吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1298-1306.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230725
基于选择集成的山区高速事故预测模型
- 1.哈尔滨工业大学 交通科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150090
2.云南省交通规划设计研究院有限公司 陆地交通气象灾害防治技术国家工程实验室,昆明 650200
Traffic accident prediction model of mountain highways based on selection integration
Xiang-hai MENG1( ),Guo-rui WANG1,Ming-yang ZHANG1,Bi-jiang TIAN1,2
),Guo-rui WANG1,Ming-yang ZHANG1,Bi-jiang TIAN1,2
- 1.School of Transportation Science and Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150090,China
2.National Engineering Laboratory for Prevention and Control Technology of Land Transport Meteorological Disasters,Yunnan Provincial Transportation Planning and Design Research Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Kunming 650200,China
摘要:
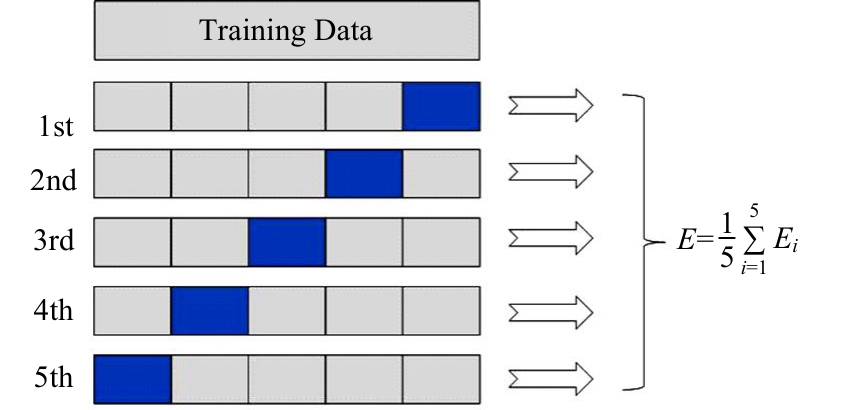
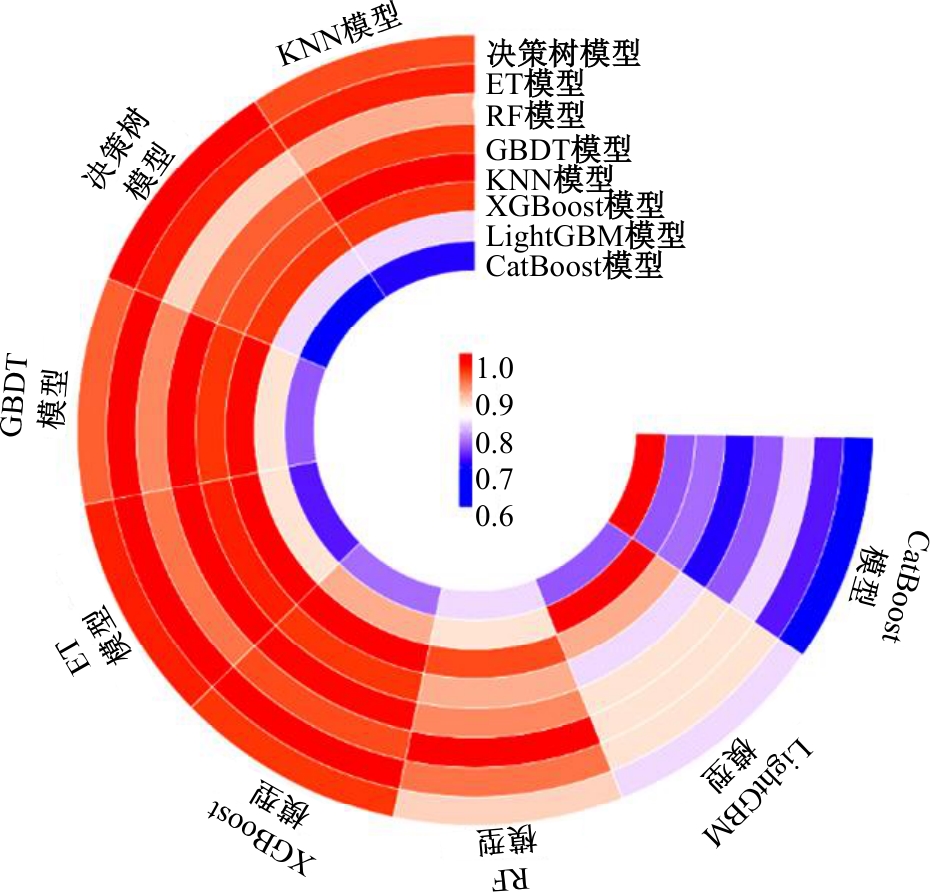
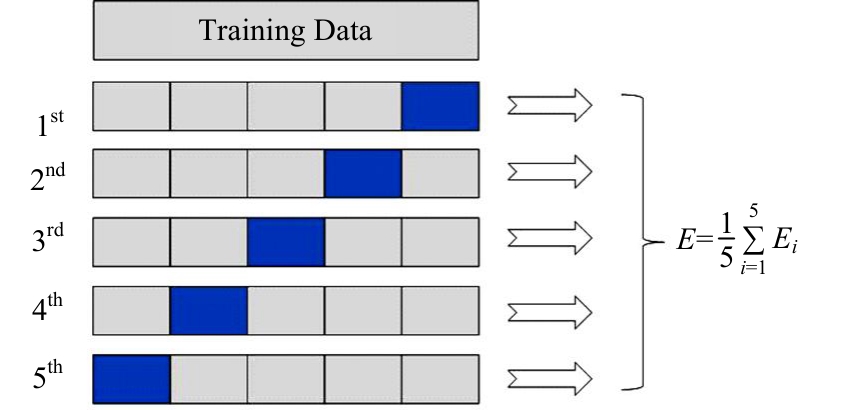
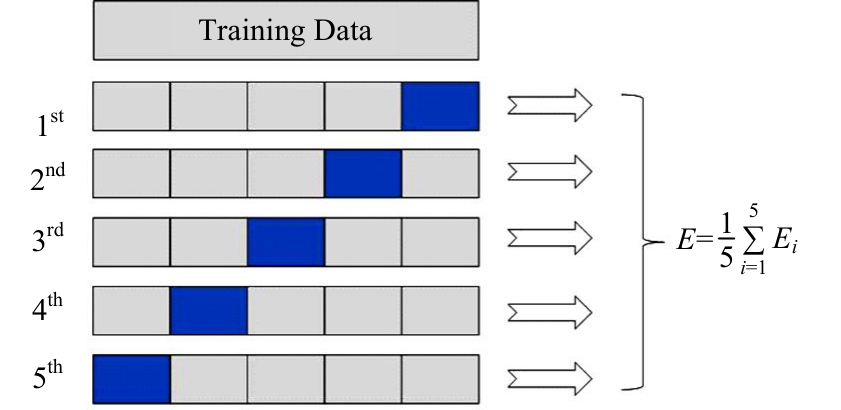
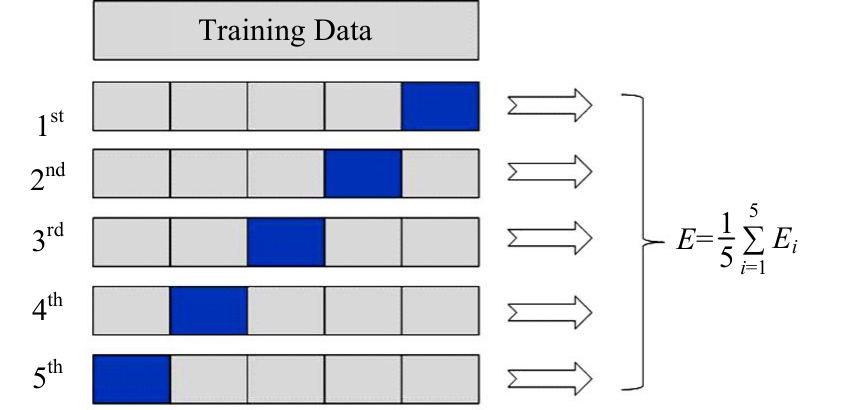
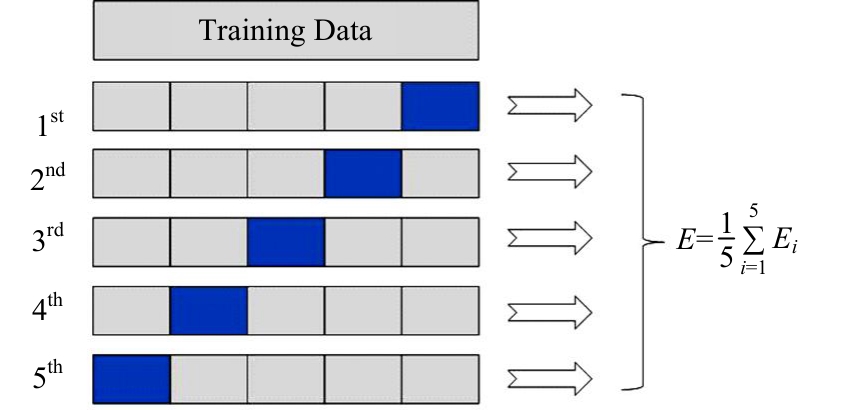
为提升交通事故预测模型的精度并减少鲁棒性,利用Stacking集成策略构建事故预测模型。首先,构建基于决策树、极端随机树等8种机器学习模型的单一事故预测模型,利用MIC检验与图着色法度量各事故预测模型的相似度,选取相似度低、多样性强的模型参与集成;其次,对单一事故预测模型结果进行Box-Cox变换,并利用特征加权法为各单一模型分别赋予不同的权重;最后,选用BP神经网络、Logistic回归等模型作为元学习器进行Stacking集成。研究结果表明:元学习器选用BP神经网络的集成模型预测精度高于其他集成模型,相较于预测精度最高的单一事故预测模型,集成模型的MAE、RMSE分别降低24%和14%,R2提高6%。
中图分类号:
- U491.31
| 1 | 张显强, 贺中华, 梁永娜, 等. 贵州省道路分形特征及其对交通事故影响机制[J]. 公路, 2017, 62(6):197-203. |
| Zhang Xian-qiang, He Zhong-hua, Liang Yong-na, et al. Fractal characteristics of road and its impact mechanism on traffic accidents in Guizhou Province[J]. Highway, 2017, 62(6): 197-203. | |
| 2 | Macedo M R, Maia M L A, Rabbani E R K, et al. Traffic accident prediction model for rural highways in Pernambuco[J]. Case Studies on Transport Policy, 2022, 10(1): 278-286. |
