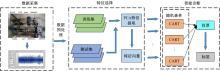
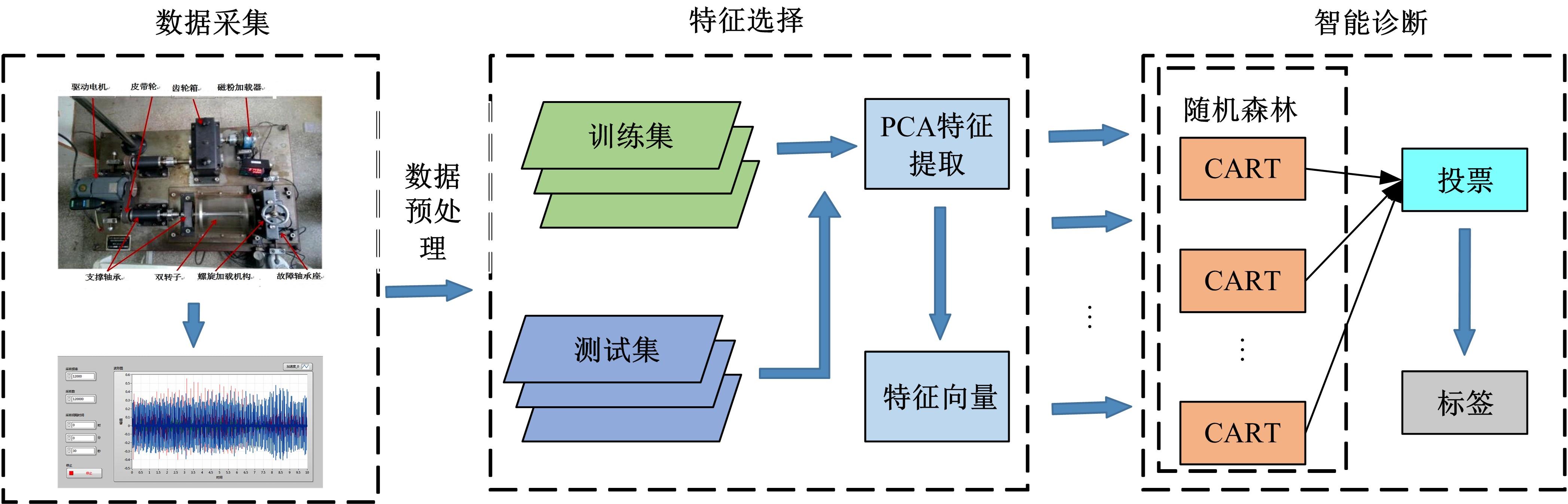
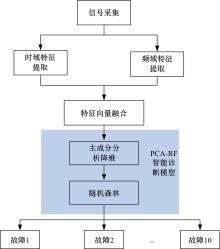
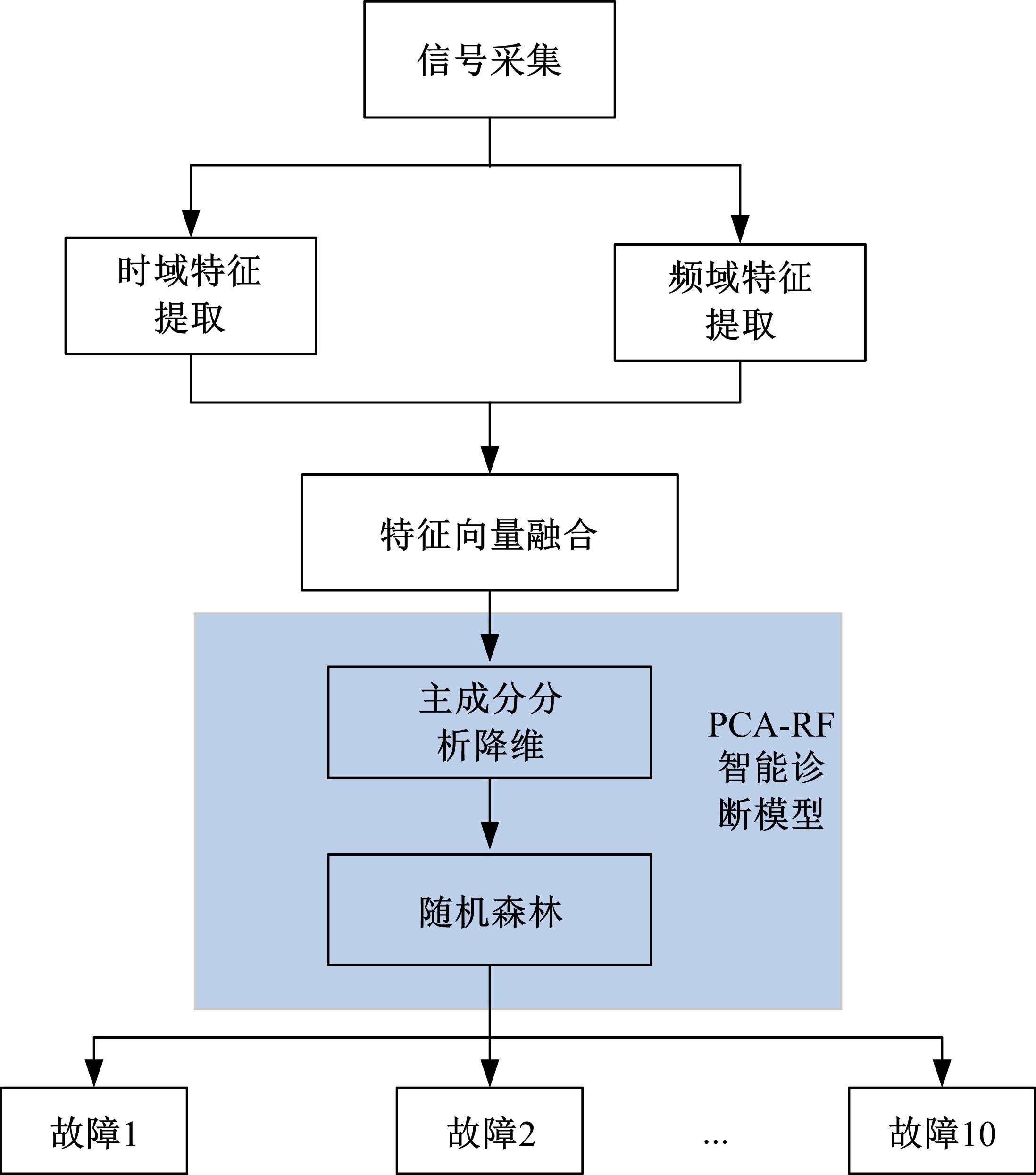
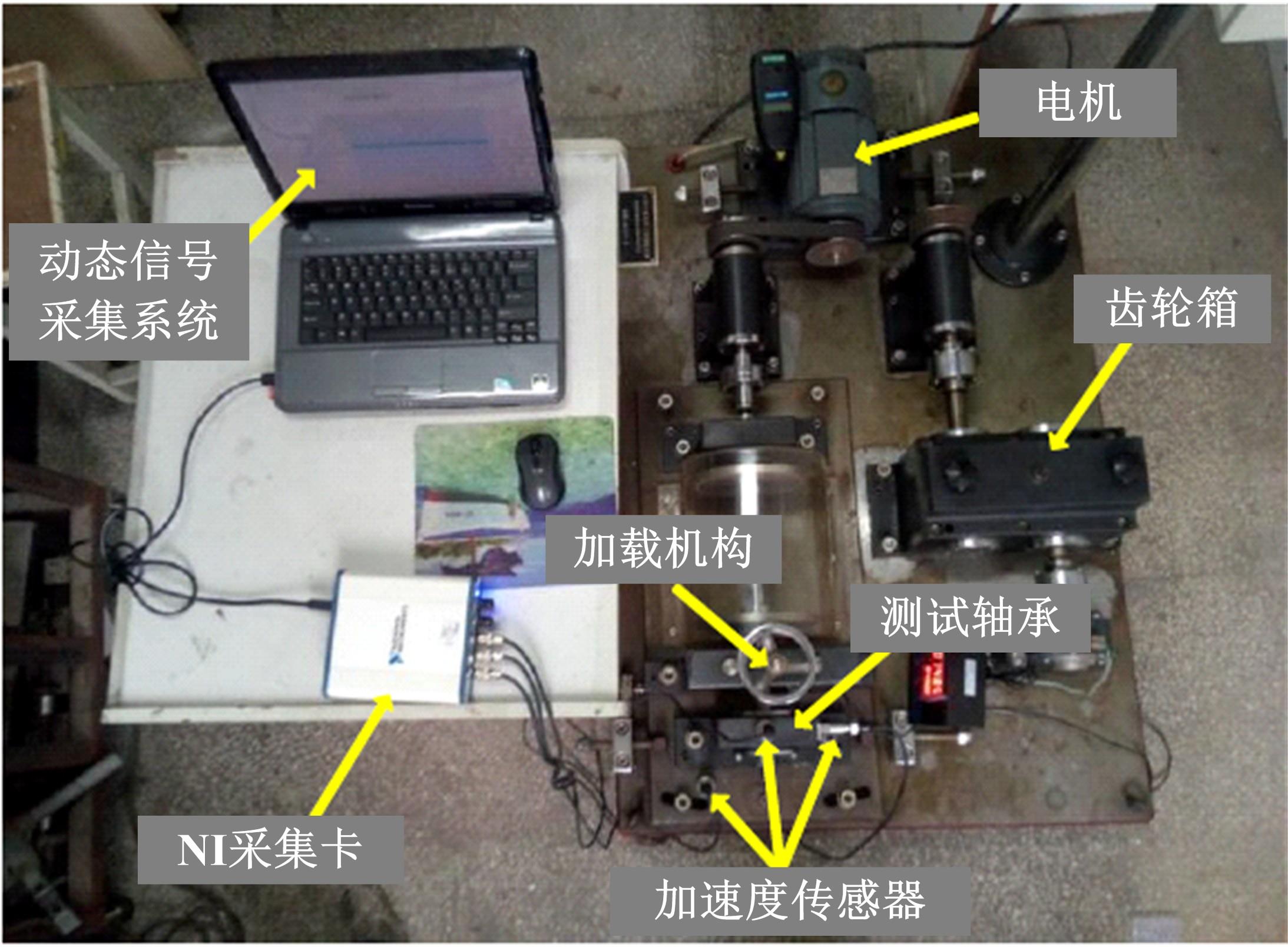
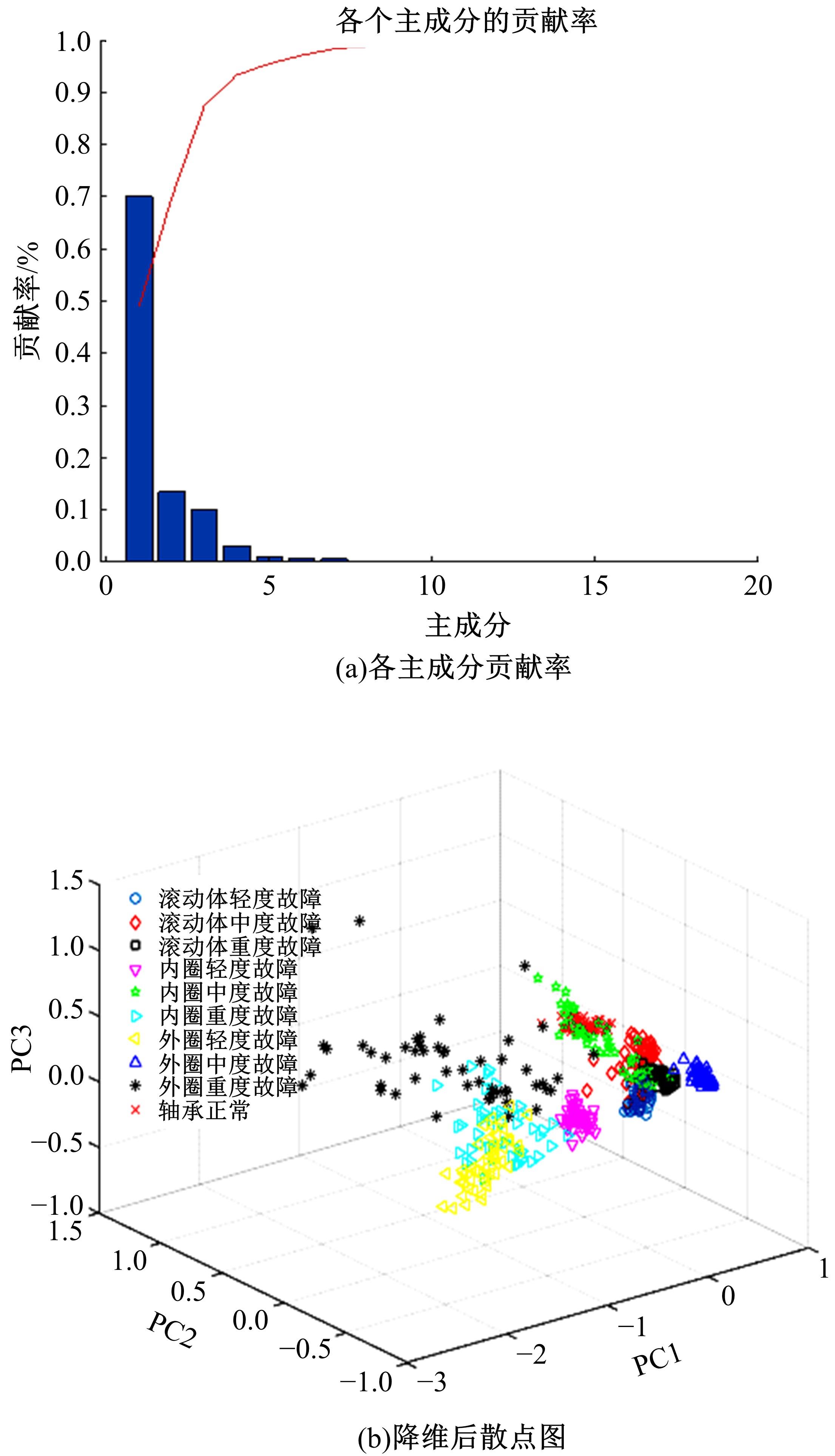
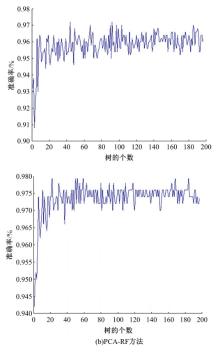
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2287-2293.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210312
Feature dimensionality reduction and random forest method in intelligent diagnosis of rolling bearings for urban rail trains
Zhen CAO1( ),Lu-yao CUI2,Bin LEI1,Jing-yi WANG3,Shuang-sheng CAO2(
),Lu-yao CUI2,Bin LEI1,Jing-yi WANG3,Shuang-sheng CAO2( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology,Xi'an 710055,China
2.Xi'an Rail Transit Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Xi'an 710016,China
3.Casco Signal Ltd. ,Shanghai 200040,China
CLC Number:
- U271
| 1 | 刘建强, 赵治博, 章国平, 等. 地铁车辆转向架轴承故障诊断方法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2015, 37(1):30-36. |
| Liu Jian-qiang, Zhao Zhi-bo, Zhang Guo-ping. Research on fault diagnosis method for bogie bearings of metro vehicle[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(1): 30-36. | |
| 2 | 姚德臣. 面向城轨列车走行安全的轴承在途故障诊断研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学轨道交通安全与控制国家重点实验室, 2015. |
| Yao De-chen. Research on the Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for the Bearing of Urban Rail Train Running Gear[D]. Beijing: State Key Laboratory of Rail Transit Safety and Control, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015. | |
| 3 | 左万里, 武小悦. 电子设备智能故障诊断技术发展综述[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2003, 25 (12) :1572-1575. |
