吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 2086-2092.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230129
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
连续生产流水线深度强化学习优化调度算法
- 1.新疆师范大学 计算机科学技术学院,乌鲁木齐 830000
2.新疆大学 软件工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830000
3.新疆大学 机械工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830000
Deep reinforcement learning optimization scheduling algorithm for continuous production line
Guang-he ZHU1( ),Zhi-qiang ZHU2,Yi-ping YUAN3
),Zhi-qiang ZHU2,Yi-ping YUAN3
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Xinjiang Normal University,Urumqi 830000,China
2.College of Software Engineering,Xinjiang University,Urumqi 830000,China
3.College of Mechanical Engineering,Xinjiang University,Urumqi 830000,China
摘要:
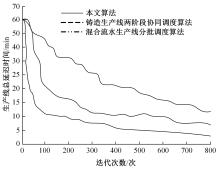
为了提高连续生产流水线的调度效果,提升生产线的加工效率,提出连续生产流水线深度强化学习优化调度算法。首先,结合蒙特卡罗算法和贝叶斯评估方法降低连续生产线流水线问题的数据复杂度;其次,采用深度神经网络模型优化流水线调度参数,对其进行评估及编码;最后,将迭代贪婪算法与深度强化学习方法结合,对调度数据问题实施模型求解,实现连续生产流水线调度。试验结果表明:本文算法的调度结果最优,综合评价结果均高于0.9531,工序延时优化至5 min以下,收敛速度较快,提升了生产线的加工效率。
中图分类号:
- TP273
| 1 | 冯昊天,王红军,常城,等.基于数字孪生的柔性生产线状态感知[J].电子测量与仪器学报,2021,35(2):17-24. |
| Feng Hao-tian, Wang Hong-jun, Chang Cheng, et al. State perception of flexible production line based on digital twin[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2021,35(2): 17-24. | |
| 2 | 牟健慧,段培永,高亮,等.基于混合遗传算法求解分布式流水车间逆调度问题[J].机械工程学报,2022,58(6):295-308. |
| Mou Jian-hui, Duan Pei-yong, Gao Liang, et al. Hybrid genetic algorithm for distributed flow shop inverse scheduling problem[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022,58(6): 295-308. | |
| 3 | 魏晓晗,张庆,蒋婷婷,等.伺服系统瞬态优化的模糊自适应深度强化学习方法[J].西安交通大学学报,2021,55(8):68-77. |
| Wei Xiao-han, Zhang Qing, Jiang Ting-ting, et al. Fuzzy adaptive deep reinforcement learning method for optimizing transient performance of servo system [J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2021,55(8): 68-77. | |
| 4 | 袁小芳,杨育辉,谭伟华,等.基于混合并行混沌优化算法的铸造生产线两阶段协同调度[J].湖南大学学报:自然科学版,2021,48(10):161-169. |
| Yuan Xiao-fang, Yang Yu-hui, Tan Wei-hua, et al. Two-stage collaborative scheduling of casting production line based on hybrid parallel chaotic optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2021,48(10): 161-169. | |
| 5 | 李静,高华钰,沈南燕,等.面向机床精密主轴加工过程的混合流水生产线分批调度研究[J].机械工程学报,2021,57(5):185-195. |
| Li Jing, Gao Hua-yu, Shen Nan-yan, et al. Research on batch scheduling of hybrid production line for machine tool precision spindle processing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021,57(5): 185-195. | |
| 6 | 闫凯.辐射流体力学数值模拟中的隐式蒙特卡罗方法[J].原子能科学技术,2021,55(3):397-404. |
| Yan Kai. Implicit monte carlo method in radiation hydrodynamics[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2021,55(3): 397-404. | |
| 7 | 江文奇,黄容,牟华伟,等.面向大规模数据精简的聚类中心点优化和FCM算法设计[J].数学的实践与认识,2021,51(17):144-151. |
| Jiang Wen-qi, Huang Rong, Mou Hua-wei, et al. Clustering center optimization and FCM algorithm design for large-scale data reduction[J]. Mathematical Practice and Understanding, 2021,51(17): 144-151. | |
| 8 | 李伊玲,李琳,刘任,等.基于非均匀单元离散法的静态逆Preisach模型分布函数辨识[J].中国电机工程学报,2021,41(15):5340-5351. |
| Li Yi-ling, Li Lin, Liu Ren, et al. The non-uniform element discretization method for identifying distribution function of static inverse Preisach model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021,41(15): 5340-5351. | |
| 9 | 任艳平,郑重,江一飞,等.融合后验概率和密度的不平衡数据欠采样方法[J].计算机工程与应用,2022,58(23):268-277. |
| Ren Yan-ping, Zheng Chong, Jiang Yi-fei, et al. Posterior probability and density-based imbalanced data undersampling[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022,58(23): 268-277. | |
| 10 | 吴喜胜,武岩波,朱敏,等.水声通信中后验符号概率密度分布及概率成形容量分析[J].声学学报,2021,46(1):35-45. |
