吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1548-1554.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220878
• 材料科学与工程 • 上一篇
软质炭黑对天然橡胶基磁流变弹性体性能的影响
- 1.吉林大学 材料科学与工程学院,长春 130022
2.长春大学 计算机科学技术学院,长春 130022
Effect of soft carbon black on properties of natural rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers
Yi LI1( ),Tian-bao LIU1,Shao-qiang WANG2(
),Tian-bao LIU1,Shao-qiang WANG2( ),Ji-cai LIANG1
),Ji-cai LIANG1
- 1.College of Materials Science and Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
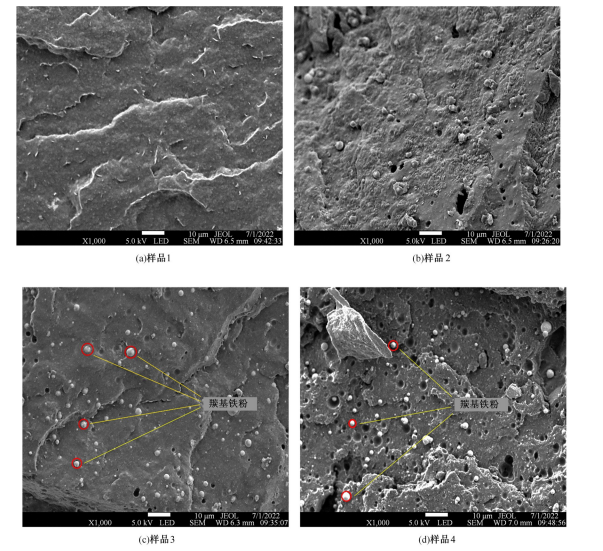
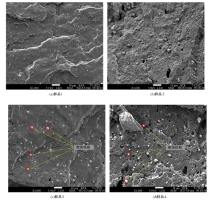
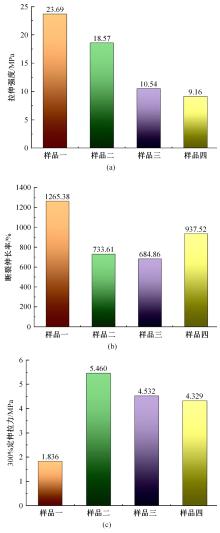
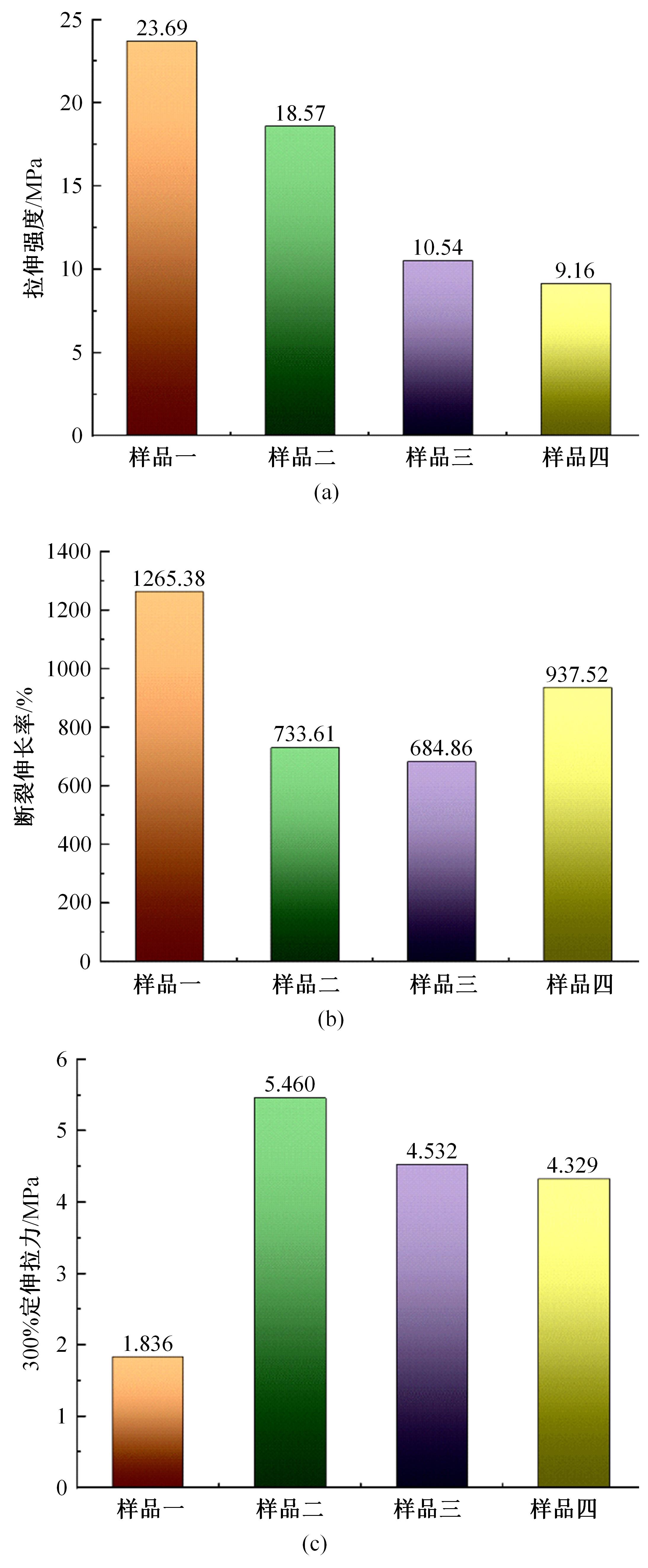
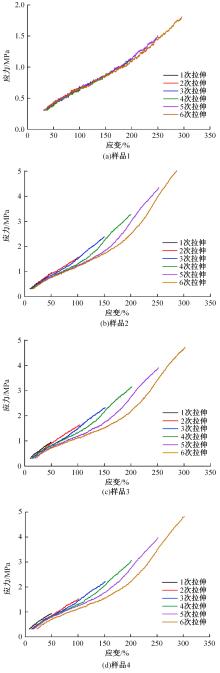
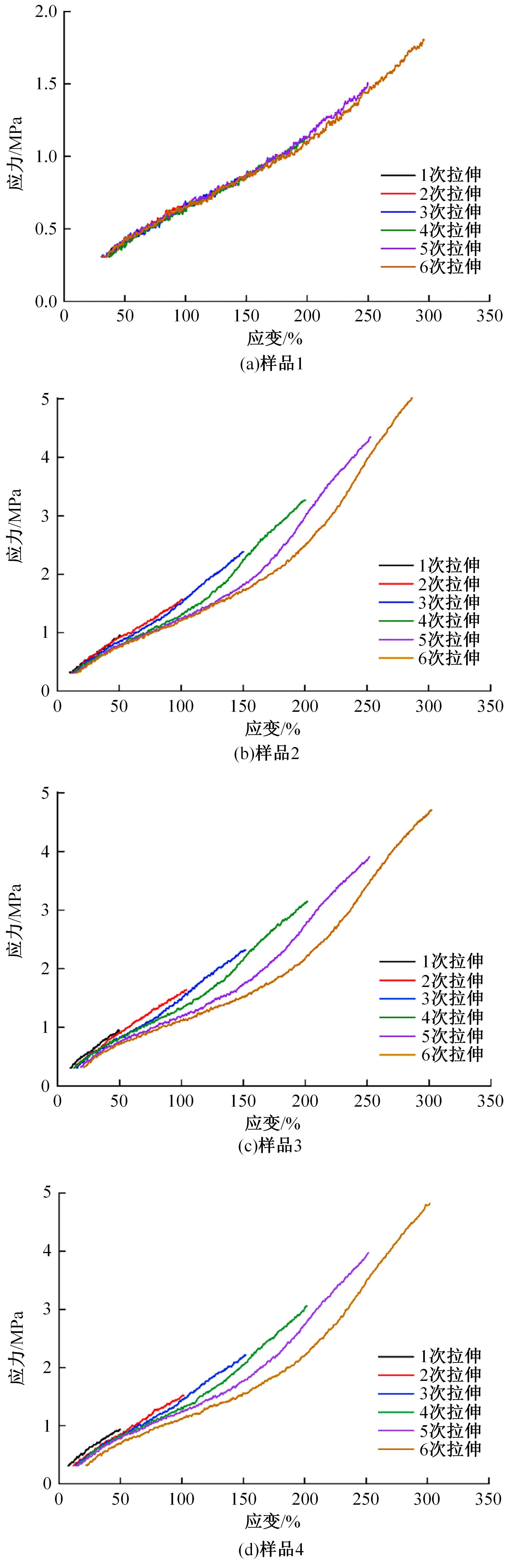
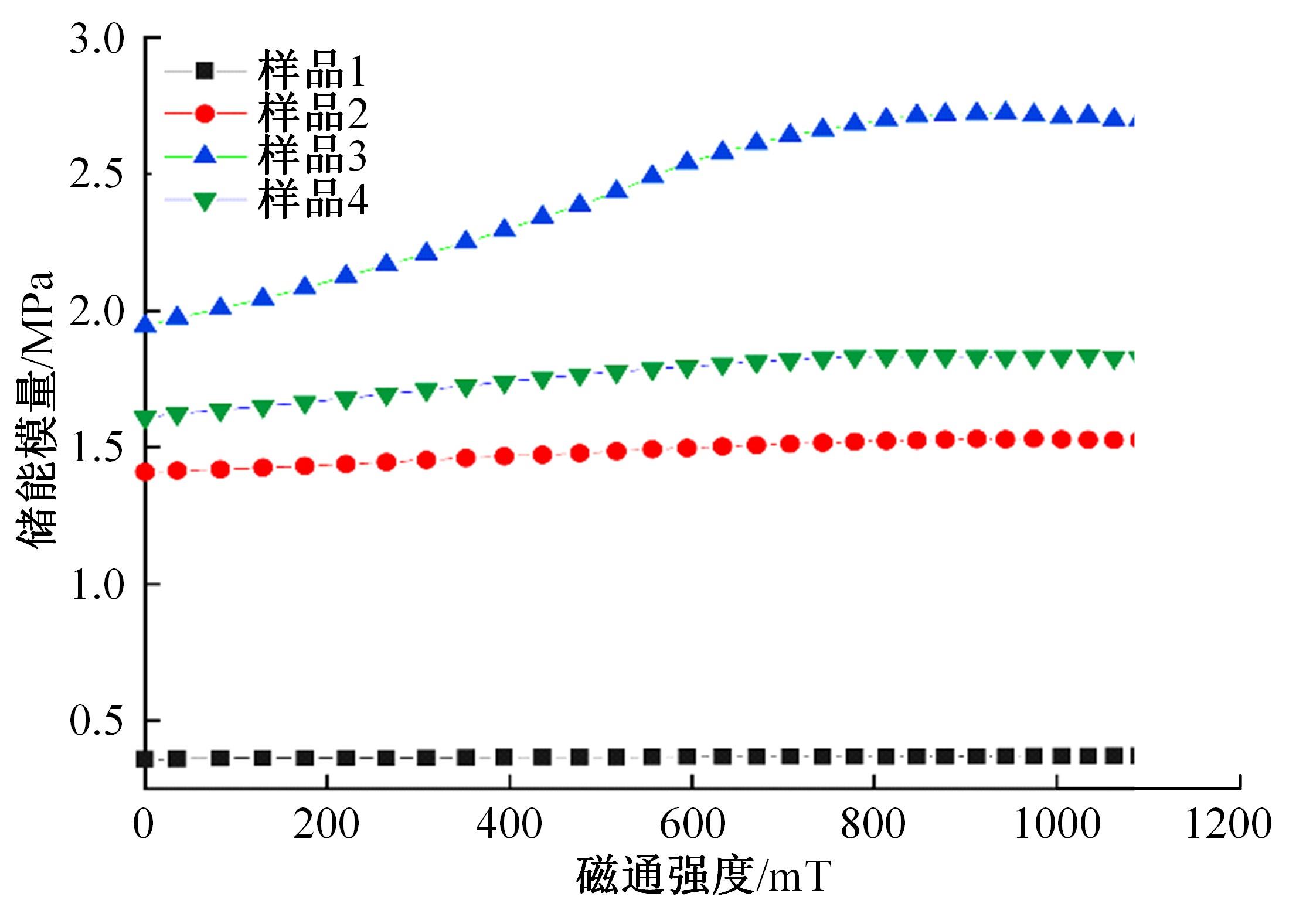
以天然橡胶为基体,使用软质炭黑和羰基铁粉制备了4种磁流变弹性体,探究了软质炭黑和磁性粒子含量对其性能的影响。使用场发射扫描电子显微镜观察其微观结构,采用电子式万能试验机和高级旋转流变仪观察分析其力学性能和磁流变效应。结果表明:软质炭黑的加入提高了磁流变弹性体的拉伸强度和300%的定伸拉力,改变了在低应变情况下磁流变弹性体的Mullins效应;羰基铁粉体积分数为30%的磁流变弹性体在添加软质炭黑后,其磁流变效应提高了3倍。因此,软质炭黑作为补强剂可以大幅提高磁流变弹性体的各项性能。
中图分类号:
- TG386
| 1 | Chen Lin, Gong Xing-long, Jiang Wan-quan, et al. Investigation on magnetorheological elastomers based on natural rubber[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42 (14): 5483-5489. |
| 2 | Blom P, Kari L. Amplitude and frequency dependence of magneto-sensitive rubber in a wide frequency range[J]. Polymer Testing, 2005, 24 (5): 656-662. |
| 3 | Chen Lin, Gong Xing-long. Damping of magnetorheological elastomers[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 15 (s1): 271-274. |
