吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2908-2921.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221623
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
不同石粉及掺量对高延性工程水泥基复合材料的性能影响
- 1.兰州交通大学 土木工程学院,兰州 730070
2.甘肃路桥第四公路工程有限责任公司 兰州 730030
Effect of different stone powder and content on properties of high ductility engineered cementitious composites
Ben-tian YU1( ),Yan-xiao LI1,Zhan-xu ZHANG2,Jun-hui SU2,Chao XIE1,Kai ZHANG1
),Yan-xiao LI1,Zhan-xu ZHANG2,Jun-hui SU2,Chao XIE1,Kai ZHANG1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
2.Gansu Road & Bridge Fourth Engineering Co. ,Ltd. ,Lanzhou 730030,China
摘要:
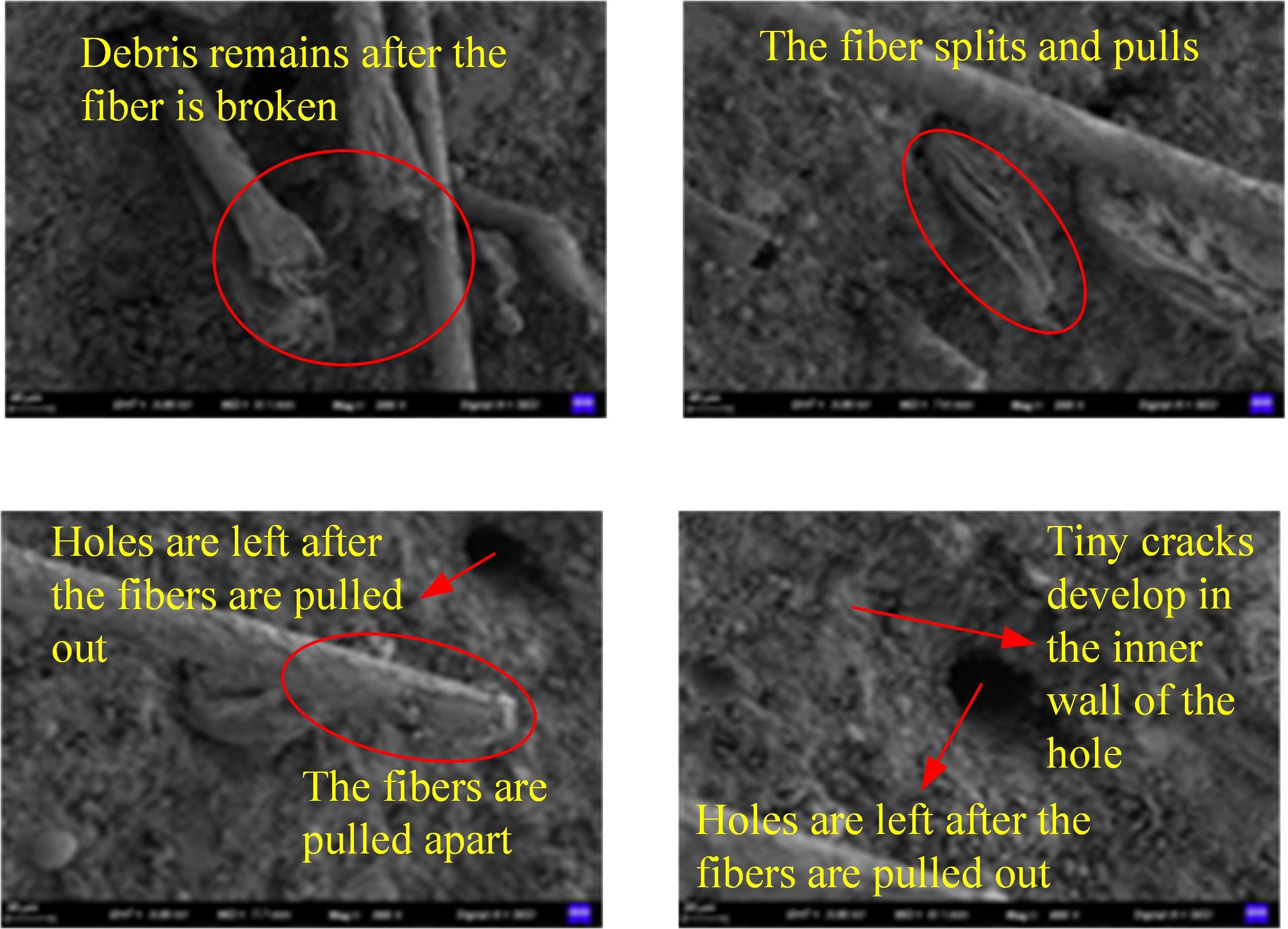
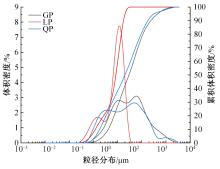
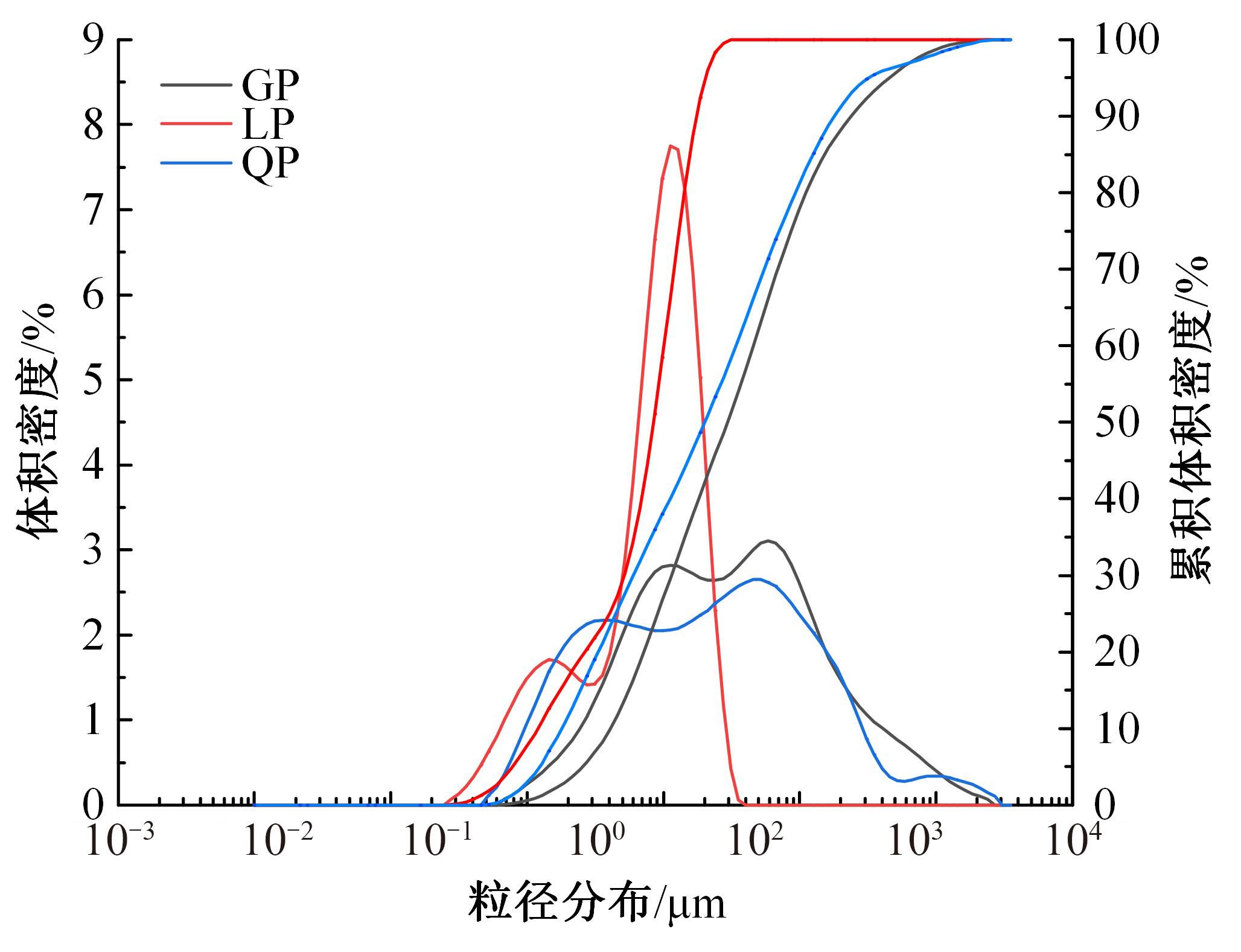
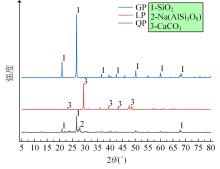
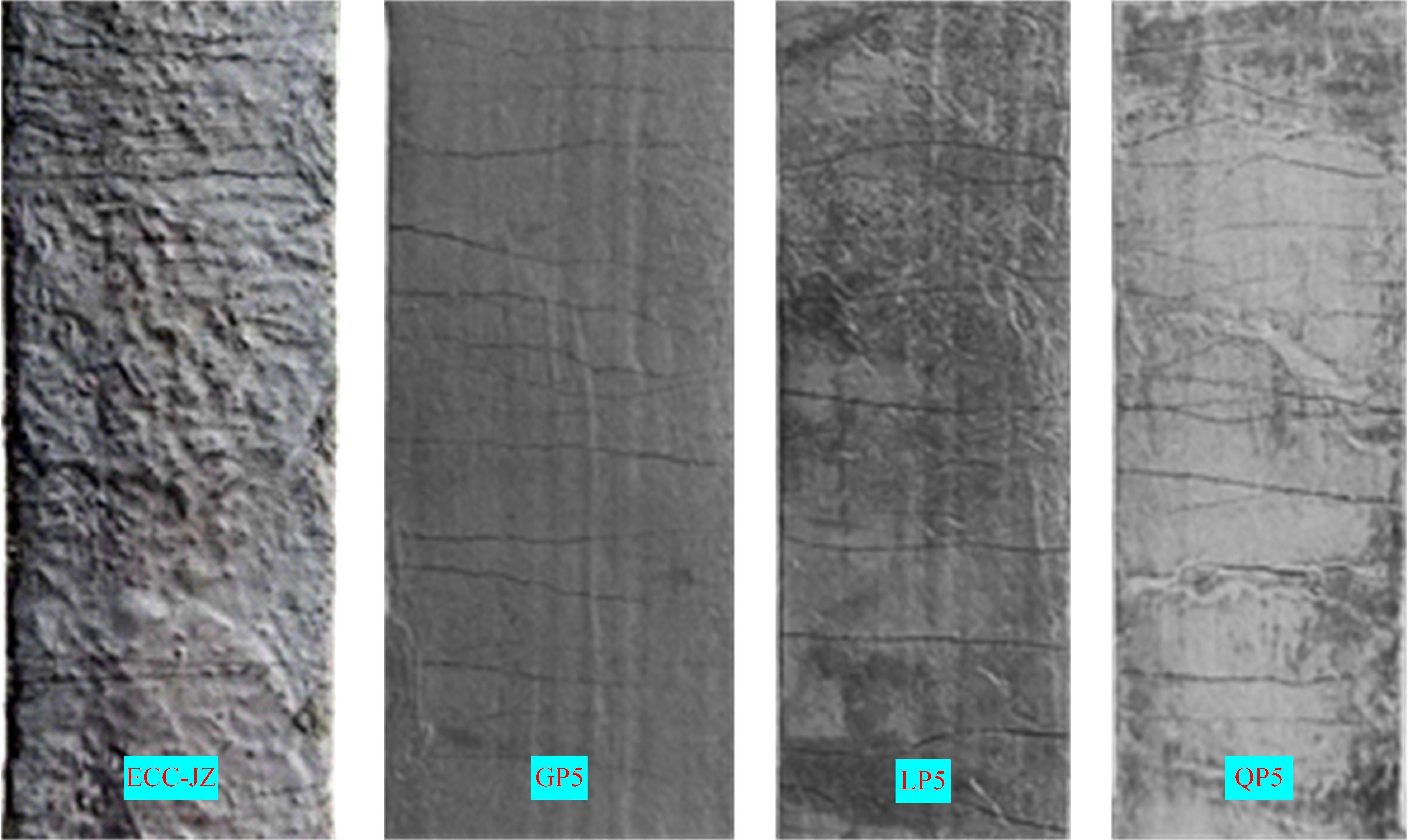
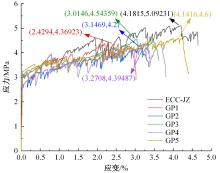
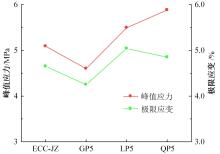
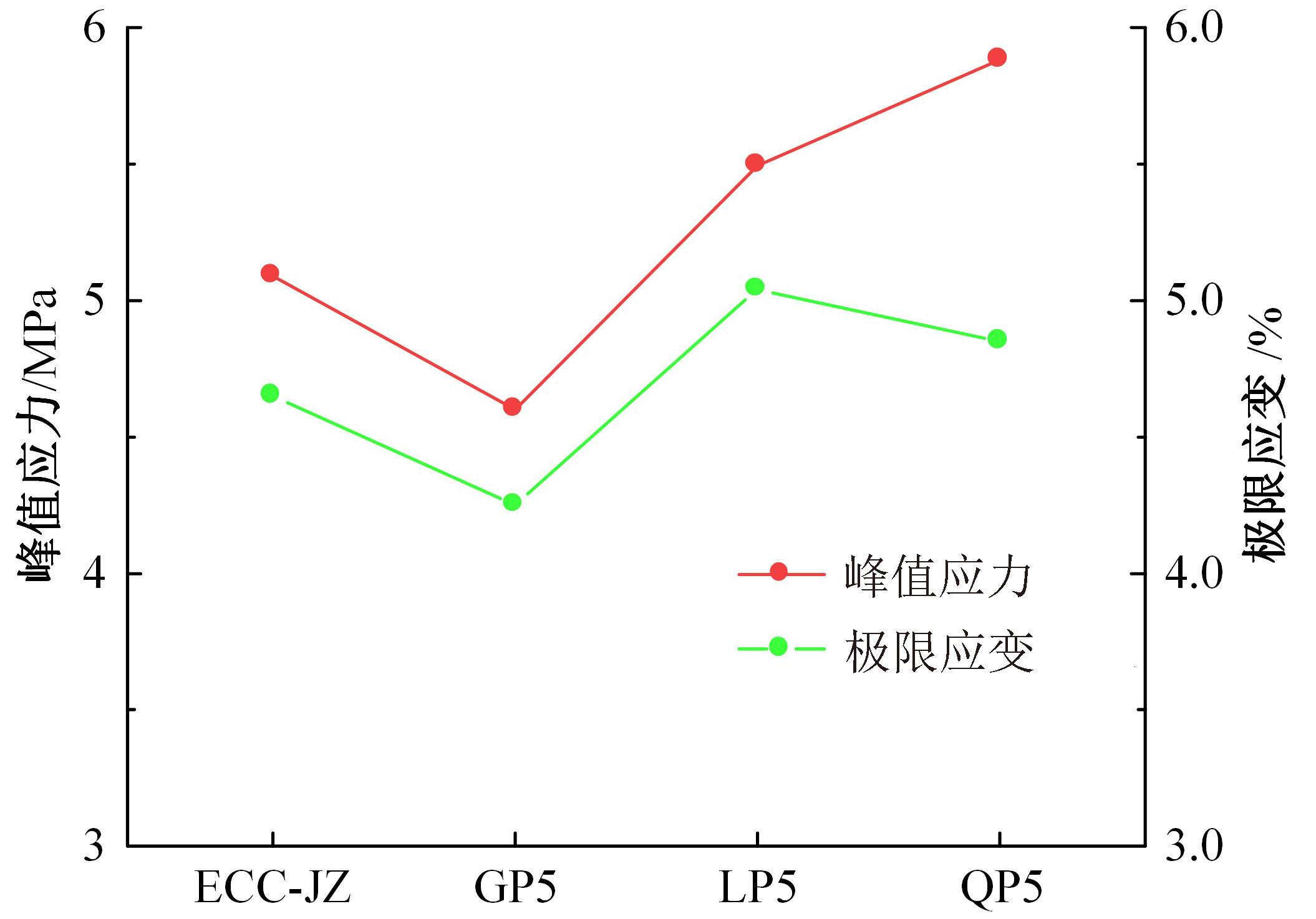
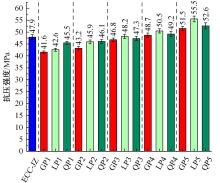
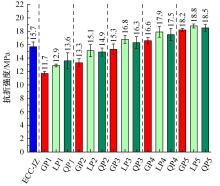
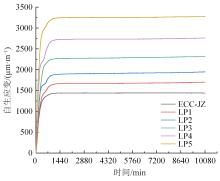
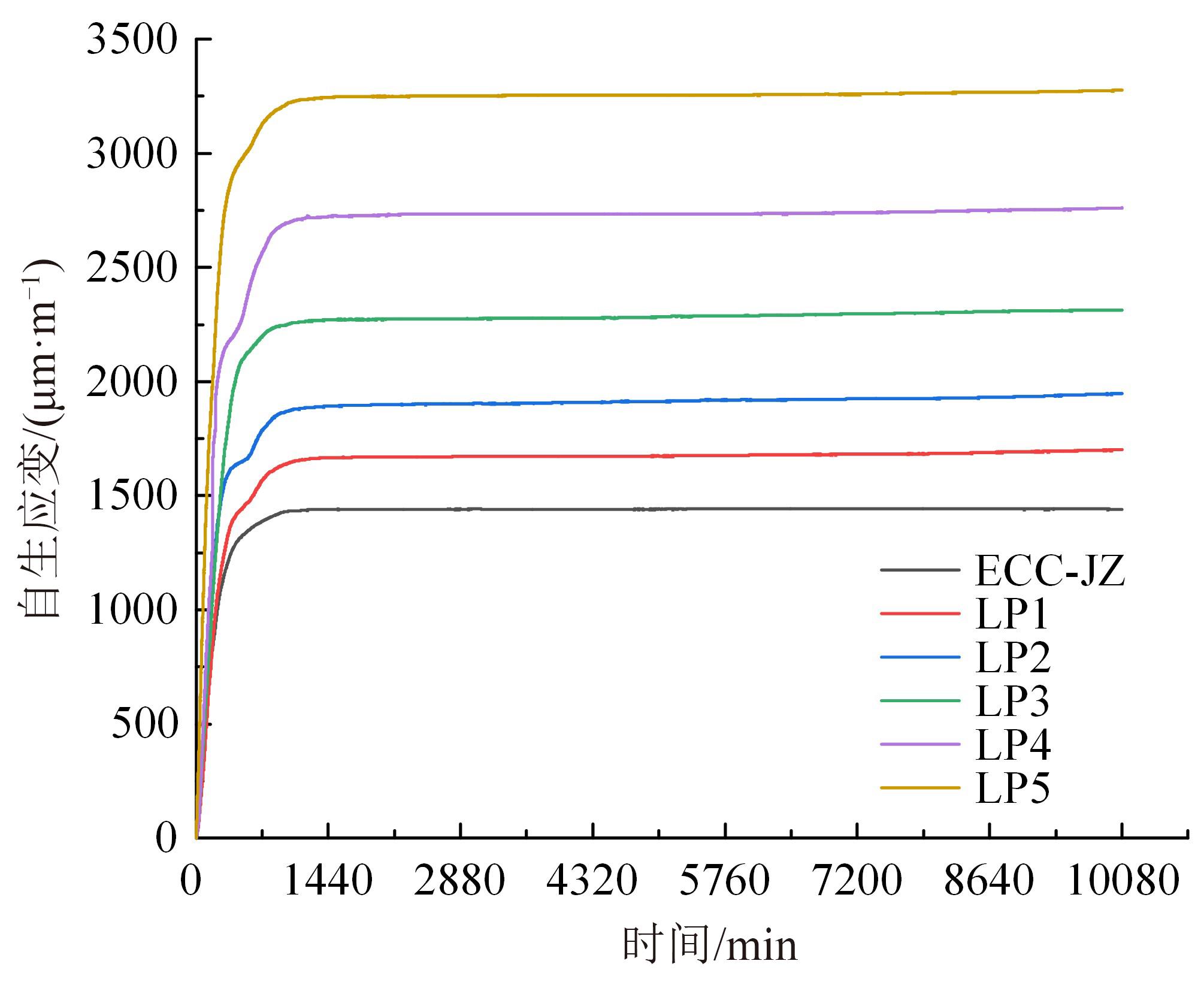
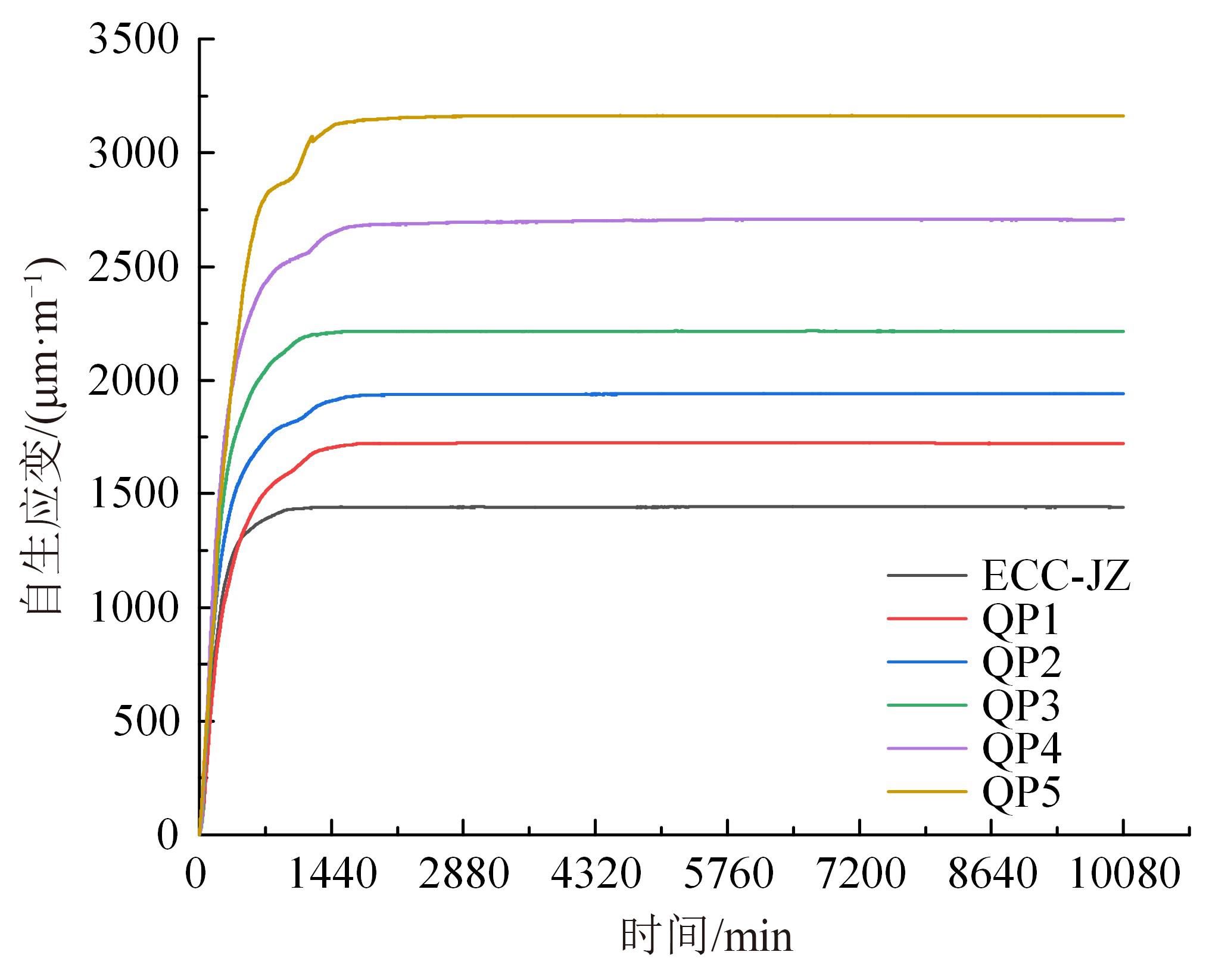
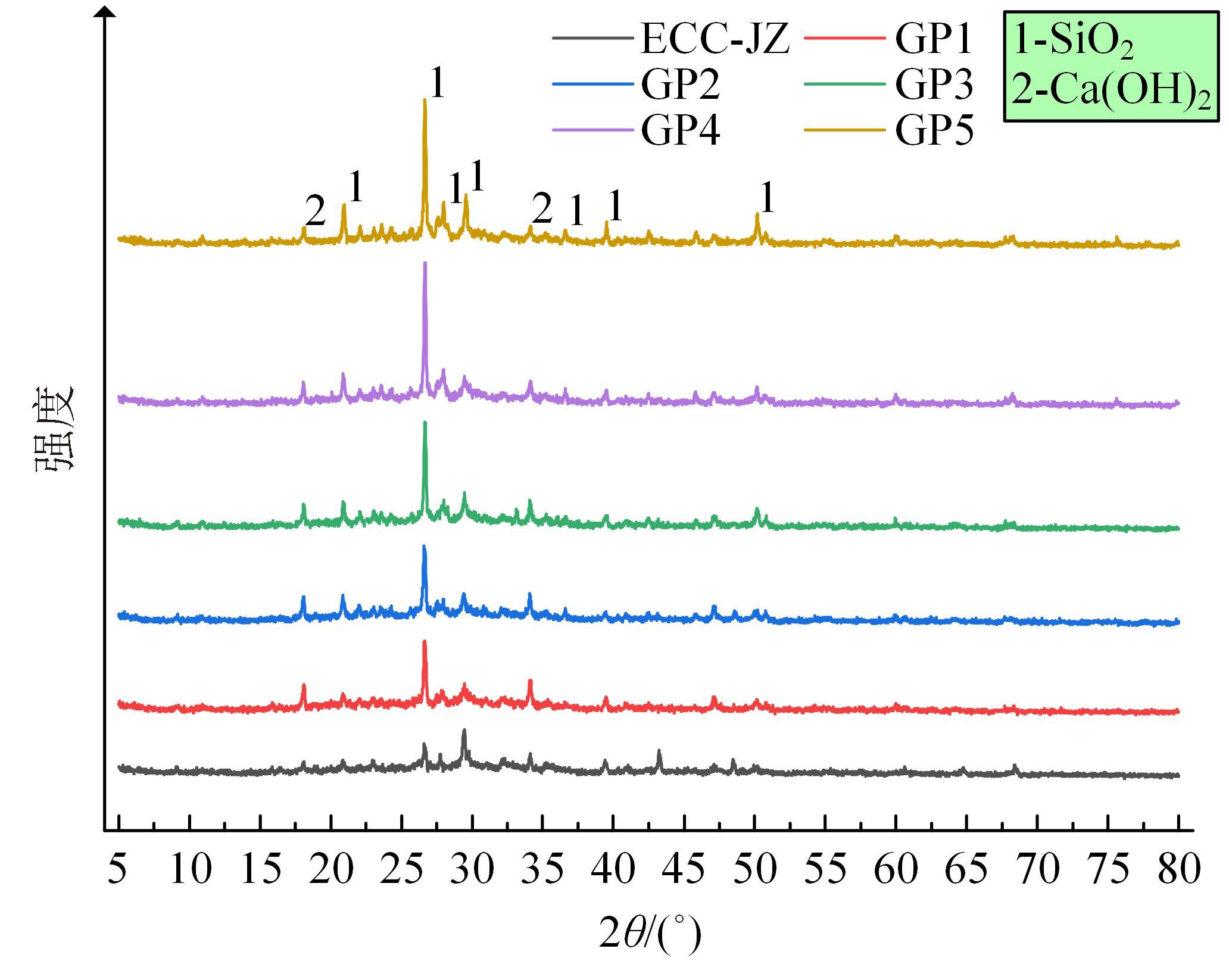
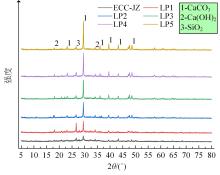
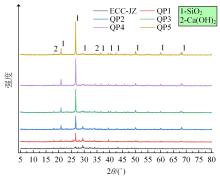
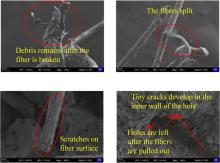
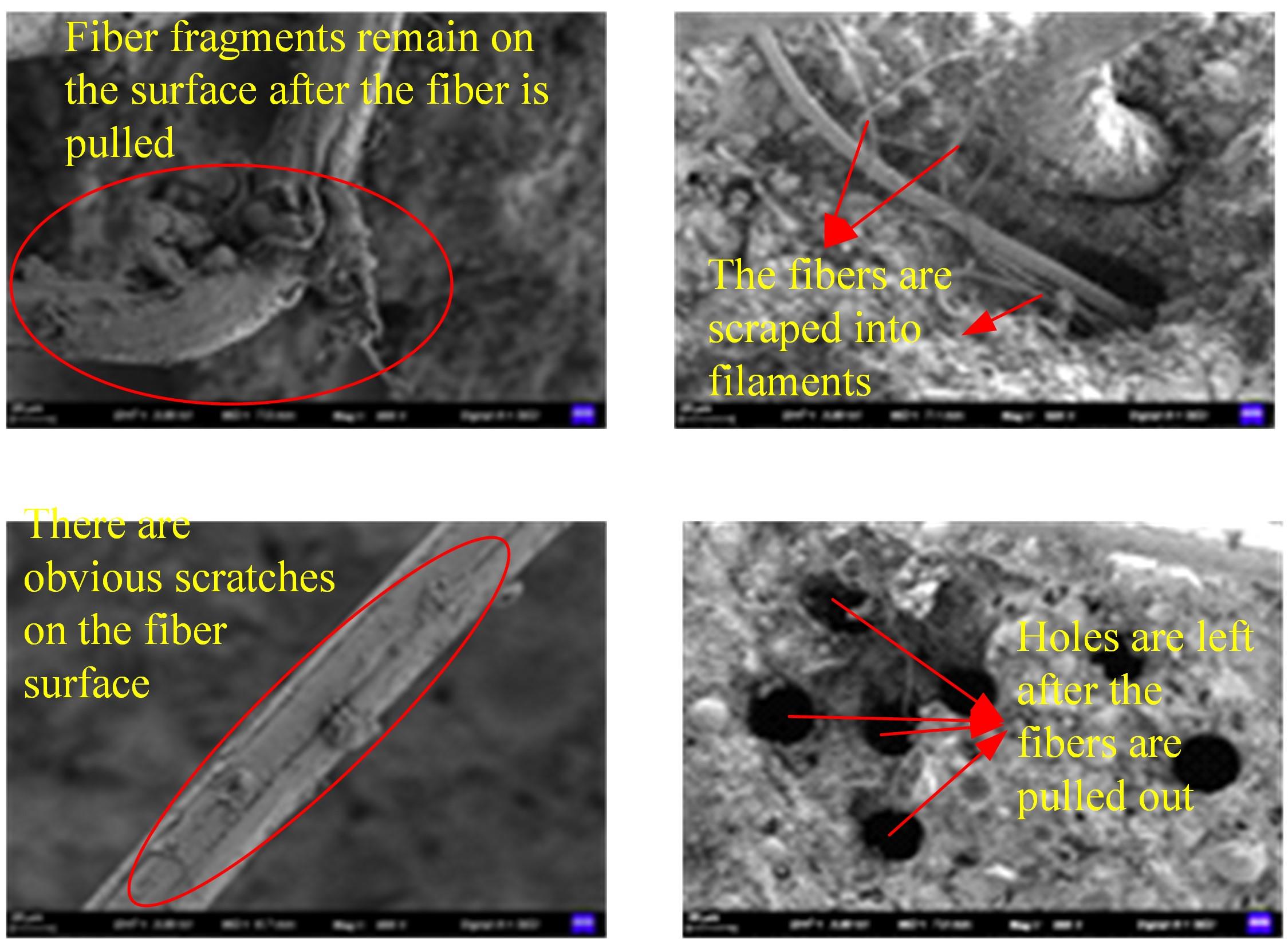
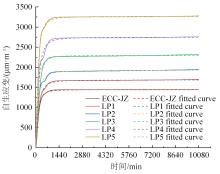
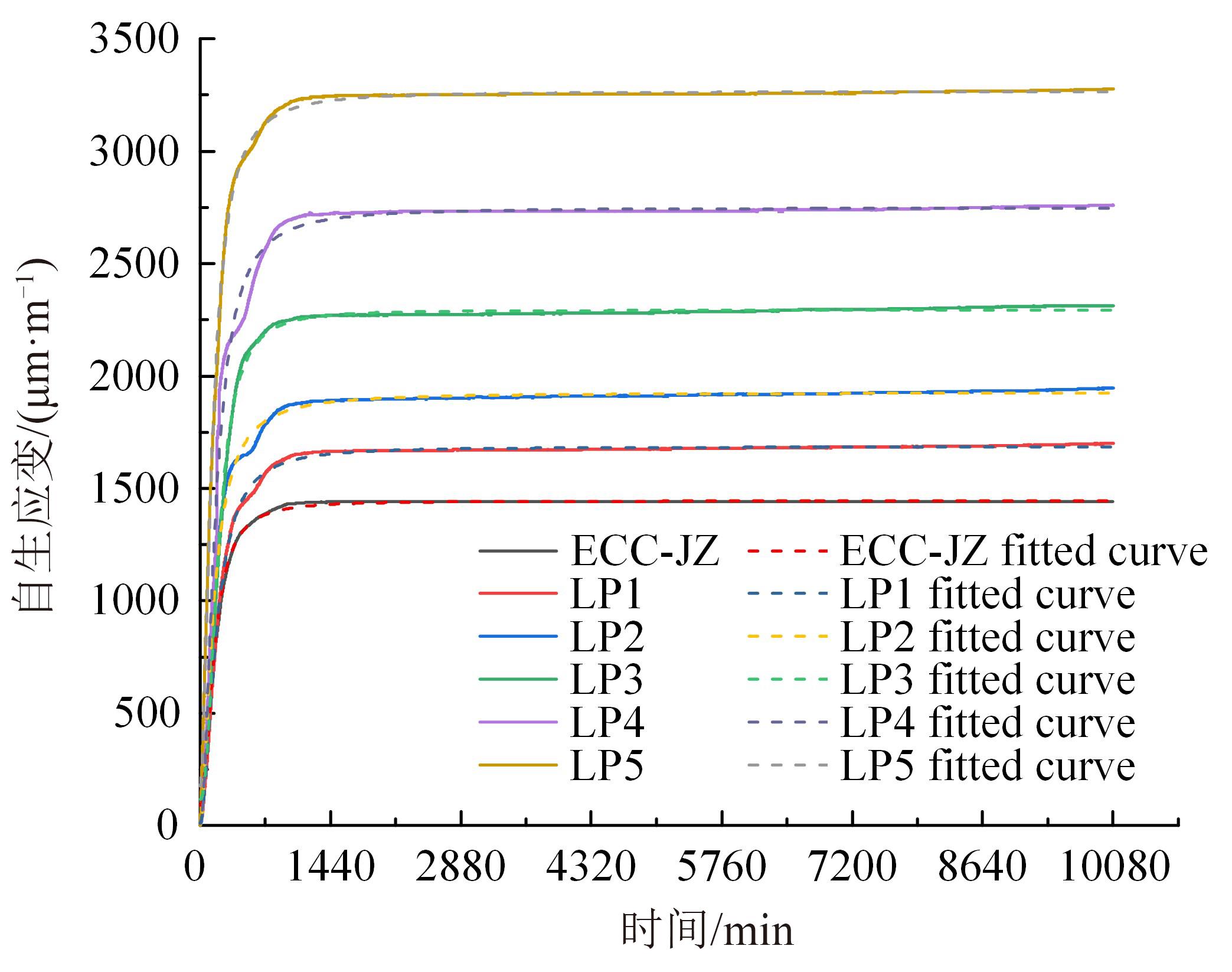
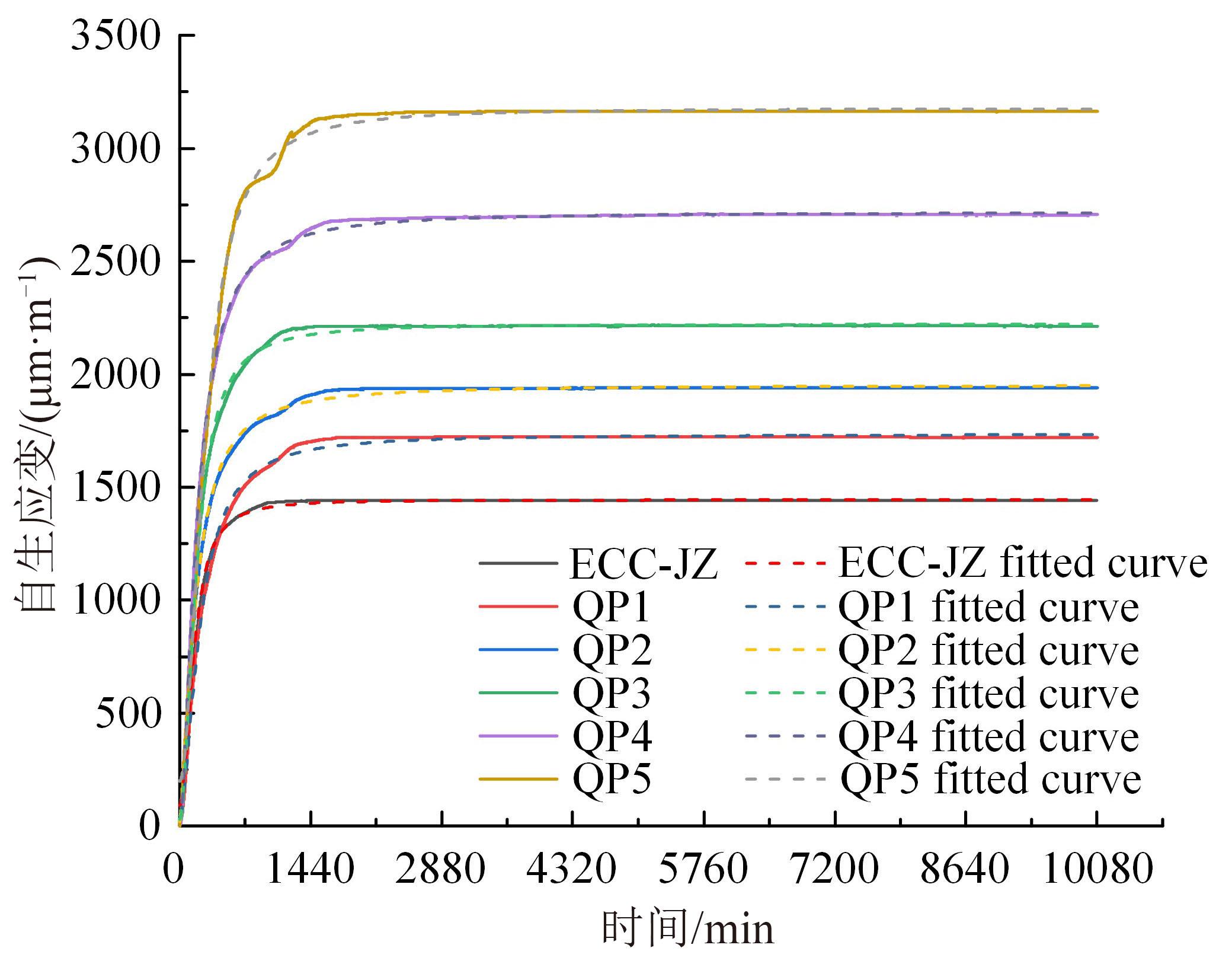
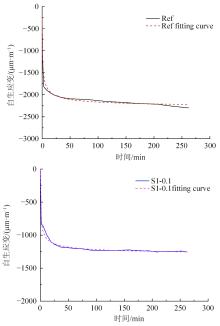
本文研究了花岗斑岩石粉(GP)、石灰石粉(LP)、石英石粉(QP)分别以20%、40%、60%、80%、100%等质量取代河砂制备工程水泥基复合材料(Engineered cementitious composites,ECC)的宏观力学性能、自收缩性能和微观结构性能。力学性能试验结果表明:各拉伸试样峰值应力和极限拉应变随石粉取代率的递增先减小后增大,而抗压强度和抗折强度随石粉取代率的增加而增加,当石粉取代率为100%时,各试样力学性能最优,其中拉伸峰值应力达到4.4 MPa及以上,极限拉应变超过4.2%,抗压强度超过50 MPa,抗折强度超过18 MPa,较基准组试样的力学性能有较大程度的提升。自收缩试验结果表明:各试样的自收缩随石粉取代率的增加而变大,当石粉完全取代时,掺GP、LP、QP的自收缩较基准试样分别增加了117.3%、127.3%、119.5%,为此,石粉取代河砂后对基体的稳定性产生了不利影响。微观结构试验结果表明:掺入石粉可以成为水化产物的成核基体并能促进其反应,其中石灰石粉促进效果最好;当各石粉掺量较大时,聚乙烯醇(PVA)纤维在基体中的分散性得到改善,基体和纤维能够共同承受荷载作用与协调变形,充分利用基体和纤维自身的强度。采用Logistic模型对自收缩试验结果进行拟合,得到的ECC自收缩预测模型预测效果较好,表明本模型具有一定的适用性。
