吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 682-692.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221441
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型
- 吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
Deep reinforcement learning augmented decision⁃making model for intelligent driving vehicles
Yan-tao TIAN( ),Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE
),Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE
- College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
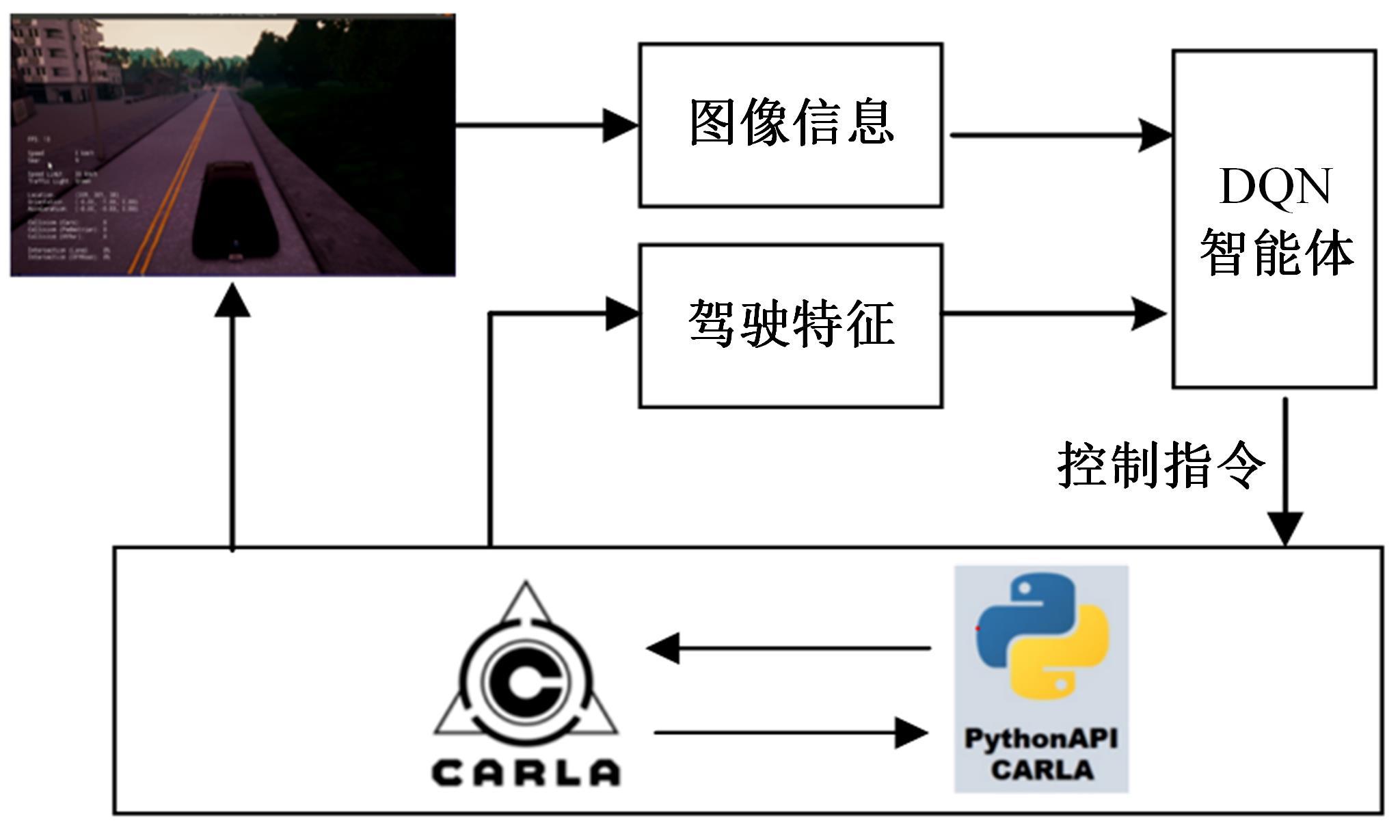
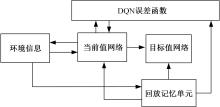
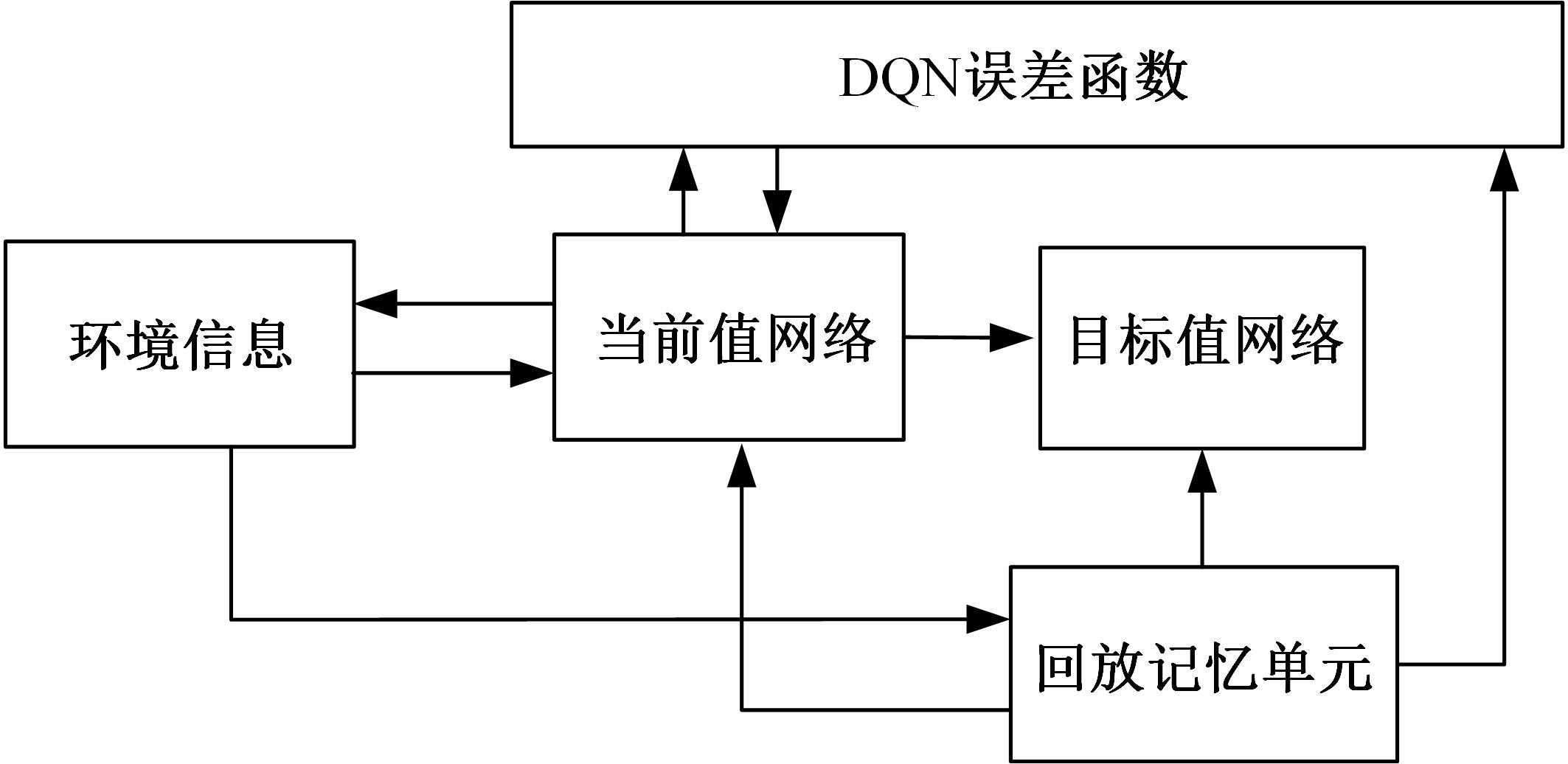
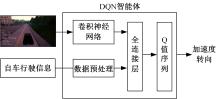
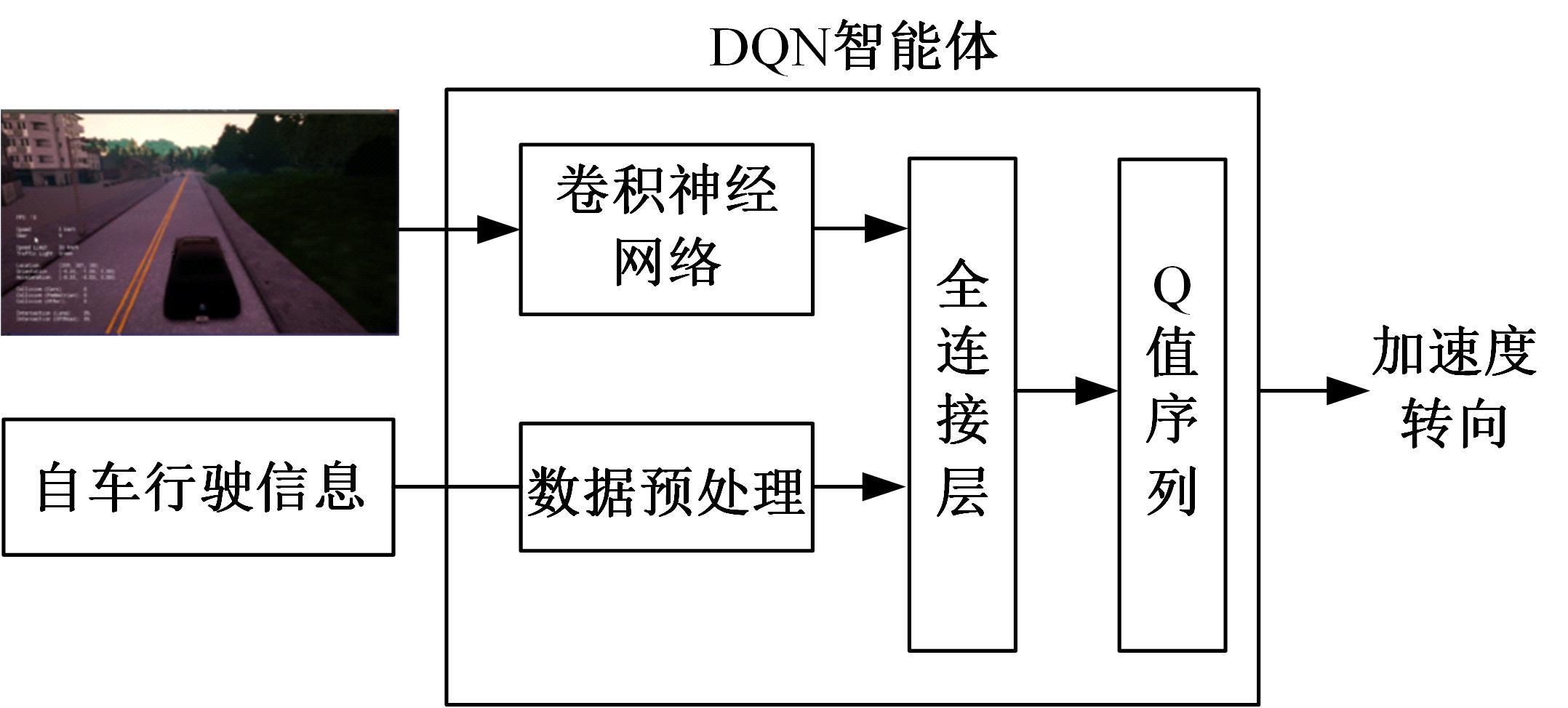
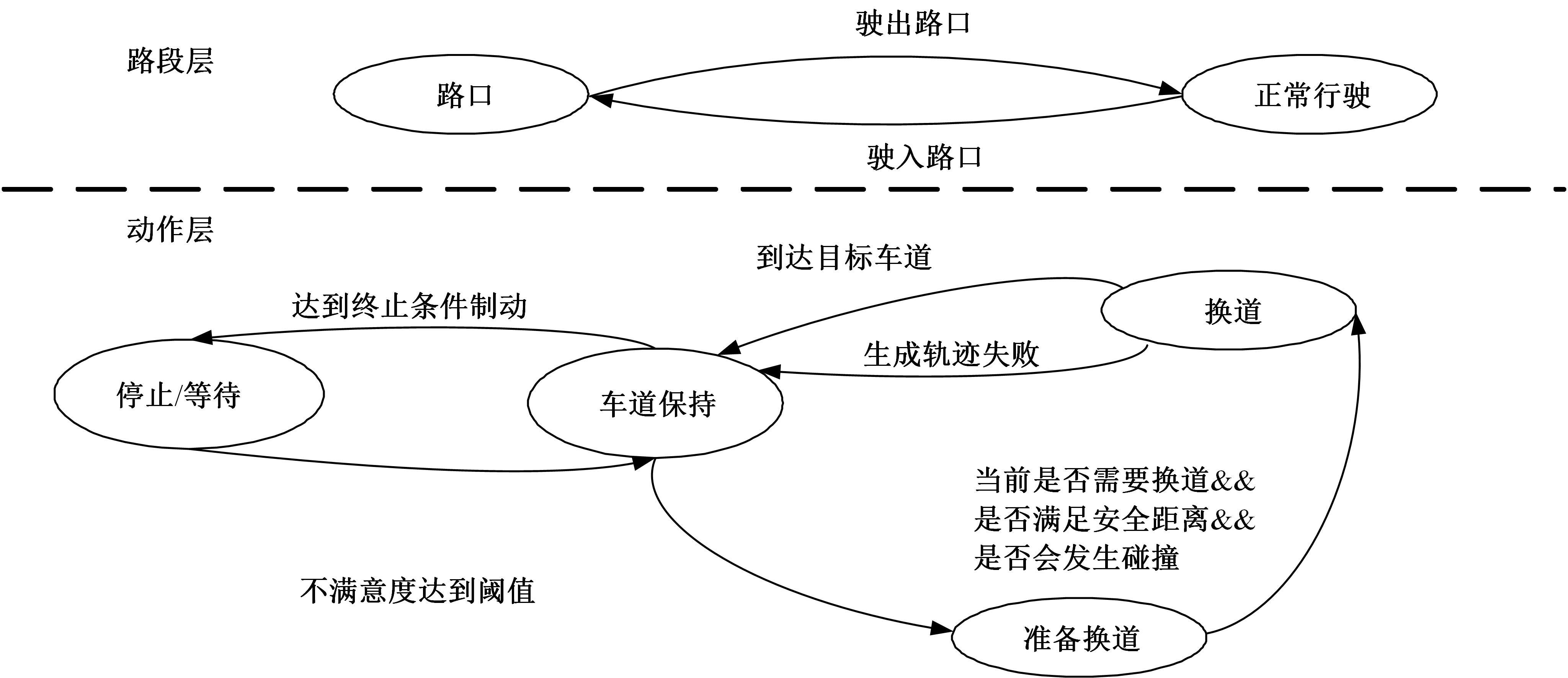
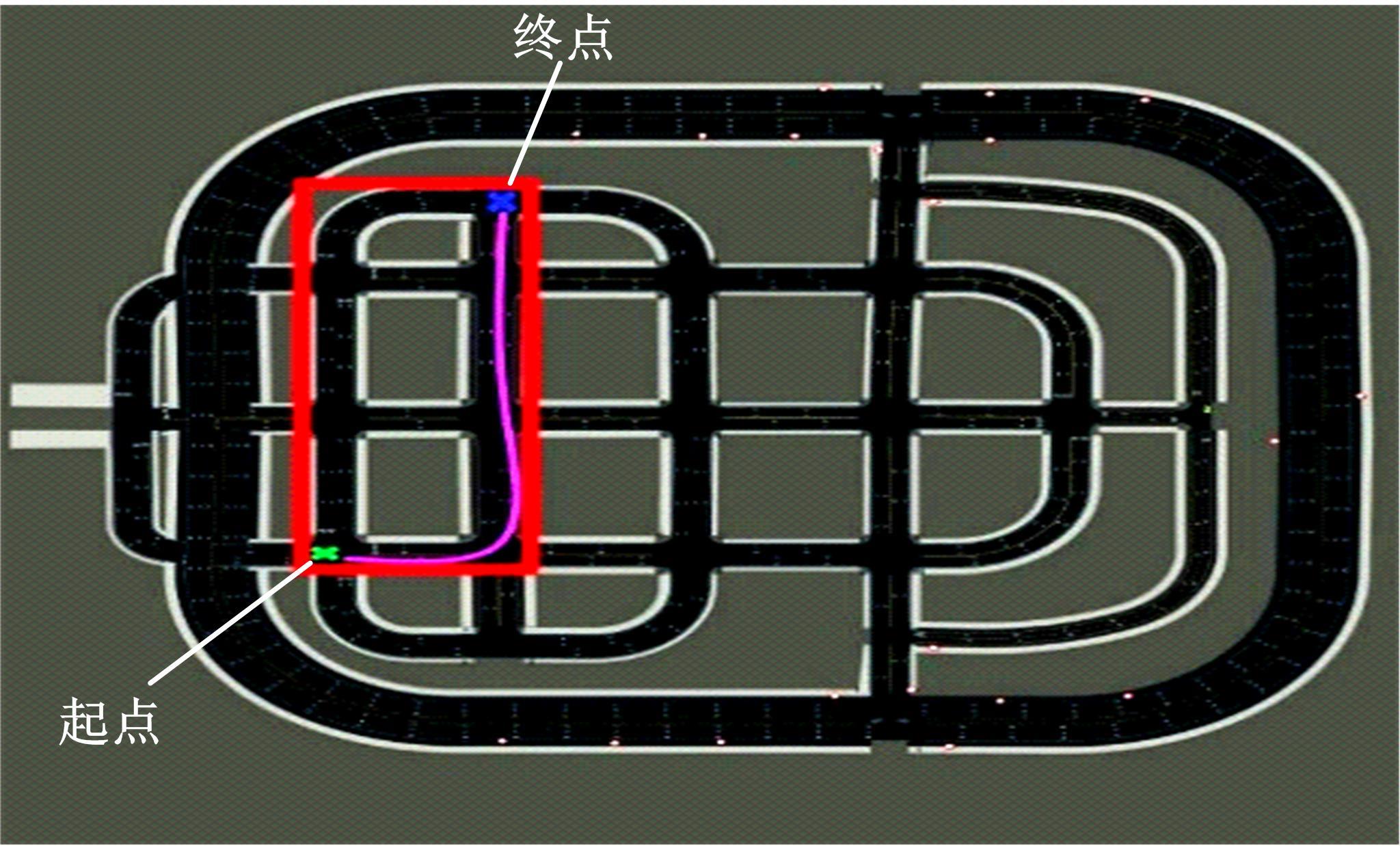
