吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 797-806.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220523
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法
- 1.哈尔滨工程大学 信息与通信工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
2.北京航天长征飞行器研究所 试验物理与计算数学国家级重点实验室,北京 100076
LSTM⁃MADDPG multi⁃agent cooperative decision algorithm based on asynchronous collaborative update
Jing-peng GAO1( ),Guo-xuan WANG1,Lu GAO2
),Guo-xuan WANG1,Lu GAO2
- 1.College of Information and Communication Engineering,Harbin Engineering University,Harbin 150001,China
2.National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Test Physics and Numerical Mathematics,Beijing Institute of Space Long March Vehicle,Beijing 100076,China
摘要:
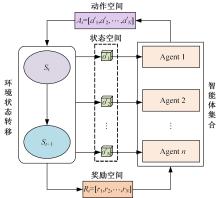
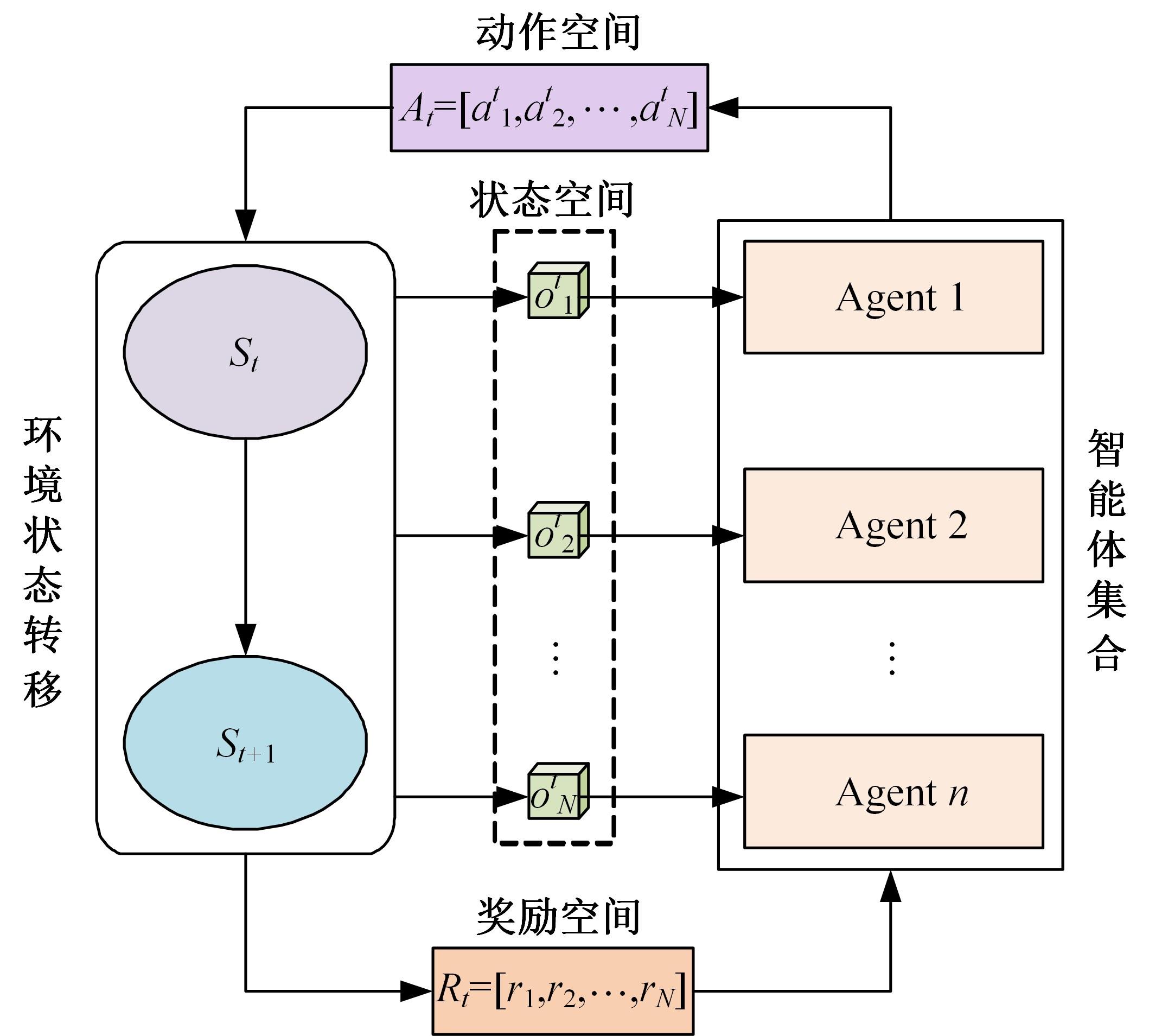
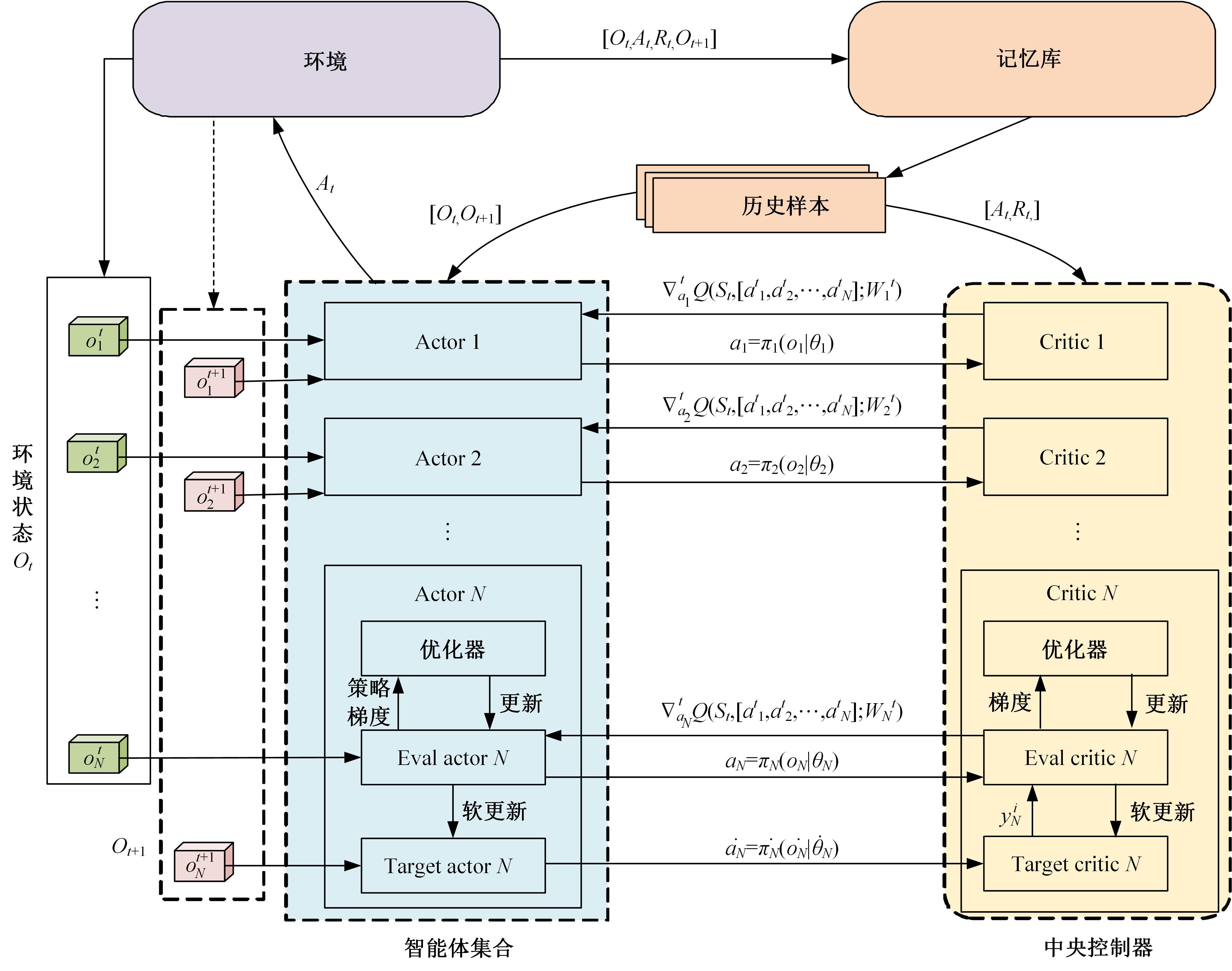
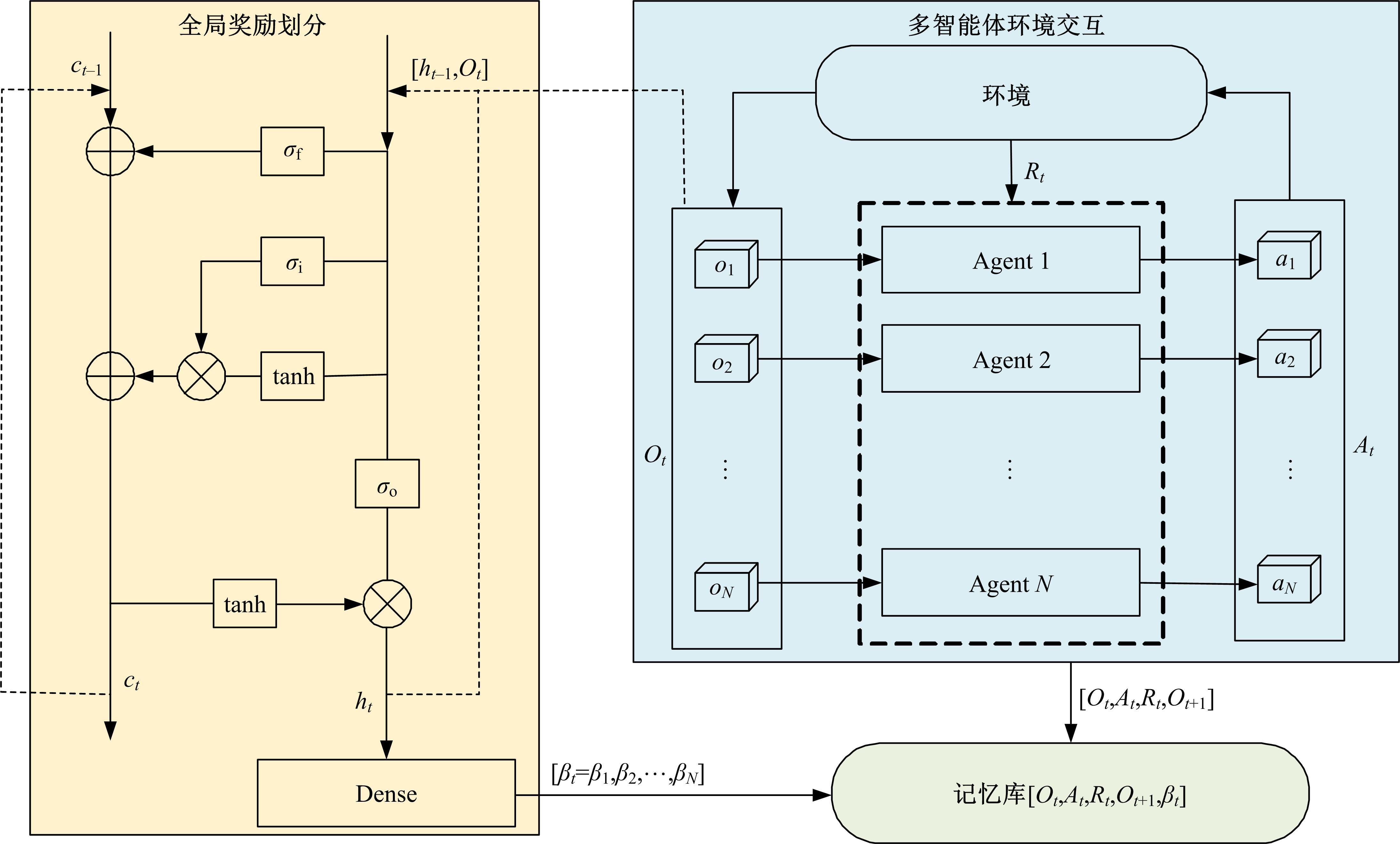
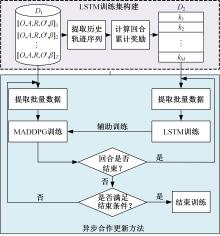
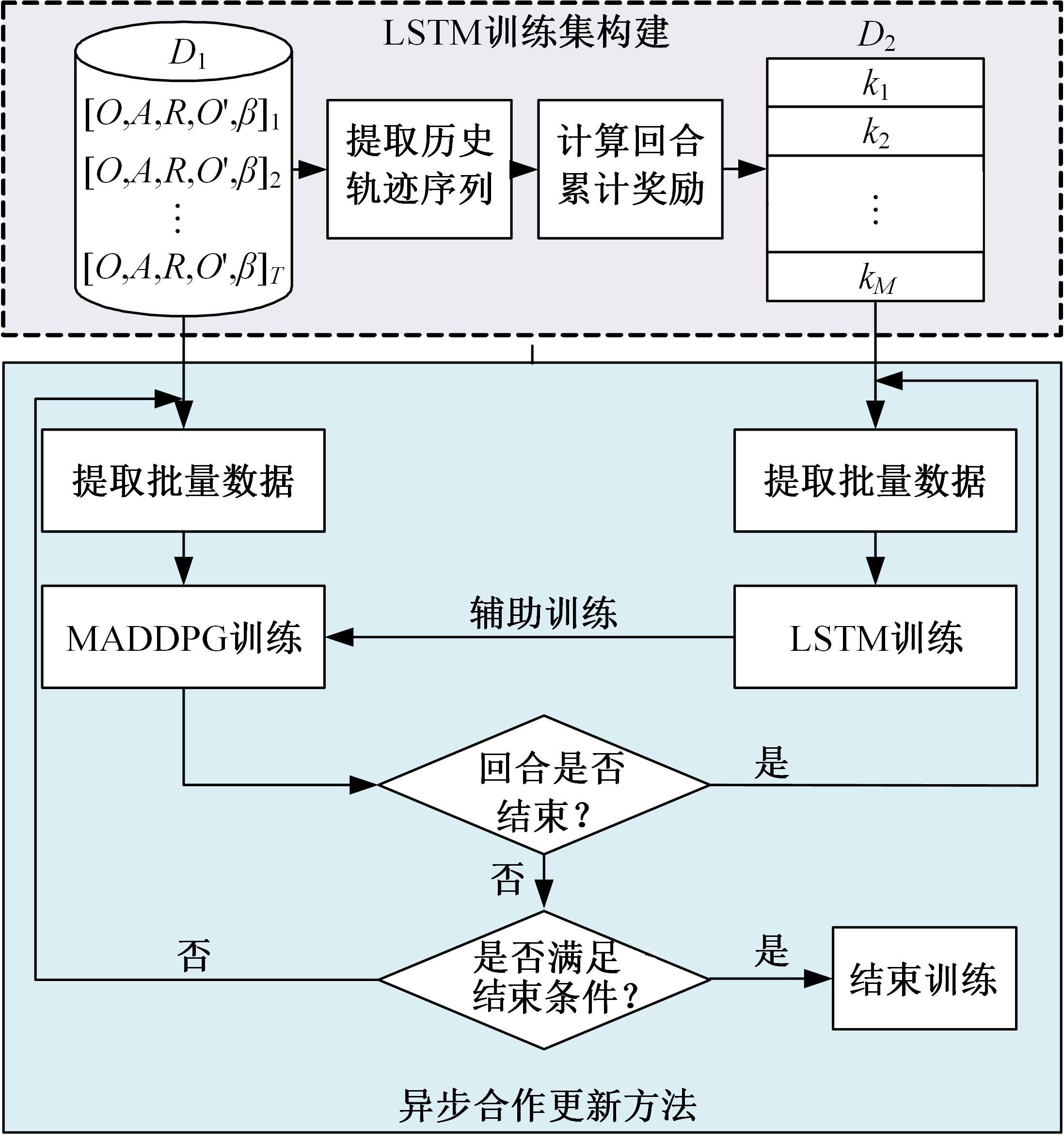
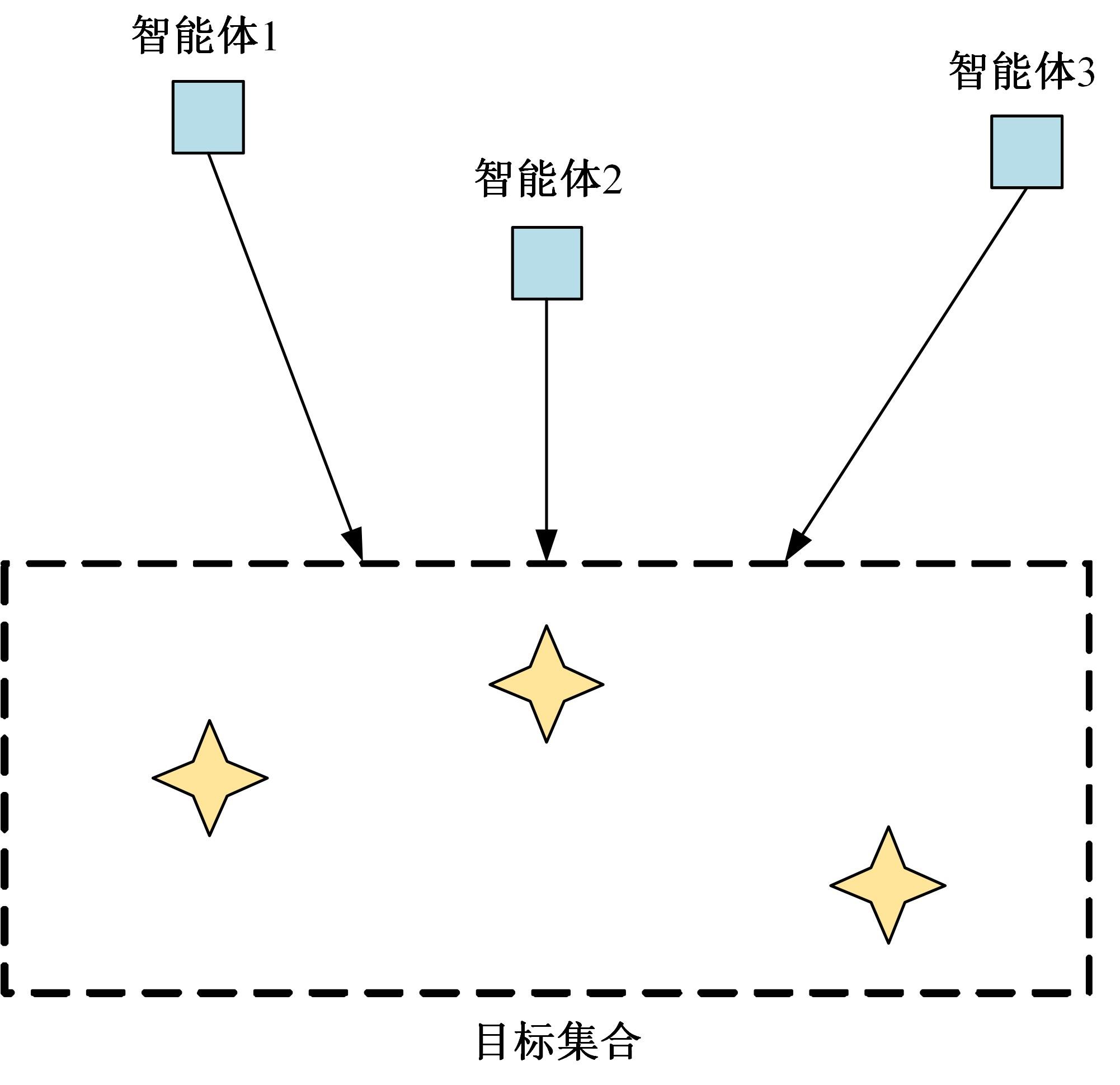
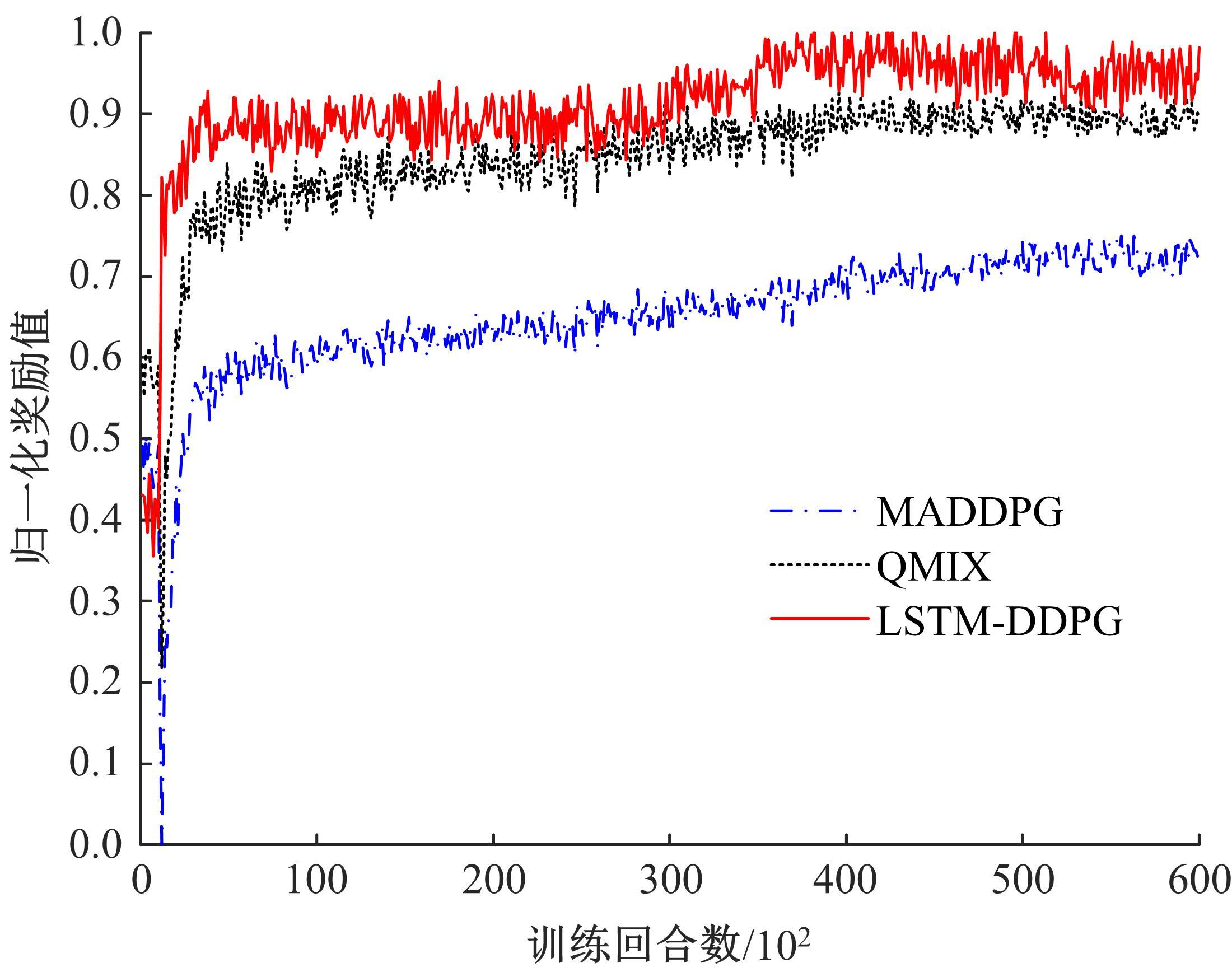
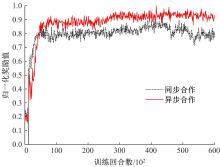
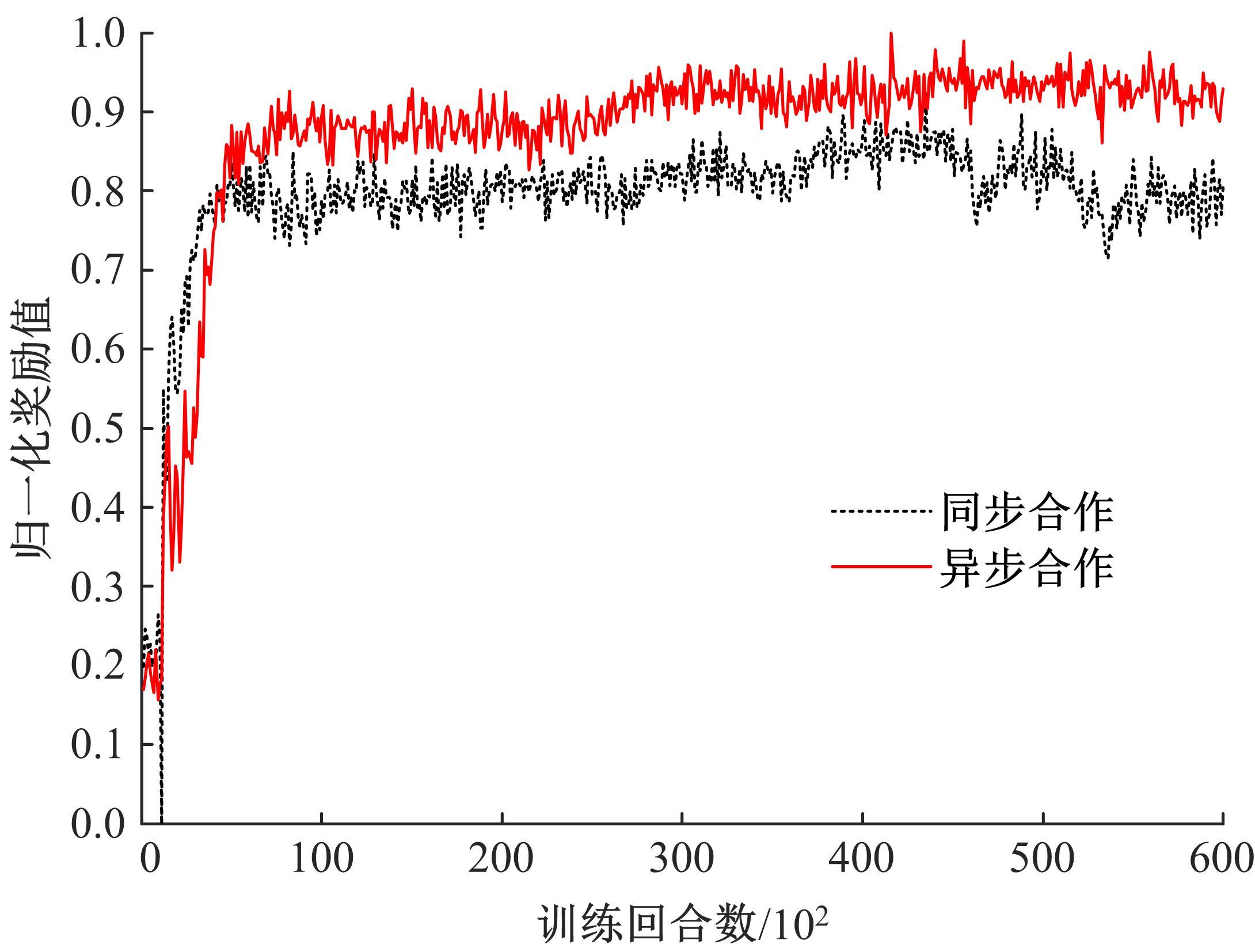
针对完全合作型任务中,多智能体深度确定性策略梯度(MADDPG)算法存在信度分配以及训练稳定性差的问题,提出了一种基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法。基于差异奖励和值分解思想,利用长短时记忆(LSTM)网络提取轨迹序列间特征,优化全局奖励划分方法,实现各智能体的动作奖励分配;结合算法联合训练需求,构建高质量训练样本集,设计异步合作更新方法,实现LSTM-MADDPG网络的联合稳定训练。仿真结果表明,在协作捕获场景中,本文算法相较于QMIX的训练收敛速度提升了20.51%;所提异步合作更新方法相较于同步更新,归一化奖励值均方误差减小了57.59%,提高了算法收敛的稳定性。
中图分类号:
- TP18
