吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1756-1762.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240566
基于噪声鲁棒性特征提取的普洱茶品种鲁棒判别方法
- 1.浙江工贸职业技术学院 人工智能学院,浙江 温州 325002
2.温州大学 计算机与人工智能学院,浙江 温州 325002
3.南京林业大学 信息科学技术学院,江苏 南京 210037
Discrimination method for Pu-er tea varieties based on noise-robust feature extraction
Xiu-zhi ZHAO1,2( ),De-hong XIE3(
),De-hong XIE3( )
)
- 1.College of Artificial Intelligence,Zhejiang Industry& Trade Vocational College,Wenzhou,325002,China
2.School of Computer and Artificial Intelligence,Wenzhou University,Wenzhou 325002,China
3.College of Information Science and Technology,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
摘要:
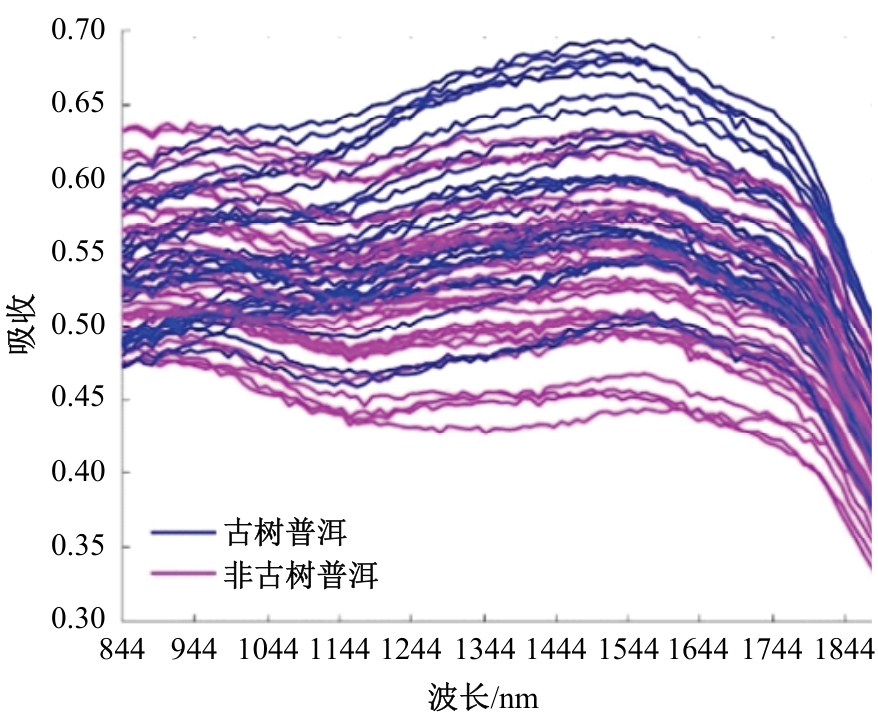
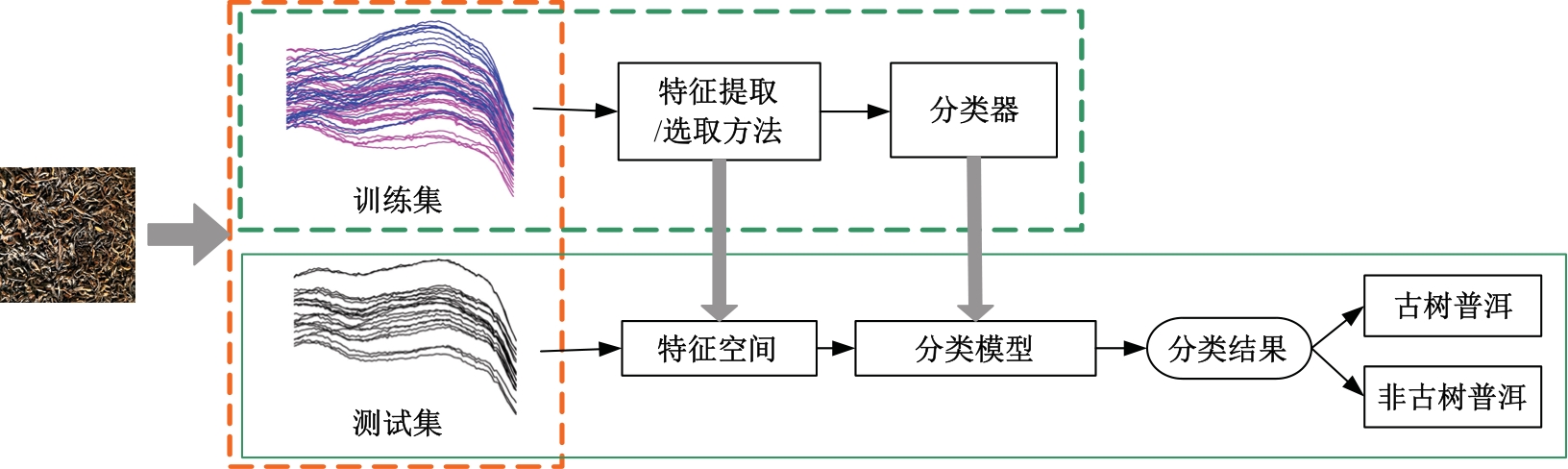
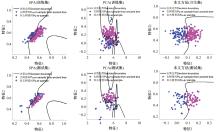
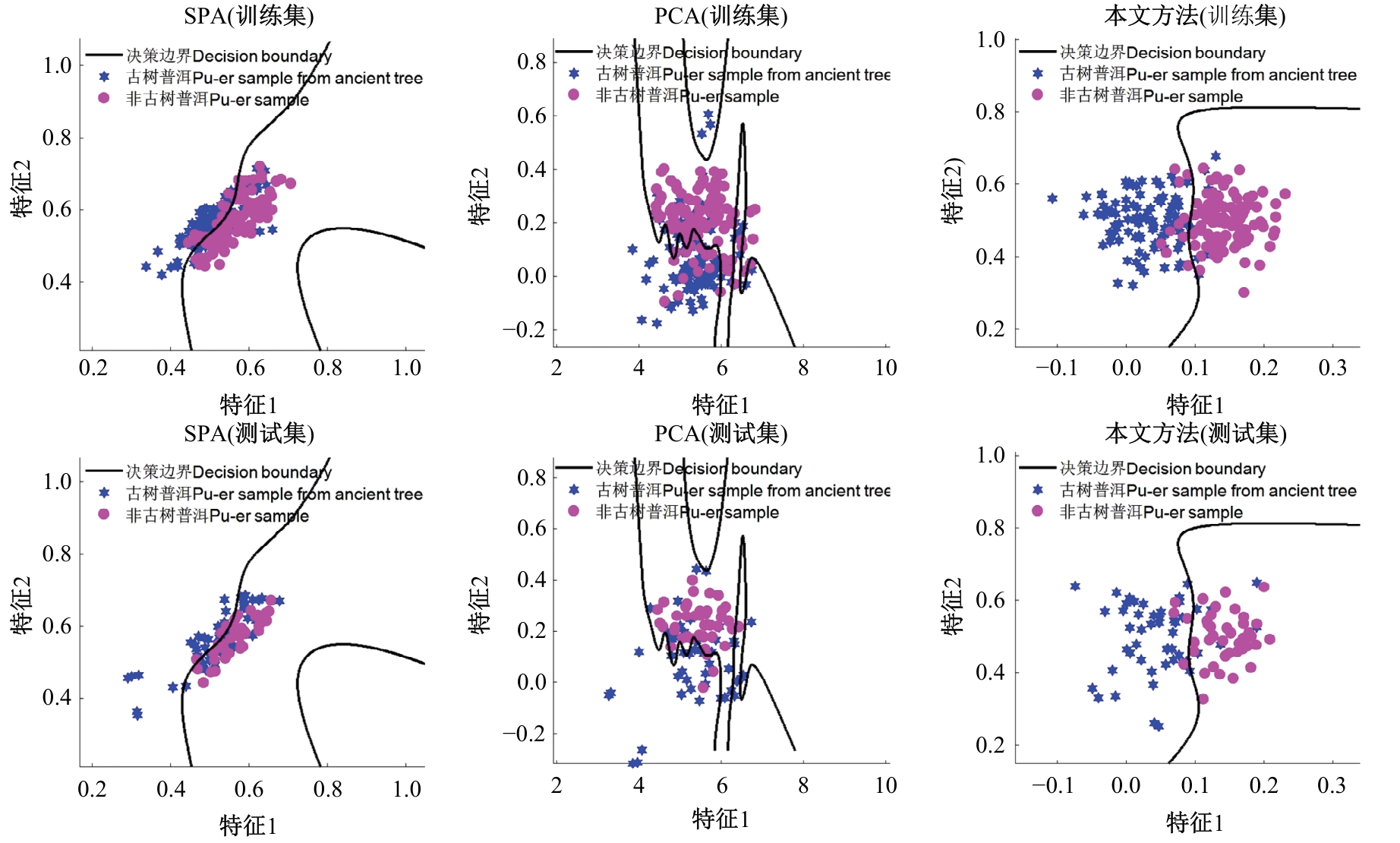
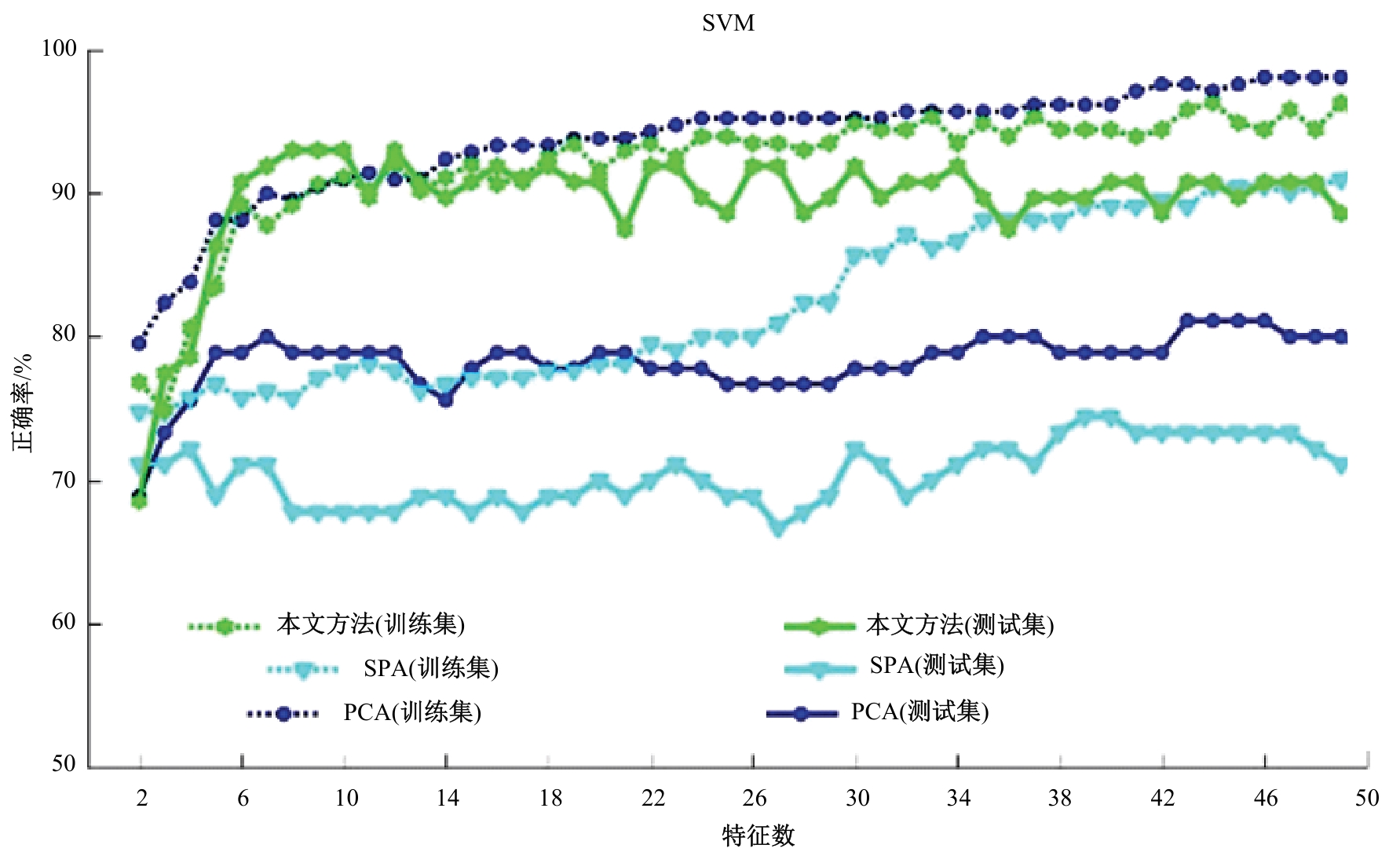
利用近红外光谱与机器学习方法快速鉴别普洱茶叶品质时,中低端近红外光谱采集设备采集的光谱存在高维、重叠和噪声大的特性,严重影响了建模准确。本文提出了一个噪声鲁棒的特征提取方法,与支持向量机(SVM)分类器结合,建立普洱茶叶品质鉴别方法。首先,利用噪声鲁棒的特征提取方法、主成分分析(PCA)与连续投影算法(SPA)对获得的近红外光谱数据进行特征提取,获得特征空间;然后利用SVM对特征提取后的数据进行训练,获得鉴别模型。模型鉴别结果比较表明,对于噪声残留近红外光谱数据,本文提出的噪声鲁棒特征提取方法能够有效抵抗噪声的影响、从高维光谱中提出特征变量,以提高模型的鉴别精度。鉴别模型预测的正确率、召回率、特效度、准确率及平衡F分数分均明显高于其他两种方法所得模型。对于古树普洱茶叶与非古树普洱茶叶的鉴别,本文鉴别模型预测的正确率和召回率分别达到了92.06%和95.38%,表明本文方法训练所得模型具有较好的鉴别能力。研究结果为实现在实际应用中精准判别普洱茶品质提供理论参考和依据。
中图分类号:
- O657.3
| [1] | 赵阳, 龚加顺, 王秋萍. 古树普洱茶生茶贮藏过程中香气成分的变化[J]. 食品科学, 2022, 43(4): 241-248. |