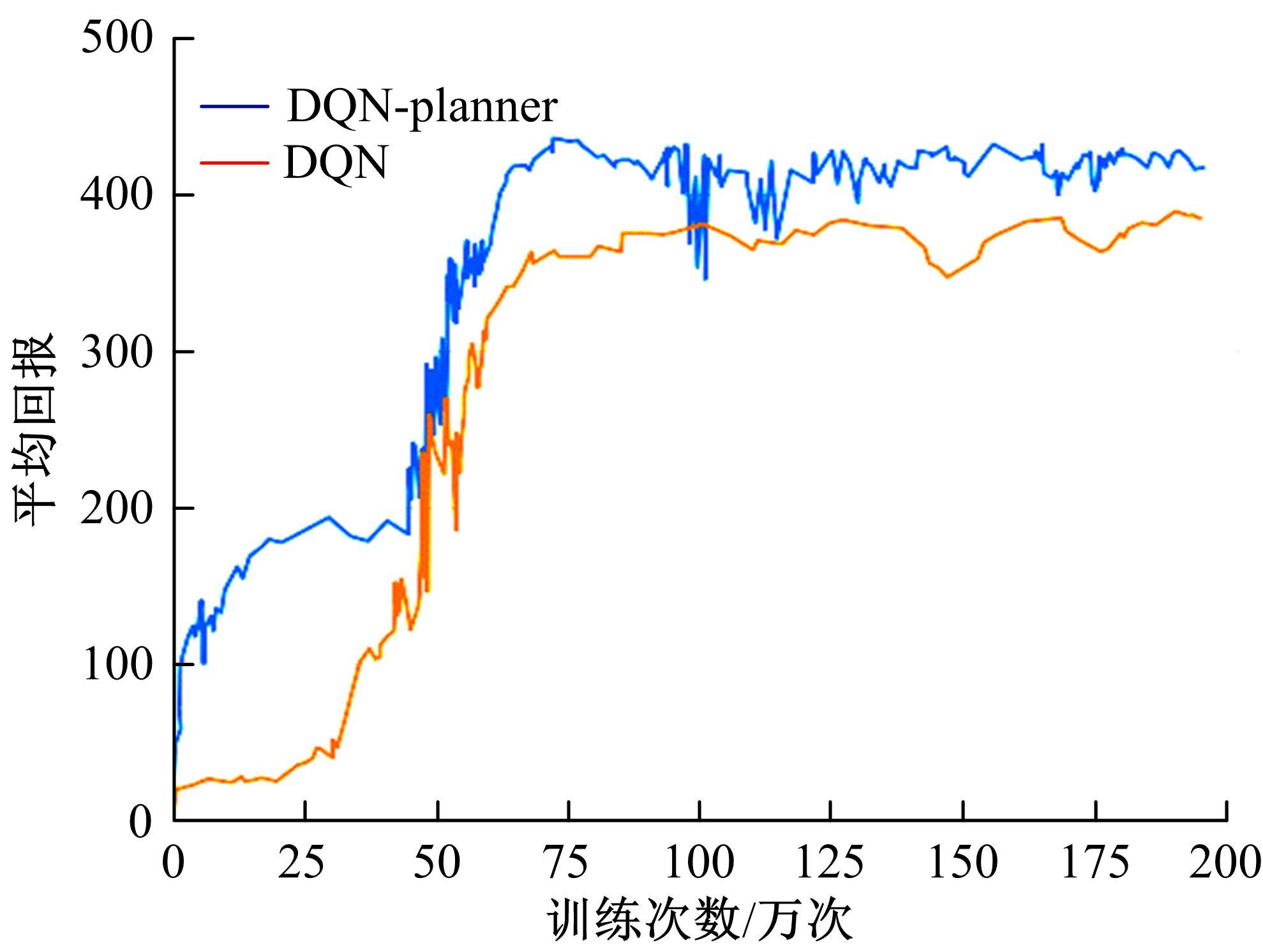
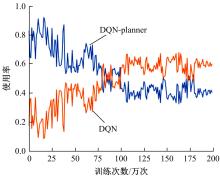
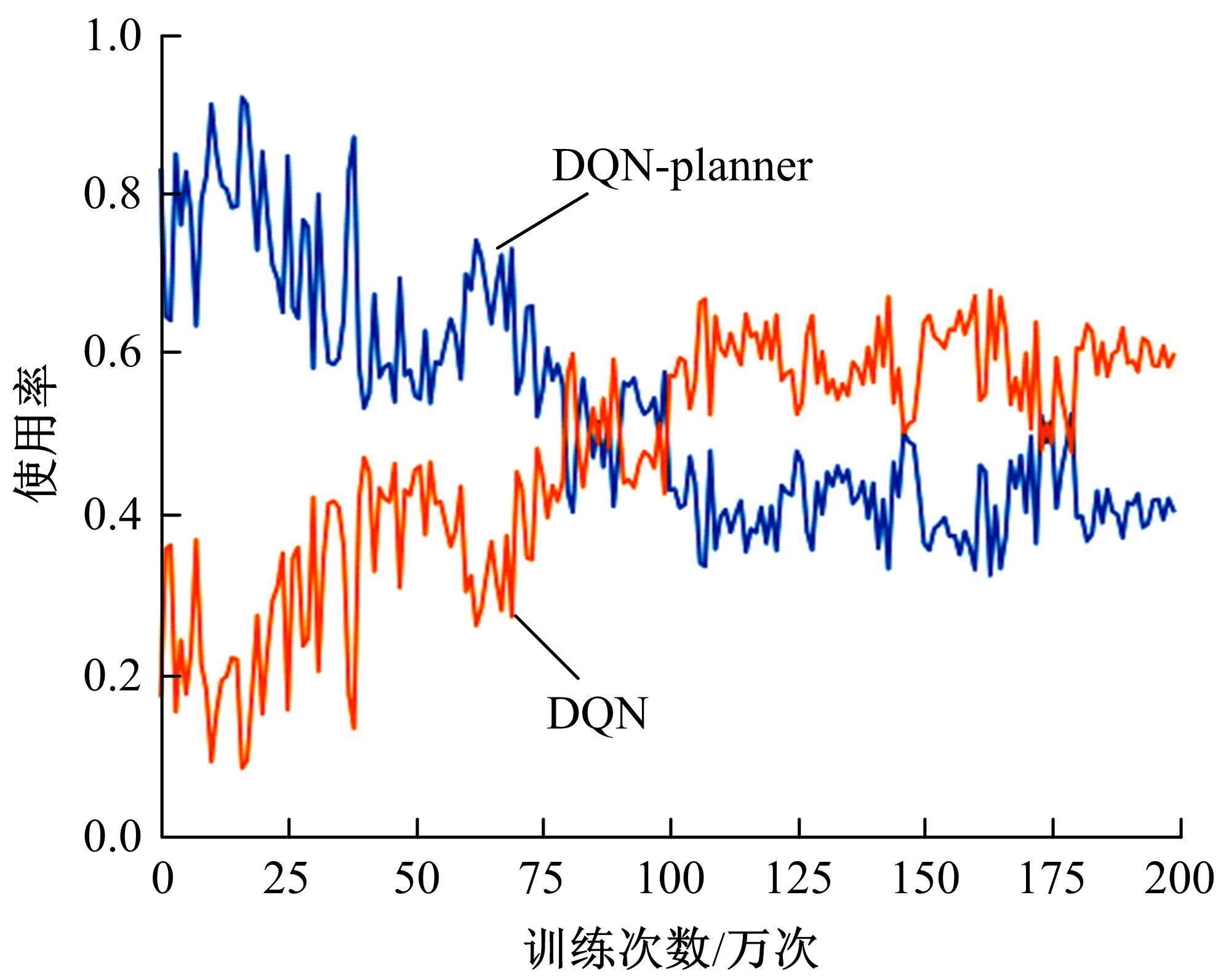
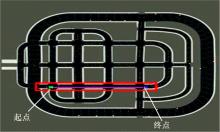
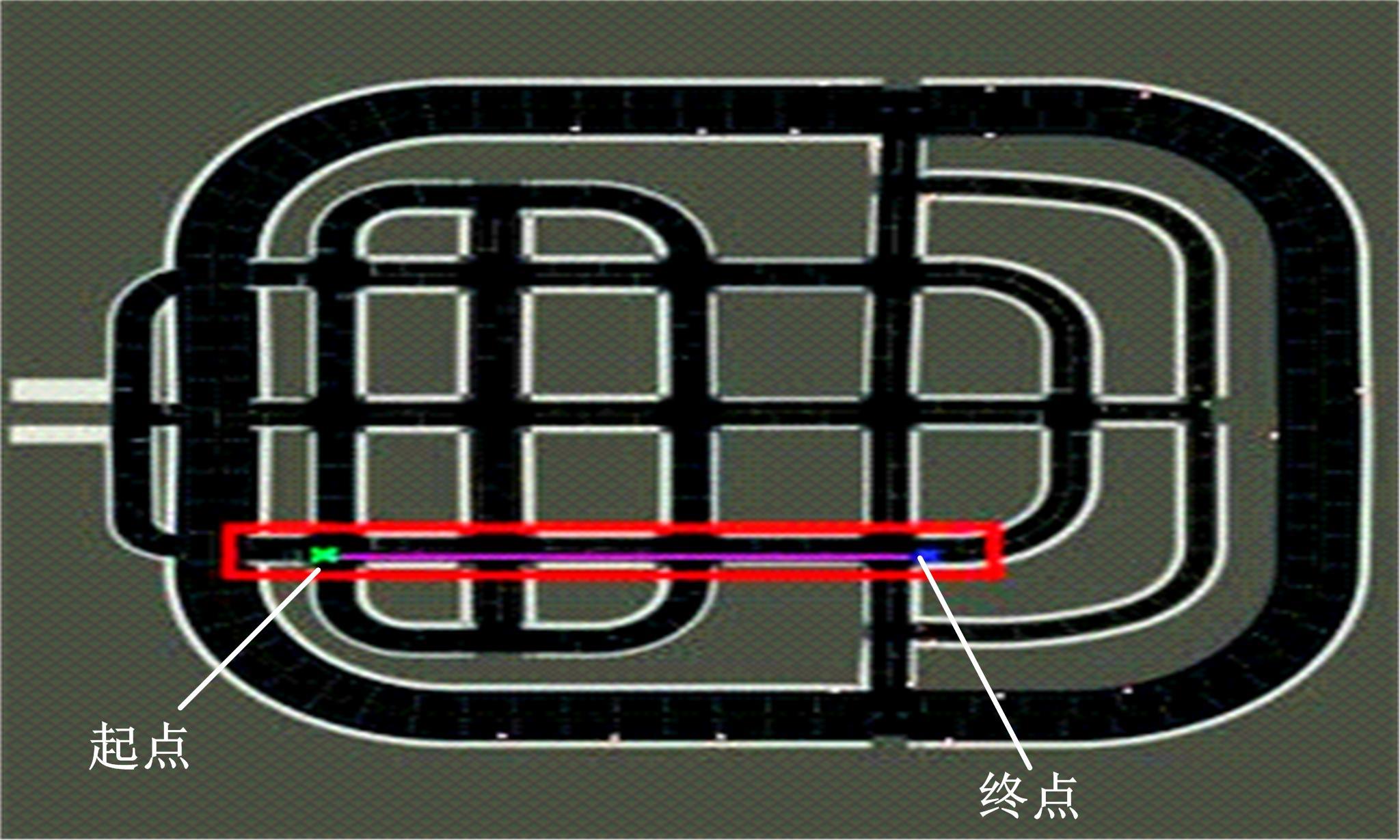
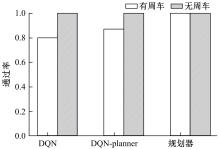
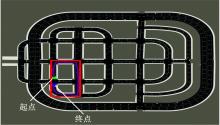
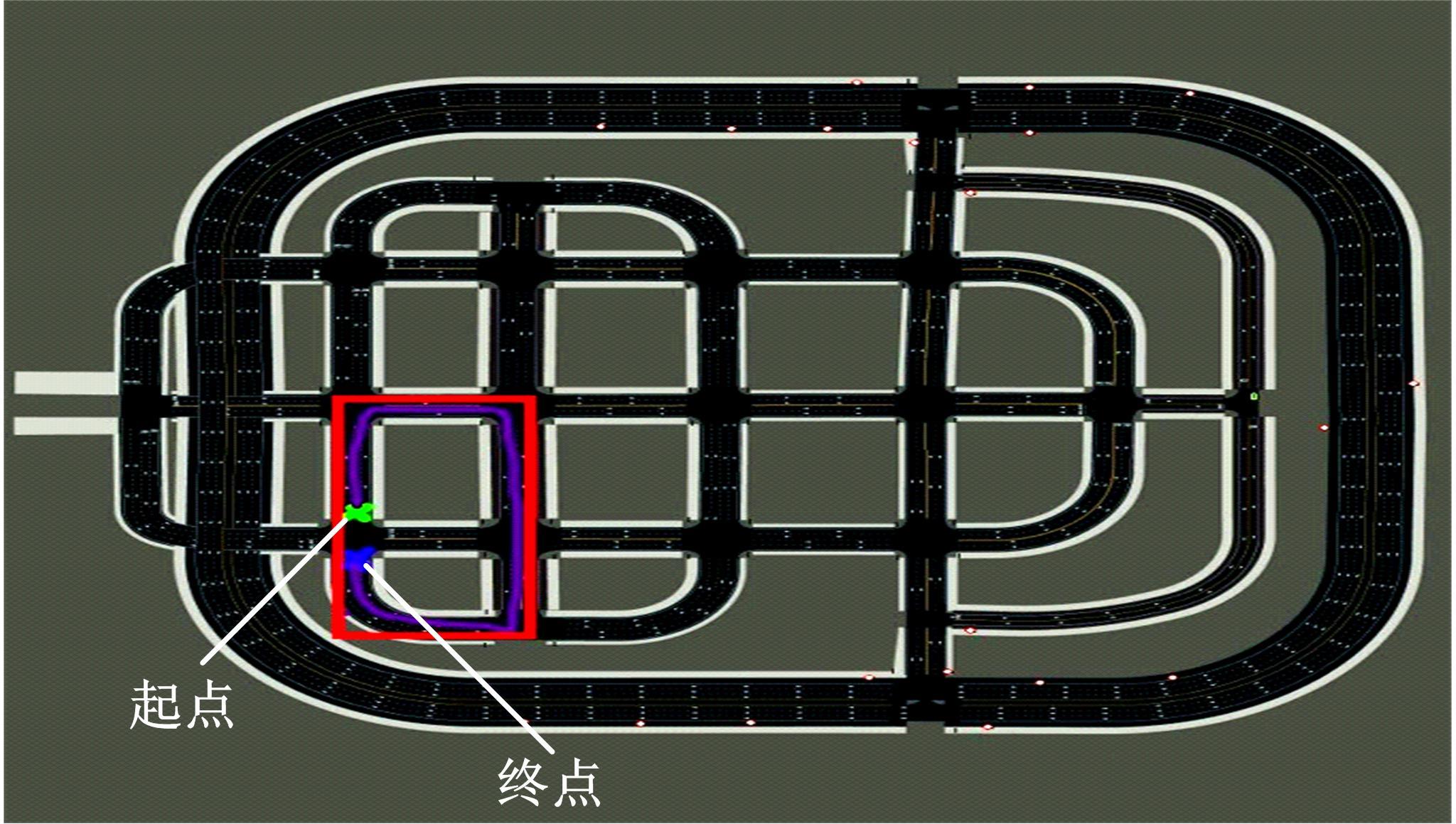
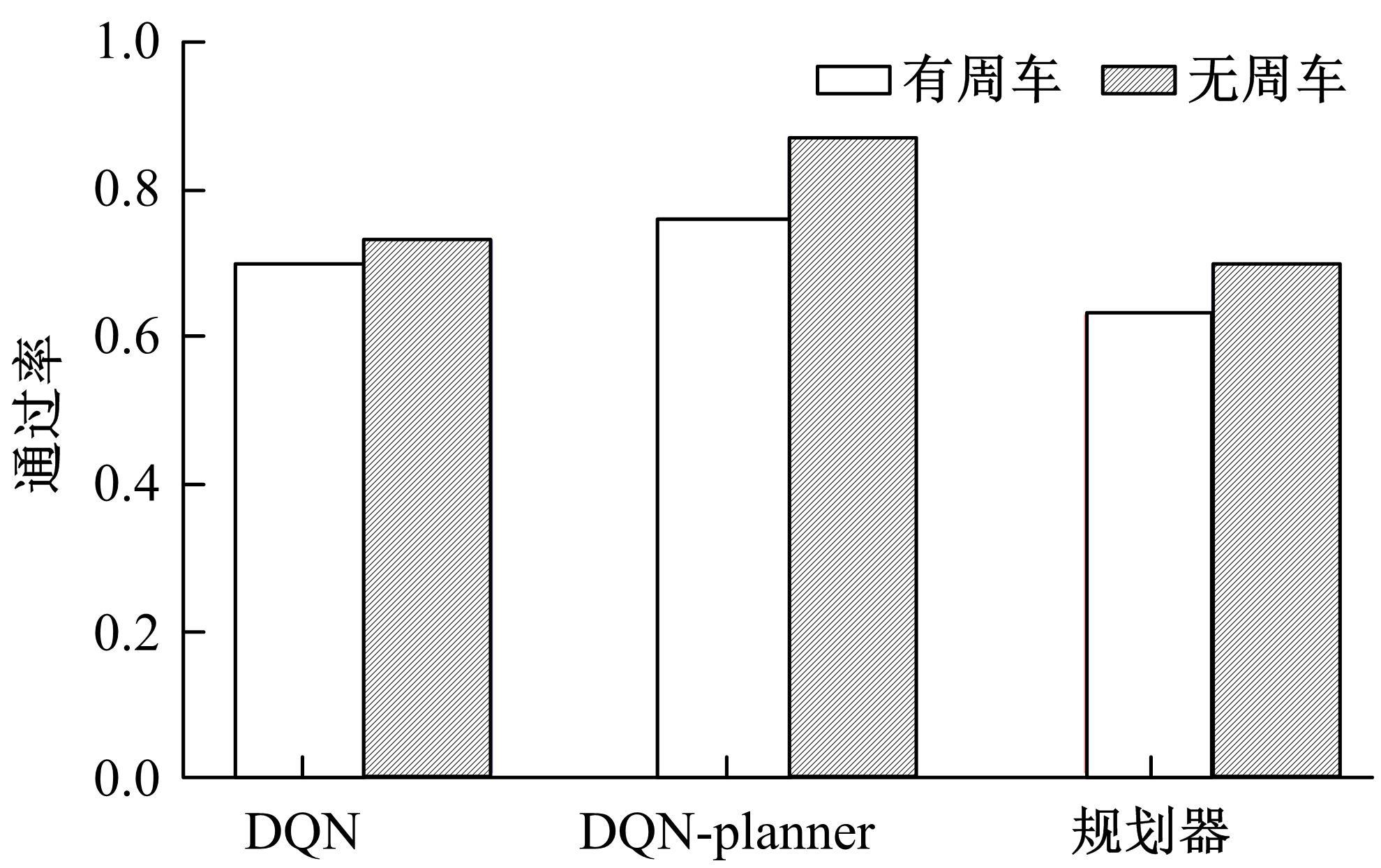
针对状态机决策模型不能有效处理冰雪环境下丰富的上下文信息和不确定因素影响等问题,构建了一种基于深度Q网络算法(DQN)的深度强化学习智能体。使用运动规划器对该智能体进行增广,将基于规则的决策规划模块和深度强化学习模型整合在一起,建立了DQN-planner模型,从而提高了强化学习智能体的收敛速度和驾驶能力。最后,基于CARLA模拟仿真平台对DQN模型和DQN-planner模型在低附着系数冰雪路面上的驾驶能力进行了对比实验,分别就训练过程和验证结果进行了分析。
中图分类号:
- U495
| 1 | 王喆, 杨柏婷, 刘昕, 等. 基于模糊聚类的驾驶决策判别[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2015,45(5): 1414-1419. |
| Wang Zhe, Yang Bai-ting, Liu Xin, et al. Discriminant analysis of driving decisions based on fuzzy clustering[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. | |