| 1 | Feng J, Li H, Huang M, et al. Learning to collaborate: multi-scenario ranking via multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, Lyon, France, 2018: 1939-1948. |
| 2 | 杨顺, 蒋渊德, 吴坚, 等. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| Yang Shun, Jiang Yuan-de, Wu Jian, et al. Autonomous driving policy learning based on deep reinforcement learning and multi-type sensor data[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. | |
| 3 | Hernandez-Leal P, Kartal B, Taylor M E. A survey and critique of multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Auto Agent Multi-Agent Systems, 2019, 33(6): 750-797. |
| 4 | Lowe R, Wu Y, Tamar Aviv, et al. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments[C]∥Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New York, USA, 2017: 6382-6393. |
| 5 | Nguyen T T, Nguyen N D, Nahavandi S. Deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent systems: a review of challenges, solutions, and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 3826-3839. |
| 6 | Holmesparker C, Taylor M E, Agogino A, et al. Cleaning the reward: counterfactual actions to remove exploratory action noise in multi-agent learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-agent Systems, Paris, France, 2014: 1353-1354. |
| 7 | Chang Y H, Ho T, Kaelbling L P. All learning is local: multi-agent learning in global reward games[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, USA,2004: 807-814. |
| 8 | Devlin S, Yliniemi L, Kudenko D, et al. Potential based difference rewards for multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, Paris, France, 2014: 165-172. |