中图分类号:
- TU528
| 1 | . 建设用砂 [S]. |
| 2 | 王立华, 段毅凡. 花岗石废料综合利用现状[J]. 石材, 2012(10): 10-12, 35. |
| Wang Li-hua, Duan Yi-fan. The present utilization situation of granite scrap[J]. Stone, 2012(10): 10-12, 35. | |
| 3 | 林基泳, 蒋勇, 吴兴颜, 等. 石粉对混凝土性能影响的研究现状[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(12): 3842-3848. |
| Lin Ji-yong, Jiang Yong, Wu Xing-yan, et al. Research status on influence of aggregate micro fines on concrete performance[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(12): 3842-3848. | |
| 4 | Ying P J, Liu F S, Ren S X, et al. The research on the effect of granite powder on concrete performance[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012, 1975(204-208): 3760-3764. |
| 5 | Jin W Z, Jiang L H, Han L, et al. Influence of curing temperature on the mechanical properties and microstructure of limestone powder mass concrete[J]. Structural Concrete, 2020, 22: 745-755. |
| 6 | Alessandra T S, Thiago F B, Lucas A R, et al. Effect of limestone powder substitution on mechanical properties and durability of slender precast components of structural mortar[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(1): 847-856. |
| 7 | Zhu P F, Yang G H, Jiang L H, et al. Influence of high volume limestone powder on hydration and microstructural development of cement[J]. Advances in Cement Research, 2020, 33(5): 1-38. |
| 8 | 朱柯. 石灰石粉对混凝土性能影响研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2015, 34(2): 492-495. |
| Zhu Ke. Limestone powder impact on performance of concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2015, 34(2): 492-495. | |
| 9 | 赵颖, 刘维胜, 王欢, 等. 石灰石粉对3D打印水泥基材料性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(): 1217-1220. |
| Zhao Ying, Liu Wei-sheng, Wang Huan, et al. Influence of limestone powder on performances of 3D printing cementitious materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(Sup.2): 1217-1220. | |