| Zuo Wan-li, Wu Xiao-yue. The summary of equipment technology development on intelligent fault diagnosis[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2003, 25(12): 1572-1575. | |
| 4 | Cheng Wei-dong, Wang Tian-yang, Wang Jin-jiang, et al. Effects and its elimination method of envelope deformation on order analysis[J].Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2015, 28(3): 470-477. |
| 5 | 丁锋, 何正嘉, 陈雪峰. 考虑损伤程度的设备运行可靠性研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2010, 44(1): 36-40. |
| Ding Feng, He Zheng-jia, Chen Xue-feng. Operational reliability evaluation of machinery considering component damaged severity[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2010, 44(1): 36-40. | |
| 6 | 林伟炜, 朱金福, 徐丽, 等. 基于主成分分析的飞机租赁业务成长研究[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2019, 36(2): 69-76, 91. |
| Lin Wei-wei, Zhu Jin-fu, Xu Li, et al. Study on aircraft leasing business growth level index based on principal component analysis[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2019, 36(2): 69-76, 91. | |
| 7 | 王依宁, 解大, 王西田, 等. 基于PCA-LSTM模型的风电机网相互作用预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(14): 4070-4081. |
| Wang Yi-ning, Xie Da, Wang Xi-tian, et al. Prediction of Interaction between grid and wind farms based on PCA-LSTM model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(14): 4070-4081. | |
| 8 | 魏伟, 刘鹏. 基于字典原子优化的滑动轴承摩擦状态识别[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2018, 32(5): 202-207. |
| Wei Wei, Liu Peng. Sliding bearing friction state recognition based on optimization of dictionary atoms[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2018, 32(5): 202-207. | |
