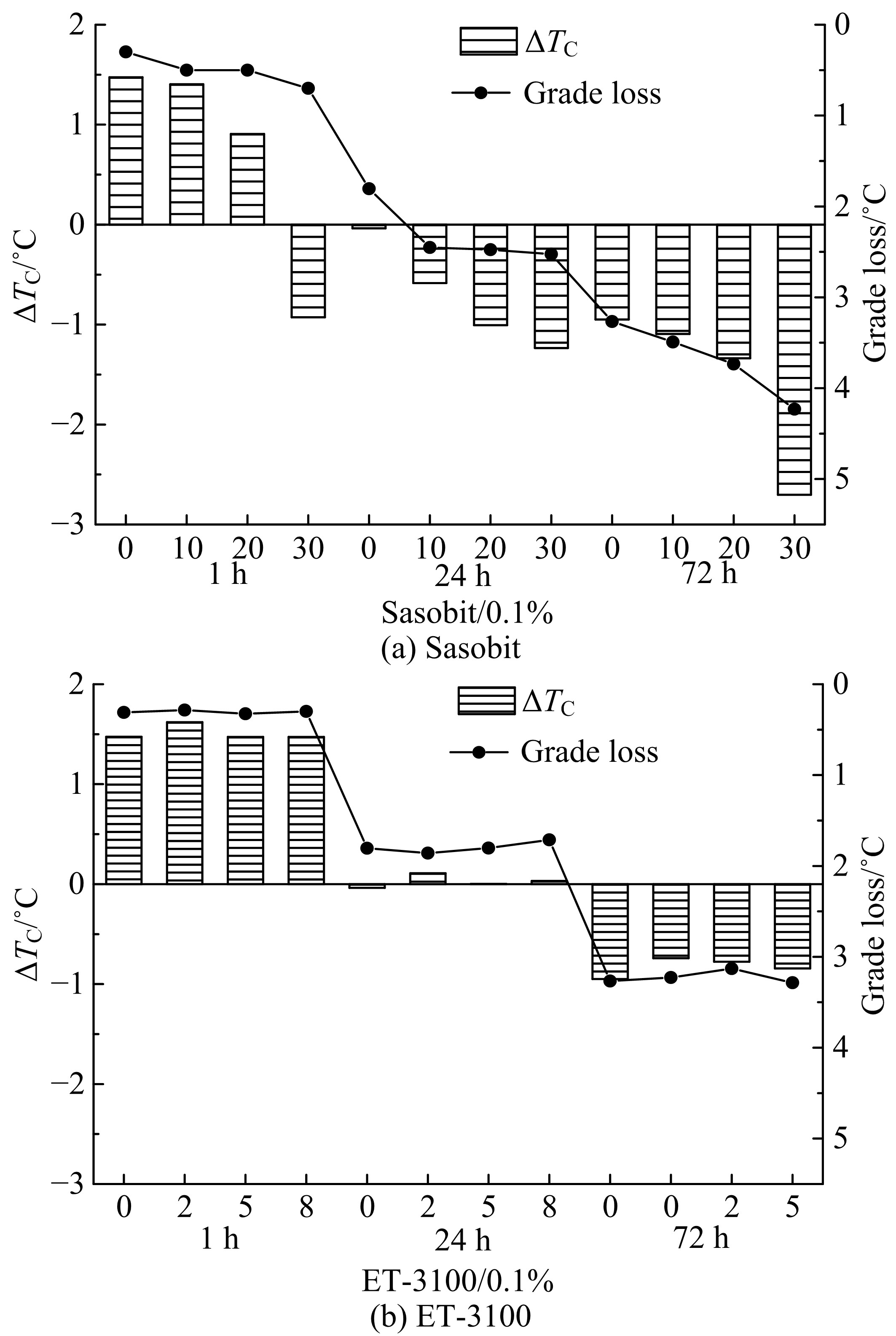
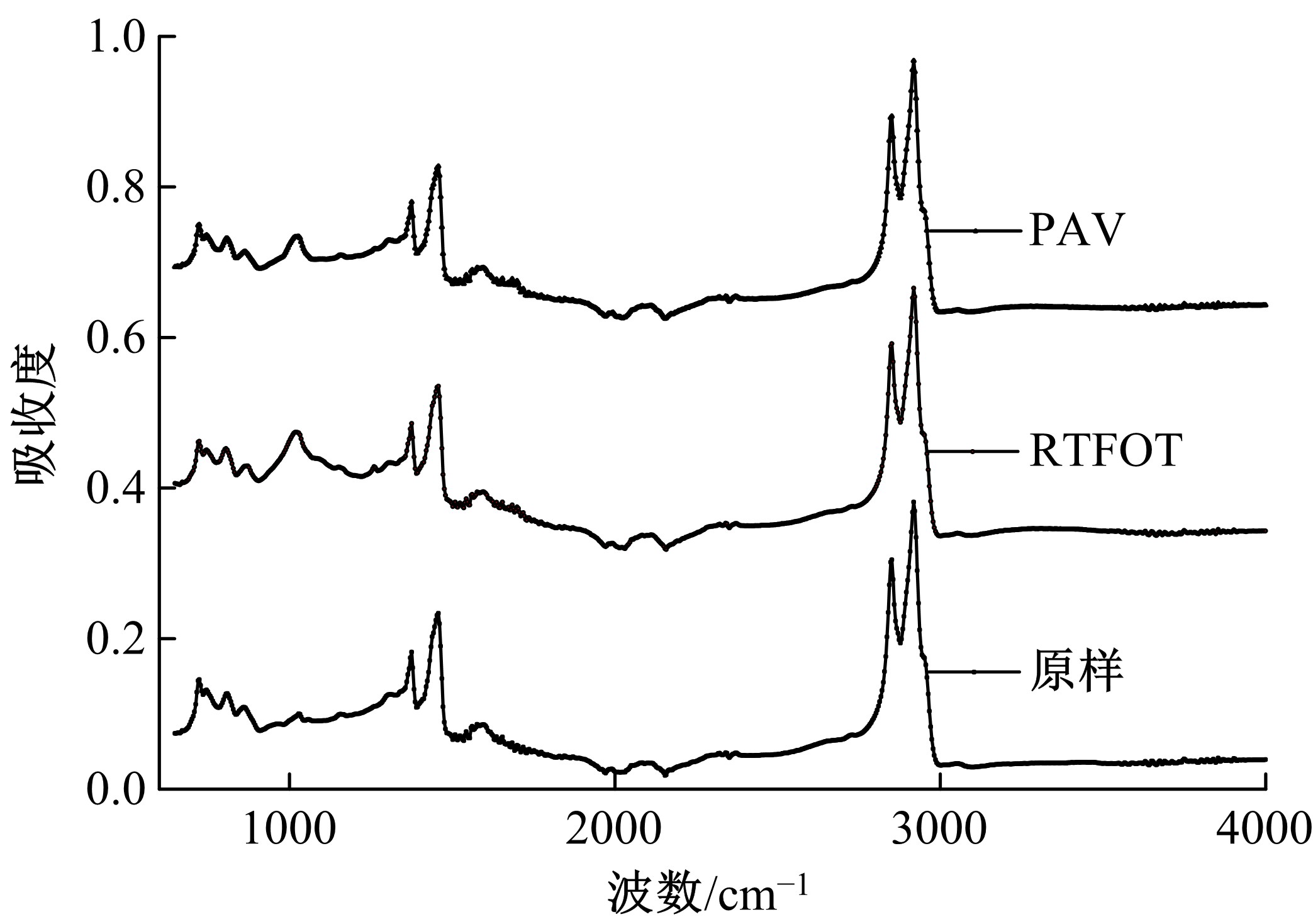
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 604-610.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190984
Effect of warm mixing agents on fracture and aging properties of asphalt
En-hui YANG1,2( ),Jia-qiu XU1,2,You-zhi TANG1,2,Ao LI1,2,Yan-jun QIU1,2
),Jia-qiu XU1,2,You-zhi TANG1,2,Ao LI1,2,Yan-jun QIU1,2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
2.Key Laboratory of Highway Engineering of Sichuan Province,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| 1 | 丁鹏, 吉泽中, 徐波, 等. 温拌成品高黏沥青及其混合料性能研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 32(4): 127-134. |
| Ding Peng, Ji Ze-zhong, Xu Bo, et al. Study on properties of warm mix finished high viscosity asphalt and mixtures[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2018, 32(4): 127-134. | |
| 2 | 王黎明, 谭忆秋, 石振武, 等. 基于冲击贯入法的温拌沥青混合料合理压实温度的确定[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(6): 1494-1499. |
| Wang Li-ming, Tan Yi-qiu, Shi Zhen-wu, et al. Determination of warm-mix asphalt reasonable compaction temperature range by impact penetration test [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(6): 1494-1499. | |
| 3 | 张苛, 张争奇. 基于温拌沥青性能的不同温拌剂效能评价[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2016, 34(3): 389-394. |
| Zhang Ke, Zhang Zheng-qi. Efficiency evaluation of different warm-mixed agents based on warm-mixed asphalt performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 34(3): 389-394. | |
| 4 | 樊亮, 胡家波, 李永镇, 等. 不同温拌剂对沥青粘弹性、疲劳性能的影响 [J]. 武汉理工大学学报: 交通科学与工程版, 2015, 39(2): 320-324. |
| Fan Liang, Hu Jia-bo, Li Yong-zhen, et al. Impact of different warm-mixing additives on viscoelasticity and fatigue properties of asphal [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 2015, 39(2):320-324. | |
| 5 | 詹小丽, 张肖宁, 谭忆秋, 等. 改性沥青低温性能评价指标研究[J].公路交通科技, 2007, 24(9): 42-45. |
| Zhan Xiao-li, Zhang Xiao-ning, Tan Yi-qiu, et al. Study on evaluation index of low temperature performance of modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research, 2007, 24(9): 42-45. | |
