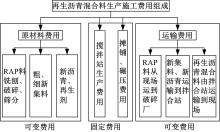
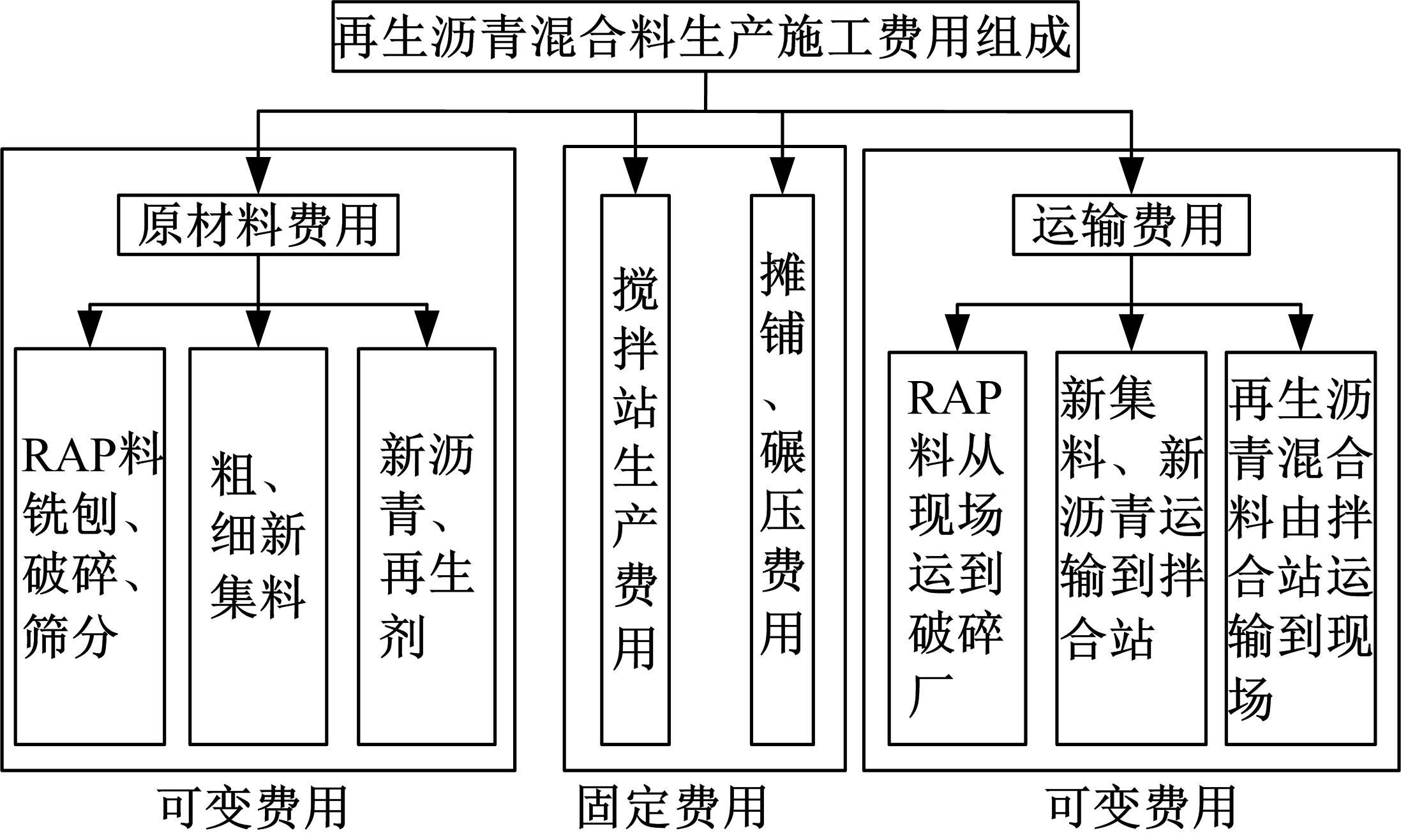
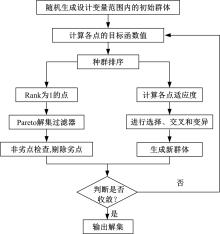
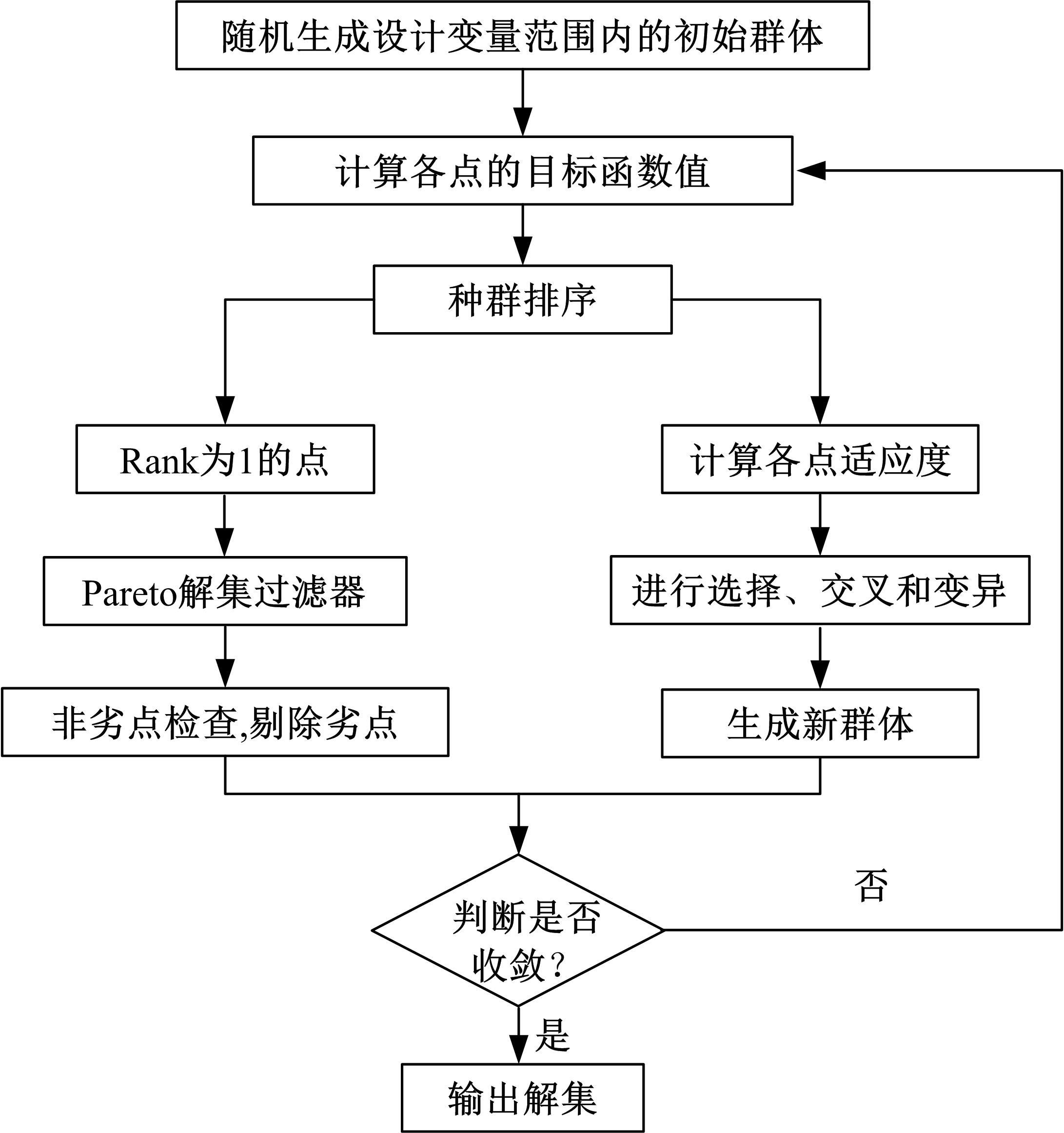
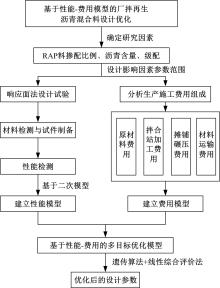
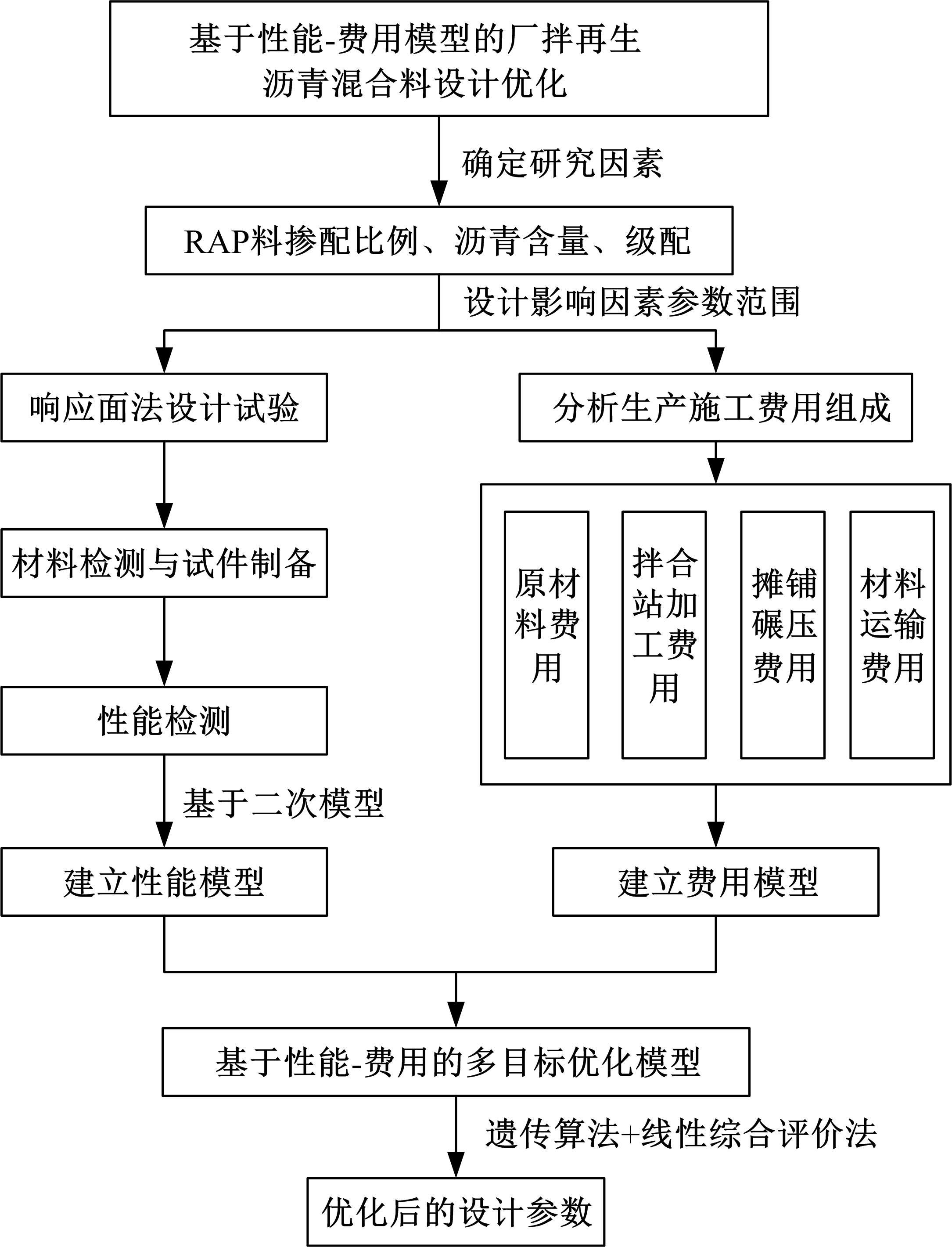
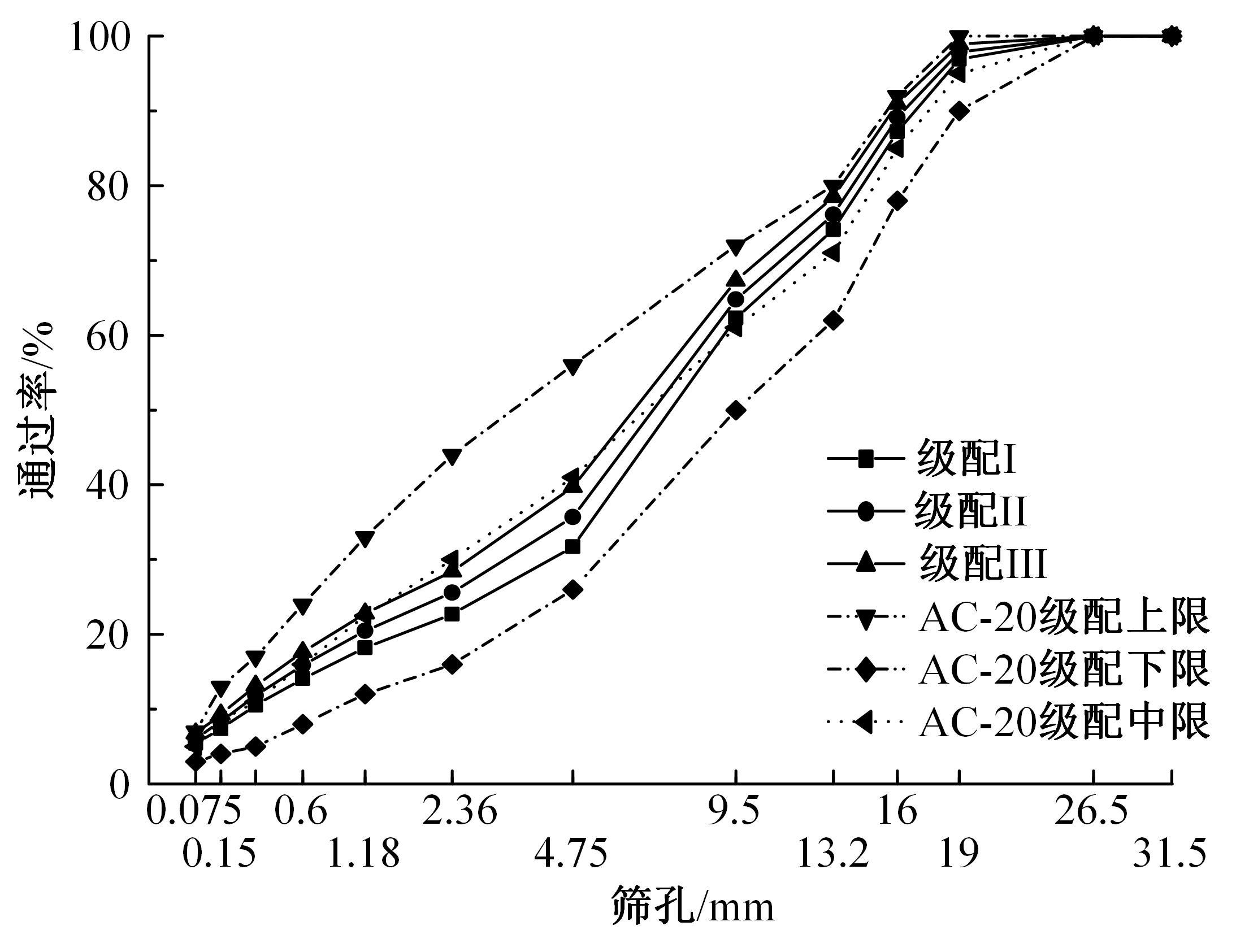
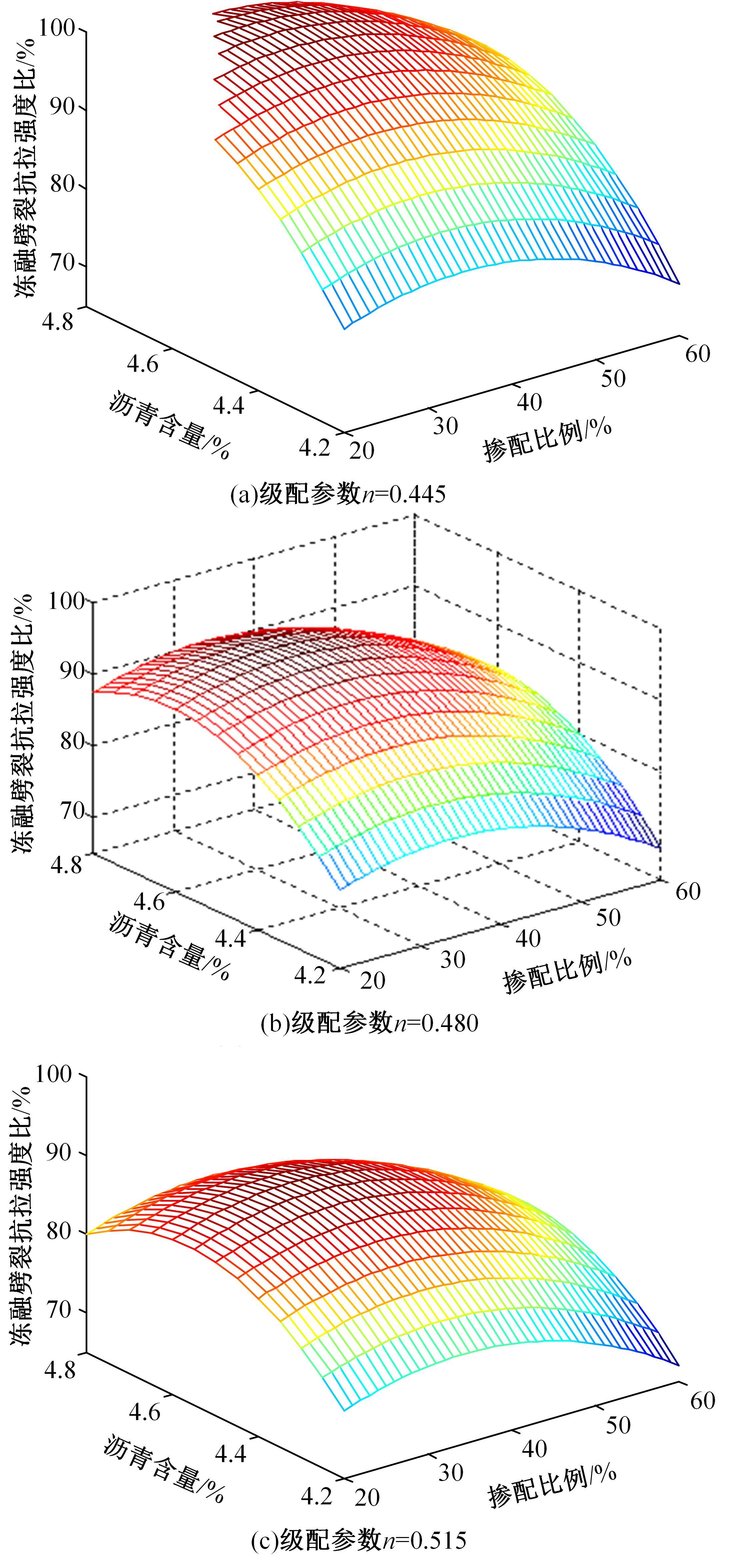
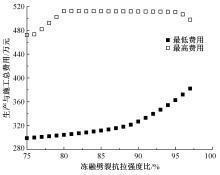
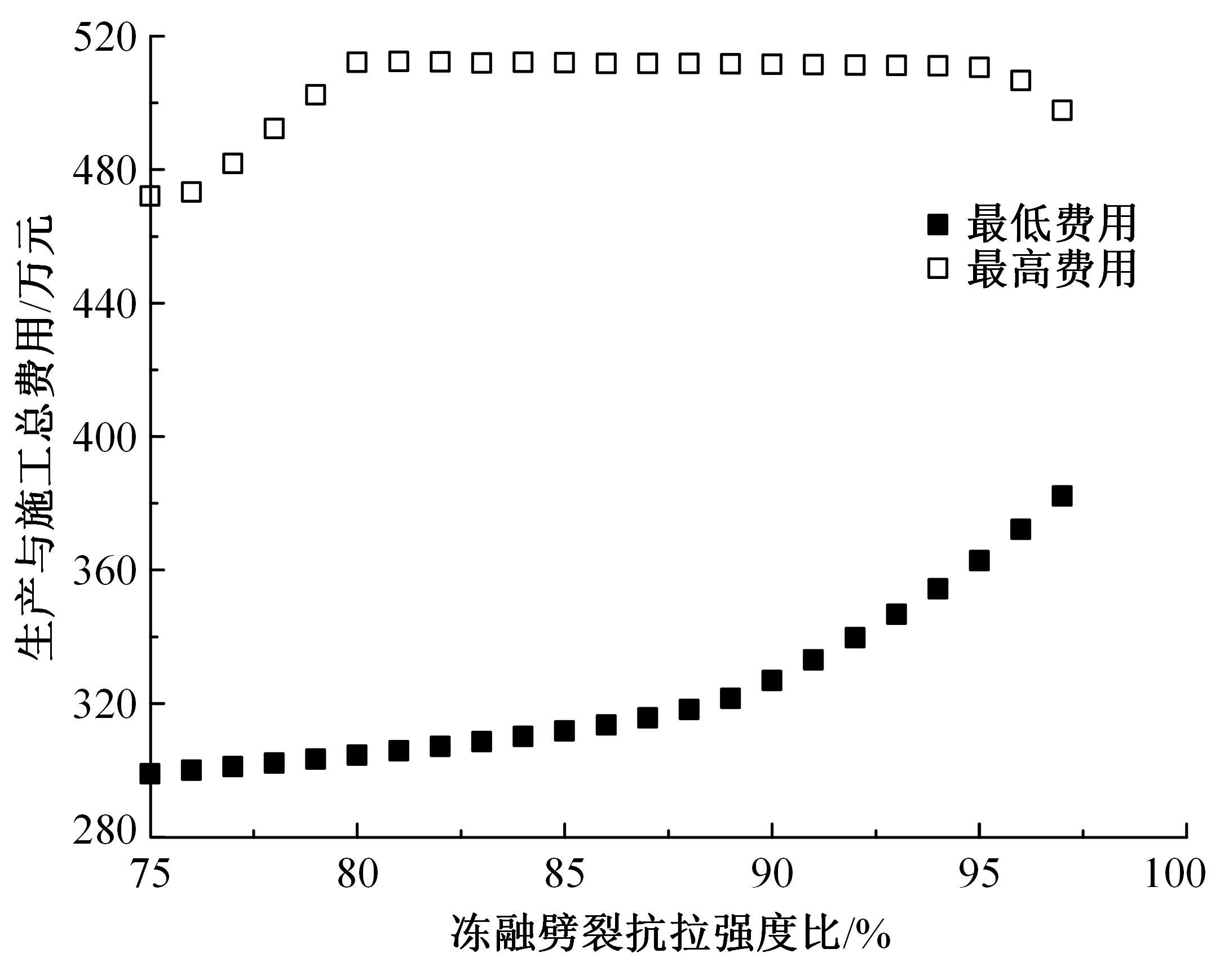
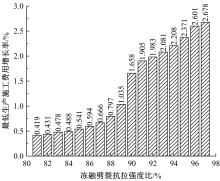
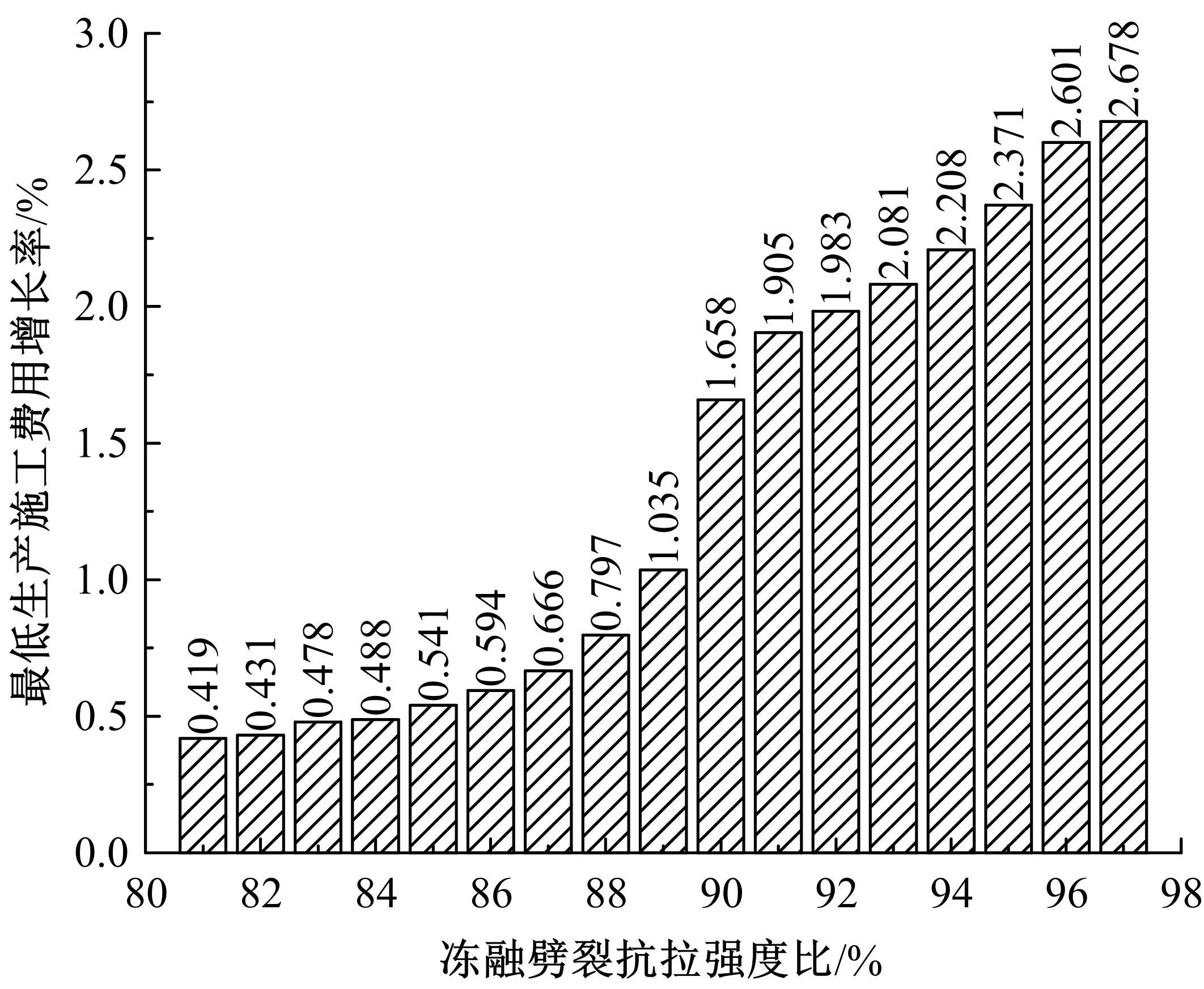
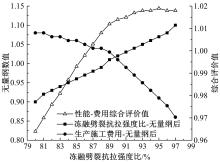
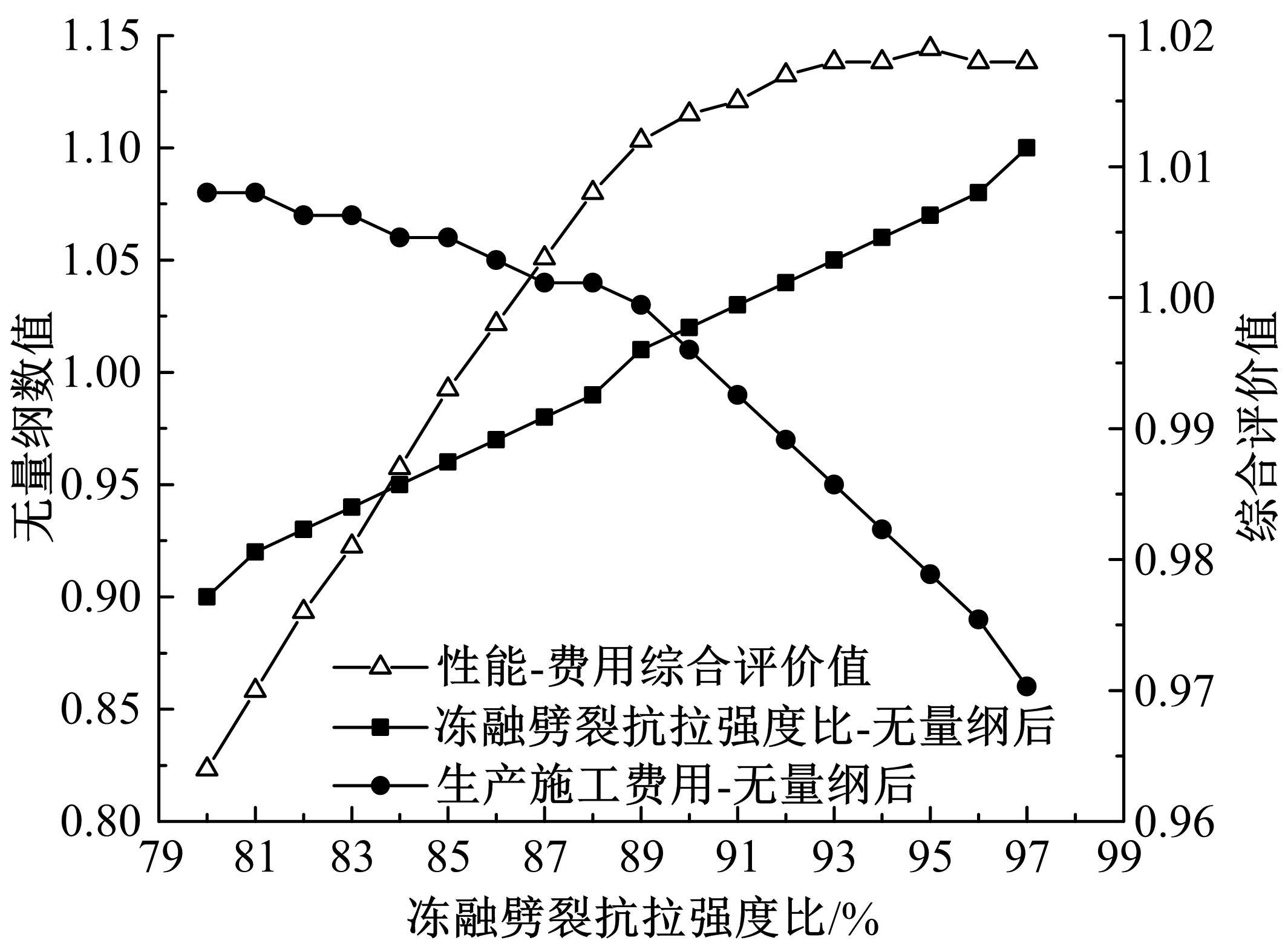
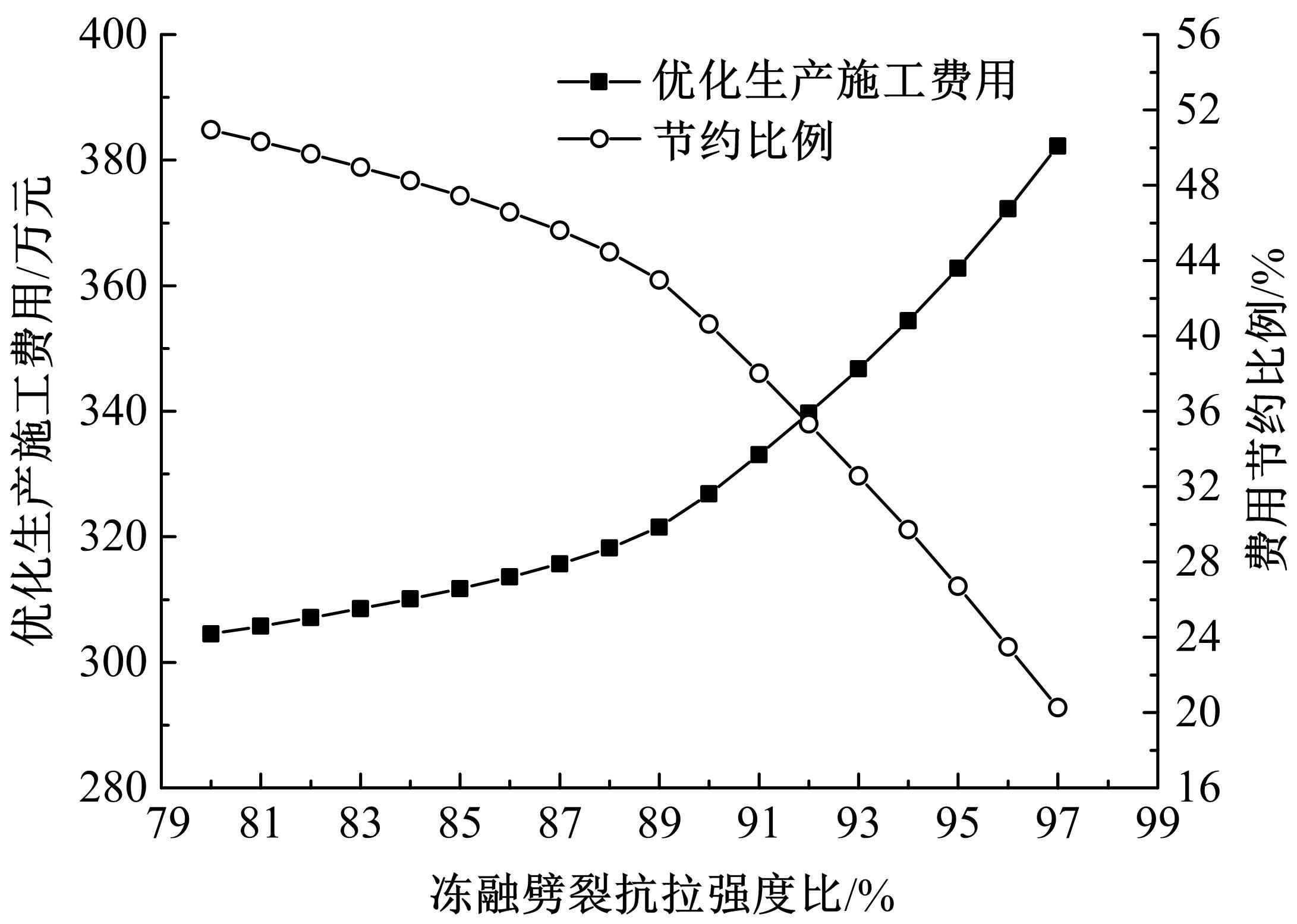
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 585-595.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200799
Optimal design on recycled hot⁃mix asphalt mixture based on performance⁃cost model
Yu-quan YAO1( ),Jian-gang YANG1,2,3(
),Jian-gang YANG1,2,3( ),Jie GAO1,2,3,Liang SONG4
),Jie GAO1,2,3,Liang SONG4
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
3.Institute of Road Engineering,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,China
4.Xinjiang Communications Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Urumqi 830057,China