| 10 | 黄伟, 孙伟. 石灰石粉掺量对超高性能混凝土水化演变的影响[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 47(4): 751-759. |
| Huang Wei, Sun Wei. Effects of limestone addition on hydration development of ultra-high performance concrete[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 47(4): 751-759. | |
| 11 | 翟盛通. 基于0~80 μm花岗岩石粉内掺掺量的水工混凝土性能及微观结构研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学水利土木工程学院, 2020. |
| Zhai Sheng-tong. Study on properties and microstructure of hydraulic concrete based on 0~80 μm granite powder content[D]. Taian: College of Hydraulic and Civil Engineering, Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| 12 | Li H F, Xia Y. Chlorine ion penetration resistance of concretes containing super-fine limestone powder[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 1790(512-515): 2961-2964. |
| 13 | Li L G, Kwan A K H. Adding limestone fines as cementitious paste replacement to improve tensile strength, stiffness and durability of concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2015, 60: 17-24. |
| 14 | 王德辉, 史才军, 贾煌飞, 等. 石灰石粉对混凝土耐久性能的影响[J]. 福州大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 46(6): 874-880. |
| Wang De-hui, Shi Cai-jun, Jia Huang-fei, et al. Effects of limestone powder on the durability of concrete[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(6): 874-880. | |
| 15 | 唐志, 贾旭秀, 王德辉. 石灰石粉在水泥浆抗氯离子渗透性中的作用机理[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(9): 2647-2653. |
| Tang Zhi, Jia Xu-xiu, Wang De-hui. Action mechanism of limestone powder on the resistance to chloride ion permeability of cement pastes[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(9): 2647-2653. | |
| 16 | 史才军, 王德辉, 贾煌飞, 等. 石灰石粉在水泥基材料中的作用及对其耐久性的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2017, 45(11): 1582-1593. |
| Shi Cai-jun, Wang De-hui, Jia Huang-fei, et al. Role of limestone powder and its effect on durability of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic society, 2017, 45(11): 1582-1593. | |
