吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 785-796.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220483
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于色彩校正和TransFormer细节锐化的水下图像增强
- 上海海洋大学 信息学院,上海 201306
Underwater image enhancement based on color correction and TransFormer detail sharpening
De-xing WANG( ),Kai GAO,Hong-chun YUAN(
),Kai GAO,Hong-chun YUAN( ),Yu-rui YANG,Yue WANG,Ling-dong KONG
),Yu-rui YANG,Yue WANG,Ling-dong KONG
- School of Information,Shanghai Ocean University,Shanghai 201306,China
摘要:
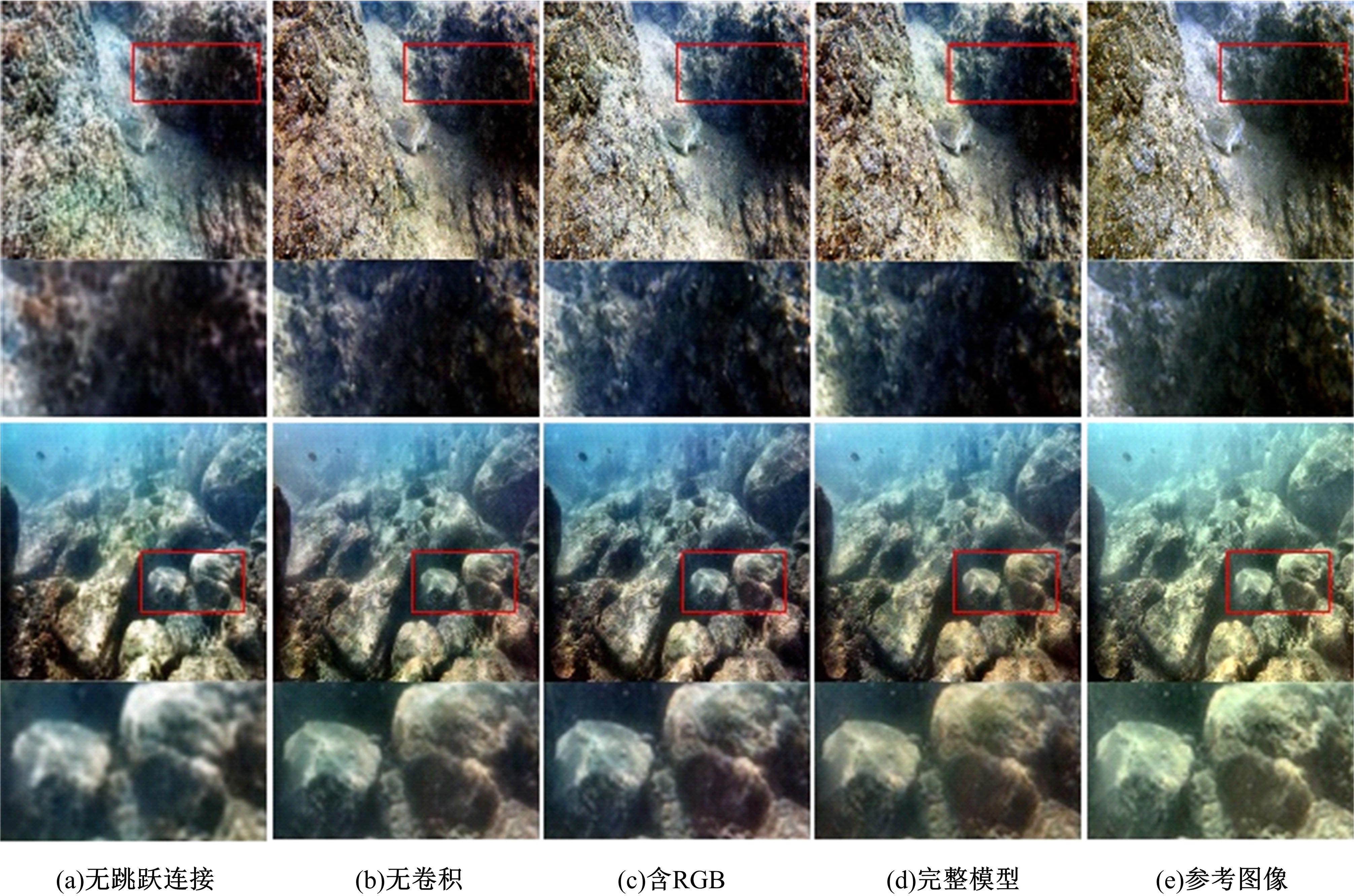
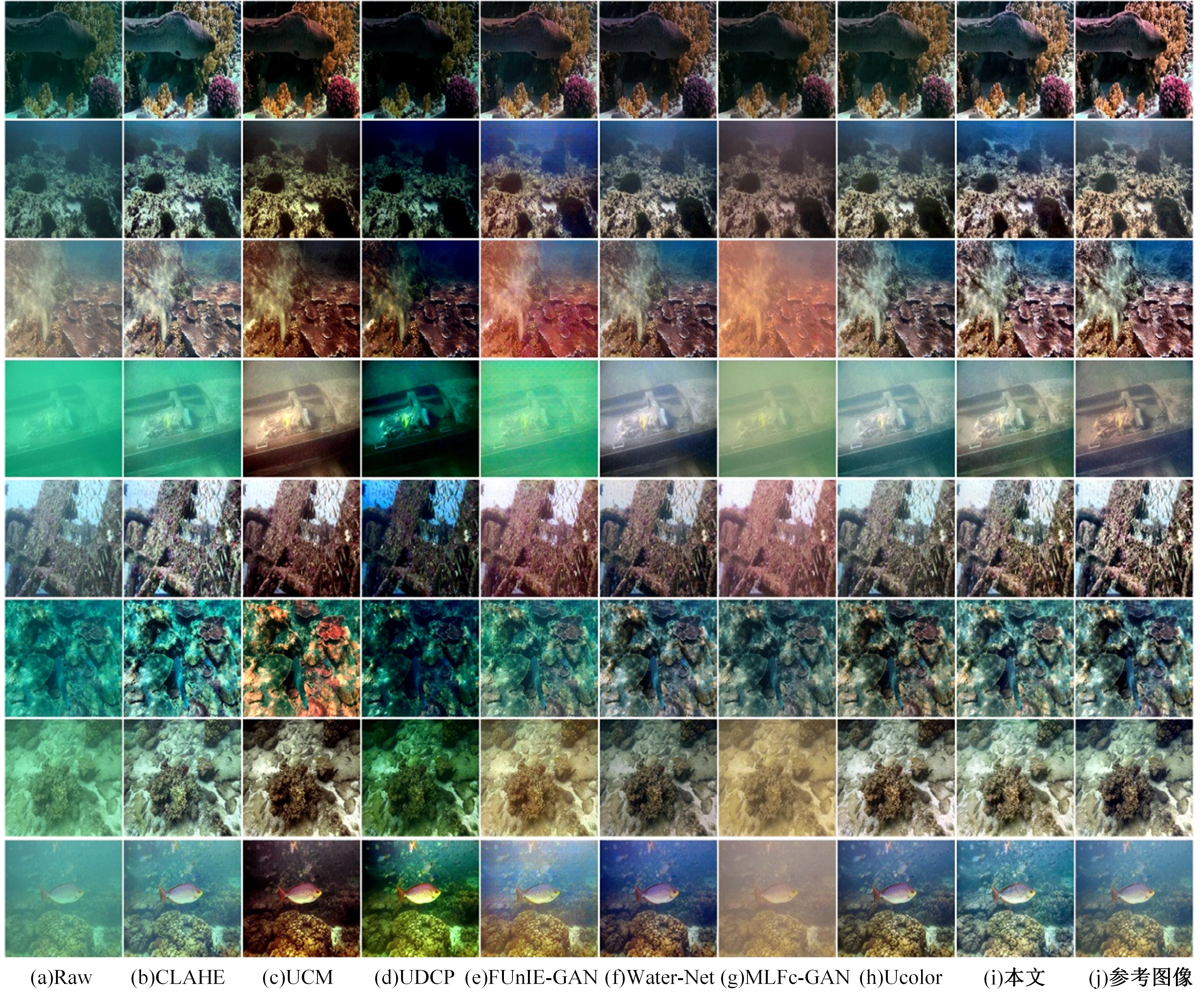
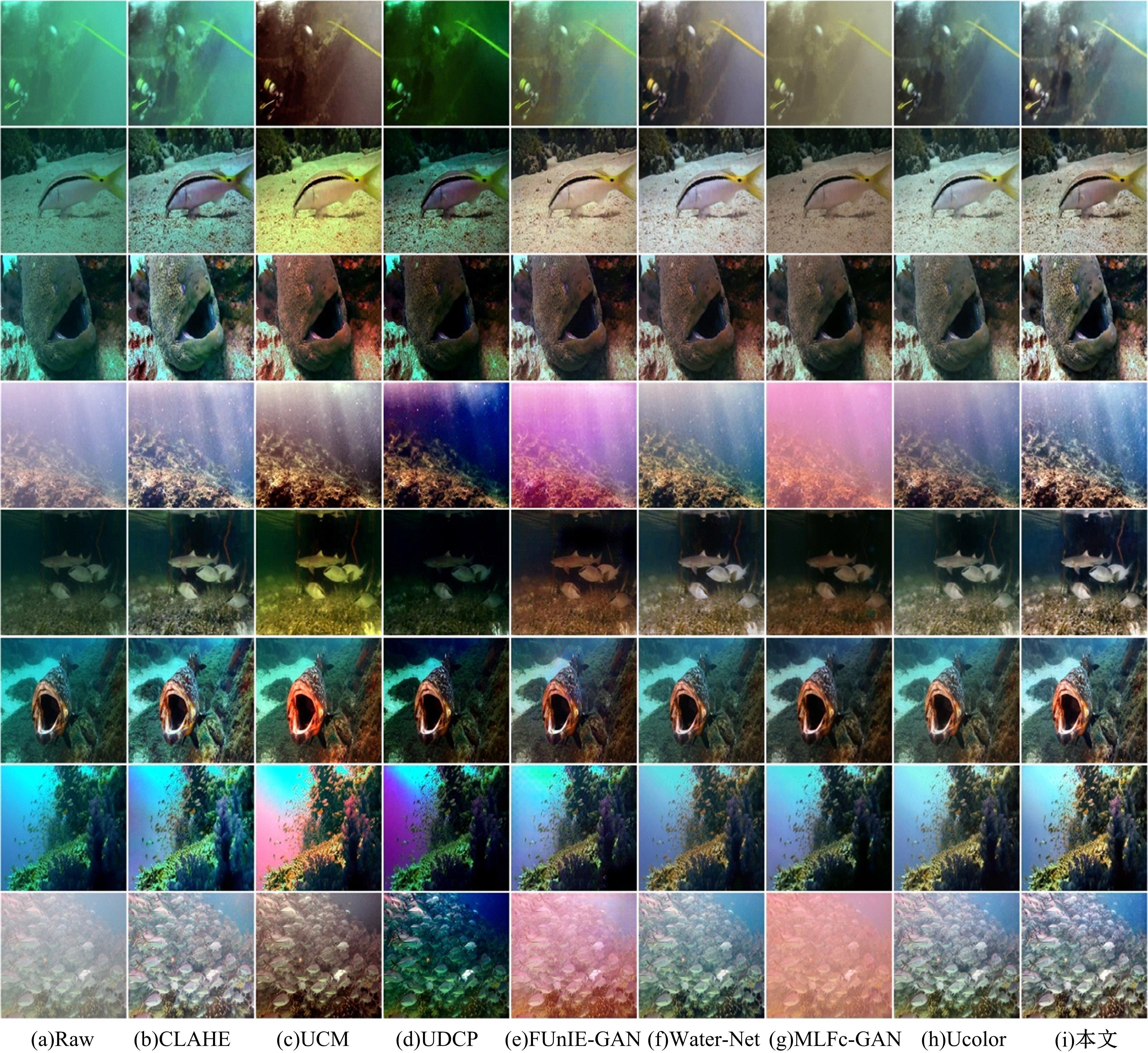
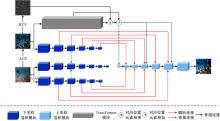
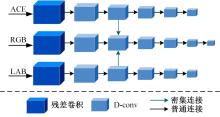
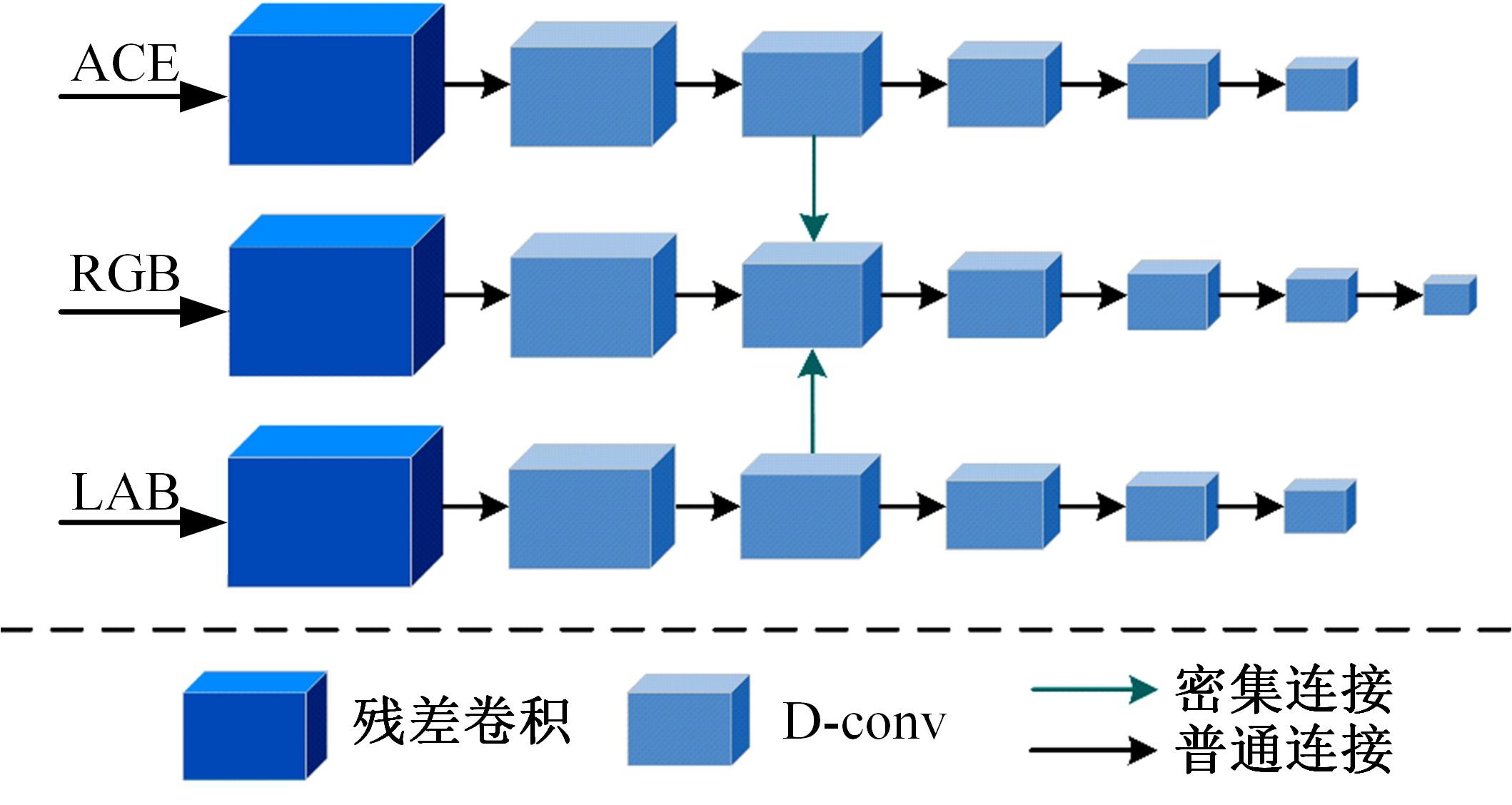
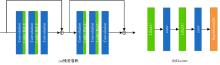
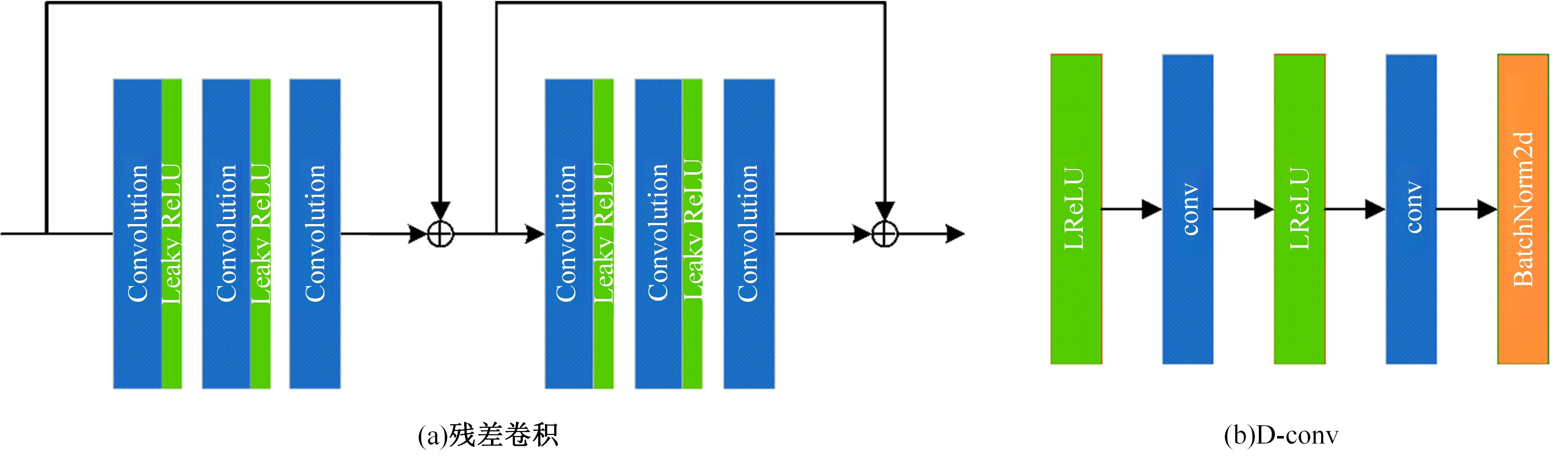
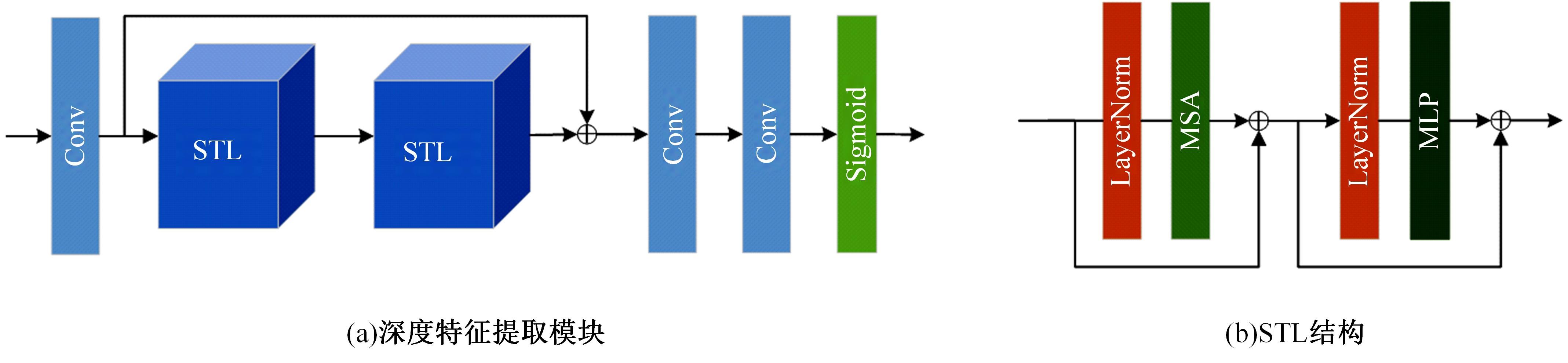
针对水下图像对比度低、细节表现差且存在色偏等问题,提出了一种多输入的基于TransFormer和卷积神经网络(CNN)的水下图像复原方法。利用TransFormer和相对总变差(RTV)构造深度特征提取模块,融合RTV提取的纹理图与TransFormer提取到的图像信息,有效增强了图像的细节特征。利用自动色彩均衡和Lab色彩空间构建色彩校正模块,提升图像对比度,同时校正颜色。利用多项损失函数约束网络收敛,得到增强后的清晰水下图像。最后,将本文方法与其他方法在测试集上进行定量和定性对比分析,实验结果表明,经过本文方法处理后的图像在清晰度、色彩表现和纹理信息方面均优于其他对比方法。