CLC Number:
- U416.2
| 1 | Gao Jie, Yang Jian-gang, Yu Di, et al. Reducing the variability of multi-source reclaimed asphalt pavement materials: a practice in China[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 278:No.122389. |
| 2 | 仰建岗,姚玉权,孙晨.不同工况对就地热再生沥青混合料性能的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(10):14-24. |
| Yang Jian-gang, Yao Yu-quan, Sun Chen. Influence of different working conditions on hot in-place recycled asphalt mixture performance[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(10):14-24. | |
| 3 | Yang Jian-gang, Tao Wen-jie, Gao Jie, et al. Measurement of particle agglomeration and aggregate breakdown of reclaimed asphalt pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 296:No.123681. |
| 4 | Madrigal D P, Lannone A, Martinez A H, et al. Effect of mixing time and temperature on cracking resistance of bituminous mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement material[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(8):No.04017058. |
| 5 | 左锋,叶奋,宋卿卿. RAP掺量对再生沥青混合料路用性能影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(4):1403-1410. |
| Zuo Feng, Ye Fen, Song Qing-qing. Influence of RAP content on road performance of recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4):1403-1410. | |
| 6 | Farooq M A, Mir M S, Sharma A. Laboratory study on use of RAP in WMA pavements using rejuvenator[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 168(20):61-72. |
| 7 | Zhu Yue-feng, Li Yan-wei, Si Chun-di, et al. Laboratory evaluation on performance of fiber-modified asphalt mixtures containing high percentage of RAP[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020(4):1-9. |
| 8 | Lu D X, Saleh M, Nguyen N H T. Effect of rejuvenator and mixing methods on behaviour of warm mix asphalt containing high RAP content[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 197(10):792-802. |
| 9 | Zhou Zhou, Gu Xing-yu, Li Qiang, et al. Use of rejuvenator, styrene-butadiene rubber latex, and warm-mix asphalt technology to achieve conventional mixture performance with 50% reclaimed asphalt pavement[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2016, 2575(1):160-167. |
| 10 | Kusam A, Malladi H, Tayebali A A, et al. Laboratory evaluation of workability and moisture susceptibility of warm-mix asphalt mixtures containing recycled asphalt pavements[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2016, 29(5):No.04016276. |