| 17 | Li C Z, Jiang L H, Xu N, et al. Mechanical and transport properties of recycled aggregate concrete modified with limestone powder[J]. Composites Part B, 2020, 197(9):No.108189. |
| 18 | 赵井辉, 刘福胜, 韦梅, 等. 花岗岩石粉细度及掺量对混凝土微观孔隙的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2016(2): 39-45. |
| Zhao Jing-hui, Liu Fu-sheng, Wei Mei, et al. Effects of granite powder fineness and addition on concrete microscopic pores[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2016(2): 39-45. | |
| 19 | Xu G Q, You Z G, Gao L, et al. The influence of combined admixture of super-fine limestone powder and low-quality fly ash on the performance of cement mortar[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 2262(652-654): 1181-1184. |
| 20 | Dong Y, Xiao K T, Yang H Q. Influence of limestone powder on the performance of cementitious materials[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 3072(541-542): 123-129. |
| 21 | 刘焕芹, 徐志峰, 李维滨, 等. 石灰石粉对硅酸盐水泥水化的影响[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2015, 33(2): 185-188. |
| Liu Huan-qin, Xu Zhi-feng, Li Wei-bin, et al. Effect of limestone powder on hydration of portland cement[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Engineering, 2015, 33(2): 185-188. | |
| 22 | 范华峰, 翟盛通, 张坤强, 等. 外掺花岗岩石粉对水工混凝土抗渗、抗冻性能的影响[J]. 混凝土, 2021(4): 61-66. |
| Fan Hua-feng, Zhai Sheng-tong, Zhang Kun-qiang, et al. Effect of the addition of granite powder on impermeability and frost resistance of hydraulic concrete[J]. Concrete, 2021(4): 61-66. | |
| 23 | Vijayalakshmi M, Sekar A S S, Sivabharathy M, et al. Utilization of granite powder waste in concrete production[J]. Defect and Diffusion Forum, 2012, 2079(330-330): 49-61. |
| 24 | Shehdeh G, Husam N, Rosa V. Experimental study of concrete made with granite and iron powders as partial replacement of sand[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2016, 9: 1-9. |