| 4 | Boczkowska A, Awietjan S F, Pietrzko S, et al. Mechanical properties of magnetorheological elastomers under shear deformation[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2012, 43 (2): 636-640. |
| 5 | Agirre-Olabide I, Elejabarrieta M J. A new magneto-dynamic compression technique for magnetorheological elastomers at high frequencies[J]. Polymer Testing, 2018, 66: 114-121. |
| 6 | Jolly M R, Carlson J D, Munoz B C. A model of the behaviour of magnetorheological materials[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 1996, 5: No.607. |
| 7 | Davis L C. Model of magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 85 (6): 3348-3351. |
| 8 | Stepanov G V, Abramchuk S S, Grishin D A, et al. Effect of a homogeneous magnetic field on the viscoelastic behavior of magnetic elastomers[J]. Polymer, 2007, 48 (2): 488-495. |
| 9 | Qiao Yan-liang, Zhang Jiang-tao, Zhang Mei, et al. A magnetic field- and frequency-dependent dynamic shear modulus model for isotropic silicone rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2021, 204:No.108637. |
| 10 | Khimi S R, Pickering K L. The effect of silane coupling agent on the dynamic mechanical properties of iron sand/natural rubber magnetorheological elastomers[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 90: 115-125. |
| 11 | Böse H, Röder R. Magnetorheological elastomers with high variability of their mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2009, 149:No.012090. |
| 12 | Lokander M, Stenberg B. Performance of isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials[J]. Polymer Testing, 2003, 22 (3): 245-251. |
