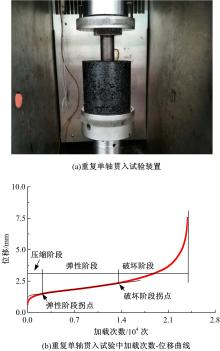
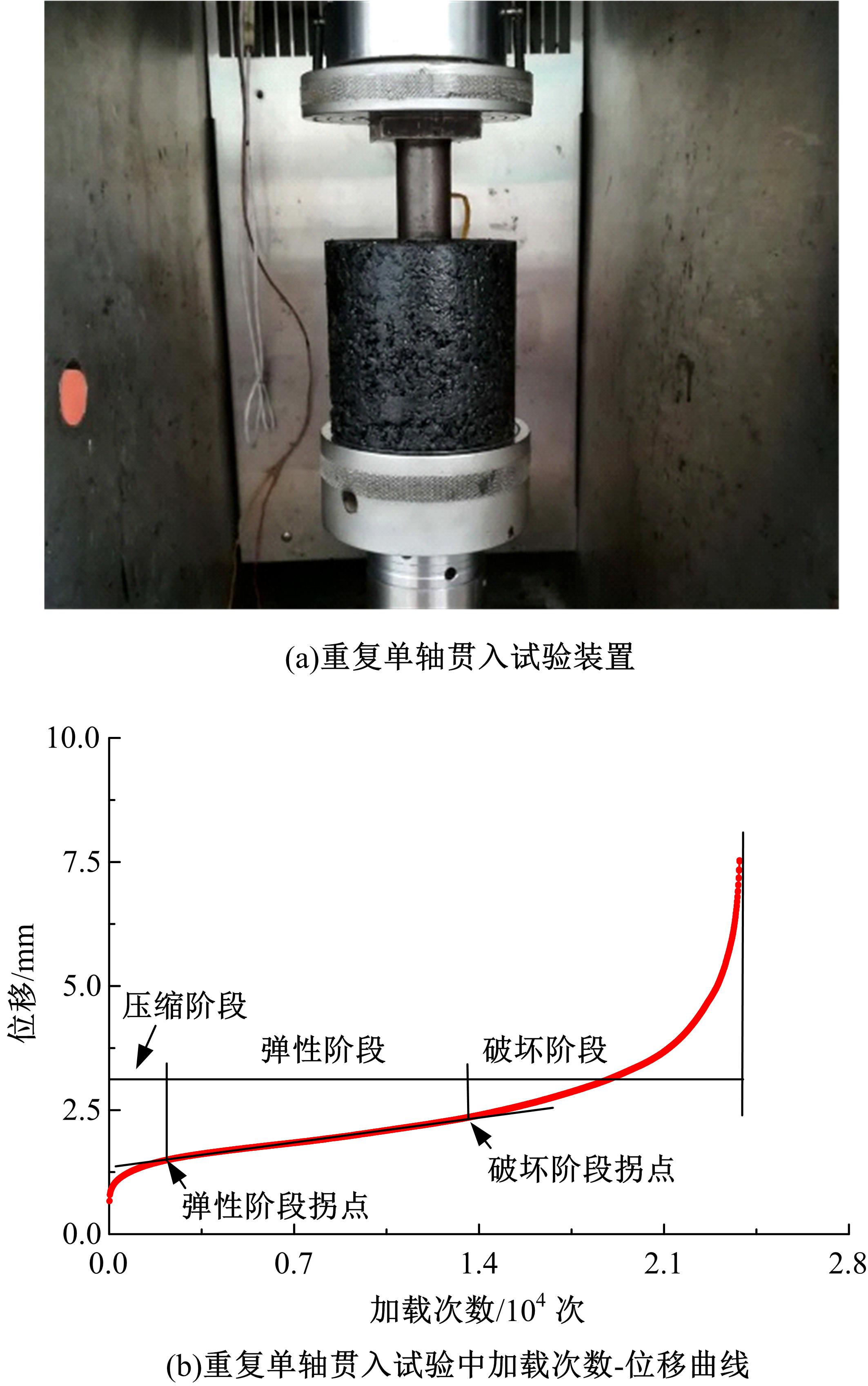
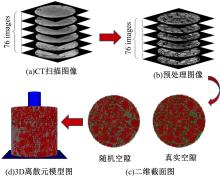
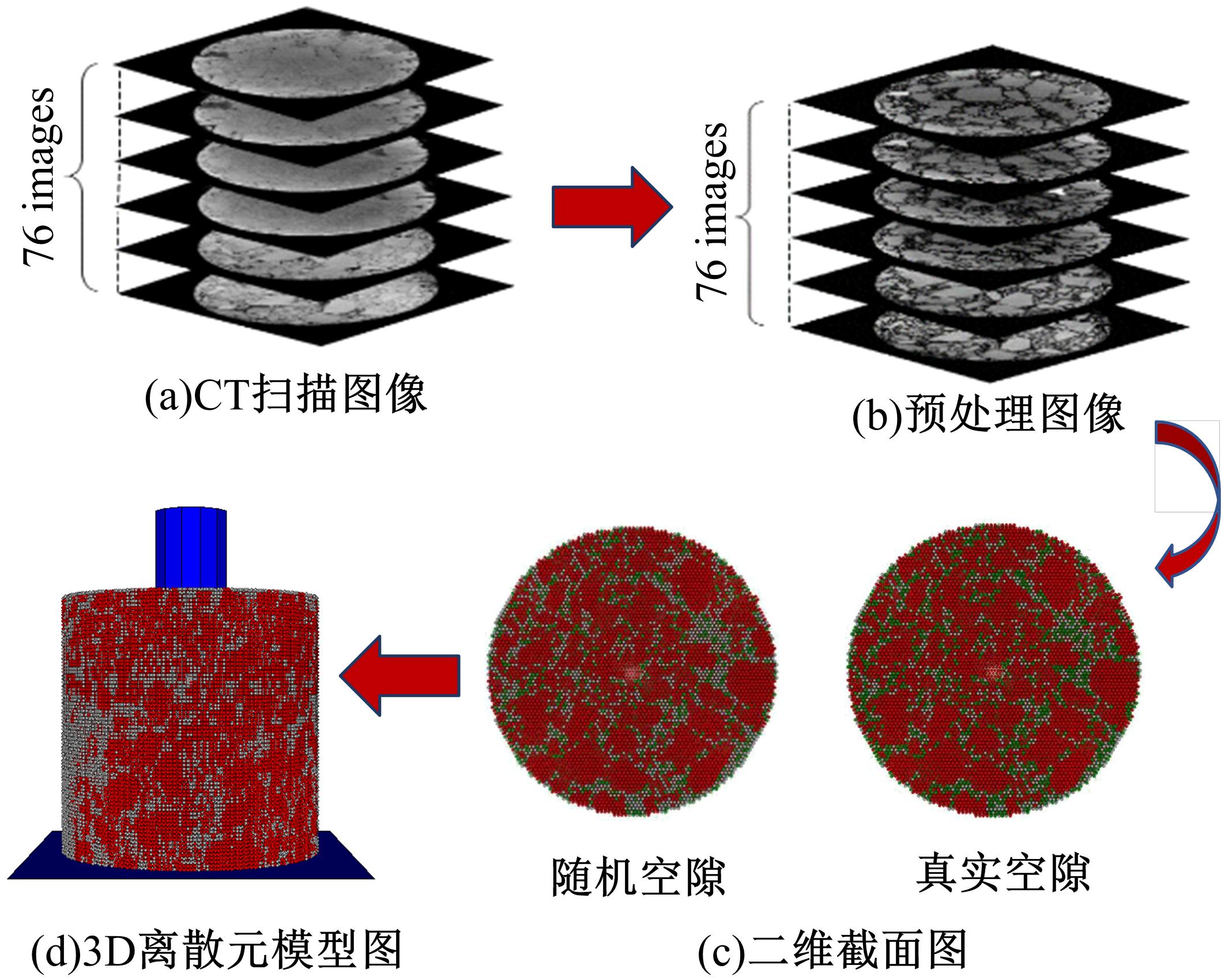
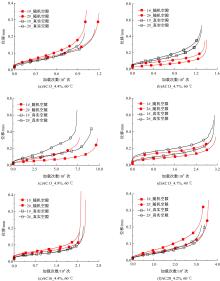
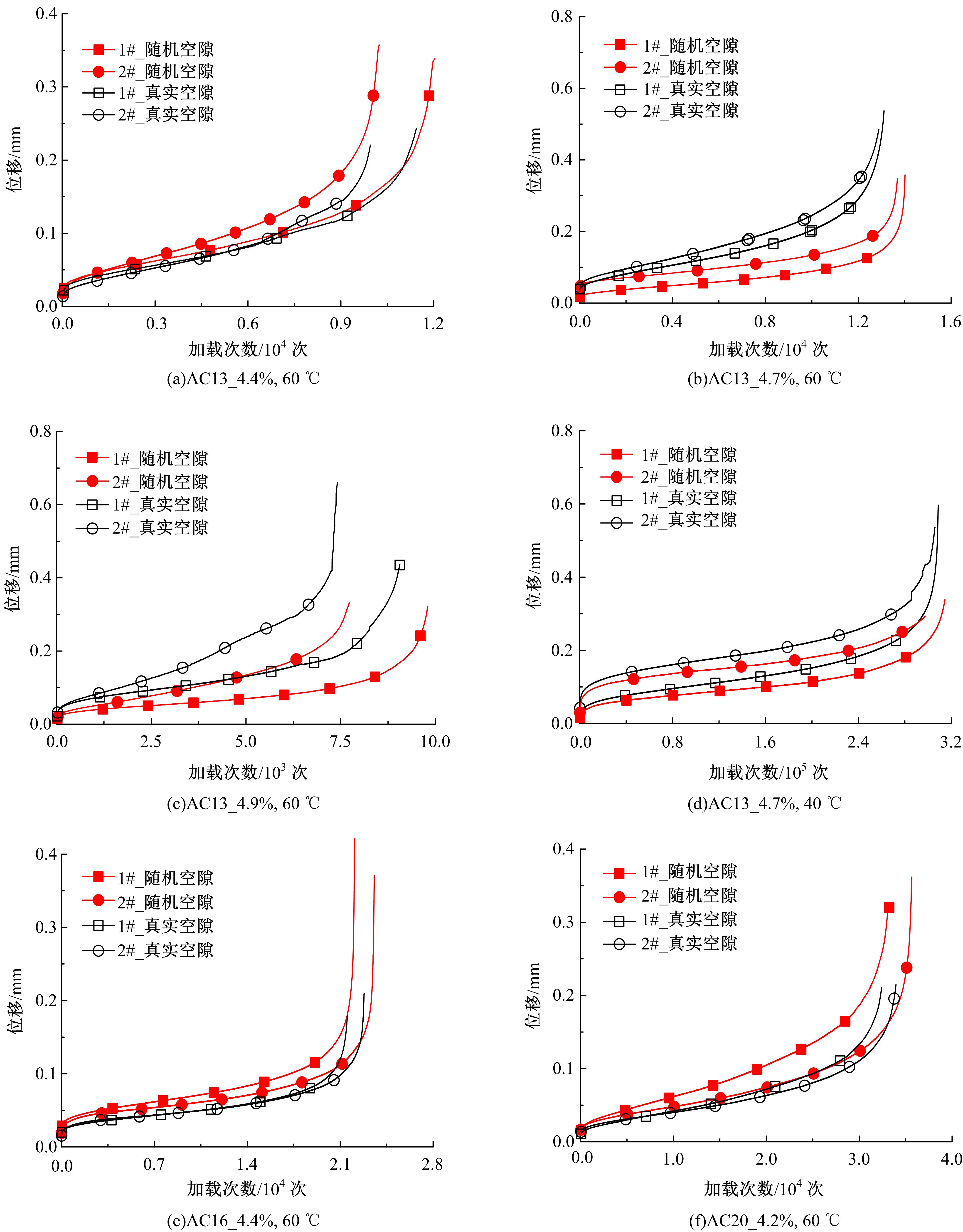
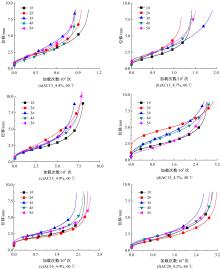
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 956-964.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200154
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of void characteristics on virtual shear fatigue life of asphalt mixtures using discrete element method
Yong PENG1( ),Han-duo YANG1,Xue-yuan LU2,Yan-wei LI3,4
),Han-duo YANG1,Xue-yuan LU2,Yan-wei LI3,4
- 1.Institute of Transportation Engineering,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,China
2.Anhui Transportation Holding Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Hefei 230088,China
3.Hebei Provincial Communications Planning and Design Institute,Shijiazhuang 050011,China
4.Research and Development Center of Transport Industry of Technologies,Materials and Equipments of Highway Construction and Maintenance,Shijiazhuang 050011,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| 1 | Monismith C L. Analytically based asphalt pavement design and rehabilitation[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1992, 1354(1):5-26. |
| 2 | Roberts F L, Kandhal P S, Brown E R, et al. Hot Mix Asphalt Materials, Mixture Design and Construction[M]. 2nd Edition. Lanham Md: National Asphalt Pavement Association, 1996. |
| 3 | 彭勇,孙立军. 空隙率对沥青混合料性能的影响[J]. 武汉理工大学学报:交通科学与工程版,2009,33(5):826-829. |
| Peng Yong, Sun Li-jun. Effects of air void content on asphalt mixture performance[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science and Engineering), 2009, 33(5):826-829. | |
| 4 | Elliot R P, Ford M C, Ghanim J M, et al. Effect of aggregate gradation variation on asphalt concrete mix properties[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1992, 1317(1):52-60. |
| 5 | Yue Z Q, Bekking W, Morin I. Application of digital image processing to quantitative study of asphalt concrete microstructure[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1995, 1492(1):53-60. |