| 25 | Lalit K G, Ashok K V. Impact on mechanical properties of cement sand mortar containing waste granite powder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 191: 155-164. |
| 26 | 刘通, 于本田, 王焕, 等. 高吸附性石粉含量对水泥砂浆力学性能及微观结构的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(8): 16-22. |
| Liu Tong, Yu Ben-tian, Wang Huan, et al. Influence of high adsorbent stone powder content on mechanical properties and microstructure of cement mortar[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2021, 38(8): 16-22. | |
| 27 | Vijayalakshmi M, Sekar A S S, Prabhu G G. Strength and durability properties of concrete made with granite industry waste[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 46: 1-7. |
| 28 | 张凌强, 陈倩, 黄兴, 等. 石粉含量对C50花岗岩机制砂混凝土性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(7): 2154-2158, 2177. |
| Zhang Ling-qiang, Chen Qian, Huang Xing, et al. Influence of stone powder content on performance of C50 granite manufactured sand concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(7): 2154-2158, 2177. | |
| 29 | 于本田, 刘通, 王焕, 等. 花岗斑岩石粉含量对混凝土性能及微观结构的影响研究[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2022, 52(5): 1052-1062. |
| Yu Ben-tian, Liu Tong, Wang Huan, et al. Influence of granite porphyry stone powder content on properties and microstructure of concrete[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(5): 1052-1062. | |
| 30 | Kishan L J, Gaurav S, Lalit K G. Durability performance of waste granite and glass powder added concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 252(C): No.119075. |
| 31 | Da Silva J L, Da Cunha Campos D B, Lordsleem A C, et al. Influence of the partial substitution of fine aggregate by granite powder in mortar on the process of natural carbonation[J]. Waste Management & Research, 2020, 38(3): 254-262. |
| 32 | Sawicz Z, Heng S S. Durability of concrete with addition of limestone powder[J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 1996, 48(175): 131-137. |
| 33 | 王雨利, 蔡基伟, 杨雷, 等. 石灰石粉对砂浆耐磨性能的影响及作用机理[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2014, 17(2): 270-273. |