| 2 | Montemerlo M, Becker J, Bhat S, et al. Junior: the stanford entry in the urban challenge[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2008, 25(9): 569-597. |
| 3 | Urmson C, Baker C, Dolan J, et al. Autonomous driving in traffic: boss and the urban challenge[J]. The AI Magazine, 2009, 30(2): 17-28. |
| 4 | Li Hong-hui, Xi Yi-kun, Lu Hai-liang, et al. Improved C4.5 algorithm based on k-means[J]. Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering, 2020, 20(1): 177-189. |
| 5 | 杜明博. 基于人类驾驶行为的无人驾驶车辆行为决策与运动规划方法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学信息科学技术学院, 2016. |
| Du Ming-bo. Research on behavioral decision making and motion planning methods of autonomous vehicle based on human driving behavior[D]. Hefei: College of Information Science and Technology, University of Science and Technology of China, 2016. | |
| 6 | 曹轩豪. 自动驾驶汽车跟驰换道运动控制与决策规划研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学通信工程学院, 2022. |
| Cao Xuan-hao. Motion control and decision planning for car following and lane changing of autonomous vehicle[D]. Changchun: College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, 2022. | |
| 7 | Isele D, Rahimi R, Cosgun A, et al. Navigating occluded intersections with autonomous vehicles using deep reinforcement learning[C]∥2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 2034-2039. |
| 8 | Li L Z, Ota K, Dong M X, et al. Humanlike driving: empirical decision-making system for autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(8): 6814-6823. |
