吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1427-1434.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210856
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法
- 1.吉林农业大学 信息技术学院,长春 130118
2.吉林省生物信息学研究中心,长春 130118
Chinese named entity recognition method based on Transformer and hidden Markov model
Jian LI1,2( ),Qi XIONG1,Ya-ting HU1(
),Qi XIONG1,Ya-ting HU1( ),Kong-yu LIU1
),Kong-yu LIU1
- 1.College of Information Technology,Jilin Agricultural University,Changchun 130118,China
2.Jilin Bioinformatics Research Center,Changchun 130118,China
摘要:
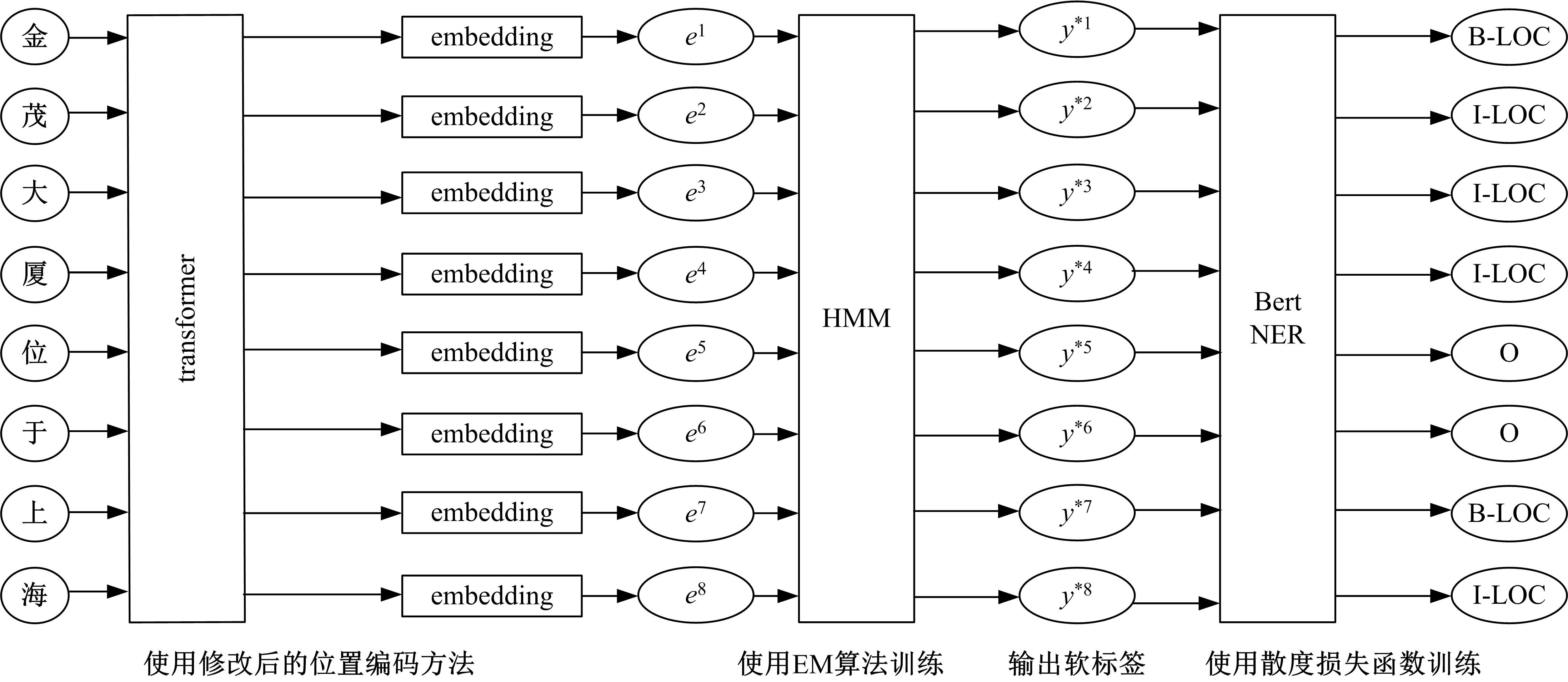
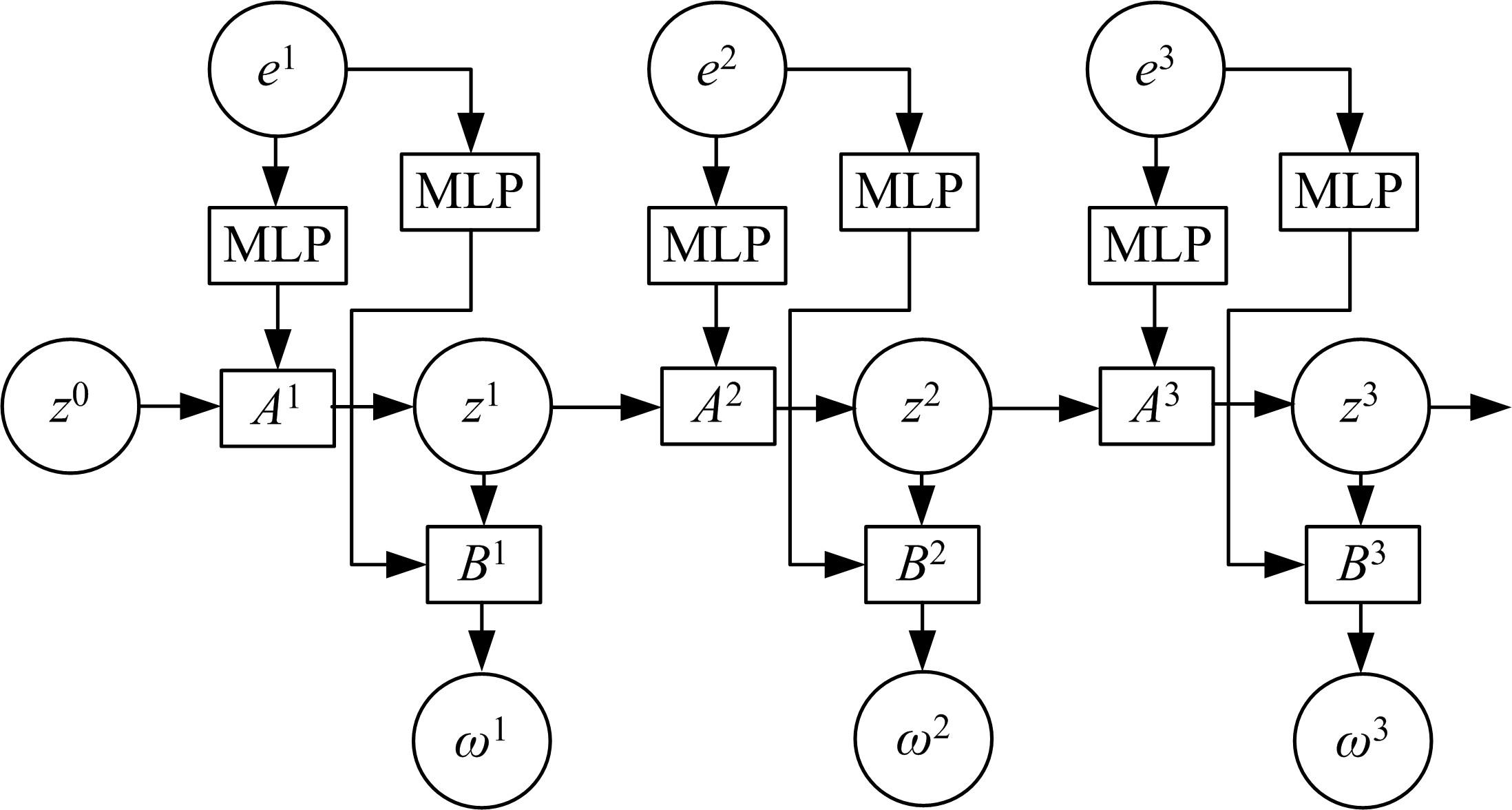
提出了一种基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的字级别中文命名实体识别方法。本文改进了Transformer模型的位置编码计算函数,使修改后的位置编码函数能表达字符之间的相对位置信息和方向性。使用Transformer模型编码后的字符序列计算转移矩阵和发射矩阵,建立隐马尔科夫模型生成一组命名实体软标签。将隐马尔科夫模型生成的软标签带入到Bert-NER模型中,使用散度损失函数更新Bert-NER模型参数,输出最终的命名实体强标签,从而找出命名实体。经过对比实验,本文方法在中文CLUENER-2020数据集和Weibo数据集上,F1值达到75.11%和68%,提升了中文命名实体识别的效果。
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | Babych B, Hartley A. Improving machine translation quality with automatic named entity recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of the 7th International EAMT Workshop on MT and other Language Technology Tools, Improving MT Through other Language Technology Tools, Resource and Tools for Building MT at EACL, Budapest, Hungary, 2003: 1-8. |
| 2 | Zelenko D, Aone C, Richardella A. Kernel methods for relation extraction[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003(3): 1083-1106. |
| 3 | Kumaran G, Allan J. Text classification and named entities for new event detection[C]∥ Proceedings of the 27th Annual International ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development In Information Retrieval, Sheffield, UK, 2004: 297-304. |
| 4 | Ramshaw L, Marcus M. Text chunking using transformation-based learning[J/OL]. (1996-03-23). [2021-09-12]. . |
| 5 | 徐智婷, 薛向阳.融合多特征的最大熵汉语命名实体识别模型[J].计算机研究与发展, 2008(6): 1004-1010. |
| Xu Zhi-ting, Xue Xiang-yang. Fusion of multiple features for chinese named entity recognition based on maximum entropy model[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2008(6): 1004-1010. | |
| 6 | 王路路, 艾山·吾买尔, 买合木提·买买提, 等.基于CRF和半监督学习的维吾尔文命名实体识别[J]. 中文信息学报, 2018, 32(11): 16-26+33. |
