吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 82-93.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210598
信号交叉口网联电动汽车自适应学习生态驾驶策略
庄伟超( ),丁昊楠,董昊轩,殷国栋(
),丁昊楠,董昊轩,殷国栋( ),王茜,周朝宾,徐利伟
),王茜,周朝宾,徐利伟
- 东南大学 机械工程学院,南京 211189
Learning based eco⁃driving strategy of connected electric vehicle at signalized intersection
Wei-chao ZHUANG( ),Hao-nan Ding,Hao-xuan DONG,Guo-dong YIN(
),Hao-nan Ding,Hao-xuan DONG,Guo-dong YIN( ),Xi WANG,Chao-bin ZHOU,Li-wei XU
),Xi WANG,Chao-bin ZHOU,Li-wei XU
- School of Mechanical Engineering,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
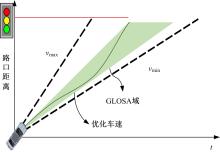
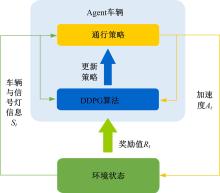
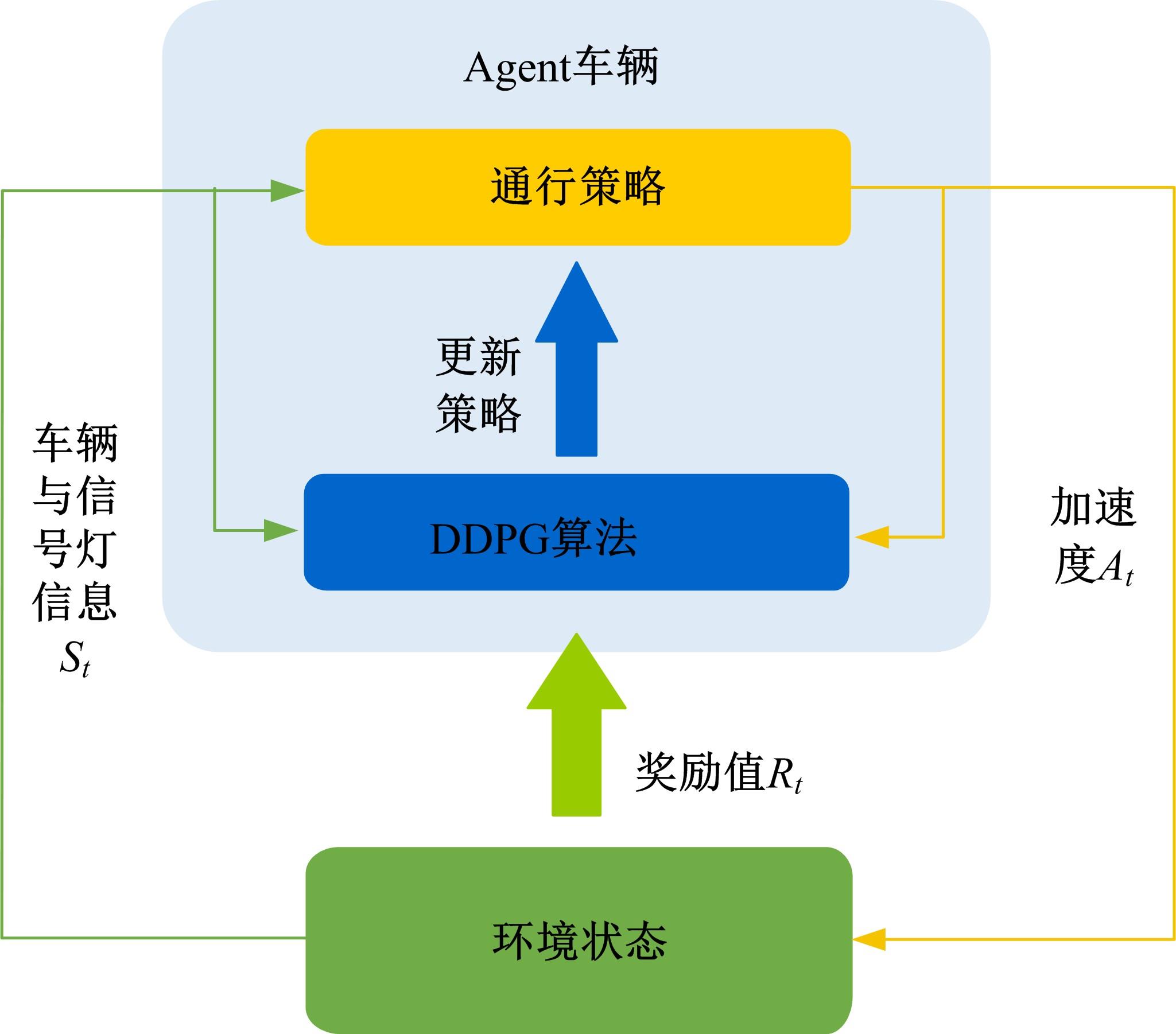
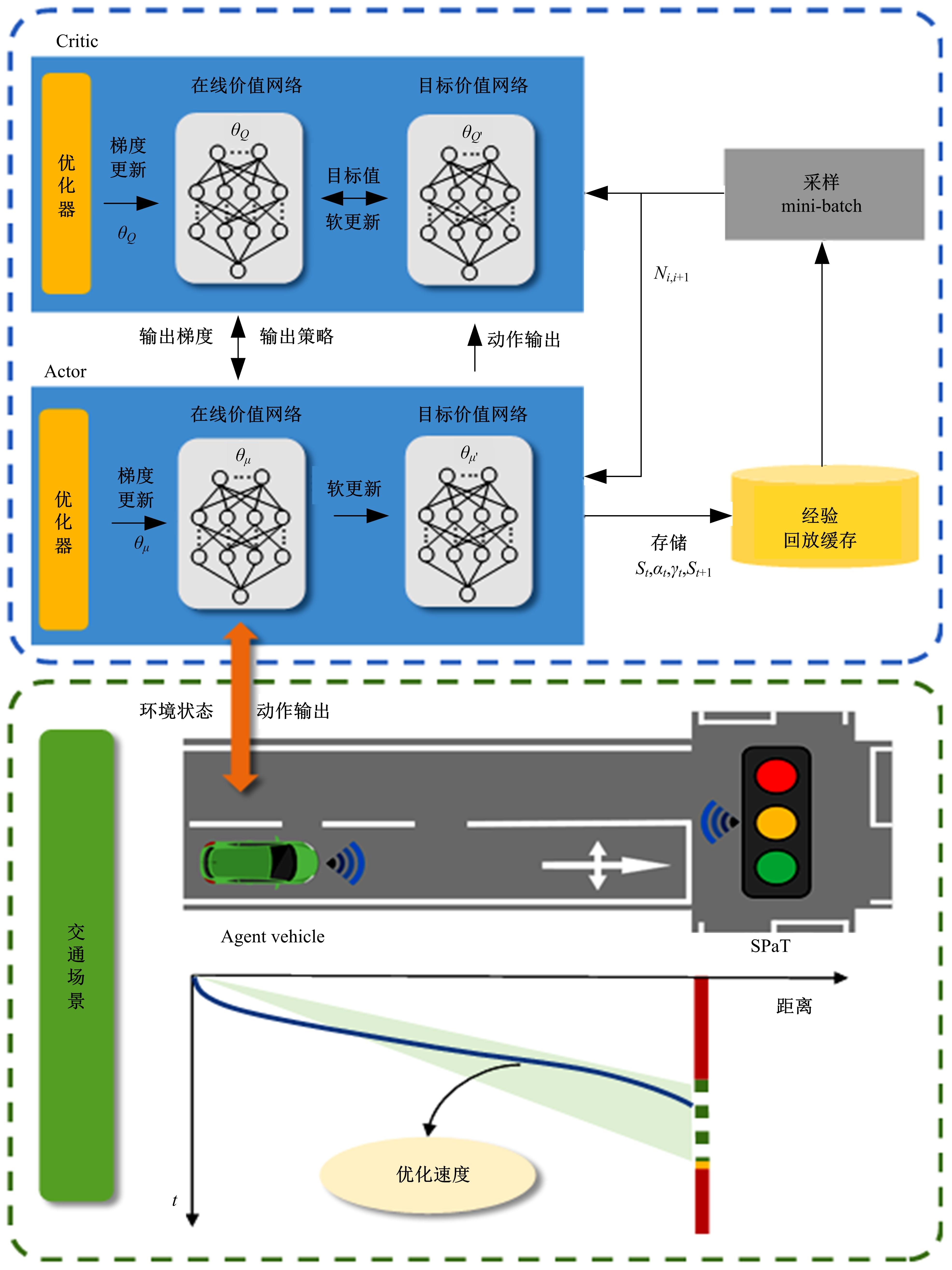
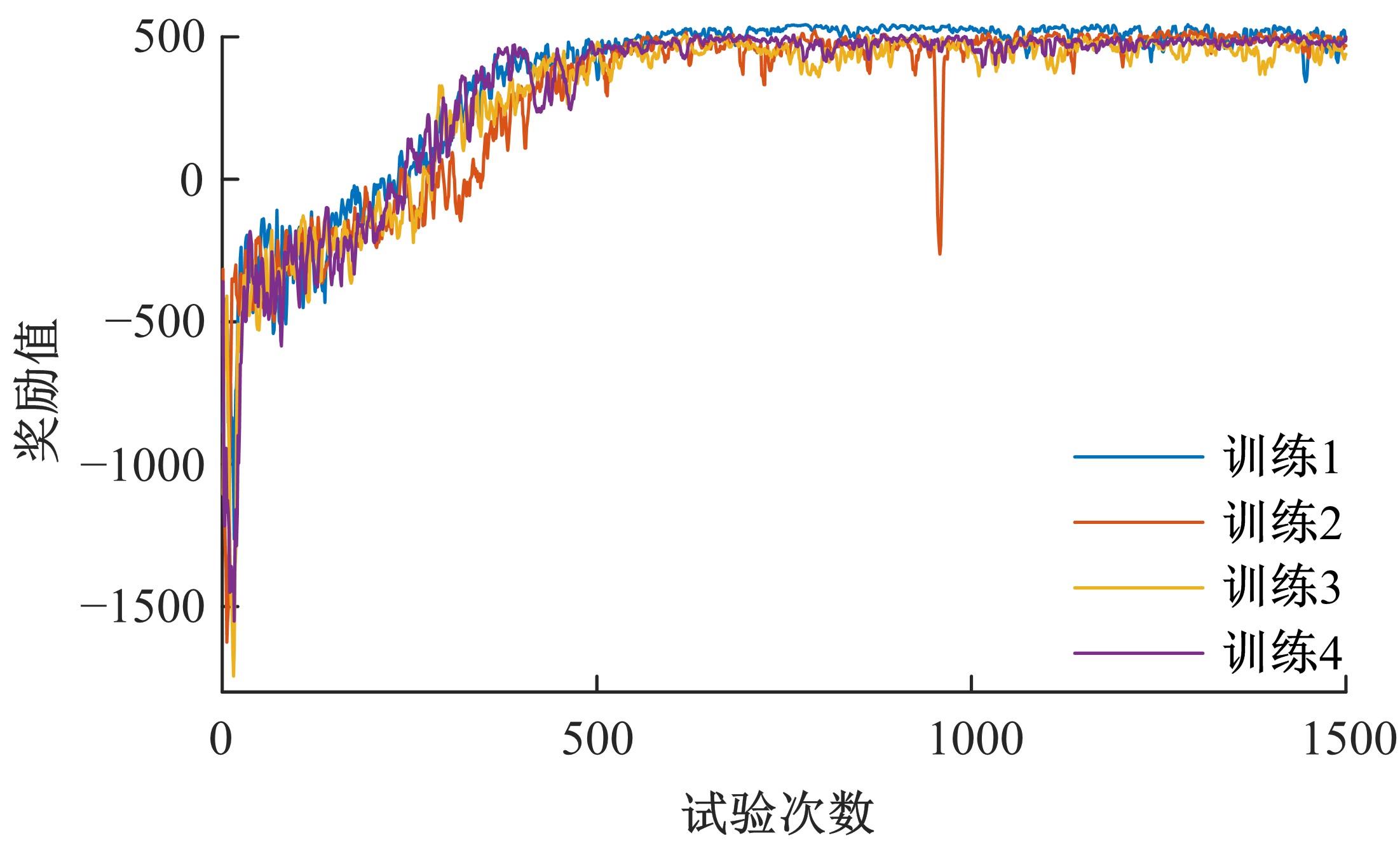
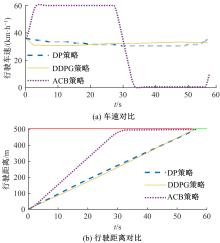
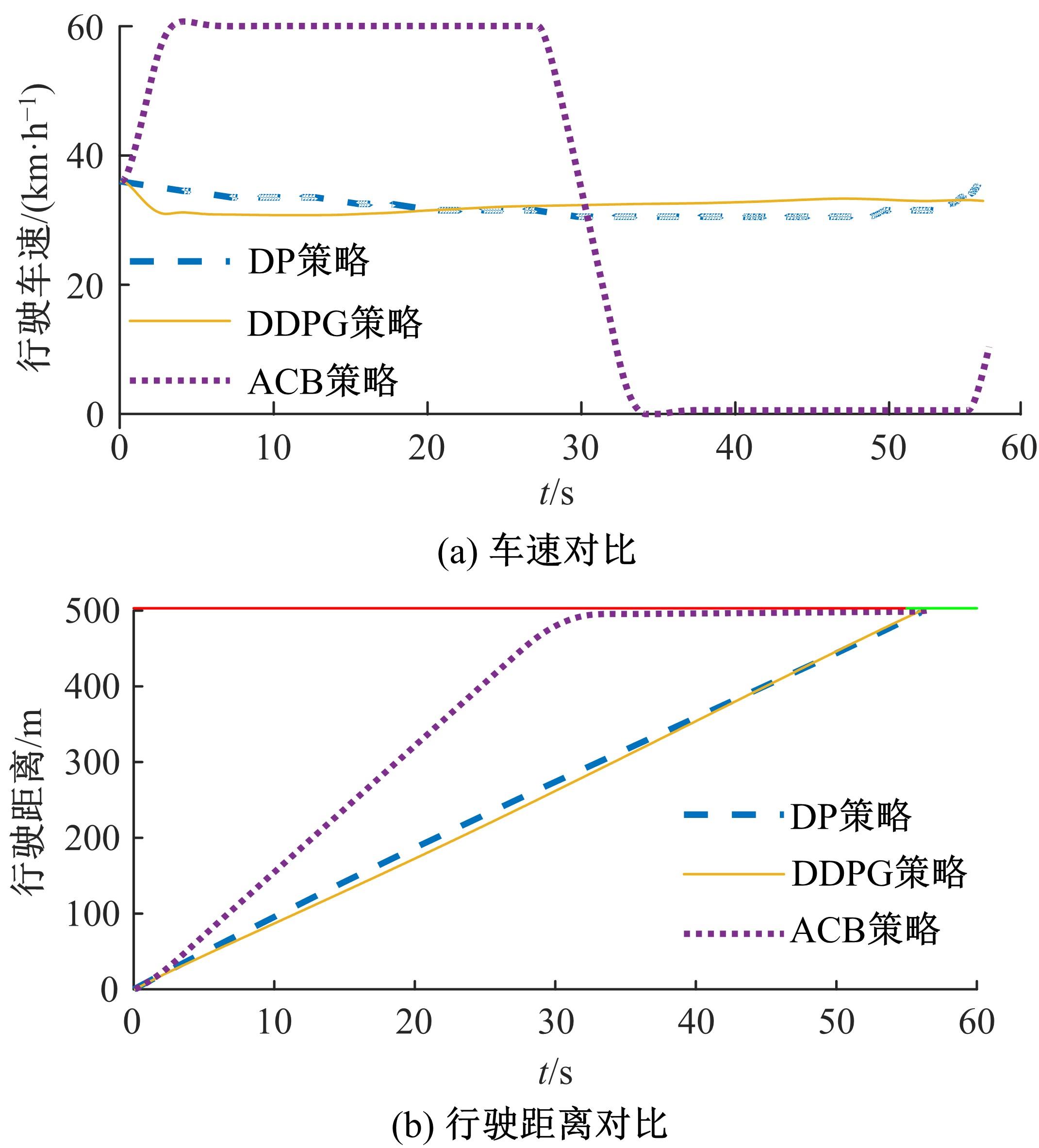
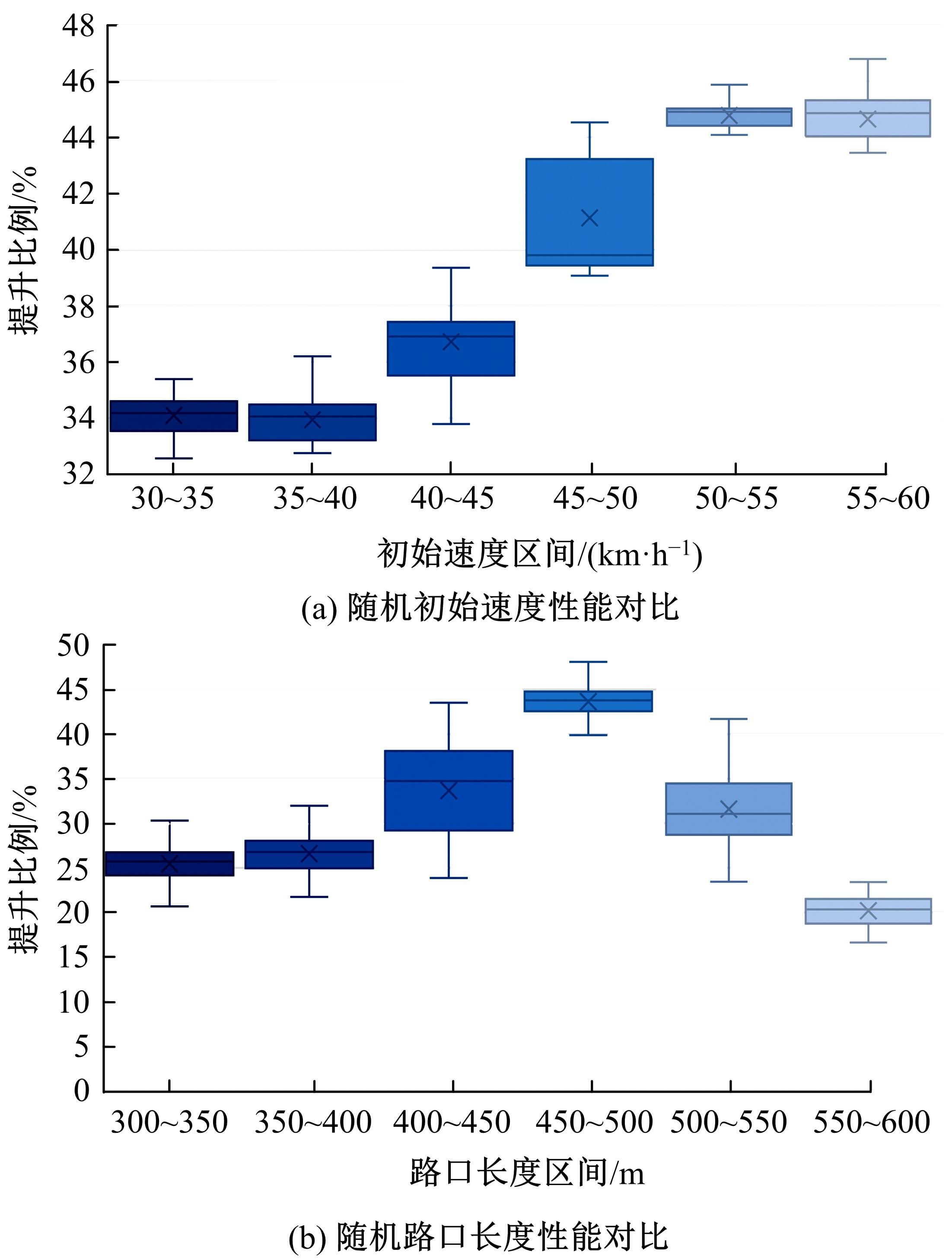
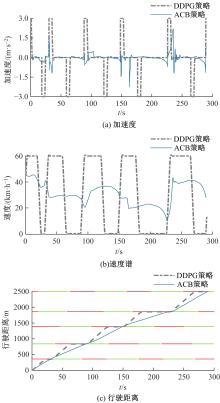
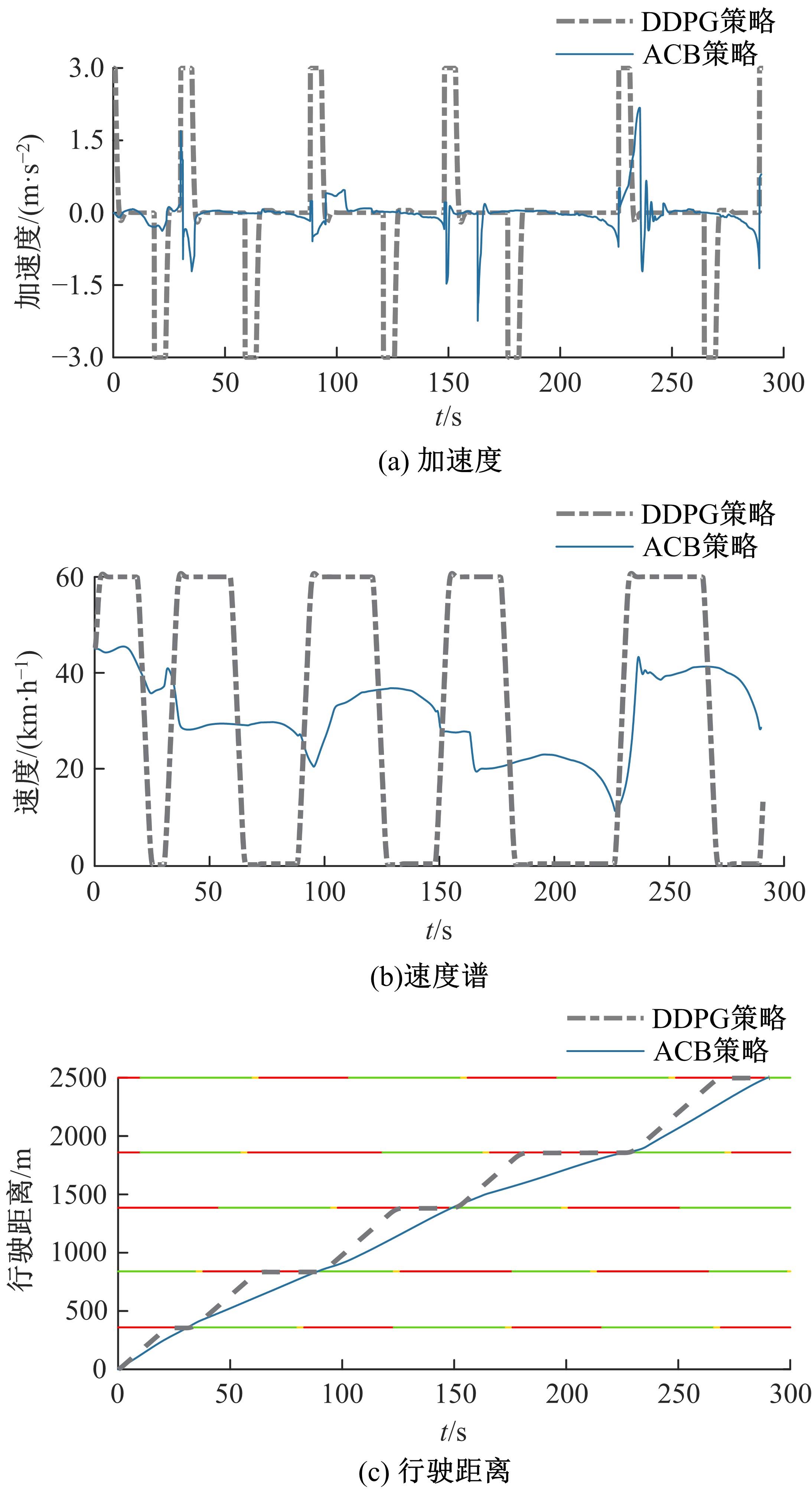
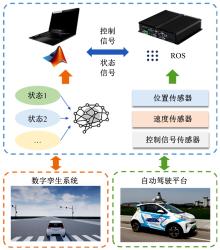