| 13 | Gong X L, Zhang X Z, Zhang P Q. Fabrication and characterization of isotropic magnetorheological elastomers[J]. Polymer Testing, 2005, 24 (5): 669-676. |
| 14 | Bica I, Anitas E, Chirigiu L. Magnetic field intensity effect on plane capacitors based on hybrid magnetorheological elastomers with graphene nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2017, 56: 407-412. |
| 15 | Bica I. Influence of the transverse magnetic field intensity upon the electric resistance of the magnetorheological elastomer containing graphite microparticles[J]. Materials Letters, 2009, 63 (26): 2230-2232. |
| 16 | Wu Jin-kui, Gong Xing-long, Fan Yan-ceng, et al. Improving the magnetorheological properties of polyurethane magnetorheological elastomer through plasticization[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 123 (4): 2476-2484. |
| 17 | Kimura Y, Kanauchi S, Kawai M, et al. Effect of Plasticizer on the Magnetoelastic Behavior for Magnetic Polyurethane Elastomers[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2015, 44 (2): 177-178. |
| 18 | Stoll A, Mayer M, Monkman G, et al. Evaluation of highly compliant magneto-active elastomers with colossal magnetorheological response[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(2): No.39793. |
| 19 | Hu Tao, Xuan Shou-hu, Ding Li, et al. Stretchable and magneto-sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire-polyurethane sponge enhanced magnetorheological elastomer[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 156: 528-537. |
| [1] | 谢超,王起才,于本田,李盛,林晓旭,鲁志铭. 聚氨酯涂膜弹性模量的AFM测定及微观结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1322-1330. |