| Zhao Yang, Gong Jia-shun, Wang Qiu-ping. Change in aroma components of raw pu-erh tea from ancient tea trees during storage[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(4): 241-248. | |
| [2] | 曾敏, 龚正礼. 基于主成分分析法构建云南古树普洱生茶香气质量评价模型[J]. 食品工业科技, 2017, 38(15): 264-269. |
| Zeng Min, Gong Zheng-li. Modeling for aroma quality evaluation of Yunnan Pu-erh raw tea made from ancient trees based on principal component analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(15): 264-269. | |
| [3] | 吴全金, 周喆, 孙威江. 近红外光谱技术在茶叶品质调控中的应用[J]. 广东农业科学, 2019, 46(1): 91-100. |
| Wu Quan-jin, Zhou Zhe, Sun Wei-jiang. Review on the application of near-infrared spectroscopy technology in tea quality management[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 46(1): 91-100. | |
| [4] | 王胜鹏, 龚自明, 高士伟, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术的恩施玉露茶保存年份的快速无损鉴别[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2015, 34(5): 111-114. |
| Wang Sheng-peng, Gong Zi-ming, Gao Shi-wei, et al. Identification of Enshi yulu tea conserved years based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015, 34(5): 111-114. | |
| [5] | Ren G, Wang Y, Ning J, et al. Highly identification of keemun black tea rank based on cognitive spectroscopy: near infrared spectroscopy combined with feature variable selection[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2020, 230: 118079. |