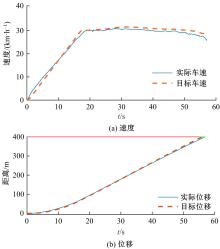
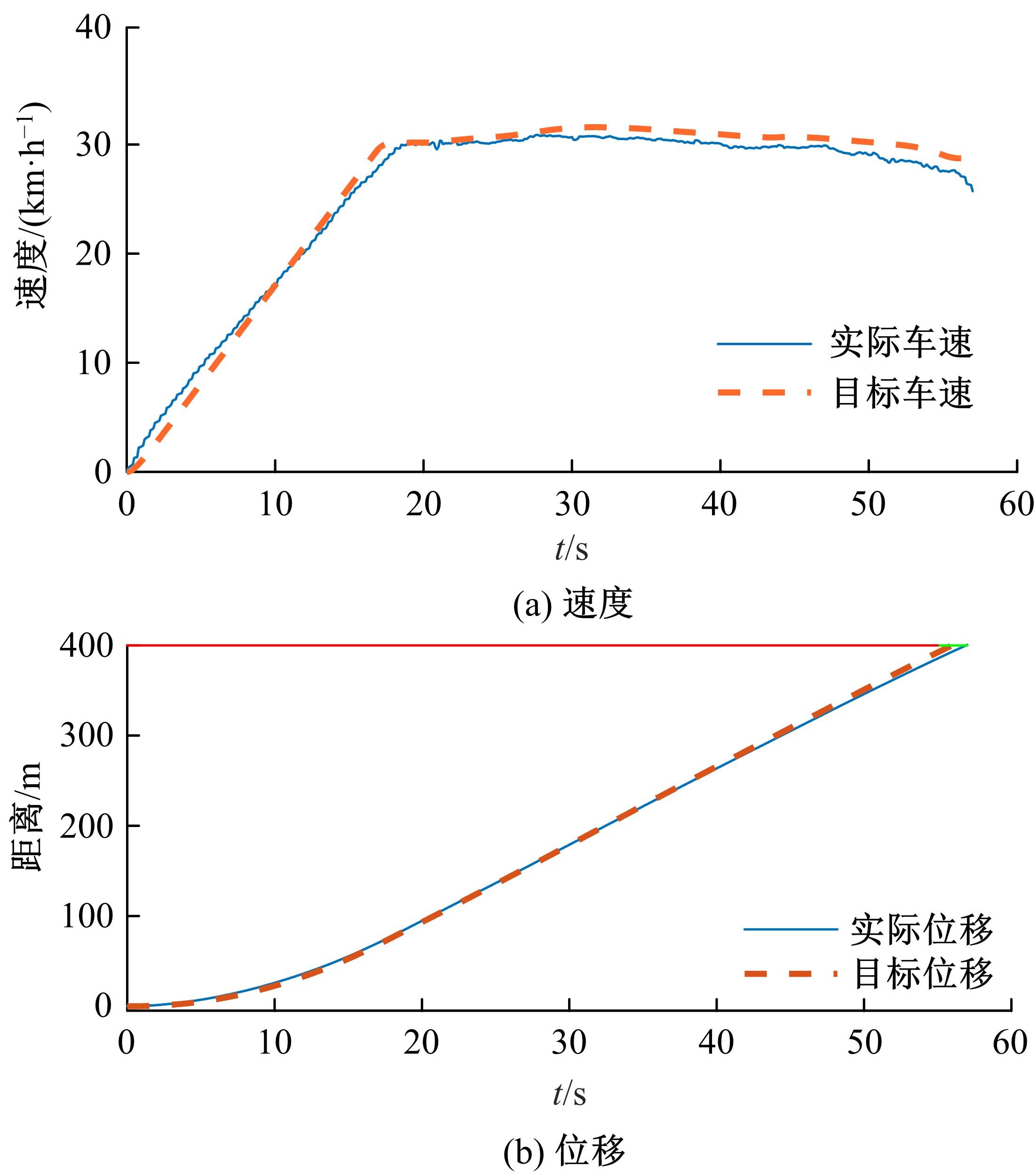
提出了一种面向信号交叉口的自适应学习生态驾驶策略。首先,搭建了电动汽车纵向动力学模型,建立了信号灯交叉路口的虚拟交通仿真环境;其次,以车辆能耗最小化与通行效率最大化为目标,耦合设计强化学习奖励函数,基于深度确定性策略梯度算法(DDPG)对车辆加速度进行实时控制与训练;最后,通过蒙特卡洛试验法,验证本文提出的强化学习生态驾驶策略在不同初始交通场景下的有效性与鲁棒性。仿真结果表明,相较于常规“加速-匀速-制动(ACB)”策略,本文提出的强化学习生态驾驶策略在单路口和多路口场景下均可有效提升通行效率和能量效率。同时,智能网联汽车数字孪生试验平台的多次实车试验表明,本文的强化学习算法控制效果良好,可以有效减少车辆路口等待时长,降低能耗同时提高通行效率。
中图分类号:
- U469.72
| 1 | 《中国公路学报》编辑部.中国汽车工程学术研究综述·2017 [J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(6): 1-197. |
| Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway. Review on China's automotive engineering research progress: 2017[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(6): 1-197. | |
| 2 | 徐兴,陈特,陈龙,等.分布式驱动电动汽车转矩节能优化分配[J].中国公路学报, 2018, 31(5): 183-190. |
| Xu Xing, Chen Te, Chen Long, et al. Optimal distribution of torque energy saving for distributed drive electric vehicles[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(5): 183-190. | |