| 3 | 马壮林, 邵春福, 李霞. 基于Logistic模型的公路隧道交通事故严重程度的影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2010, 40(2): 423-426. |
| Ma Zhuang-lin, Shao Chun-fu, Li Xia. Analysis of factors affecting accident severity in highway tunnels based on Logistic model[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(2): 423-426. | |
| 4 | 陈英, 袁华智, 黄中祥, 等. 零截尾负二项模型在交叉口事故预测中的应用[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(4): 146-154. |
| Chen Ying, Yuan Hua-zhi, Huang Zhong-xiang, et al. Modeling intersection traffic crashes using a zero-truncated negative binomial model[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(4): 146-154. | |
| 5 | Roland J, Way P D, Firat C, et al. Modeling and predicting vehicle accident occurrence in Chattanooga, Tennessee[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021(149): 105-117. |
| 6 | Ihueze C C, Onwurah U O. Road traffic accidents prediction modelling: an analysis of Anambra State, Nigeria[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018(7), 112: 21-29. |
| 7 | 谢学斌, 孔令燕. 基于ARIMA和XGBoost组合模型的交通事故预测[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(1):277-284. |
| Xie Xue-bin, Kong Ling-yan. On the ways to the traffic accident prediction based on the ARIMA and XGBoost combined model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(1): 277-284. | |
| 8 | 纪俊红, 昌润琪, 温廷新. 基于GSK-AdaBoost-LightGBM的交通事故死亡人数预测研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(1): 24-28. |
| Ji Jun-hong, Chang Run-qi, Wen Ting-xin. Prediction of traffic accident death toll based on GSK-AdaBoost-LightGBM[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(1): 24-28. | |
| 9 | Vilaa M, Macedo E, Coelho M C. A rare event modelling approach to assess injury severity risk of vulnerable road users[J]. Safety, 2019, 5(2): 29-38. |