| [6] | 韩广, 王小燕, 陈思琪, 等. 提高近红外光谱法检测人体血液等复杂溶液成分准确度的研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(7): 1993-1997. |
| Han Guang, Wang Xiao-yan, Chen Si-qi, et al. Research progress on improving the accuracy of near inf rared spectroscopy detection of human blood and other complex solution components[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(7): 1993-1997. | |
| [7] | 谢德红, 李俊锋, 刘菂, 等. 基于改进Hodrick-Prescott分解模型的近红外自适应降噪方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(5): 1650-1655. |
| Xie De-hong, Li Jun-feng, Liu Di, et al. An improved hodrick-prescott decomposition based near-infrared adaptive denoising method[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(5): 1650-1655. | |
| [8] | Yang H, Li L L, Li G H, et al. A novel feature extraction method for ship-radiated noise[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(4): 604-617. |
| [9] | 董春旺, 梁高震, 安霆, 等. 红茶感官品质及成分近红外光谱快速检测模型建立[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(24): 306-313. |
| Dong Chun-wang, Liang Gao-zhen, An Ting, et al. Near-infrared spectroscopy detection model for sensory quality and chemical constituents of black tea[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(24): 306-313. | |
| [10] | 刘鹏, 艾施荣, 杨普香, 等. 非线性流形降维方法结合近红外光谱技术快速鉴别不同海拔的茶叶[J]. 茶叶科学, 2019, 39(6): 715-722. |
| Liu Peng, Ai Shi-rong, Yang Pu-xiang, et al. Nonlinear manifold dimensionality reduction methods for quick discrimination of tea at different altitude by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2019, 39(6): 715-722. | |