| 3 | Michael Sivak, Brandon Schoettle. Eco-driving: strategic, tactical, and operational decisions of the driver that influence vehicle fuel economy[J]. Transport Policy, 2012, 22: 96-99. |
| 4 | 付锐,张雅丽,袁伟.生态驾驶研究现状及展望[J].中国公路学报, 2019, 32(3): 1-12. |
| Fu Rui, Zhang Ya-li, Yuan Wei. Research status and prospects of eco-driving[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(3): 1-12. | |
| 5 | Ye Fei, Hao Peng, Qi Xue-wei, et al. Prediction-based eco-approach and departure at signalized intersections with speed forecasting on preceding vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 20(4): 1378-1389. |
| 6 | 金辉,张俊.智能车经济性起步车速规划研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(2): 270-277. |
| Jin Hui, Zhang Jun. Research on economic speed planning of intelligent vehicle for starting stage[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(2): 270-277. | |
| 7 | 洪金龙,高炳钊,董世营,等.智能网联汽车节能优化关键问题与研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021,34(11):306-334. |
| Hong Jin-long, Gao Bing-zhao, Dong Shi-ying, et al. Key problems and research progress of energy saving optimization for intelligent connected vehicles[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021,34(11):306-334. | |
| 8 | Rainer Stahlmann, Malte Möller, Alexej Brauer, et al. exploring GLOSA systems in the field: technical evaluation and results[J]. Computer Communications, 2018, 120: 112-124. |
| 9 | 陈浩, 庄伟超, 殷国栋, 等.网联电动汽车信号灯控路口经济性驾驶策略[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 51(1): 178-186. |
| Chen Hao, Zhuang Wei-chao, Yin Guo-dong, et al. Eco-driving control strategy of connected electric vehicle at signalized intersection[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 51(1): 178-186. | |
| 10 | Hao Peng, Wu Guo-yuan, Kanok Boriboonsomsin, et al. Eco-approach and departure (EAD) application for actuated signals in real-world traffic[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 20(1): 30-40. |
| 11 | 解少博,辛宗科,李会灵,等.插电式混合动力公交车电池配置和能量管理策略协同优化的研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(6): 625-631, 645. |