| 11 | 周刚,李培国,陈天泉,等. 聚酯纤维及沥青对高RAP掺量沥青混合料路用性能的研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版,2016,35(4):40-46, 105. |
| Zhou Gang, Li Pei-guo, Chen Tian-quan, et al. Polyester fiber content and asphalt content's impact on the road performance of high RAP content asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Sciences),2016, 35(4):40-46, 105. | |
| 12 | Jahanbakhsh H, Karimi M M, Naseri H, et al. Sustainable asphalt concrete containing high reclaimed asphalt pavements and recycling agents: Performance assessment, cost analysis, and environmental impact[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 244: No.118837. |
| 13 | 单景松,李峰,杜贝贝. 基于价值工程的国省道沥青路面结构决策[J]. 公路交通科技, 2014, 31(1):26-31. |
| Shan Jing-song, Li Feng, Du Bei-bei. Decision-making of asphalt pavement structure of national and provincial highways based on value engineering[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2014, 31(1):26-31. | |
| 14 | Bressi S, Pittet M, Dumont A G, et al. A framework for characterizing RAP clustering in asphalt concrete mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 106: 564-574. |
| 15 | 靳卫东, 梁春雨. 公路施工组织与概预算[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2020. |
| 16 | 马涛, 赵永利, 黄晓明. 沥青路面厂拌热再生关键技术[M]. 南京:东南大学出版社, 2015. |
| 17 | 张文修, 梁怡. 遗传算法的数学基础[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2003. |
| 18 | 熊颖,陈维,姚玉权,等. 基于马歇尔指标的就地热再生沥青混合料再生剂用量分析[J]. 公路交通科技:应用技术版,2019,15(8):80-84. |
| Xiong Ying, Chen Wei, Yao Yu-quan, et al. Analysis on the amount of regenerant in hot recycling asphalt mixture based on Marshall index[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development (Application Technology Edition), 2019, 15(8): 80-84. | |
| 19 | . 公路工程集料试验规程 [S]. |
| 20 | . 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程 [S]. |
| 21 | . 公路沥青路面再生技术规范 [S]. |
| 22 | 樊旭英,李印冬,李章珍,等. 再生沥青混合料级配优化设计[J]. 公路与汽运,2018(4):62-65. |
| Fan Xu-ying, Li Yin-dong, Li Zhang-zhen, et al. Gradation optimization design of recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Highways & Automotive Applications,2018(4):62-65. | |
| 23 | Concha J L, Norambuena-Contreras J. Thermophysical properties and heating performance of self-healing asphalt mixture with fibres and its application as a solar collector[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 178: No.115632. |