| 9 | 高振海, 孙天骏, 何磊, 等. 汽车纵向自动驾驶的因果推理型决策[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. |
| Gao Zhen-hai, Sun Tian-jun, He Lei, et al. Causal reasoning decision-making for vehicle longitudinal automatic driving[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. | |
| 10 | Barto A G, Mahadevan S. Recent advances in hierarchical reinforcement learning[J]. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems, 2003, 13(1/2): 41-77. |
| 11 | Russell S J, Norvig P. Artificial Intelligence: a Modern Approach[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1995. |
| 12 | Toledo T, Koutsopoulos H N, Ben-akiva M. Integrated driving behavior modeling[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2007, 15(2): 96-112. |
| 13 | Kurzer K, Engelhorn F, Zoellner J M, et al. Decentralized cooperative planning for automated vehicles with hierarchical monte carlo tree search[C]∥2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Hawaii, USA, 2018:452-459. |
| 14 | Sefati M, Chandiramani J, Kreiskoether K, et al. Towards tactical behaviour planning under uncertainties for automated vehicles in urban scenarios[C]∥2017 IEEE 20th International Conference On Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 2018: 1-7. |
| 15 | Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature(London), 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. |
| 16 | Mnih V, Badia A P, Mirza M, et al. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, San Diego, USA, 2016:1-10 |
| 17 | Li C J, Czarnecki K. Urban driving with multi-objective deep reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems,Montreal,Canada,2019: 359-367. |