| 6 | Obaidat M T, Msaeid H R, Gharaybeh F, et al. An innovative digital image analysis approach to quantify the percentage of voids in mineral aggregates of bituminous mixtures[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 1998, 25(6):1041-1049. |
| 7 | Masad E, Muhunthan B, Shashidhar N, et al. Internal structure characterization of asphalt concrete using image analysis[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering (Special Issue on Image Processing), 1999, 13(2):88-95. |
| 8 | Rao C B. Development of 3-D image analysis techniques to determine shape and size properties of coarse aggregate[D]. Urbana-Champagne: Department of Civil Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2001. |
| 9 | Kose S. Development of a virtual test procedure for asphalt concrete[D]. Madison City: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2002. |
| 10 | Sefidmazgi N R, Tashman L, Bahia H. Internal structure characterization of asphalt mixtures for rutting performance using imaging analysis[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2012, 13(Sup.1):21-37. |
| 11 | 彭勇,孙立军,王元清,等. 数字图像处理在沥青混合料均匀性评价中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2007,37(2):334-337. |
| Peng Yong, Sun Li-jun, Wang Yuan-qing, et al. Application of digital image processing in evaluating homogeneity of asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2007, 37(2):334-337. | |
| 12 | Tashman L, Masad E, D'angelo J, et al. X-ray tomography to characterize air void distribution in superpave gyratory compacted specimens[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2002, 3(1):19-28. |
| 13 | Masad E, Button J. Implications of experimental measurements and analyses of the internal structure of hot-mix asphalt[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2004, 1891(1):212-220. |
| 14 | Chen J S, Huang B S, Shu X. Air-void distribution analysis of asphalt mixture using discrete element method[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2013, 25(10):1375-1385. |
| 15 | 王聪,郭乃胜,赵颖华,等. 不同成型方法和级配的沥青混合料内部空隙特征[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2014,44(1):74-80. |
