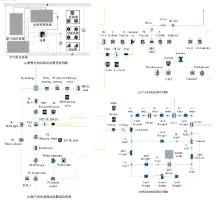
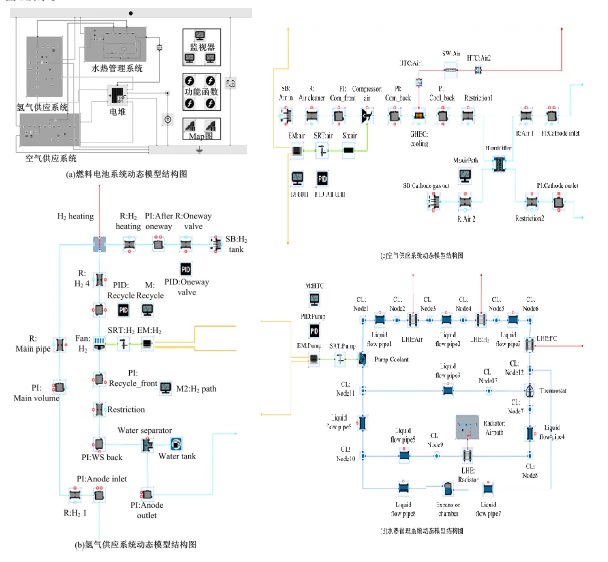
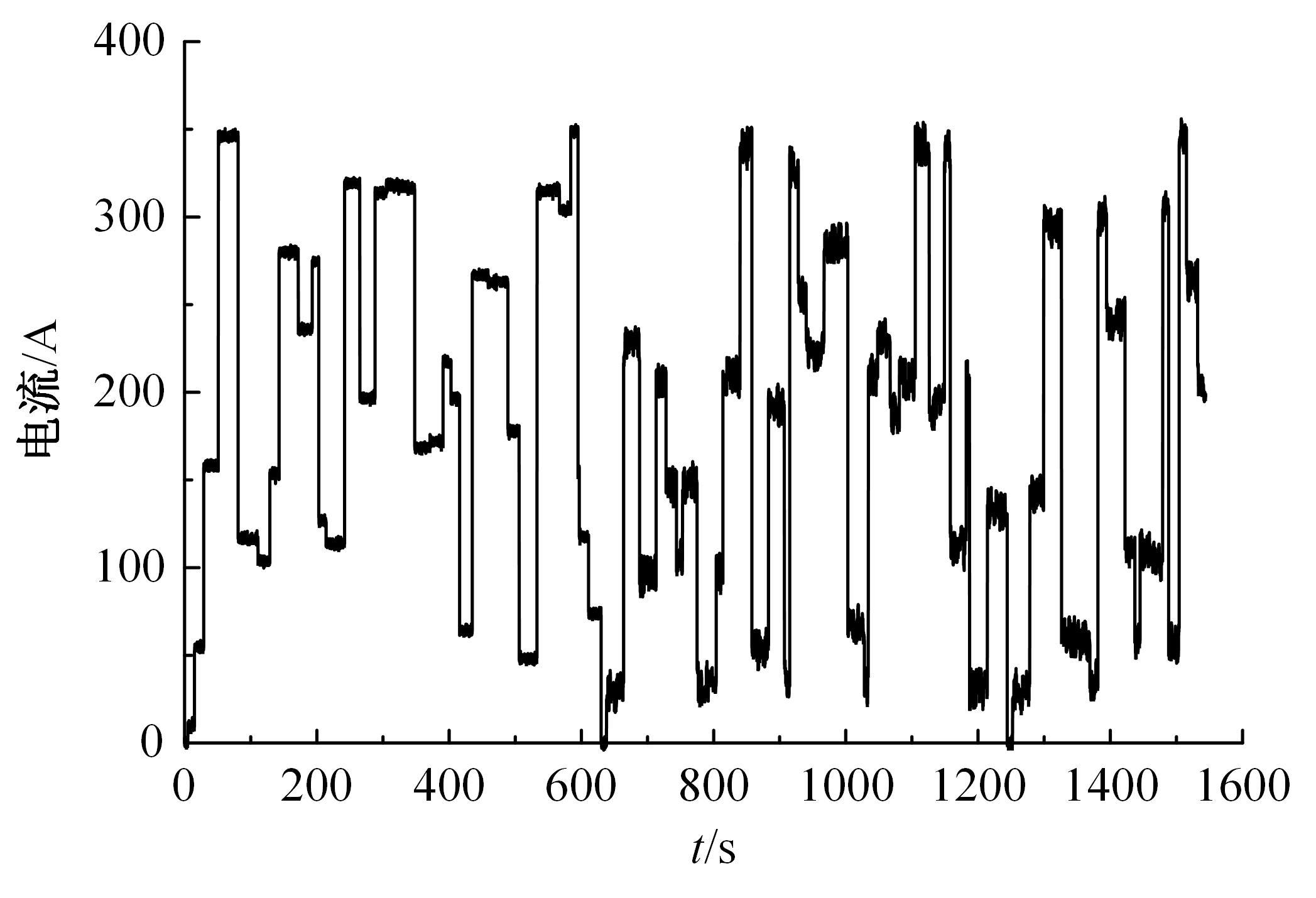
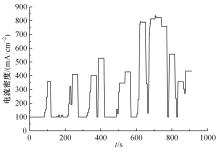
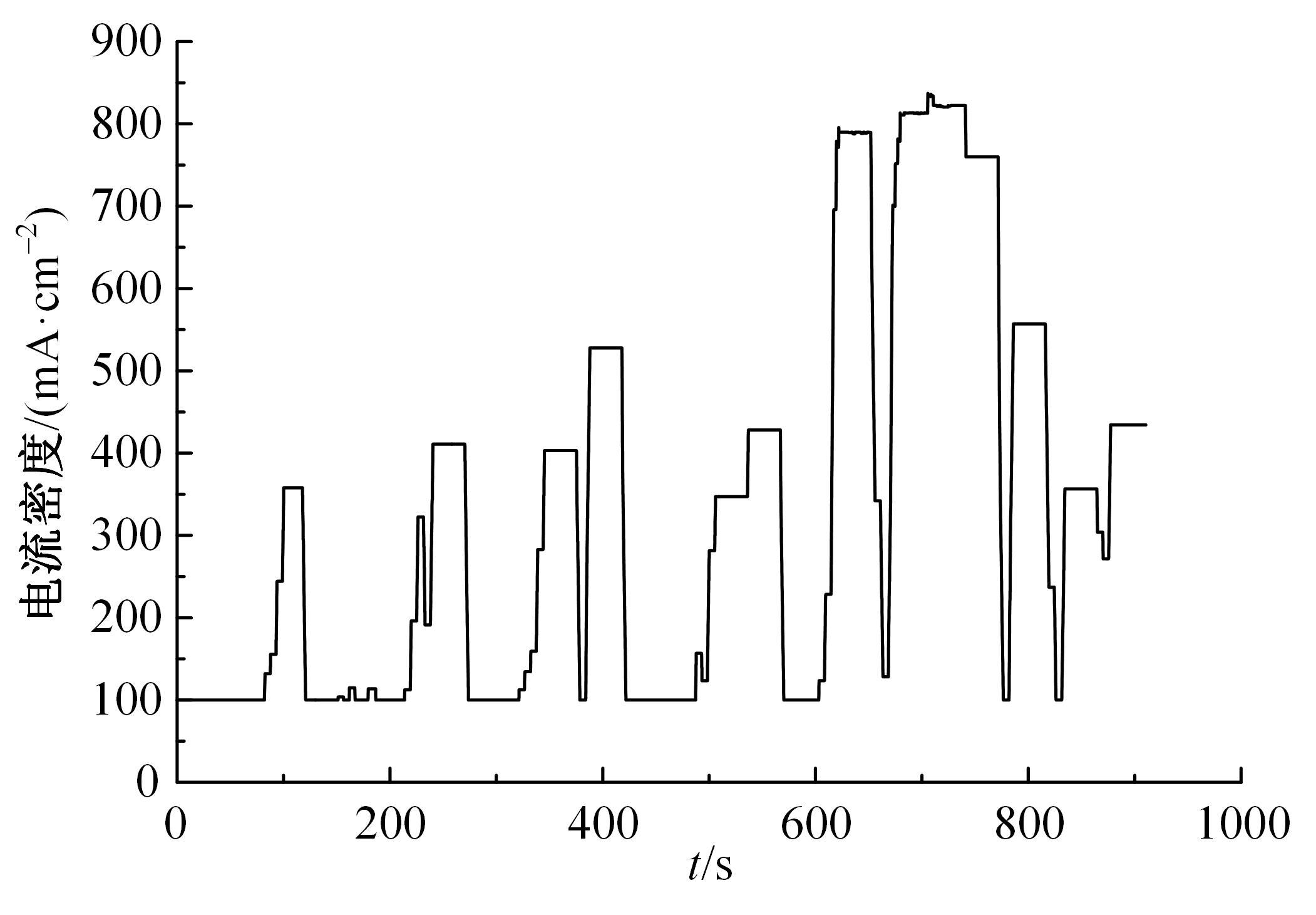
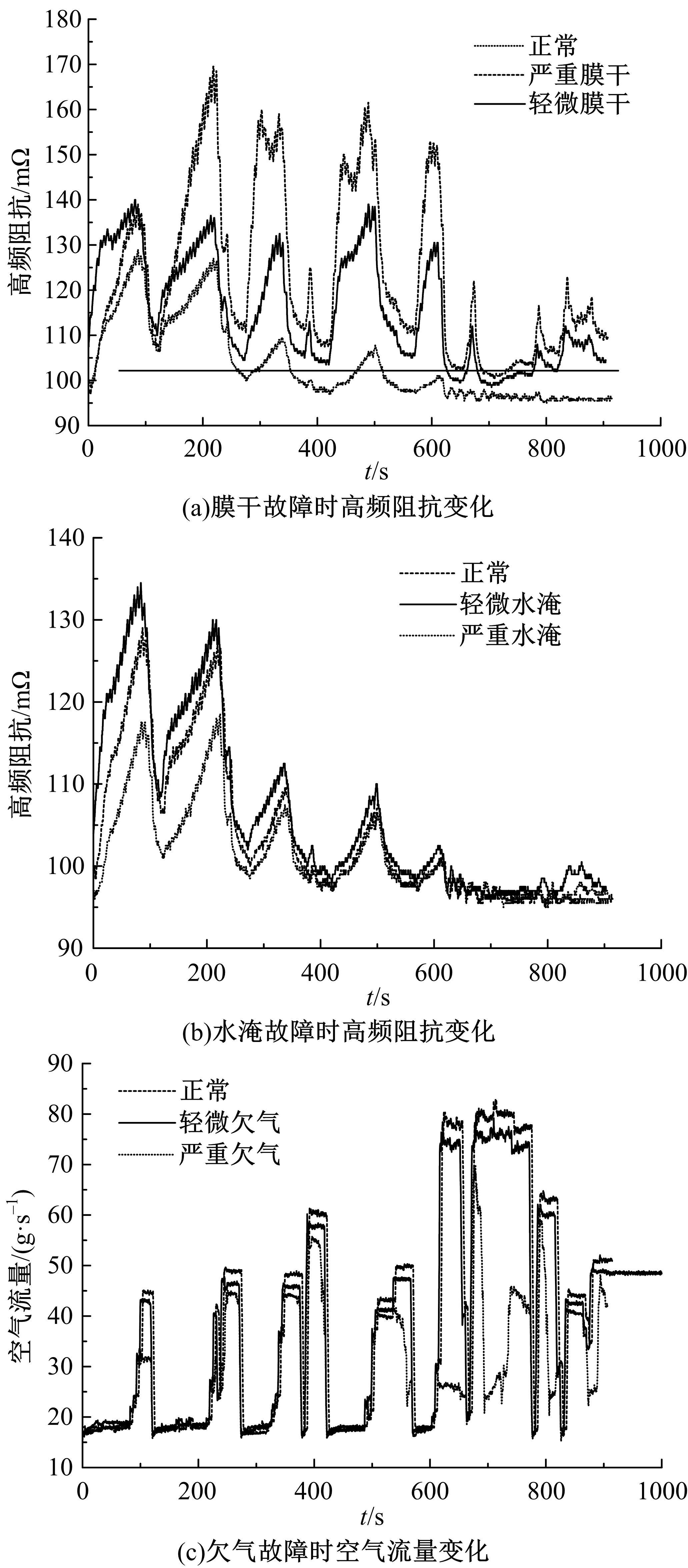
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2107-2118.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220062
Data-driven online adaptive diagnosis algorithm towards vehicle fuel cell fault diagnosis
Ke-yong WANG1,2( ),Da-tong BAO1,Su ZHOU1(
),Da-tong BAO1,Su ZHOU1( )
)
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Shanghai Hydrogen Propulsion Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201804,China
CLC Number:
- TK91
| 1 | 中国汽车工程学会. 节能与新能源汽车技术路线图[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2021. |
| 2 | Benmouna A, Mohamed B, Daniel D, et al. Fault diagnosis methods for proton exchange membrane fuel cell system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(2): 1534-1543. |
| 3 | 周苏,胡哲,文泽军. 基于K均值和支持向量机的燃料电池在线自适应故障诊断[J]. 同济大学学报, 2019, 47(2): 255-260. |
| Zhou Su, Hu Zhe, Wen Ze-jun. A K-means/support vector machine based self-adaptive online fault diagnosis method for fuel cell system[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2019, 47(2): 255-260. | |
| 4 | Gu X, Hou Z J, Cai J. Data-based flooding fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell systems using LSTM networks[J]. Energy and AI, 2021, 4: No. 100056. |
| 5 | Shao M, Zhu X J, Cao H F, et al. An artificial neural network ensemble method for fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system[J]. Energy, 2014, 67: 268-275. |
| 6 | Sanchez D G, Garcia-Ybarra P L. PEMFC operation failure under severe dehydration[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(8): 7279-7288. |