| Wang Lu-lu, Wumaier Aishan, Maimaiti Maihemuti, et al. A semi-supervised approach to uyghur named entity recognition based on CRF[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2018, 32(11): 16-26+33. | |
| 7 | 燕杨, 文敦伟, 王云吉, 等.基于层叠条件随机场的中文病历命名实体识别[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1843-1848. |
| Yan Yang, Wen Dun-wei, Wang Yun-ji, et al. Name entity recognition in chinese medical records based on cascaded conditional random field[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1843-1848. | |
| 8 | Morwal S, Jahan N, Chopra D. Named entity recognition using hidden markov model[J]. International Journal on Natural Language Computing, 2012, 1(4): 15-23. |
| 9 | 李抵非, 田地, 胡雄伟.基于深度学习的中文标准文献语言模型[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(2): 596-599. |
| Li Di-fei, Tian Di, Hu Xiong-wei. Standard literature language model based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 596-599. | |
| 10 | Lafferty J D, McCallum A, Pereira F C N. Conditional random fields: probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data[C]∥ Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, Williamstown, USA, 2001: 282-289. |
| 11 | 郭晓然, 罗平, 王维兰.基于Transformer编码器的中文命名实体识别[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| Guo Xiao-ran, Luo Ping, Wang Wei-lan. Chinese named entity recognition based on Transformer encoder[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. | |
| 12 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[J/OL]. [2017-12-06]. |
| 13 | Radford A, Narasimhan K, Salimans T, et al. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training[J], 2018. |
| 14 | Rei M, Crichton G, Pyysalo S. Attending to characters in neural sequence labeling models[C]∥International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Osaka, Japan, 2016: 309-318. |
| 15 | 李明扬, 孔芳.融入自注意力机制的社交媒体命名实体识别[J].清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 59 (6):461-467. |
| Li Ming-yang, Kong Fang. Combined self-attention mechanism for named entity recognition in social media[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2019, 59(6): 461-467 | |
| 16 | Yan H, Deng B, Li X N, et al. TENER: adapting transformer encoder for named entity recognition[J/OL]. [2019-12-10]. . |