| 6 | Wu C F, Zeng M L. Effects of additives for warm mix asphalt on performance grades of asphalt binders[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2018, 193: 87-96. |
| 7 | 乐金朝, 李威. Sasobit改性沥青技术性能研究[J]. 郑州大学学报: 理学版, 2018, 50(1): 107-115. |
| Yue Jin-chao, Li Wei. Study on performance of Sasobit modified asphalt binder[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 50(1): 107-115. | |
| 8 | 熊锐, 乔宁, 褚辞, 等. 掺盐沥青胶浆低温流变及粘附特性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| Xiong Rui, Qiao Ning, Chu Ci, et al. Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortars[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. | |
| 9 | 郑传峰, 佴磊, 张力, 等. SEAM改性沥青流变特性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(5): 1284-1289. |
| Zhen Chuan-feng, Nie Lei, Zhang Li, et al. Rheological properties of SEAM modified asphalt binder[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1284-1289. | |
| 10 | Andriescu A, Hesp S A M, Youtcheff J S. Essential and plastic works of ductile fracture in asphalt binders[J]. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2004, 1875(1): 1-7. |
| 11 | Tabatabaee H A, Velasquez R, Bahia H U. Modeling thermal stress in asphalt mixtures undergoing glass transition and physical hardening[J]. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2012,4: 106-114. |
| 12 | AA―16. Provisional standard method of test for determination of performance grade of physical sged ssphalt using extended bending beam rheometer(BBR) method[S]. |
| 13 | Broberg K B. On stable crack growth[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 1975, 23(3): 215-237. |
| 14 | Mai Y W, Cotterell B. On the essential work of ductile fracture in polymers[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1986, 32(2): 105-125. |
| 15 | 谭忆秋, 符永康, 纪伦, 等. 橡胶沥青低温性能评价指标[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2016, 48(3): 66-70. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Fu Yong-kang, Ji Lun, et al. Rubber asphalt low temperature performance evaluation index [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2016,48(3):66-70. | |