| 9 | 彭虹. 中国食用菌出口影响因素主成分分析与变化趋势预测[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2020, 41(10): 125-131. |
| Peng Hong. Study on export forecast of edible fungi in China based on principal component-grey prediction model[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2020, 41(10): 125-131. | |
| 10 | 傅军栋, 邹欢, 康水华. PSO-SVM算法在智能建筑环境监控系统中的应用[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2016, 147(1): 121-127. |
| Fu Jun-dong, Zou Huan, Kang Shui-hua. Application of PSO-SVM algorithm in environmental monitoring system of intelligent building[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2016, 147(1): 121-127. | |
| 11 | 谢丽蓉, 杨欢, 李进卫, 等. 基于GA-ENN特征选择和参数优化的双馈风电机组轴承故障诊断[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(1): 149-156. |
| Xie Li-rong, Yang Huan, Li Jin-Wei, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis using GA-ENN based feature selection and parameters optimization for doubly-fed wind turbine[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(1): 149-156. | |
| 12 | 古莹奎, 承姿辛, 朱繁泷. 基于主成分分析和支持向量机的滚动轴承故障特征融合分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2015, 26(20): 2778-2783. |
| Gu Ying-kui, Cheng Zi-xin, Zhu Fan-long. Rolling bearing fault feature fusion based on PCA and SVM[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 26(20): 2778-2783. | |
| 13 | 陈亮, 周国模, 杜华强, 等. 基于随机森林模型的毛竹林CO2通量模拟及其影响因子[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(8): 1-12. |
| Chen Liang, Zhou Guo-mo, Du Hua-qiang, et al. Simulation of CO2 Flux and Controlling Factors in Moso Bamboo Forest Using Random Forest Algorithm[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2018, 54(8): 1-12. | |