| 7 | Canut J M L, Latham R, Mérida W, et al. Impedance study of membrane dehydration and compression in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 192(2): 457-466. |
| 8 | Hui L, Tang Y H, Wang Z W, et al. A review of water flooding issues in the proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 178(1): 103-117. |
| 9 | Zhang C Z, Zhou W J, Lan Z, et al. An experimental study on anode water management in high temperature PEM fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(13): 4666-4672. |
| 10 | Shimpalee S, Beuscher U, Zee J W V. Analysis of GDL flooding effects on PEMFC performance[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(24): 6748-6754. |
| 11 | O'Rourke J, Ramani M, Arcak M. In situ detection of anode flooding of a PEM fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(16): 6765-6770. |
| 12 | Kim M, Jung N, Eom K S, et al. Effects of anode flooding on the performance degradation of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 266: 332-340. |
| 13 | Benmouna A, Becherif M, Depernet D, et al. Fault diagnosis methods for proton exchange membrane fuel cell system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(2): 1534-1543. |
| 14 | 朱添麟. 基于电压调节的车载燃料电池空气供给系统建模与控制[D]. 长春: 吉林大学通信工程学院, 2021. |
| Zhu Tian-lin. Modeling and control of vehicle fuel cell air supply system based on voltage regulation[D]. Changchun: College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, 2021. | |
| 15 | 杨朵. 燃料电池空气供给系统控制与故障诊断策略研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学计算机科学与技术学院, 2021. |
| Yang Duo. Research on control and fault diagnosis strategy fuel cell air supply system[D]. Hefei: School of Computer and Control Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, 2021. | |