中图分类号:
- TP751
| 1 | Skarlatos D, Agrafiotis P, Menna F, et al. Ground control networks for underwater photogrammetry in archaeological excavations[C]∥Proceedings of the 3rd IMEKO International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, Lecce, Italy, 2017: 23-25. |
| 2 | Chuang M C, Hwang J N, Kresimir W. A feature learning and object recognition framework for underwater fish images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2016, 25(4): 1862-1872. |
| 3 | Trahanias P E, Venetsanopoulos A N. Institute of electric and electronic engineer. color image enhancement through 3-D histogram equalization[C]∥11th IAPR International Conference on Image, Speech and Signal Analysis, The Hague, Netherlands, 1992: 545-548. |
| 4 | Zuiderveld. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization[J/OL]. [2022-04-18]. |
| 5 | Zou W, Wang X, Li K, et al. Self-tuning underwater image fusion method based on dark channel prior[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Qingdao, China, 2016: 788-793. |
| 6 | AbuNaser A, Doush I A, Mansour N, et al. Underwater image enhancement using particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2015, 24(1): 99-115. |
| 7 | Hitam M S, Awalludin E A, Yussof W N J H W Y, et al. Mixture contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization for underwater image enhancement[C]∥International Conference on Computer Applications Technology, Sousse, Tunisia, 2013: 1-5. |
| 8 | Ancuti C, Ancuti C O, Bekaert P. Enhancing underwater images and videos by fusion[C]∥2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 2012: 81-88. |
| 9 | Zhang S, Wang T, Dong J, et al. Underwater image enhancement via extended multi-scale Retinex[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 245: 1-9. |
| 10 | Akkaynak D, Treibitz T, Sea-thru: a method for removing water from underwater images[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 1682-1691. |
| 11 | Trucco E, Olmos-Antillon T. Self-tuning underwater image restoration[J].IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2006, 31(2): 511-519. |
| 12 | McGlamery B L. A computer model for underwater camera systems[J/OL]. [2022-04-18]. |
| 13 | Jaffe J S. Computer modeling and the design of optimal underwater imaging systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1990, 15(2): 101-111. |