| [2] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [3] | 李志军,刘浩,张立鹏,李振国,邵元凯,李智洋. 过滤壁结构对颗粒捕集器深床过滤影响的模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 422-434. |
| [4] | 崔亚楠, 韩吉伟, 冯蕾, 李嘉迪, 王乐. 盐冻循环条件下改性沥青微细观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 452-458. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟, 董晓龙, 张霖, 胡晓利. 块体材料弹性模量的四点弯曲自动测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 140-145. |
| [6] | 关庆丰, 李艳, 侯秀丽, 杨盛志, 王晓彤. 固溶态Mg-Gd-Y-Nd合金强流脉冲电子束表面改性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1200-1205. |
| [7] | 关庆丰,季乐,蔡杰,杨盛志,刘世超,张在强,侯秀丽. 强流脉冲电子束轰击作用下3Cr13不锈钢的微观结构及性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 712-717. |
| [8] | 关庆丰, 邹阳, 张在强, 关锦彤, 苏景新, 王志平. 强流脉冲电子束作用下纯铜的微观结构与腐蚀性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 964-969. |
| [9] | 李秀娟, 梁云虹, 张志辉, 任露泉. 杨树叶片的微观结构及拉伸特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 440-443. |
| [10] | 房岩, 孙刚, 丛茜, 郭华曦. 蝗虫翅表面微观结构及疏水耦合机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 419-422. |
| [11] | 詹小丽, 张肖宁, 王端宜, 卢亮. 基于DMA方法的沥青胶浆微观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(04): 916-920. |
| [12] | 弯艳玲,丛茜,金敬福,王晓俊 . 蜻蜓翅膀微观结构及其润湿性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(03): 732-0736. |
| [13] | 卢广林,汪春花,王毅,邱小明 . Ag基钎料钎焊立方氮化硼的焊接性与微观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(05): 1088-1092. |
| [14] | 董文,王海东,李光玉,谈俭军 . Nd:YAG脉冲激光氧化Cr膜的微观表面[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(01): 17-21. |
| [15] | 宋雨来,刘耀辉,朱先勇,王素环,于思荣. 钕对AZ91镁合金组织及机械性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(03): 289-0293. |
|
||