| 16 | 孙田. 重卡用大功率燃料电池发动机空气供给控制策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学机械与电子控制工程学院, 2020. |
| Sun Tian. Research on control strategy of high power fuel cell engine air supply for heavy-duty truck[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical and Electronic Control Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 17 | 陈旭, 胡广地, 邓宇翔, 等. PEMFC燃料饥饿控制策略综述[J]. 电池, 2019, 49(2): 163-167. |
| Chen Xu, Hu Guang-di, Deng Yu-xiang, et al. Review of fuel starvation control strategies for PEMFC[J]. Battery, 2019, 49(2):163-167. | |
| 18 | 黄亮, 彭清, 谢长君, 等. 基于差分进化优化的支持向量机燃料电池故障诊断[J]. 电源技术, 2021, 45(10): 1316-1319. |
| Huang Liang, Peng Qing, Xie Chang-jun, et al. Fuel cell fault diagnosis for support vector machines optimized based on differential evolution algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 45(10): 1316-1319. | |
| 19 | 张少哲, 戴海峰, 袁浩, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池电化学阻抗谱敏感性研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(14): 40-51. |
| Zhang Shao-zhe, Dai Hai-feng, Yuan Hao, et al. Sensiblity study on electrochemical impedance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Joural of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(14): 40-51. | |
| 20 | 贾坤晗. 进气相对湿度对车用燃料电池性能影响的研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学机电与车辆工程学院, 2021. |
| Jia Kun-han. Research on the effects of inlet relative humidity on the performance of vehicle fuel cells[D]. Beijing: School of Mechatronics and Vehicle Engineering, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2021. | |
| 21 | 何红曈. 质子交换膜燃料电池内部水含量特性分析[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学机电与车辆工程学院, 2021. |
| He Hong-tong. Analysis of the variation characteristics of water content in the flow channel of PEMFC[D]. Beijing: School of Mechatronics and Vehicle Engineering, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2021. | |