| 24 | . 公路沥青路面施工技术规范 [S]. |
| [1] | Quan-ping XIA,Jiang-ping GAO,Hao-yuan LUO,Qi-gong ZHANG,Zhi-jie LI,Fei YANG. Low⁃temperature performance of composite modified hard asphalt used in high modulus asphalt concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [2] | Hong-xun ZHAO,Zhao-jun YANG,Chuan-hai CHEN,Hai-long TIAN,Li-ping WANG. Optimal design of acceleration test of motorized spindle of numerical control Machine Tool considering parameter weight [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 409-416. |
| [3] | Zi-ling ZHANG,Xiong HU,Yin QI,Wei WANG,Zhi-qiang TAO,Zhi-feng LIU. An approach for error allocation of machine tool based on vector projection response surface method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 384-391. |
| [4] | Wei-zhi DONG,Shuang ZHANG,Fu ZHU. Evaluation of pavement performance of asphalt mixture based on extension analytic hierarchy process [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| [5] | Wu-ping RAN,Hui-min CHEN,Ling LI,Li-qun FENG. Evolution law and model estimation and modification of resilience modulus of coarse grained soil subgrade under wet and dry cycle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2079-2086. |
| [6] | Chang-ping WEN,Huan-xia REN. Constitutive relation with double yield surfaces of bioenzyme⁃treated expansive soil based on Lade model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1716-1723. |
| [7] | Zhe-pu XU,Qun YANG. Short⁃term maintenance operation start time optimization based on real⁃time traffic map data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1763-1774. |
| [8] | Yuan-yuan WANG,Lu SUN,Wei-dong LIU,Jin-shun XUE. Constraint improvement of binocular reconstruction algorithm used to measure pavement three-dimensional texture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1342-1348. |
| [9] | Yong PENG,Han-duo YANG,Xue-yuan LU,Yan-wei LI. Effect of void characteristics on virtual shear fatigue life of asphalt mixtures using discrete element method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 956-964. |