| Wang Cong, Guo Nai-sheng, Zhao Ying-hua, et al. Air voids distribution of asphalt mixtures in different compaction methods and aggregate gradations[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(1):74-80. | |
| 16 | Kose S, Guler M, Bahia H, et al. Distribution of strains within hot-mix asphalt binders: applying imaging and finite-element techniques[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2000, 1728(1):21-27. |
| 17 | Soares J B, de Freitas F A C, Allen D H. Considering material heterogeneity in crack modeling of asphaltic mixtures[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2003, 1832(1):113-120. |
| 18 | Dai Q L, Sadd M H, You Z P. A micromechanical finite element model for linear and damage-coupled viscoelastic behaviour of asphalt mixture[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2006, 30:1135-1158. |
| 19 | Rotherburg L, Bogobowecz A, Haas R, et al. Micromechanical modeling of asphalt concrete in connection with pavement rutting problems[C]∥International Conference on Asphalt Pavements, Nottingham, United Kingdom, 1992:01404192. |
| 20 | Buttlar W, You Z. Discrete element modeling of asphalt concrete: microfabric approach[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2007, 1757(1):111-118. |
| 21 | Abbas A, Masad E, Papagiannakis A, et al. Modelling asphalt mastic stiffness using discrete element analysis and micromechanics-based models[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2005, 6(2):137-146. |
| 22 | Kim H, Wagoner M P, Buttlar W. Simulation of fracture behavior in asphalt concrete using a heterogeneous cohesive zone discrete element model[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2008, 20(8):552-563. |
| 23 | You Z, Liu Y, Dai Q. Three-dimensional microstructural-based discrete element viscoelastic modeling of creep compliance tests for asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2011, 23(1):79-87. |
| 24 | Peng Y, Harvey J, Sun L J. Micromechanical modeling of aggregate homogeneity influence on the indirect tensile strength of asphalt mixtures using the three-dimensional discrete element method[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(11):04017211. |