| 22 | 卫超强. 不同参数对质子交换膜燃料电池输出特性的影响[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学机械与运载工程学院, 2021. |
| Wei Chao-qiang. Effects of different parameters on the outpour characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[D]. Taiyuan: School of Mechanics and Transportation Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 23 | Devlin S J. Pearson correlation coefficient[EB/OL]. [2021-12-11]. |
| [1] | Pei ZHANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Chang-qing DU,Fu-wu YAN,Chi-hua LU. Oxygen excess ratio control method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air system for vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [2] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [3] | Yao-wang PEI,Feng-xiang CHEN,Zhe HU,Shuang ZHAI,Feng-lai PEI,Wei-dong ZHANG,Jie-ran JIAO. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on adaptive LQR control [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [4] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Qi WU,Yuan-song LI,Tian-de MO,Yu LI,Li-ping HUANG,Jian-hong SU,Wei-dong ZHANG. Matching,simulation and optimization for 2.5 ton fuel cell/battery hybrid forklift [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [5] | Xiao-hua WU,Zhong-wei YU,Zhang-ling ZHU,Xin-mei GAO. Fuzzy energy management strategy of fuel cell buses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
| [6] | Qing GAO,Hao-dong WANG,Yu-bin LIU,Shi JIN,Yu CHEN. Experimental analysis on spray mode of power battery emergency cooling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1733-1740. |
| [7] | Kui-yang WANG,Ren HE. Recognition method of braking intention based on support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1770-1776. |