| 9 | Foerster J N, Farquhar G, Afouras T, et al. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients[C]∥Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 2974-2982. |
| 10 | Chen J, Guo L, Jia J, et al. Resource allocation for IRS assisted SGF NOMA transmission: a MADRL approach[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(4): 1302-1316. |
| 11 | Sunehag P, Lever G, Gruslys A, et al. Value decomposition networks for cooperative multi-agent learning based on team reward[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-agent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 2085-2087. |
| 12 | Rashid T, Samvelyan M, Schroeder C, et al. QMIX: monotonic value function factorization for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 4295-4304. |
| 13 | Son K, Kim D, Kang W J, et al. QTRAN: learning to factorize with transformation for cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5887-5896. |
| 14 | 施伟, 冯旸赫, 程光权, 等. 基于深度强化学习的多机协同空战方法研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1610-1623. |
| Shi Wei, Feng Yang-he, Cheng Guang-quan, et al. Research on multi-aircraft cooperative air combat method based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Automation Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1610-1623. | |
| 15 | Wan K, Wu D, Li B, et al. ME-MADDPG: an efficient learning based motion planning method for multiple agents in complex environments[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 37(3): 2393-2427. |
| 16 | 王乃钰, 叶育鑫, 刘露, 等. 基于深度学习的语言模型研究进展[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(4): 1082-1115. |