| 25 | Peng Y, Bao J X. Micromechanical analysis of asphalt-mixture shear strength using the three-dimensional discrete element method[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 30(11):04018302. |
| 26 | Ma T, Zhang D Y, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of air voids on the high-temperature creep behavior of asphalt mixture based on three-dimensional discrete element modeling[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 89:304-313. |
| 27 | Ma T, Zhang Y, Zhang D Y, et al. Influences by air voids on fatigue life of asphalt mixture based on discrete element method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 126:785-799. |
| 28 | Ren J L, Sun L. Characterizing air void effect on fracture of asphalt concrete at low-temperature using discrete element method[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017,170:23-43. |
| 29 | 邵显智. 沥青混合料抗剪性能影响因素及剪切疲劳试验研究[D]. 上海:同济大学交通运输工程学院,2005. |
| Shao Xian-zhi. Study on influence factors and fatigue experiment about shear properties of asphalt mixtures[D]. Shanghai: College of Transportation Engineering, Tongji University, 2005. | |
| 30 | Peng Y, Gao H, Lu X Y, et al. Micromechanical discrete element modeling of asphalt mixture shear fatigue performance[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2020, 32(7):04020183. |
| [1] | Wei-gang ZHU,Chao ZHU,Ya-qiu ZHANG,Hai-bin WEI. Construction and quality evaluation of digital elevation model based on convolution grid surface fitting algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [2] | Yong-chun CHENG,He LI,Li-ding LI,Hai-tao WANG,Yun-shuo BAI,Chao CHAI. Analysis of mechanical properties of asphalt mixture affected by aggregate based on grey relational degree [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [3] | Ya-feng GONG,Yun-ze PANG,Bo WANG,Guo-jin TAN,Hai-peng BI. Mechanical properties of new prefabricated box culvert structure based on road conditions in Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [4] | En-hui YANG,Jia-qiu XU,You-zhi TANG,Ao LI,Yan-jun QIU. Effect of warm mixing agents on fracture and aging properties of asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 604-610. |