| Wang Yu-li, Cai Ji-wei, Yang Lei, et al. Influence of limestone powder on abrasion resistance of mortar and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2014, 17(2): 270-273. | |
| 34 | 武军宝. 石粉对混凝土性能的影响研究[D].重庆: 重庆交通大学材料科学与工程学院, 2020. |
| Wu Jun-bao. Study on the influence of stone powder on concrete properties[D].Chongqing: School ol Materials Science and Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 35 | Yang H F, Liang D Y, Deng Z H, et al. Effect of limestone powder in manufactured sand on the hydration products and microstructure of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 188: 1045-1049. |
| 36 | Li V C. Performance driven design of fiber reinforced cementitious composites[C]∥Proceedings of 4th RILEM International Symposium on Fiber Reinforced Concrete, London,UK, 1992: 12-30. |
| 37 | Li V C, Leung C K Y. Steady-state and multiple cracking of short random fiber composites[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1992, 118(11): 2246-2264. |
| 38 | Li V C. Engineered cementitious composites (ECC)-tailored composites through micromechanical modeling[C]∥Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Present and the Future, Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Montreal, Canada,1998: 64-97. |
| 39 | Siad H, Alyousif A, Keskin O K, et al. Influence of limestone powder on mechanical, physical and self-healing behavior of engineered cementitious composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 99: 1-10. |
| 40 | Jung H H, Bang Y L, Yun Y K. Composite properties and micromechanical analysis of highly ductile cement composite incorporating limestone powder[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(2): 151-161. |
| 41 | Li Y L, Deng D H, Sierens Z, et al. Effect of limestone powder on fracture and flexural behaviour of PVA fibre reinforced SAC[J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 2019, 72(24): 1243-1259. |