| 16 | Anderson R M, King G N, Hanson D I, et al. Evaluation of the relationship between asphalt binder properties and non-load related cracking[J]. Asphalt Paving Technology, 2011, 80(4): 615-663. |
| 17 | AA―16. Standard practice for design considerations when using reclaimed zsphalt shingles in asphalt mixtures [S]. |
| 18 | 罗浩原, 欧阳铖霏, 冷慧康, 等. 基于临界裂纹尖端位移的沥青抗疲劳性能评价[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(4): 969-977. |
| Luo Hao-yuan, Ouyang Cheng-fei, Leng Hui-kang, et al. Fatigue performance evaluation of asphalt binder based on crack tip opening displacement[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(4): 969-977. | |
| 19 | 罗浩原, 邱延峻, 苏婷, 等. 自研环保无机硅胶温拌剂的综合性能鉴评[J/OL].[2019-11-12]. |
| 20 | 马育, 何兆益, 何亮, 等. 温拌橡胶沥青的老化特征与红外光谱分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2015, 32(1): 13-18. |
| Ma Yu, He Zhao-yi, He Liang, et al. Analysis on aging characteristics and infrared spectroscopy of warm mix asphalt-rubber[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015, 32(1): 13-18. | |
| 21 | 耿九光. 沥青老化机理及再生技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2009. |
| Geng Jiu-guang. Study on the aging mechanism and recycling technique of asphalt[D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2009. |
| [1] | Yu FANG,Li-jun SUN. Urban bridge performance decay model based on survival analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 557-564. |
| [2] | Wen-ting DAI,Ze-hua SI,Zhen WANG,Qi WANG. Test on road performance of soils stabilized by sisal fiber and ionic soil stabilizer with cement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 589-593. |
| [3] | Ying WANG,Ping LI,Teng-fei NIAN,Ji-bin JIANG. Short-term water damage characteristics of asphalt mixture based on dynamic water scour effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [4] | Ping WAN,Chao-zhong WU,Xiao-feng MA. Discriminating threshold of driving anger intensity based on driving behavior features by ROC curve analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [5] | Rui XIONG,Ning QIAO,Ci CHU,Fa YANG,Bo-wen GUAN,Yan-ping SHENG,Dong-yu NIU. Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortars [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| [6] | Chun-feng ZHU,Yong-chun CHENG,Chun-yu LIANG,Bo XIAO. Road performance experiment of diatomite⁃basalt fiber composite modified asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [7] | Sheng-tong DI,Chao JIA,Wei-guo QIAO,Kang LI,Kai TONG. Loading rate effect of meso⁃damage characteristics of crumb rubber concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [8] | Yun-long ZHANG,Liu-guang ZHOU,Jing WANG,Chun-li WU,Xiang LYU. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of silty sand and subgrade slope stability [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [9] | Yong PENG,Hua GAO,Lei WAN,Gui-ying LIU. Numerical simulation of influence factors of splitting strength of asphalt mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [10] | Xiao⁃zhen LI,Jun⁃zhe LIU,Yan⁃hua DAI,Zhi⁃min HE,Ming⁃fang BA,Yu⁃shun LI. Effect of carbonation on nitrite ion distribution in cement paste [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [11] | Tian⁃lai YU,Hai⁃sheng LI,Wei HUANG,Si⁃jia WANG. Shear strengthening of reinforced concrete beam with prestressed steel wire ropes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [12] | Xiao⁃ming HUANG,Qing⁃qing CAO,Xiu⁃yu LIU,Jia⁃ying CHEN,Xing⁃lin ZHOU. Simulation of vehicle braking performance on rainy daysbased on pavement surface fractal friction theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [13] | Jing WANG,Xiang LYU,Xiao⁃long QU,Chun⁃ling ZHONG,Yun⁃long ZHANG. Analysis of relationship between subgrade soil shear strength and chemical and minerals component [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [14] | LI Yi,LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun. Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [15] | NIAN Teng-fei, LI Ping, LIN Mei. Micro-morphology and gray entropy analysis of asphalt characteristics functional groups and rheological parameters under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
|
||