| 14 | Chiang J, Chen Y. Underwater image enhancement by wavelength compensation and dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2012, 21(4): 1756-1769. |
| 15 | Peng Y T, Cao K M, Cosman P C. Generalization of the dark channel prior for single image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2018, 27(6): 2856-2868. |
| 16 | Akkaynak D, Treibitz T. A revised underwater image formation model[C]∥2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 6723-6732. |
| 17 | Ding X, Wang Y, Zheng L, et al. Towards Underwater Image Enhancement Using Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Networks[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018. |
| 18 | Li J, Skinner K A, Eustice R M, et al. WaterGAN: unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2018,3(1): 387-394. |
| 19 | Fabbri C, Jahidul I M, Sattar J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. [2022-04-28]. |
| 20 | Li C, Guo C, Ren W, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2019, 29: 4376-4389. |
| 21 | Wang Y D, Guo J C, Gao H, et al. UIEC^2-Net: CNN-based underwater image enhancement using two color space[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 96: No. 116250. |
| 22 | Liu Z, Lin Y T, Cao Y, et al. Swin Transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[J/OL]. [2022-04-28]. |
| 23 | Xu L, Yan Q, Xia Y, et al. Structure extraction from texture via relative total variation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(6): 1-10. |
| 24 | Getreuer P. Automatic color enhancement (ACE) and its fast implementation[J]. Image Processing on Line, 2012, 2: 266-277. |
| 25 | Li C, Anwar S, Hou J, et al. Underwater image enhancement via medium transmission-guided multi-color space embedding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4985-5000. |
| 26 | Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T H, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 5967-5976. |
| 27 | Zhao H, Gallo O, Frosio I, et al. Loss functions for neural networks for image processing[EB/OL]. [2022-04-28]. |
| 28 | Islam M J, Xia Y, Sattar J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227-3234. |
| 29 | Li C, Anwar S. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 98(1): No. 107038. |