| [10] | Wei-gang ZHU,Chao ZHU,Ya-qiu ZHANG,Hai-bin WEI. Construction and quality evaluation of digital elevation model based on convolution grid surface fitting algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [11] | Yong-chun CHENG,He LI,Li-ding LI,Hai-tao WANG,Yun-shuo BAI,Chao CHAI. Analysis of mechanical properties of asphalt mixture affected by aggregate based on grey relational degree [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [12] | Ya-feng GONG,Yun-ze PANG,Bo WANG,Guo-jin TAN,Hai-peng BI. Mechanical properties of new prefabricated box culvert structure based on road conditions in Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [13] | En-hui YANG,Jia-qiu XU,You-zhi TANG,Ao LI,Yan-jun QIU. Effect of warm mixing agents on fracture and aging properties of asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 604-610. |
| [14] | Ji-cheng HUANG,Cheng SHEN,Ai-min JI,Xian-wang LI,Bin ZHANG,Kun-peng TIAN,Hao-lu LIU. Optimization of cutting⁃conveying key working parameters of hemp harvester [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 772-780. |
| [15] | Kai-yu YANG,Wei LIU,Tian-hao WANG,Xian-li YU,Yin-han GAO,Xi-lai MA. A calculation method for uncertainty of crosstalk in multi⁃conductor transmission line [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 747-753. |
|
||