| 18 | Chen J, Yuan B, Tomizuka M. Model-free deep reinforcement learning for urban autonomous driving[C]∥2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), New York, USA, 2019: 2765-2771. |
| [1] | 田彦涛,许富强,王凯歌,郝子绪. 考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [2] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [3] | 何科,丁海涛,许男,郭孔辉. 基于摄像头和车道线的增强定位系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 663-673. |
| [4] | 王登峰,陈宏利,那景新,陈鑫. 单双搭接接头经高温老化后的失效对比[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 346-354. |
| [5] | 张佩,王志伟,杜常清,颜伏伍,卢炽华. 车用质子交换膜燃料电池空气系统过氧比控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [6] | 王克勇,鲍大同,周苏. 基于数据驱动的车用燃料电池故障在线自适应诊断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [7] | 曹起铭,闵海涛,孙维毅,于远彬,蒋俊宇. 质子交换膜燃料电池低温启动水热平衡特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [8] | 隗海林,王泽钊,张家祯,刘洋. 基于Avl-Cruise的燃料电池汽车传动比及能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [9] | 刘岩,丁天威,王宇鹏,都京,赵洪辉. 基于自适应控制的燃料电池发动机热管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [10] | 李丞,景浩,胡广地,刘晓东,冯彪. 适用于质子交换膜燃料电池系统的高阶滑模观测器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2203-2212. |
| [11] | 陈凤祥,伍琪,李元松,莫天德,李煜,黄李平,苏建红,张卫东. 2.5吨燃料电池混合动力叉车匹配、仿真及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [12] | 武小花,余忠伟,朱张玲,高新梅. 燃料电池公交车模糊能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
| [13] | 池训逞,侯中军,魏伟,夏增刚,庄琳琳,郭荣. 基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [14] | 裴尧旺,陈凤祥,胡哲,翟双,裴冯来,张卫东,焦杰然. 基于自适应LQR控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [15] | 胡广地,景浩,李丞,冯彪,刘晓东. 基于高阶燃料电池模型的多目标滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2182-2191. |
|
||