| [8] | Jun-cheng WANG,Lin-feng LYU,Jian-min LI,Jie-yu REN. Optimal sliding mode ABS control for electro⁃hydraulic composite braking of distributed driven electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1751-1758. |
| [9] | Han-wu LIU,Yu-long LEI,Xiao-feng YIN,Yao FU,Xing-zhong LI. Multi⁃point control strategy optimization for auxiliary power unit of range⁃extended electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1741-1750. |
| [10] | Hong-bo YANG,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Nian-cheng GUO,Yan-yan ZHAO. Optimization of tooth surface modification based on a two-stage reduction gear system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1541-1551. |
| [11] | Guang-ming NIE,Bo XIE,Yan-tao TIAN. Design of cooperative adaptive cruise control algorithm based on Frenet framework [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1687-1695. |
| [12] | Shuai HAO,Chuan-tai CHENG,Jun-nian WANG,Jun-yuan ZHANG,You YU. Ergonomic optimization and test evaluation of sports SUV cockpit layout design [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1477-1488. |
| [13] | Jia-xu ZHANG,Chong GUO,Chen WANG,Jian ZHAO,Xin-zhi WANG. Performance evaluation of automatic parking system based on hardware in the loop simulation platform [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1552-1560. |
| [14] | Chen HUA,Run-xin NIU,Biao YU. Methods and applications of ground vehicle mobility evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [15] | Xiong LI,Feng-chong LAN,Ji-qing CHEN,Fang TONG. Comparison of injuries in front impact between Hybird III dummy model and CHUBM human biomechanical model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1264-1272. |
|
||