| Xie Shao-bo, Xin Zong-ke, Li Hui-ling, et al. A study on coordinated optimization on battery capacity and energy management strategy for a plug-in hybrid electric bus[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(6): 625-631, 645. | |
| 12 | Li Chun-ming, Zhang Tao, Sun Xiao-xia, et al. Connected ecological cruise control strategy considering multi-intersection traffic flow[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 219378-219390. |
| 13 | Han Ji-hun, Ardalan Vahidi, Antonio Sciarretta. Fundamentals of energy efficient driving for combustion engine and electric vehicles: an optimal control perspective[J]. Automatica, 2019, 103: 558-572. |
| 14 | 朱冰,蒋渊德,赵健,等.基于深度强化学习的车辆跟驰控制[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(6):53-60. |
| Zhu Bing, Jiang Yuan-de, Zhao Jian, et al. A car-following control algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2019,32(6):53-60. | |
| 15 | Wu Yuan-kai, Tan Hua-chun, Peng Jian-kun, et al. Deep reinforcement learning of energy management with continuous control strategy and traffic information for a series-parallel plug-in hybrid electric bus[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 247: 454-466. |
| 16 | Li Yue-cheng, He Hong-wen, Amir Khajepour, et al. Energy management for a power-split hybrid electric bus via deep reinforcement learning with terrain information[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 255: 113762. |
| 17 | Zhou Mo-fan, Yu Yang, Qu Xiao-bo. Development of an efficient driving strategy for connected and automated vehicles at signalized intersections: a reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21(1): 433-443. |
| 18 | Zhu Zhao-xuan, Shobhit Gupta, Abhishek Gupta, et al. A deep reinforcement learning framework for eco-driving in connected and automated hybrid electric vehicles[J/OL].[2021-01-13]. . |
| 19 | Dimitri Bertsekas. Reinforcement Learning and Optimal Control[M]. Belmont: Athena Scientific, 2019. |