| [1] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [2] | 肖明尧,李雄飞,朱芮. 基于NSST域像素相关分析的医学图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [3] | 金小俊,孙艳霞,于佳琳,陈勇. 基于深度学习与图像处理的蔬菜苗期杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [4] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [5] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [6] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [7] | 荣鑫,刘洪海,殷作耀,林海翔,边庆华. 基于图像处理的集料级配在线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2847-2855. |
| [8] | 杨怀江,王二帅,隋永新,闫丰,周跃. 简化型残差结构和快速深度残差网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. |
| [9] | 贾海洋,夏睿,吕安祺,管噌璇,陈娟,王雷. 基于模板融合的超声医学影像全景拼接方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 916-924. |
| [10] | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,李建桥,邓湘金,邹猛,薛龙. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [11] | 郭晓然,罗平,王维兰. 基于Transformer编码器的中文命名实体识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| [12] | 李健,刘孔宇,任宪盛,熊琦,窦雪峰. 基于自适应阈值的Canny算法在MRI边缘检测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 712-719. |
| [13] | 刘富,刘璐,侯涛,刘云. 基于优化MSR的夜间道路图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 323-330. |
| [14] | 刘哲, 徐涛, 宋余庆, 徐春艳. 基于NSCT变换和相似信息鲁棒主成分分析模型的图像融合技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1614-1620. |
| [15] | 车翔玖, 王利, 郭晓新. 基于多尺度特征融合的边界检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
|
||