| 14 | 冯文卿, 眭海刚, 涂继辉, 等. 高分辨率遥感影像的随机森林变化检测方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(11): 1880-1890. |
| Feng Wen-qing, Sui Hai-gang, Tu Ji-hui, et al. Change detection method for high resolution remote sensing images using random forest[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(11): 1880-1890. | |
| 15 | 徐卓飞, 刘凯, 张海燕. 基于经验模式分解和主元分析的滚动轴承故障诊断方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(23): 133-139. |
| Xu Zhuo-fei, Liu Kai, Zhang Hai-yan. A fault diagnosis method for rolling bearings based on empirical mode decomposition and principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(23) : 133-139. | |
| 16 | 来海锋, 韩斌, 厉力华. 基于集成类随机森林方法的神经胶质瘤特征基因选择的研究[J]. 生物物理学报, 2010, 26(9): 833-845. |
| Lai Hai-feng, Han Bin, Li Li-hua. An intefrated semi-random forests based approach to gene selection for glioma classification[J]. Acta Biophysica Sinica, 2010, 26(9): 833-845. | |
| 17 | Svetnik V, Liaw A, Tong C . et al. Random forest: a classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 2003, 43 (6) : 1947-1958. |
| 18 | 李文峰, 戴豪民, 许爱强. 时域新指标和PNN 在滚动轴承故障诊断中的应用[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2016, 35(9): 1382-1386. |
| Li Wen-feng, Dai Hao-min, Xu Ai-qiang. New time domain index and probabilistic neural network and their application in fault diagnosis of rolling bearing[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2016, 35(9): 1382-1386. | |
| 19 | 冯桓榰, 张来斌, 石帅. 等 . 基于小波包熵的轴承状态监测和早期故障诊断技术[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(18): 5177-5181. |
| Feng Heng-zhi, Zhang Lai-bin, Shi Shuai . et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on wavelet energy entropy[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2013, 13(18): 5177-5181. | |