| Wang Nai-yu, Ye Yu-xin, Liu Lu, et al. Language models based on deep learning: a review[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(4): 1082-1115. | |
| 17 | Pan Z Y, Zhang Z Z, Chen Z X. Asynchronous value iteration network[C]∥Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Red Hook, USA, 2018: 169-180. |
| [1] | 刘浏,丁鲲,刘姗姗,刘茗. 基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [2] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [3] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [4] | 田彦涛,季言实,唱寰,谢波. 深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [5] | 刘春晖,王思长,郑策,陈秀连,郝春蕾. 基于深度学习的室内导航机器人避障规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [6] | 庄伟超,丁昊楠,董昊轩,殷国栋,王茜,周朝宾,徐利伟. 信号交叉口网联电动汽车自适应学习生态驾驶策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 82-93. |
| [7] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [8] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [9] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [10] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [11] | 王忠立,王浩,申艳,蔡伯根. 一种多感知多约束奖励机制的驾驶策略学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2718-2727. |
| [12] | 雷景佩,欧阳丹彤,张立明. 基于知识图谱嵌入的定义域值域约束补全方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 154-161. |
| [13] | 李志华,张烨超,詹国华. 三维水声海底地形地貌实时拼接与可视化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 180-186. |
| [14] | 欧阳丹彤,张必歌,田乃予,张立明. 结合格局检测与局部搜索的故障数据缩减方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [15] | 徐艳蕾,何润,翟钰婷,赵宾,李陈孝. 基于轻量卷积网络的田间自然环境杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
|
||