| 10 | Xing L, He J, Li Y, et al. Comparison of different models for evaluating vehicle collision risks at upstream diverging area of toll plaza[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2020(135): 86-97. |
| 11 | Kwon O H, Rhee W, Yoon Y, et al. Application of classification algorithms for analysis of road safety risk factor dependencies[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2015(75): 1-15. |
| 12 | Zeng K H, Chou S H, Chan F H, et al. Agent-centric risk assessment: accident anticipation and risky region localization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2222-2230. |
| 13 | 宁静, 佘红艳, 赵东, 等. 一种路网级交通事故风险预测方法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2022, 45(2): 72-78. |
| Ning Jing, She Hong-yan, Zhao Dong, et al. A road-level traffic accident risk prediction method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022, 45(2): 72-78. | |
| 14 | Lin L, Wang Q, Sadek A W. A novel variable selection method based on frequent pattern tree for real-time traffic accident risk prediction[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015(55): 444-459. |
| 15 | 孙棣华, 唐亮, 付青松, 等. 基于量子神经网络的道路交通事故预测[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010, 10(5): 104-109. |
| Sun Di-hua, Tang Liang, Fu Qing-song, et al. Road traffic accidents forecasting based on quantum neural network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2010, 10(5): 104-109. | |
| 16 | 覃薇. 基于负二项回归分析的高速公路神经网络事故预测模型[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Qin Wei. Neural network crash prediction model of freeway based on negative binomial regression analysis[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. | |
| 17 | 范中洲, 赵羿, 周宁, 等. 基于灰色BP神经网络组合模型的水上交通事故数预测[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(3): 857-861. |
