | 谭国金,欧吉,艾永明,杨润超. 基于改进DeepLabv3+模型的桥梁裂缝图像分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 173-179. |
| [3] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [4] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [5] | 薛珊,张亚亮,吕琼莹,曹国华. 复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [6] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [7] | 王振,杨宵晗,吴楠楠,李国坤,冯创. 基于生成对抗网络的序列交叉熵哈希[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3536-3546. |
| [8] | 周丰丰,颜振炜. 基于混合特征的特征选择神经肽预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3238-3245. |
| [9] | 朱冰,李紫薇,李奇. 基于改进SegNet的遥感图像建筑物分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 248-254. |
| [10] | 王俊杰,农元君,张立特,翟佩臣. 基于施工场景的视觉关系检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 226-233. |
| [11] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [12] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [13] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [14] | 李娜,谭韶生. 基于空间邻域信息的击剑连续动作图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1639-1644. |
| [15] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
|
||