| 42 | Kang S H, Jeong Y, Tan K H, et al. High-volume use of limestone in ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete for reducing cement content and autogenous shrinkage[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 213: 292-305. |
| 43 | Kazim T, Serhat D. The mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites containing limestone powder replaced by microsilica sand[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2013, 40(2): 151-157. |
| 44 | Turk K, Nehdi M L. Coupled effects of limestone powder and high-volume fly ash on mechanical properties of ECC[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 164: 185-192. |
| 45 | Turk K, Demirhan S. Effect of limestone powder on the rheological, mechanical and durability properties of ECC[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2017, 21(9): 1151-1170. |
| 46 | JSCE. Recommendations for design andconstruction of high performance fiber reinforcedcement composites with multiple fine cracks[R].Tokyo: Japan Society of Civil Engineers, 2008. |
| 47 | . 建筑砂浆性能测试方法标准 [S]. |
| 48 | . 水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法) [S]. |
| 49 | Li Y Z, Guan X C, Zhang C C, et al. Development of high-strength and high-ductility ECC with saturated multiple cracking based on the flaw effect of coarse river sand[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2020, 32(11):No.04020317. |
| 50 | Soroka I, Stern N. Calcareous fillers and the compressive strength of portland cement[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1976, 6(3): 367-376. |
| 51 | Jean P, Sophie H, Bernard G. Influence of finely ground limestone on cement hydration[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 1999, 21(2): 99-105. |
| 52 | Bentz D P. Modeling the influence of limestone filler on cement hydration using CEMHYD3D[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2005, 28(2): 124-129. |
| 53 | Weerdt K D, Haha M B, Saout G L, et al. Hydration mechanisms of ternary Portland cements containing limestone powder and fly ash[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2010, 41(3): 279-291. |