| [5] | Wen-ting DAI,Ze-hua SI,Zhen WANG,Qi WANG. Test on road performance of soils stabilized by sisal fiber and ionic soil stabilizer with cement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 589-593. |
| [6] | Yu FANG,Li-jun SUN. Urban bridge performance decay model based on survival analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 557-564. |
| [7] | Ying WANG,Ping LI,Teng-fei NIAN,Ji-bin JIANG. Short-term water damage characteristics of asphalt mixture based on dynamic water scour effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [8] | Ping WAN,Chao-zhong WU,Xiao-feng MA. Discriminating threshold of driving anger intensity based on driving behavior features by ROC curve analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [9] | Rui XIONG,Ning QIAO,Ci CHU,Fa YANG,Bo-wen GUAN,Yan-ping SHENG,Dong-yu NIU. Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortars [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| [10] | Chun-feng ZHU,Yong-chun CHENG,Chun-yu LIANG,Bo XIAO. Road performance experiment of diatomite⁃basalt fiber composite modified asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [11] | Sheng-tong DI,Chao JIA,Wei-guo QIAO,Kang LI,Kai TONG. Loading rate effect of meso⁃damage characteristics of crumb rubber concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [12] | Yun-long ZHANG,Liu-guang ZHOU,Jing WANG,Chun-li WU,Xiang LYU. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of silty sand and subgrade slope stability [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [13] | Yong PENG,Hua GAO,Lei WAN,Gui-ying LIU. Numerical simulation of influence factors of splitting strength of asphalt mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [14] | Xiao⁃zhen LI,Jun⁃zhe LIU,Yan⁃hua DAI,Zhi⁃min HE,Ming⁃fang BA,Yu⁃shun LI. Effect of carbonation on nitrite ion distribution in cement paste [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [15] | Tian⁃lai YU,Hai⁃sheng LI,Wei HUANG,Si⁃jia WANG. Shear strengthening of reinforced concrete beam with prestressed steel wire ropes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
|
||