| 20 | Xu Xin, Zuo Lei, Li Xin, et al. A reinforcement learning approach to autonomous decision making of intelligent vehicles on highways[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 50(10): 3884-3897. |
| 21 | Pi Jian-zong. A reinforcement learning framework for autonomous eco-driving[D]. The Ohio State University, 2020. |
| 22 | John Schulman, Filip Wolski, Prafulla Dhariwal, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[J/OL].[2017-04-23].. |
| 23 | David Silver, Guy Lever, Nicolas Heess, et al. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms[C]∥ International Conference on Machine Learning, Detroit, USA, 2014: 387-395. |
| [1] | 陈磊,王杨,董志圣,宋亚奇. 一种基于转向意图的车辆敏捷性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [2] | 陈鑫,张冠宸,赵康明,王佳宁,杨立飞,司徒德蓉. 搭接焊缝对铝合金焊接结构轻量化设计的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [3] | 张勇,毛凤朝,刘水长,王青妤,潘神功,曾广胜. 基于Laplacian算法的汽车外流场畸变网格优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [4] | 汪少华,储堃,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 基于有限时间扩张状态观测的HEV鲁棒复合协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [5] | 尹燕莉,黄学江,潘小亮,王利团,詹森,张鑫新. 基于PID与Q⁃Learning的混合动力汽车队列分层控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1481-1489. |
| [6] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [7] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [8] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于NSGA⁃II的斜齿轮宏观参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [9] | 赵睿,李云,胡宏宇,高镇海. 基于V2I通信的交叉口车辆碰撞预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [10] | 陈小波,陈玲. 定位噪声统计特性未知的变分贝叶斯协同目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
| [11] | 田彦涛,季言实,唱寰,谢波. 深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [12] | 张建,刘金波,高原,刘梦可,高振海,杨彬. 基于多模交互的车载传感器定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 772-780. |
| [13] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [14] | 刘嫣然,孟庆瑜,郭洪艳,李嘉霖. 图注意力模式下融合高精地图的周车轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 792-801. |
| [15] | 谢波,高榕,许富强,田彦涛. 低附着路况条件下人车共享转向系统稳定控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 713-725. |
|
||