| 54 | Wu L S, Yu Z H, Zhang C, et al. Shrinkage and tensile properties of ultra-high-performance engineered cementitious composites(UHP-ECC) containing superabsorbent polymers(SAP) and united expansion agent (UEA)[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 339(7): No.127697. |
| [1] | 李义,刘天宝,王绍强,梁继才. 软质炭黑对天然橡胶基磁流变弹性体性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1548-1554. |
| [2] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [3] | 谢超,王起才,于本田,李盛,林晓旭,鲁志铭. 聚氨酯涂膜弹性模量的AFM测定及微观结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1322-1330. |
| [4] | 李志军,刘浩,张立鹏,李振国,邵元凯,李智洋. 过滤壁结构对颗粒捕集器深床过滤影响的模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 422-434. |
| [5] | 崔亚楠, 韩吉伟, 冯蕾, 李嘉迪, 王乐. 盐冻循环条件下改性沥青微细观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 452-458. |
| [6] | 高小建, 孙博超, 叶焕, 王子龙. 矿物掺合料对自密实混凝土流变性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 439-444. |
| [7] | 关庆丰, 李艳, 侯秀丽, 杨盛志, 王晓彤. 固溶态Mg-Gd-Y-Nd合金强流脉冲电子束表面改性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1200-1205. |
| [8] | 关庆丰,季乐,蔡杰,杨盛志,刘世超,张在强,侯秀丽. 强流脉冲电子束轰击作用下3Cr13不锈钢的微观结构及性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 712-717. |
| [9] | 关庆丰, 邹阳, 张在强, 关锦彤, 苏景新, 王志平. 强流脉冲电子束作用下纯铜的微观结构与腐蚀性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 964-969. |
| [10] | 李秀娟, 梁云虹, 张志辉, 任露泉. 杨树叶片的微观结构及拉伸特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 440-443. |
| [11] | 房岩, 孙刚, 丛茜, 郭华曦. 蝗虫翅表面微观结构及疏水耦合机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 419-422. |
| [12] | 刘曙光, 闫敏, 闫长旺, 郭荣跃. 聚乙烯醇纤维强化水泥基复合材料的抗盐冻性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 63-67. |
| [13] | 詹小丽, 张肖宁, 王端宜, 卢亮. 基于DMA方法的沥青胶浆微观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(04): 916-920. |
| [14] | 弯艳玲,丛茜,金敬福,王晓俊 . 蜻蜓翅膀微观结构及其润湿性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(03): 732-0736. |
| [15] | 卢广林,汪春花,王毅,邱小明 . Ag基钎料钎焊立方氮化硼的焊接性与微观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(05): 1088-1092. |
|
||