| 20 | 张永祥, 李军, 孙云岭. 基于遗传算法和峰度最佳的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2007, 26(8): 122-124. |
| Zhang Yong-xiang, Li Jun, Sun Yun-ling. Study on design method of resonant demodulation apparatus for rolling elements bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2007, 26(8): 122-124. |
| [1] | Ke-yong WANG,Da-tong BAO,Su ZHOU. Data-driven online adaptive diagnosis algorithm towards vehicle fuel cell fault diagnosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [2] | Qi-ming CAO,Hai-tao MIN,Wei-yi SUN,Yuan-bin YU,Jun-yu JIANG. Hydrothermal characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cell start⁃up at low temperature [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [3] | Hai-lin KUI,Ze-zhao WANG,Jia-zhen ZHANG,Yang LIU. Transmission ratio and energy management strategy of fuel cell vehicle based on AVL⁃Cruise [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [4] | Yan LIU,Tian-wei DING,Yu-peng WANG,Jing DU,Hong-hui ZHAO. Thermal management strategy of fuel cell engine based on adaptive control strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [5] | Cheng LI,Hao JING,Guang-di HU,Xiao-dong LIU,Biao FENG. High⁃order sliding mode observer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2203-2212. |
| [6] | Pei ZHANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Chang-qing DU,Fu-wu YAN,Chi-hua LU. Oxygen excess ratio control method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air system for vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [7] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [8] | Yao-wang PEI,Feng-xiang CHEN,Zhe HU,Shuang ZHAI,Feng-lai PEI,Wei-dong ZHANG,Jie-ran JIAO. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on adaptive LQR control [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [9] | Guang-di HU,Hao JING,Cheng LI,Biao FENG,Xiao-dong LIU. Multi⁃objective sliding mode control based on high⁃order fuel cell model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2182-2191. |
| [10] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Qi WU,Yuan-song LI,Tian-de MO,Yu LI,Li-ping HUANG,Jian-hong SU,Wei-dong ZHANG. Matching,simulation and optimization for 2.5 ton fuel cell/battery hybrid forklift [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [11] | Xiao-hua WU,Zhong-wei YU,Zhang-ling ZHU,Xin-mei GAO. Fuzzy energy management strategy of fuel cell buses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
| [12] | Qing GAO,Hao-dong WANG,Yu-bin LIU,Shi JIN,Yu CHEN. Experimental analysis on spray mode of power battery emergency cooling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1733-1740. |
| [13] | Kui-yang WANG,Ren HE. Recognition method of braking intention based on support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1770-1776. |
| [14] | Jun-cheng WANG,Lin-feng LYU,Jian-min LI,Jie-yu REN. Optimal sliding mode ABS control for electro⁃hydraulic composite braking of distributed driven electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1751-1758. |
| [15] | Qiang GUO,Ming-song LI,Kai ZHOU. Multi⁃mode radar signal sorting based on potential distance graph and improved cloud model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1904-1911. |
|
||