| 17 | Li Y, Shetty P, Liu L, et al. BERtifying the hidden markov model for multi-source weakly supervised named entity recognition[J/OL]. [2021-03-30]. . |
| 18 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[J/OL]. [2019-03-24]. 。 |
| 19 | Christian T. Classification on soft labels is robust against label noise[C]∥ Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Knowledge based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, Part I, KES ' 08, Heidelberg, Berlin, 2008: 65-73. |
| 20 | Liang C, Yu Y, Jiang H M, et al. Bond: bert-assisted open-domain named entity recognition with distant supervision[C]∥KDD'20: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, New York, USA, 2020: 1054-1064. |
| 21 | Xu L, Dong Q Q, Yu C, et al. Cluener2020: fine-grained name entity recognition for chinese[J/OL]. [2020-01-20]. . |
| 22 | Peng N Y, Dredze M. Named entity recognition for chinese social media with jointly trained embeddings[C]∥Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 2015: 548-554. |
| [1] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [2] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [3] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [4] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [5] | 雷景佩,欧阳丹彤,张立明. 基于知识图谱嵌入的定义域值域约束补全方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 154-161. |
| [6] | 李志华,张烨超,詹国华. 三维水声海底地形地貌实时拼接与可视化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 180-186. |
| [7] | 欧阳丹彤,张必歌,田乃予,张立明. 结合格局检测与局部搜索的故障数据缩减方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [8] | 徐艳蕾,何润,翟钰婷,赵宾,李陈孝. 基于轻量卷积网络的田间自然环境杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
| [9] | 杨勇,陈强,曲福恒,刘俊杰,张磊. 基于模拟划分的SP⁃k⁃means-+算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1808-1816. |
| [10] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [11] | 董延华,刘靓葳,赵靖华,李亮,解方喜. 基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1405-1413. |
| [12] | 刘富,梁艺馨,侯涛,宋阳,康冰,刘云. 模糊c-harmonic均值算法在不平衡数据上改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1447-1453. |
| [13] | 郭晓然,罗平,王维兰. 基于Transformer编码器的中文命名实体识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| [14] | 尚福华,曹茂俊,王才志. 基于人工智能技术的局部离群数据挖掘方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 692-696. |
| [15] | 赵海英,周伟,侯小刚,张小利. 基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 293-302. |
|
||