| Wu Xi-sheng, Wu Yan-bo, Zhu Min, et al. The probability density distribution of the a posteriori symbols and probabilistic shaping capacity analysis in underwater acoustic communication[J]. Acta Acustica, 2021,46(1): 35-45. | |
| 11 | 袁博文,朱丰,刘兆鹏,等.知识图谱的预警探测体系探测效能贝叶斯评估方法[J].现代防御技术,2022,50(1):74-80. |
| Yuan Bo-wen, Zhu Feng, Liu Zhao-peng, et al. Bayesian evaluation method for detection efficiency of early warning detection system based on knowledge graph[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2022,50(1): 74-80. | |
| 12 | 李晓瑜,胡勇,卢俊邑,等.基于量子条件主方程的隐马尔可夫模型[J].电子科技大学学报,2021,50(5):644-649, 642. |
| Li Xiao-yu, Hu Yong, Lu Jun-yi, et al. Hidden markov model based on the quantum conditional master equation[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021,50(5): 644-649, 642 | |
| 13 | 周上尧.非线性MS-DSGE模型的条件最优粒子滤波与贝叶斯估计[J].数量经济技术经济研究,2021,38(3):160-180. |
| Zhou Shang-yao. Conditional optimal particle filter and bayesian estimation of nonlinear MS-DSGE model[J]. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 2021,38(3): 160-180. | |
| 14 | 赵荣珍,薛勇,吴耀春.改进的D-t-SNE滚动轴承故障数据集降维方法[J].兰州理工大学学报,2022,48(3):42-49. |
| Zhao Rong-zhen, Xue Yong, Wu Yao-chun. Rolling bearing fault data set dimension reduction method of improved D-t-SNE[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2022,48(3): 42-49. | |
| 15 | 秦浩翔,韩玉艳,陈庆达,等.求解阻塞混合流水车间调度的双层变异迭代贪婪算法[J].控制与决策,2022,37(9):2323-2332. |
| Qin Hao-xiang, Han Yu-yan, Chen Qing-da, et al. A double level mutation iterated greedy algorithm for blocking hybrid flow shop scheduling[J]. Control and Decision, 2022,37(9): 2323-2332. | |
| 16 | 张梓琪,钱斌,胡蓉.混合交叉熵算法求解复杂零等待流水线调度问题[J].控制理论与应用,2021,38(12):1919-1934. |
| Zhang Zi-qi, Qian Bin, Hu Rong. Hybrid cross-entropy algorithm for solving complex no-wait flow-shop scheduling problem[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2021,38(12): 1919-1934. | |
| 17 | 罗磊,陈照云,王俪璇.用户QoS感知的GPU集群深度学习任务动态调度[J].计算机工程与科学,2021,43(8):1331-1340. |
| Luo Lei, Chen Zhao-yun, Wang Li-xuan. User QoS-aware deep learning task dynamic scheduling on GPU clusters[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2021,43(8): 1331-1340. | |
| 18 | 陈浩杰,黄锦,左兴权,等.基于宽度&深度学习的基站网络流量预测方法[J].郑州大学学报:工学版,2022,43(1):7-13. |
| Chen Hao-jie, Huang Jin, Zuo Xing-quan, et al. Base station network traffic prediction method based on wide&deep learning[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University(Engineering Science), 2022,43(1): 7-13. | |
| 19 | 高强, 郭大权, 李飞,等. 改进启发算法在半导体生产调度中的应用研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(10):392-396. |
| Gao Qiang, Guo Da-quan, Li Fei, et al. Research and application of improved heuristic algorithm in semiconductor production scheduling[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021,38(10): 392-396. |
| [1] | 高敬鹏,王国轩,高路. 基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [2] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [3] | 田彦涛,季言实,唱寰,谢波. 深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [4] | 王清永,曲伟强. 基于线性规划的城市轨道交通运行调度优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3446-3451. |
| [5] | 宋世军,樊敏. 基于谱聚类的多维数据集异常数据检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2917-2922. |
| [6] | 庄伟超,丁昊楠,董昊轩,殷国栋,王茜,周朝宾,徐利伟. 信号交叉口网联电动汽车自适应学习生态驾驶策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 82-93. |
| [7] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [8] | 王忠立,王浩,申艳,蔡伯根. 一种多感知多约束奖励机制的驾驶策略学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2718-2727. |
| [9] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [10] | 吕帅,刘京. 基于深度强化学习的随机局部搜索启发式方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1420-1426. |
| [11] | 杨顺,蒋渊德,吴坚,刘海贞. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [12] | 李勇,陈贺新,赵刚 ,孙中华,陈绵书 . 基于可变k近邻LLE数据降维的图像检索方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(04): 946-949. |
|
||