| Fan Zhong-zhou, Zhao Yi, Zhou Ning, et al. Integrated model for forecasting waterway traffic accidents based on the Gray-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20(3): 857-861. |
| [1] | 金庆良,周鑫森,陈翼,吴承文. 基于群智能增强核极限学习机的创新人才预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1763-1771. |
| [2] | 赵秀芝,谢德红. 基于噪声鲁棒性特征提取的普洱茶品种鲁棒判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1756-1762. |
| [3] | 梅生启,刘晓东,王兴举,李旭峰,武腾,程相旭. 基于参数相关性分析和机器学习算法的高强混凝土徐变预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1595-1603. |
| [4] | 岳昊,常笑,刘建业,曲秋莳. 引入车辆窗的定制公交线路优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1266-1274. |
| [5] | 吴文静,邓淳淳,贾洪飞,孙舒航. 内涝影响下路网畅通可靠度评估及关键路段识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1250-1257. |
| [6] | 王军,司昌馥,王凯鹏,付强. 融合集成学习技术和PSO-GA算法的特征提取技术的入侵检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1396-1405. |
| [7] | 戴银飞,周秀贞,刘玉宝,刘志远. 基于CAN总线数据的车载网络入侵检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 857-865. |
| [8] | 马书红,张俊杰,陈西芳,廖国美. 利用出租车时序数据识别城市功能区[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 603-613. |
| [9] | 高天洋,胡大伟,姜瑞森,吴雪,刘慧甜. 基于模块化车辆的区域灵活接驳公交线路优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 537-545. |
| [10] | 李昱燃,汪飞,朱才华,韩飞,李岩. 污染天气居民通勤模式选择影响因素的链式效用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 577-590. |
| [11] | 徐慧智,蒋时森,王秀青,陈爽. 基于深度学习的车载图像车辆目标检测和测距[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [12] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [13] | 郑长江,陶童统,陈志超. 基于流量可调重分配的级联失效模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [14] | 温晓岳,钱国敏,孔桦桦,缪月洁,王殿海. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [15] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,严丽平. 基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
|