| [11] | Canova L D S, Vallese F D, Pistonesi M F, et al. An improved successive projections algorithm version to variable selection in multiple linear regression[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2023, 1274: 341560. |
| [12] | Pang L, Wang L, Yuan P, et al. Rapid seed viability prediction of Sophora japonica by improved successive projection algorithm and hyperspectral imaging[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2022, 123: 104143. |
| [13] | Ghosh T, Kirby M. Linear centroid encoder for supervised principal component analysis[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 155: 110634. |
| [14] | Cardoso V G K, Poppi R J. Non-invasive identification of commercial green tea blends using NIR spectroscopy and support vector machine[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2021, 164: 106052. |
| [15] | Pang Y, Wang Y, Lai X, et al. Enhanced kriging leave-one-out cross-validation in improving model estimation and optimization[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 414: 116194. |
| [16] | Luque A, Carrasco A, Martín A, et al. The impact of class imbalance in classification performance metrics based on the binary confusion matrix[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 91: 216-231. |
| [1] | 金庆良,周鑫森,陈翼,吴承文. 基于群智能增强核极限学习机的创新人才预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1763-1771. |
| [2] | 赵男男,金凤,丁宏钰. 基于权重优化AF的非线性主动噪声控制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1722-1727. |
| [3] | 梅生启,刘晓东,王兴举,李旭峰,武腾,程相旭. 基于参数相关性分析和机器学习算法的高强混凝土徐变预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1595-1603. |
| [4] | 王军,司昌馥,王凯鹏,付强. 融合集成学习技术和PSO-GA算法的特征提取技术的入侵检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1396-1405. |
| [5] | 孟祥海,王国锐,张明扬,田毕江. 基于选择集成的山区高速事故预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1298-1306. |
| [6] | 戴银飞,周秀贞,刘玉宝,刘志远. 基于CAN总线数据的车载网络入侵检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 857-865. |
| [7] | 王娜,崔月磊,李杨,王子从. 基于小波包对数能量图的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 494-502. |
| [8] | 董华松,连远锋. 海量数字媒体视频无损转码重压缩的轻量化检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 741-747. |
| [9] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [10] | 赖丹晖,罗伟峰,袁旭东,邱子良. 复杂环境下多模态手势关键点特征提取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2288-2294. |
| [11] | 程文,张成春,孙潇伟,沈淳,吴正阳,陈正武. 脊状结构用于翼型自噪声控制试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2385-2392. |
| [12] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [13] | 王长建,刘久明,张锦洲,李斌. 基于高速摄影技术的行星减速箱故障激光序列脉冲诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1869-1875. |
| [14] | 陈城,史培新,贾鹏蛟,董曼曼. 基于MK-LSTM算法的盾构掘进参数相关性分析及结构变形预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1624-1633. |
| [15] | 牛世峰,于士杰,刘彦君,马冲. 基于手环数据的愤怒驾驶行为实时检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3505-3512. |
|